{quality development}
How to properly write your project
Università degli Studi di Catania
Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica


{quality development}
How to properly write your project
Università degli Studi di Catania - Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica - 2025

{quality development}
How to properly write your project
# Intro
whoami
Hi, I am Stefano Borzì 👋
Open-source developer
Full Stack Developer at "Royal BAM Group"
PhD student at University of Catania
$


# Intro
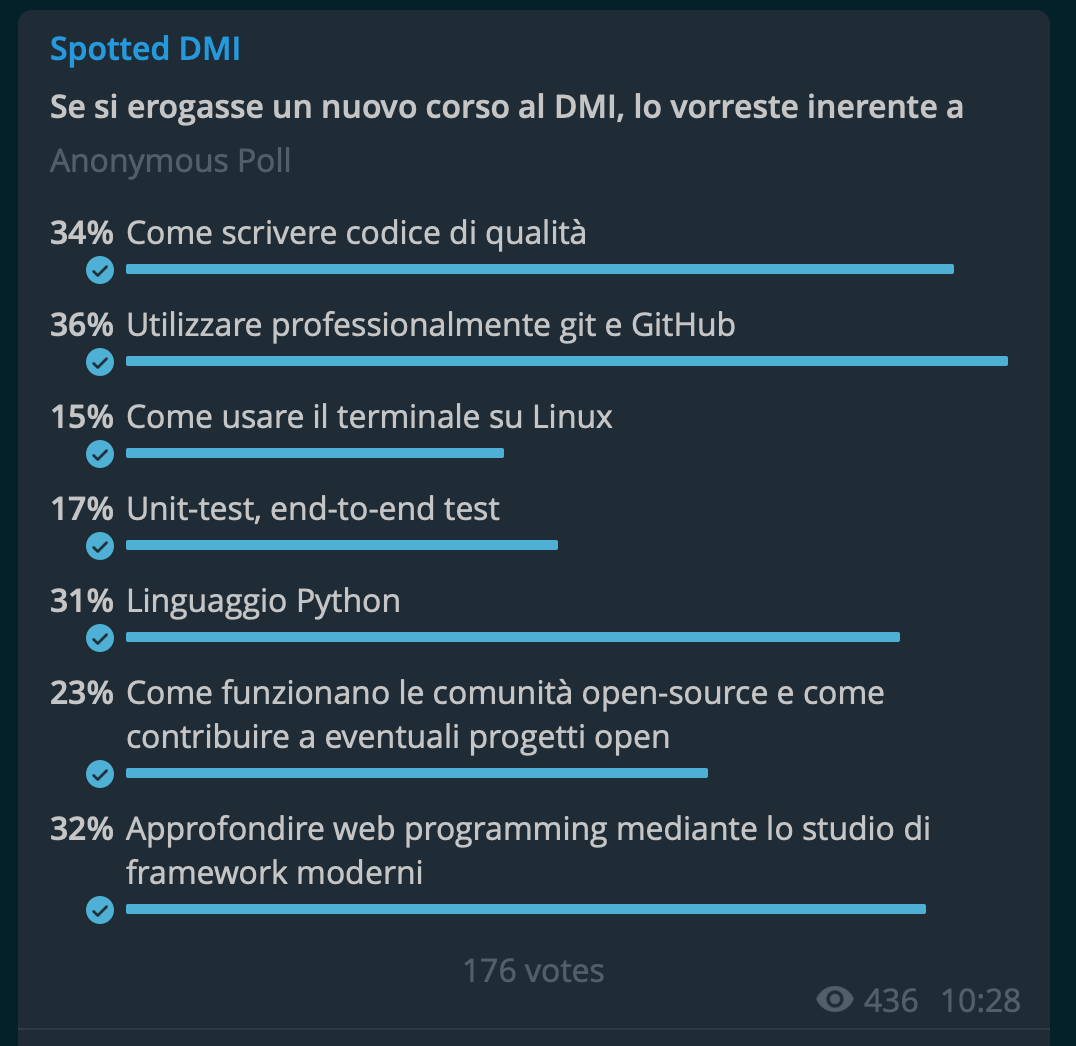
Course introduction
- Shell UNIX
- Git
- GitHub
- Opensource
- Python
- Unit-test
- SOLID principles
- CI / CD pipeline & tools














# Intro
Exam
Mini-project in a group of two

# Shell UNIX
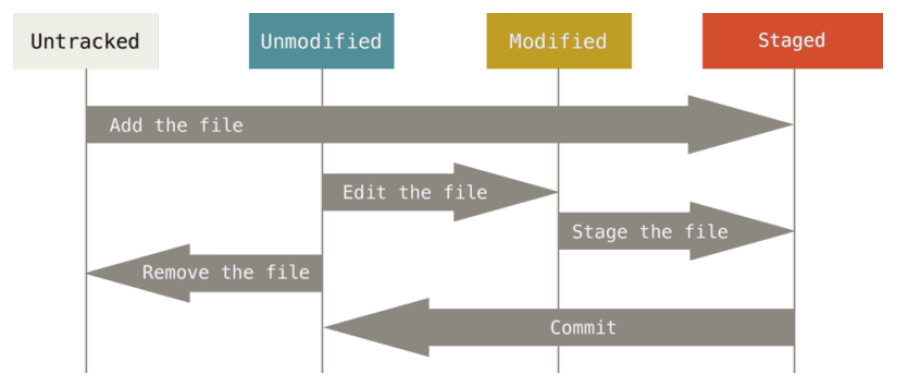
Shell UNIX
Mandatory to use for servers


Shell UNIX
What is a Shell?
The shell is a program where users can type commands, where it’s possible to create an empty directory with only one line of code.
What is?
Learning
Learning
Using a shell allows to be sure about what you are doing without having the mask of a GUI.
# Shell UNIX
Shell vs GUI
The shell is faster and it allows to learn more than a GUI.
GUI?
# Shell UNIX
# Shell UNIX

# Shell UNIX

Useful commands #1
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ls | show files and directories |
| man | read manual |
| cd | open directories |
| mv | move (or rename) file |
| cp | copy file or directory (-r) |
| rm | remove file or directory (-r) |
| pwd | (current) path working directory |
| mkdir | create a directory |
| nano, vim, ed | terminal text editor |
# Shell UNIX
cd directory_name
# Shell UNIX
cd ..
$
$
cd
ls path
# Shell UNIX
ls -f
$
$
ls
ls
$
ls test_*
$
ls *.cpp
$
ls ?.cpp
$
rm -r path/of/directory/
# Shell UNIX
rm -rf path/of/directory
$
$
rm
rm path/of/file
$
The shell does not have a trash bin: once something is deleted, it’s really gone.

# Shell UNIX
pwd
pwd - return the absolute path of the working directory
$
= ~/
/home/helias/
Pathnames
/home/helias/Desktop/file.png
# Shell UNIX
absolute path
home/helias/Desktop/file.png
relative path
./home/helias/Desktop/file.png
Desktop/file.png
./Desktop/file.png
=
.. upper directory
. current directory
TAB button
# Shell UNIX

superpower: autocomplete
Useful commands #2
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| cat | displays the contents of its inputs |
| head | displays the first 10 lines of its input |
| tail | displays the last 10 lines of its input. |
| command > [file] | redirects a command’s output to a file (overwriting any existing content). |
| command >> [file] | appends a command’s output to a file. |
| [first] | [second] | it is a pipeline: the output of the first command is used as the input to the second. |
| grep [filter] | grep part of input based on filter |
# Shell UNIX
Useful commands #3
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+C | halts the current command |
| Ctrl+Z | stops the current command, resume it in the background |
| Ctrl+R | type to bring up a recent command |
| Ctrl+L, clear | clean the terminal |
| !! | repeats the last command |
| exit | log out of current session |
| more, less | read a file part by part |
# Shell UNIX
Useful commands #4
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| $@ | take all inputs parameters |
| $1 | take the first input parameter |
| $2 | take the second input parameter |
| wget | "web get", download from URL |
| curl | transfer a URL, send http requests |
| zip | it allows to compress directories and/or files |
| mysql / mysqldump | client mysql |
# Shell UNIX
Secure SHell (SSH)
# Shell UNIX

RSA
# Shell UNIX




private
key
public
key






Alice
Bob
public
key
private
key
SSH key
# Shell UNIX

private
key
public
key




Bob

# Shell UNIX
man
$
What manual page do you want?
$
woman
$
-bash: woman: command not found
$
alias woman = man
$
What manual page do you want?
$
woman
$
tmux - cheatsheet
# Shell UNIX
Cltr+B + D # detach session
$
tmux new -s new-session
$
tmux a -t new-session
$
Exercises #1
# Shell UNIX
- make a directory called first
- change directory to the first folder
- create a file called person.txt
- change the name of person.txt to another.txt
- make a copy of the another.txt file and call it copy.txt
- remove the copy.txt file
- make a copy of the first folder and call it second
- delete the second folder
- Create a bash script that executes automatically all these tasks waiting 1 second for each task using sleep
Exercises #2
# Shell UNIX
- What does the man command do? Type in man rm. How do you scroll and get out?
- Look at the man page for ls. What does the -l flag do? What does the -a flag do?
- Type the following command to download and save the contents of google.com: curl https://www.google.com > google.html
- Use less to look at the contents of google.html.
- Look at the man page for less. Read the section on -p (/pattern). Search for the text hplogo in the google.html file.
- What is the shortcut to clear the terminal?
- What is an absolute path?
- What is an relative path?
- What do the r and f flags do with the rm command?
alias exercises
# Shell UNIX
echo "hello world" | espeak -v it
$
zipthis DIRECTORY
$
notify MESSAGE
$
Challenge: extend notify-me
# Shell UNIX
Extend the bash script notify.sh into other bash scripts that allow to send single file or directory (zipped), using:
$ tg-send path/of/the/file/or/directory
Bonus feature:
- recognize if the file is more than 50 MB, in that case the Telegram API will block you, so it is better to warn the user about it
- use telegram client (not bot) API to overcome the 50 MB limit and get 2 GB as limit.
References:
- https://github.com/Helias/Notify-me
- https://github.com/azerothcore/telegram-automated-db-backup
# GIT
Git
A way to manage your project


2005
# GIT










# GIT

# GIT

https://ohmygit.org/

https://github.com/firstcontributions/first-contributions
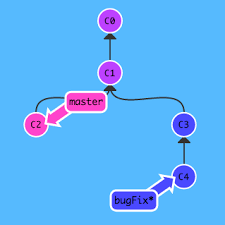
https://learngitbranching.js.org/
# GIT
$ git config
$ git add
$ git rm
$ git mv
$ git commit -m 'desc commit'
$ git checkout -b branch_name # craete a new branch
$ git checkout branch_name
$ git merge REMOTE BRANCH # ex. git merge origin master
$ git reset
$ git revert
$ git status
$ git log
$ git diff
$ git init
$ git clone
$ git remote → git remote add, git remote -v, git remote rm
$ git fetch
$ git pull
$ git push
# GIT
Linux (or WSL), via package manager:
$ apt install git
Mac via Homebrew or MacPort:
$ brew install git
$ port install git
Windows
https://gitforwindows.org/
How to install GIT



# GIT
$ git config --global user.name "Stefano Borzì"
$ git config --global user.email "stefano@example.com"
$ git config --global core.editor nano
$ git config --list
user.name=Stefano Borzì
user.email=stefano@example.com
core.editor=nano
...
$ git config user.name
Stefano Borzì
# GIT
$ git init
$ git add
$ git rm
$ git mv
$ git status
$ git diff
$ git commit -m 'desc commit'
$ git log
# GIT
git status
# GIT
# GIT
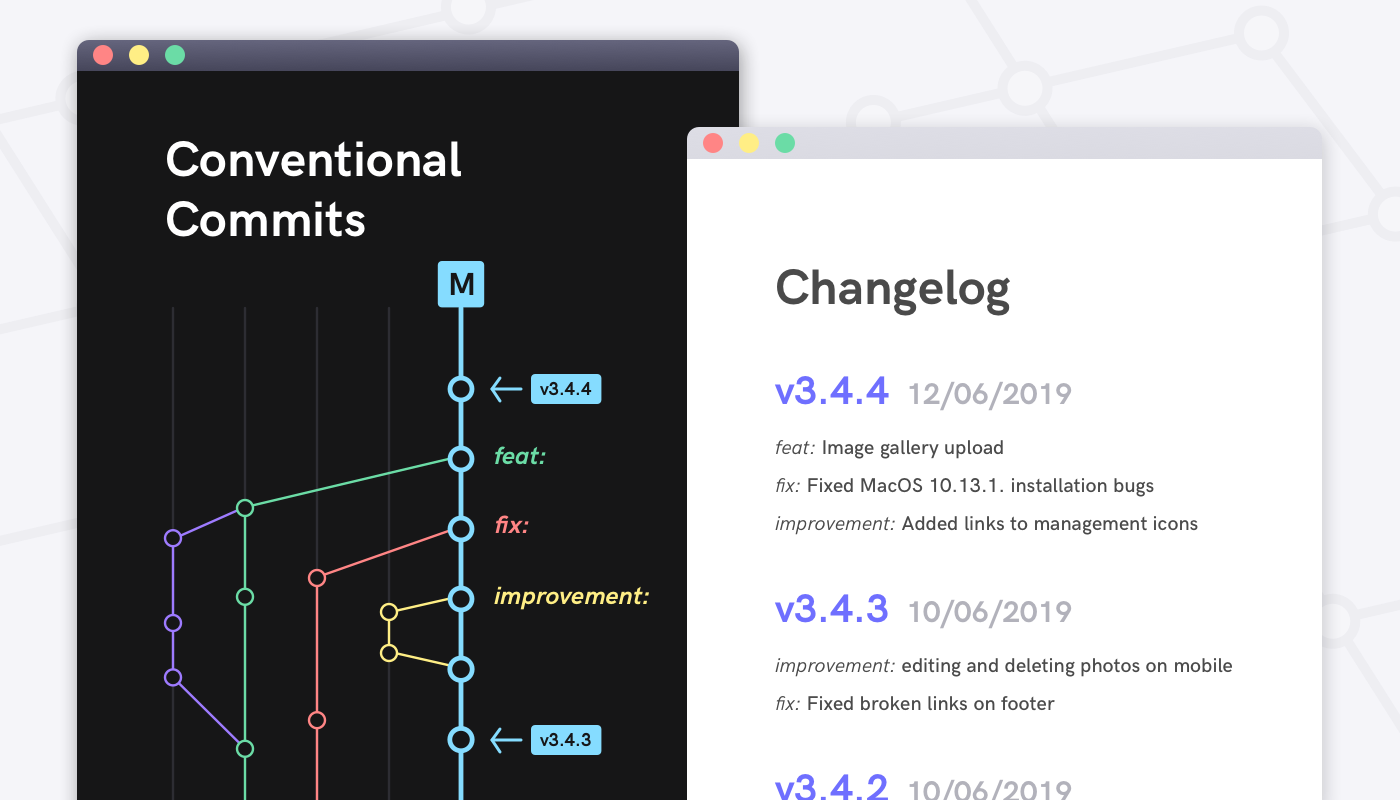
fix: for a fix ex. fix(main): windows build
feat: implementing a new feature ex. feat(home): add footer
docs: for documentation. ex. doc(contribution): add contribution guidelines
refactor: for refactoring purposes ex. refactor(tests): replace all "pippo" variables
test: adding unit-tests, e2e-etest ex. test(lessons): add unit-tests for lesson
chore: minor improvements ex. chore(merge): solve conflict
Conventional Commits
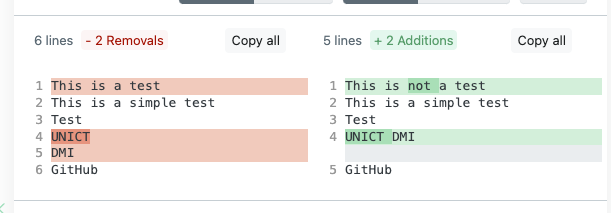
# GIT
git diff
# GIT
checkout, revert, reset
$ git checkout [COMMIT]
$ git revert [COMMIT]
$ git reset
# GIT
Branches and Merges
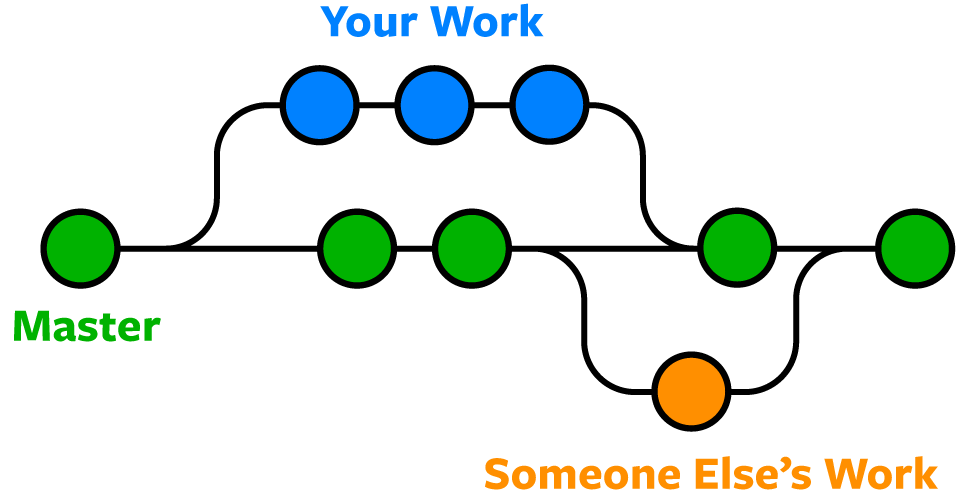



# GIT
Branches and Merges
# craete a new branch and checkout
$ git checkout -b branch_name
$ git checkout branch_name
$ git merge [REMOTE] BRANCH
# ex. git merge origin master
# GIT
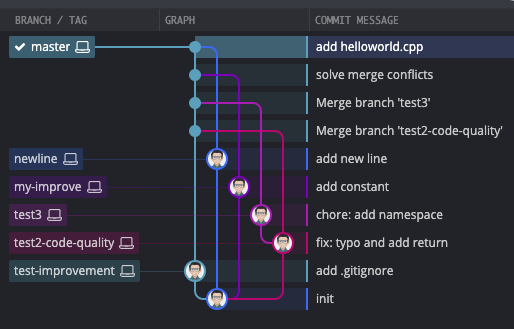
Branches and Merges

# GIT
DMI Bot - network graph
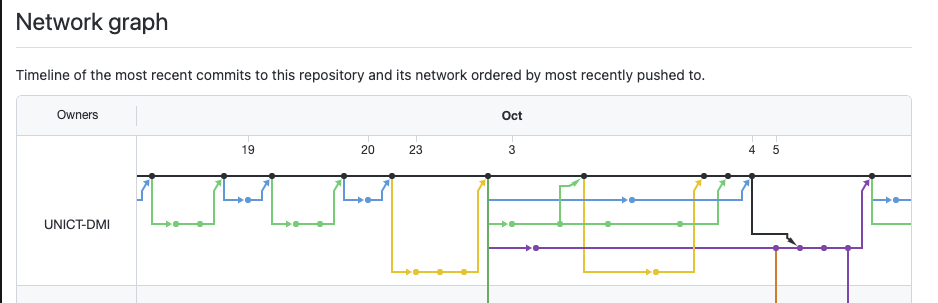
# GIT
.gitignore
https://git-scm.com/docs/gitignore
# See http://help.github.com/ignore-files/ for more about ignoring files.
# compiled output
/dist
/tmp
*.js.map
# dependencies
/node_modules
# IDEs and editors
/.idea
.project
.classpath
.c9/
*.launch
.settings/
*.sublime-workspace
.vscode/*
# System Files
.DS_Store
Thumbs.db
# GIT

GIT LFS
# GIT
GIT LFS
# GIT
Visual Studio Code plugins
Git related
- Git Lens
- Git History
Generic plugins
- sonarlint
- change-case

# GIT
Exercise
wget https://bit.ly/3ucdNHK
$
/*
Make a BRANCH per each task.
- fix warning and errors
- fix the code
- make N dynamic, let the user choose N
- remove unused
- make some improvements on your own
*/
# GIT
$ git config
$ git init
$ git add
$ git rm
$ git mv
$ git commit -m 'desc commit'
$ git checkout -b branch_name # craete a new branch
$ git checkout branch_name
$ git merge BRANCH # ex. git merge feature-1
$ git reset
$ git revert
$ git status
$ git log
$ git diff
all the commands shown so far
# GITHUB
GitHub
Git and cloud



2007
# GITHUB
What is GitHub?
# GITHUB

Bitbucket
GitLab


GitHub


# GITHUB
github.com/torvalds
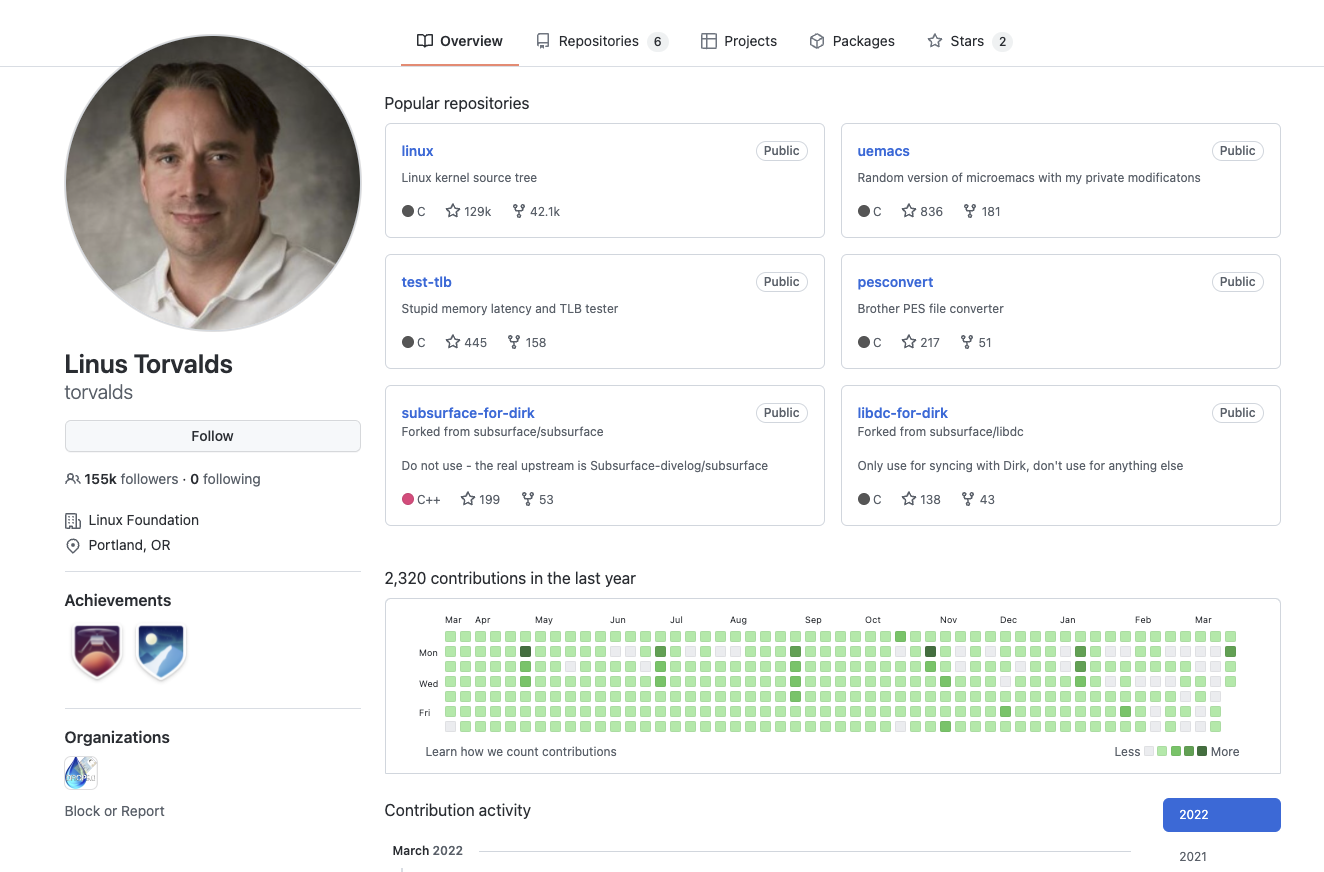
# GITHUB
GitHub organizations
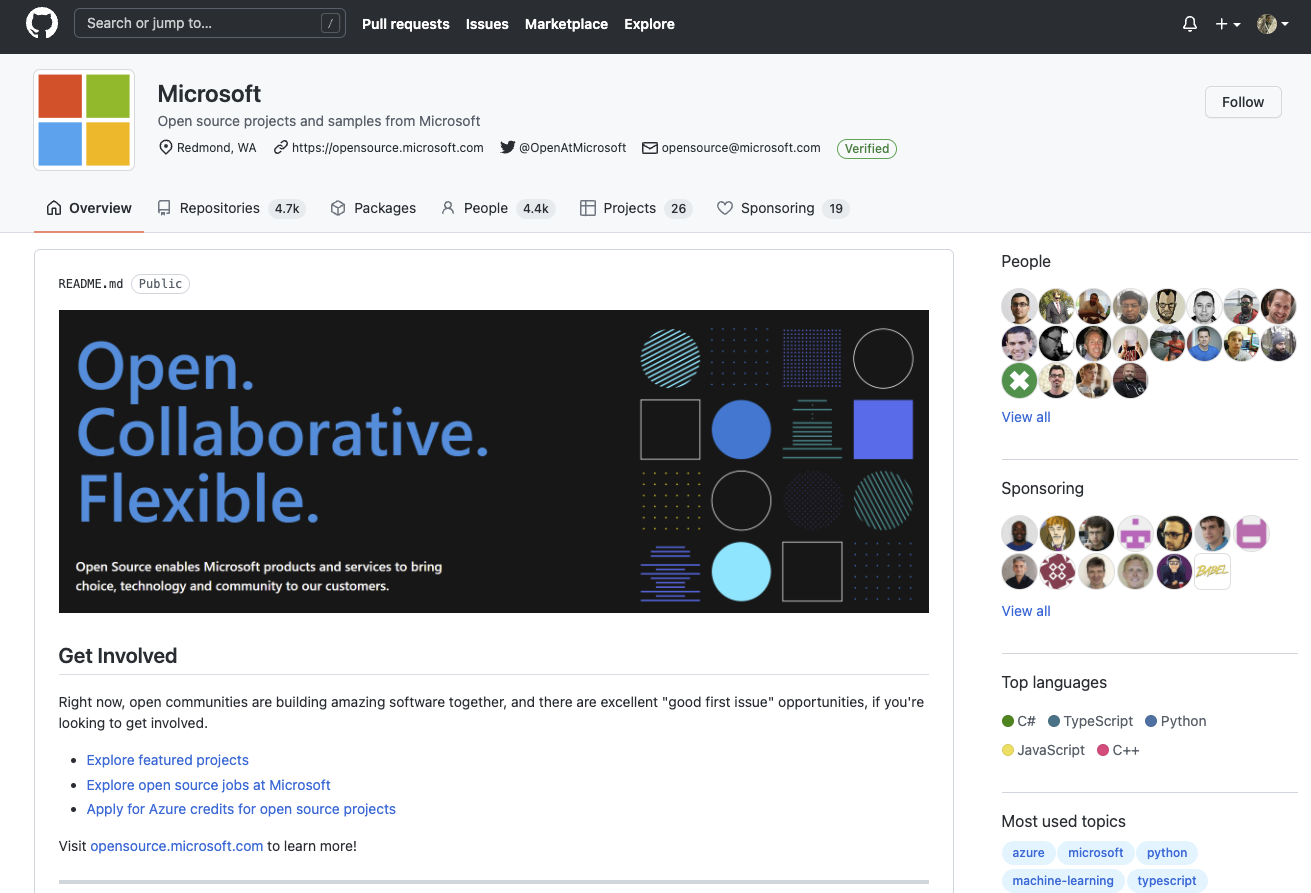
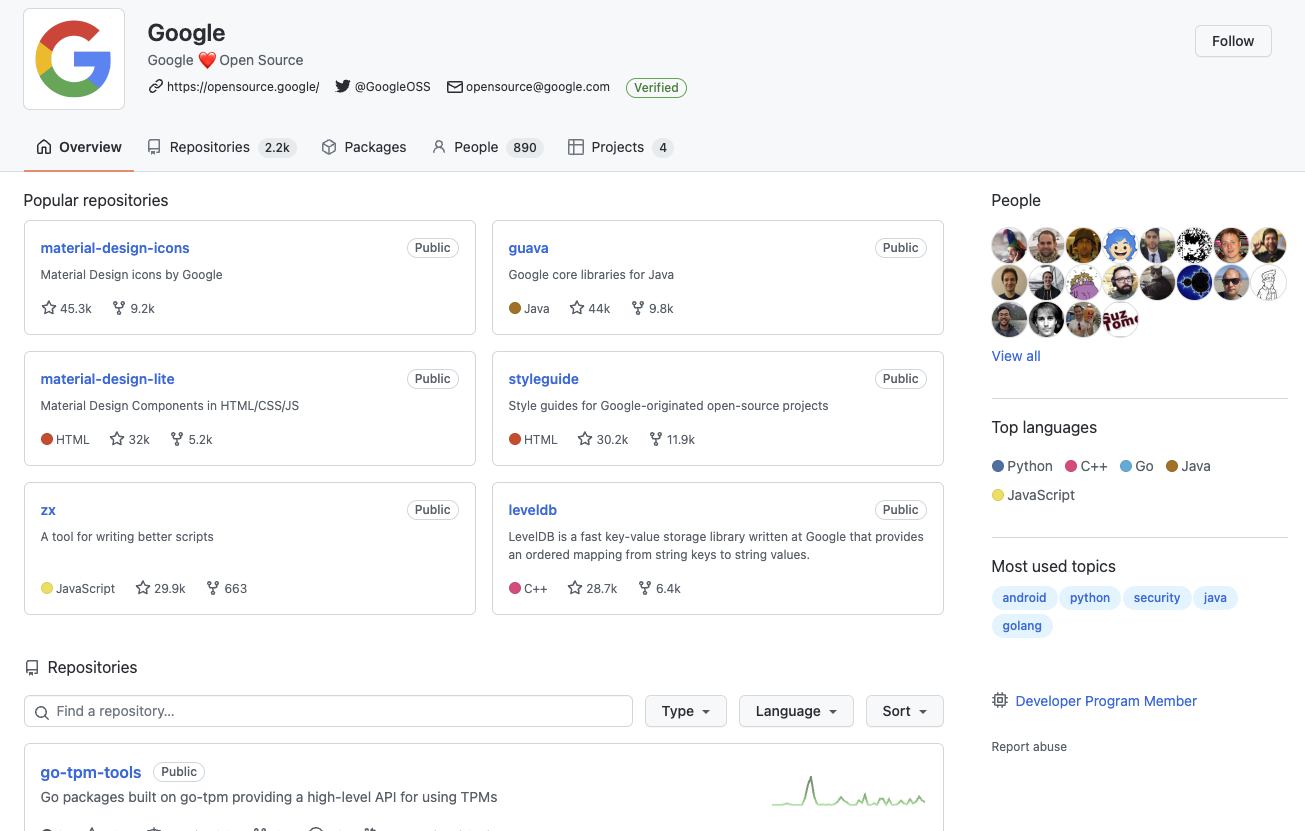
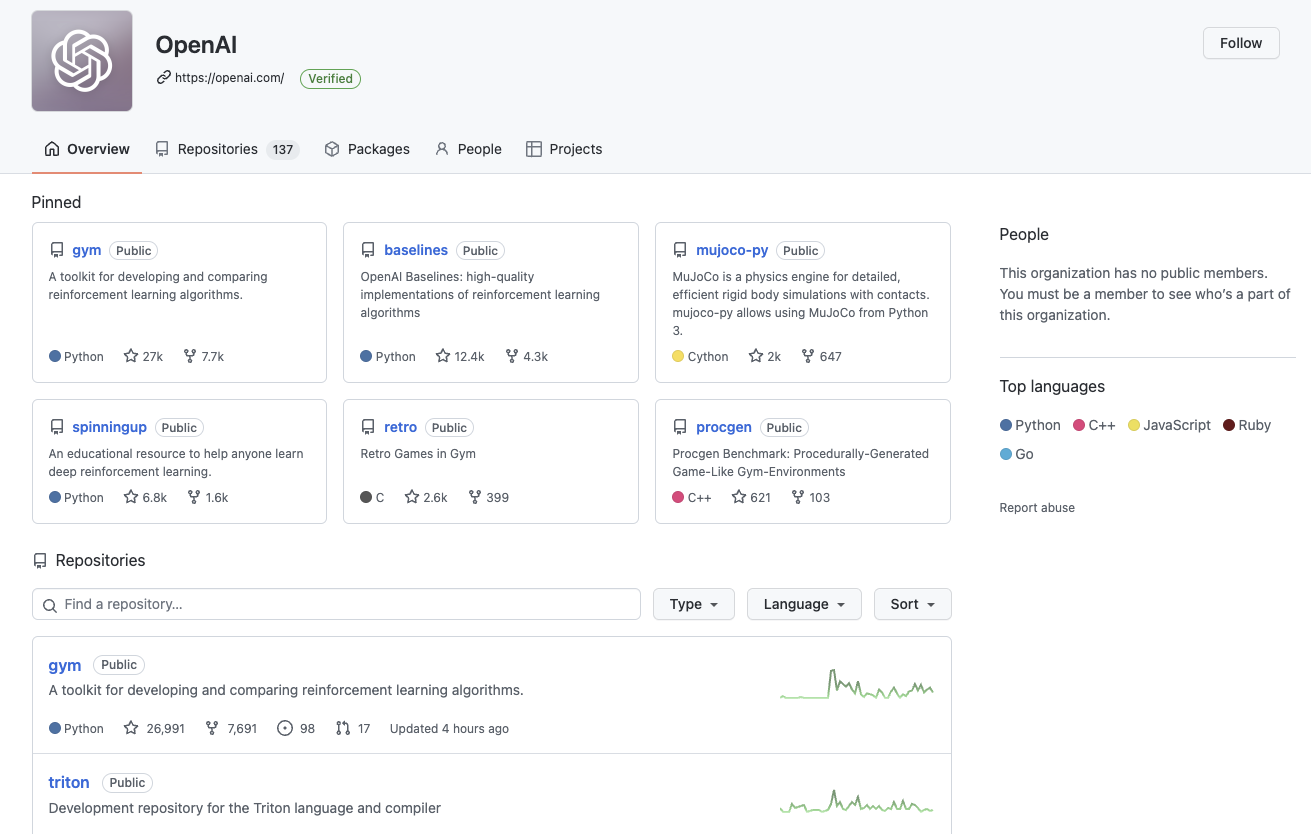
# GITHUB
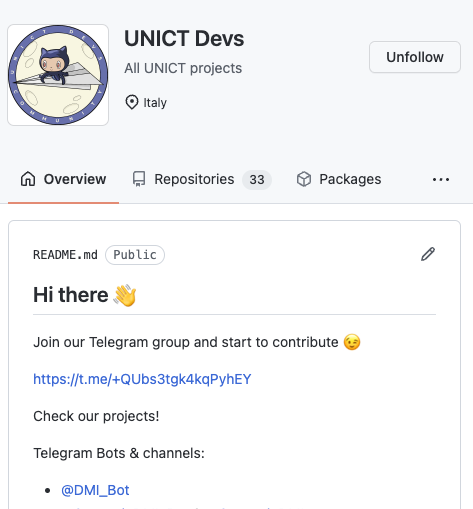
Followers - Following - Stars
# GITHUB
Repository
# GITHUB
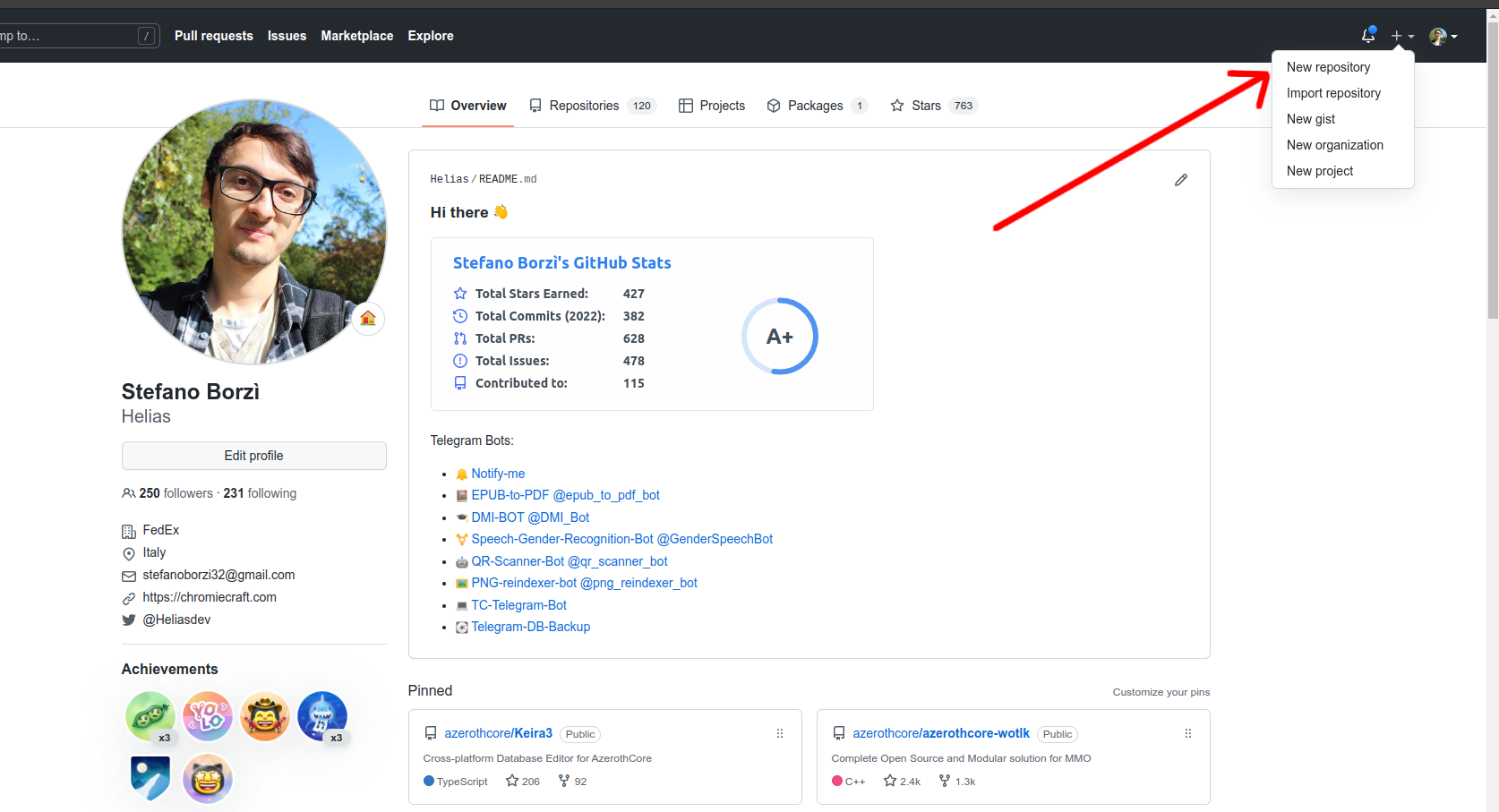
Create a new repository - 1
# GITHUB
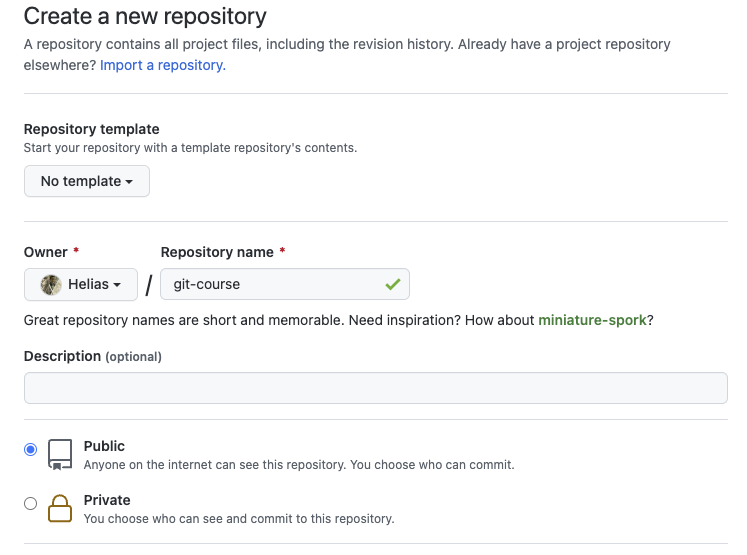
Create a new repository - 2
# GITHUB
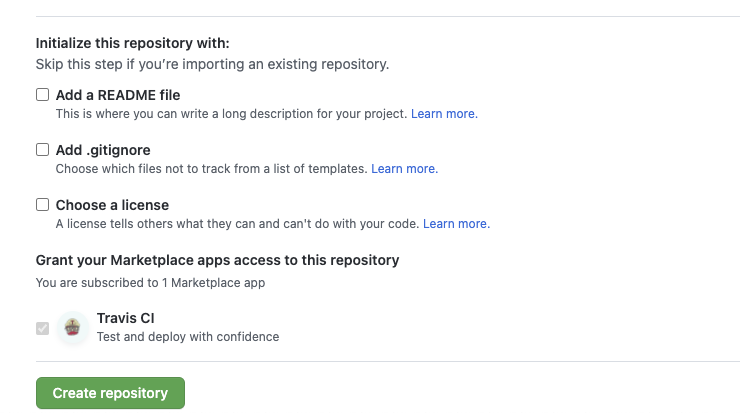
Create a new repository - 3
# GITHUB
$ git init
$ git clone
$ git remote [-v, add, rm]
$ git fetch
$ git pull
$ git push
Update your repository
# GITHUB
Update your repository
# GITHUB
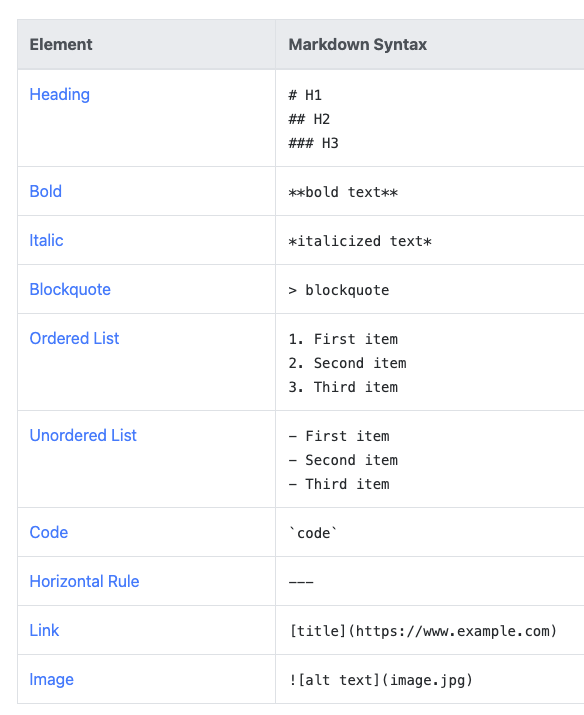
Markdown - cheat sheet
# GITHUB
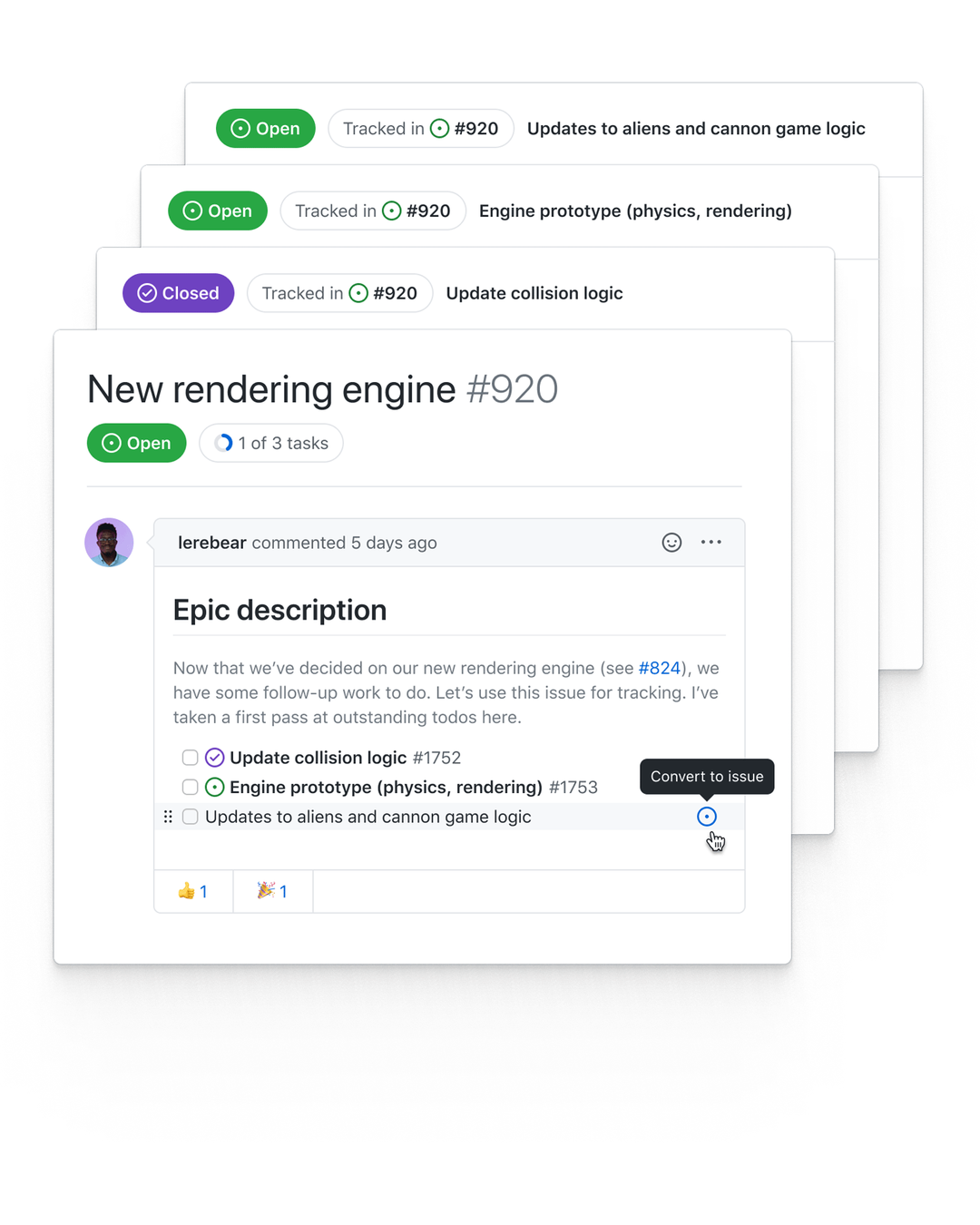
GitHub issues
# GITHUB
Telegram & GitHub
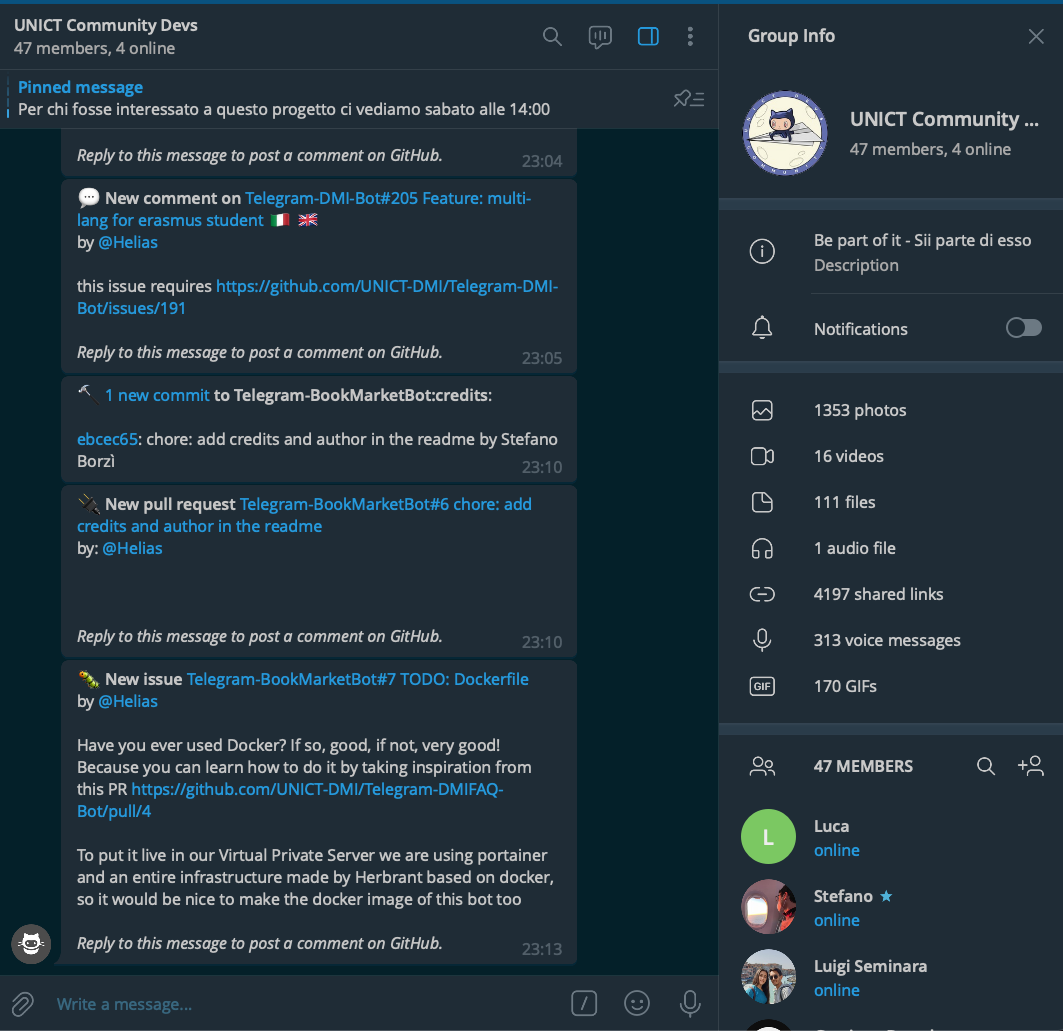
# GITHUB
GitHub Projects
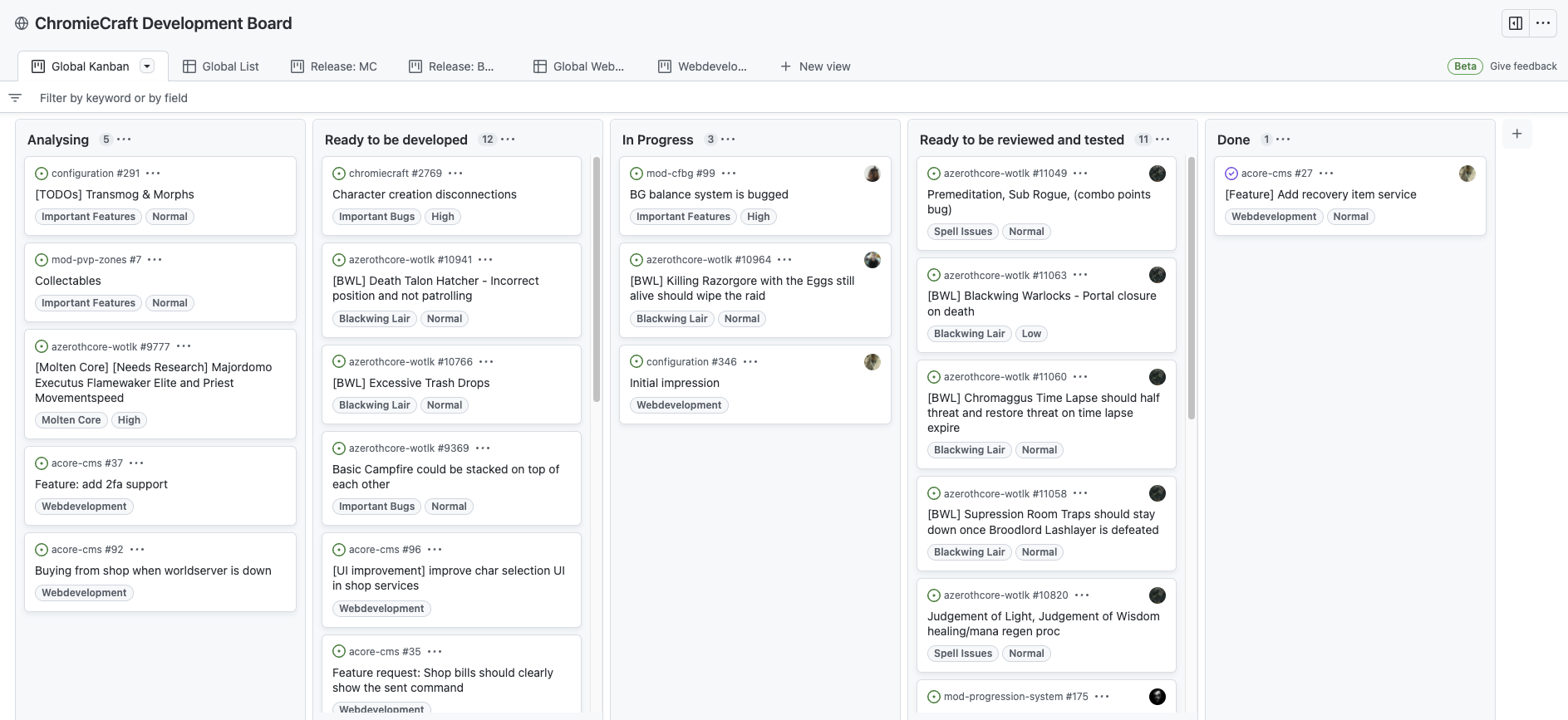
# GITHUB
GitHub Pages
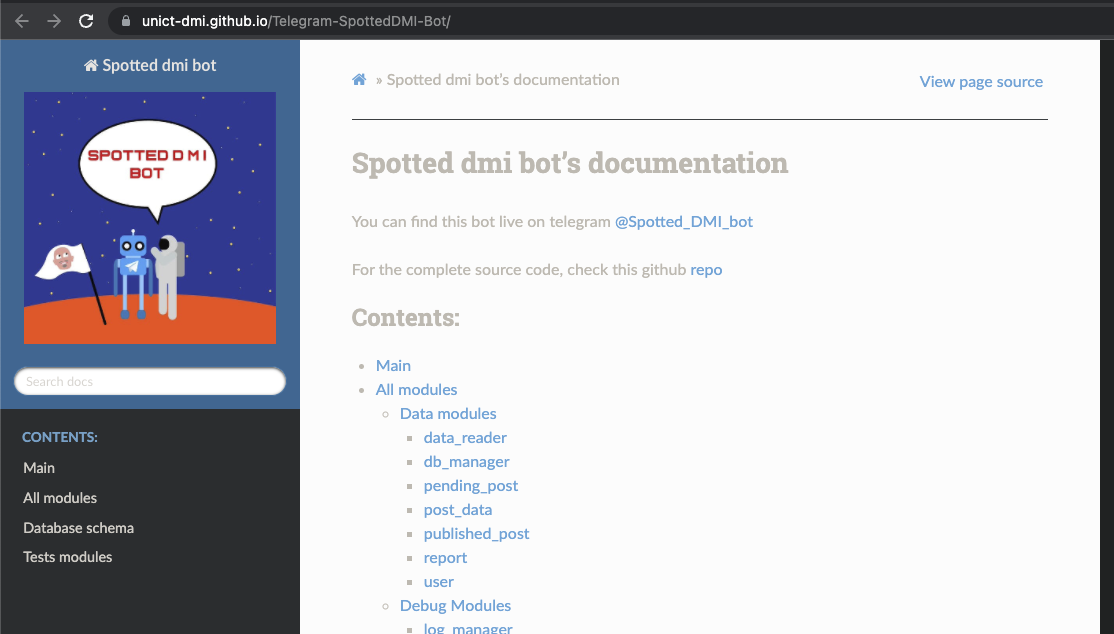
# GITHUB
Pull Request
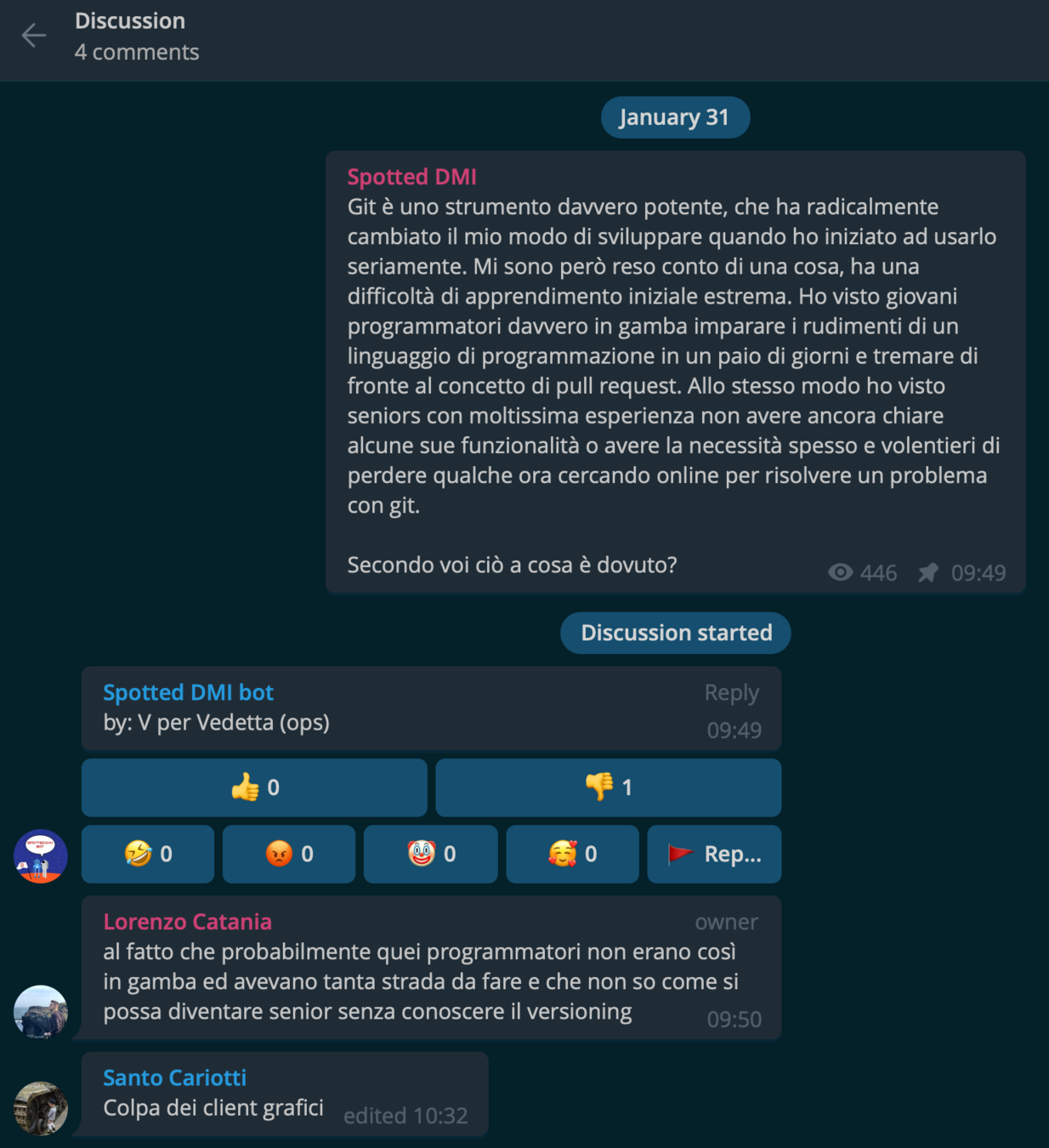
# GITHUB
Pull Request
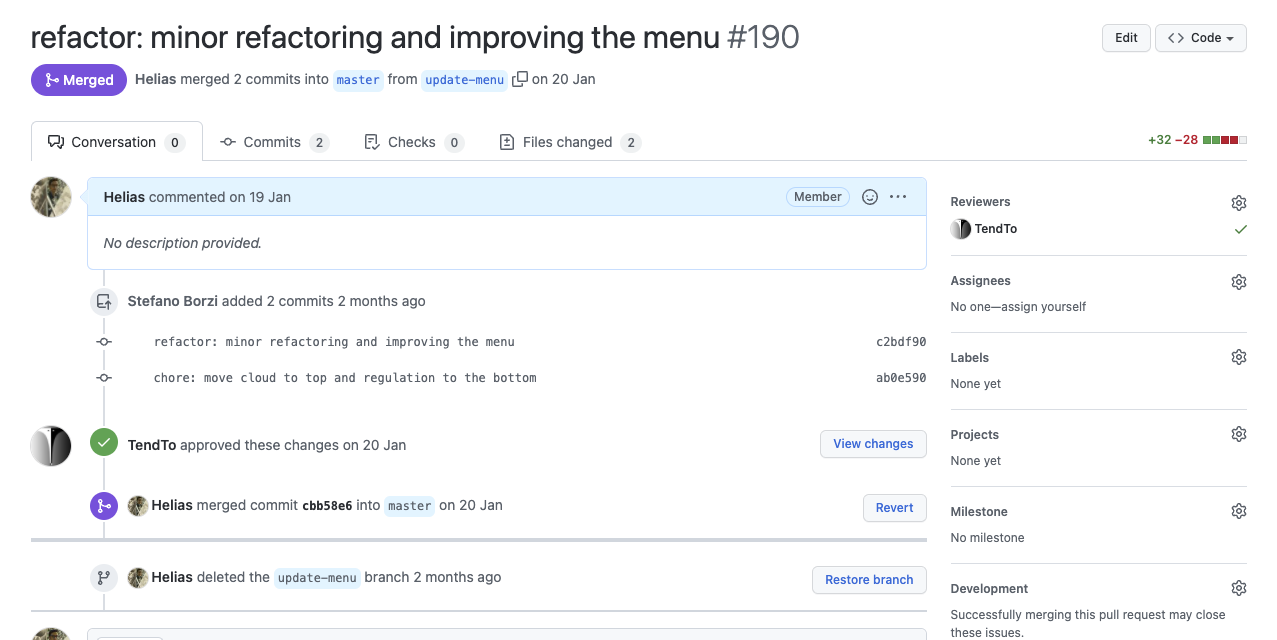
# GITHUB
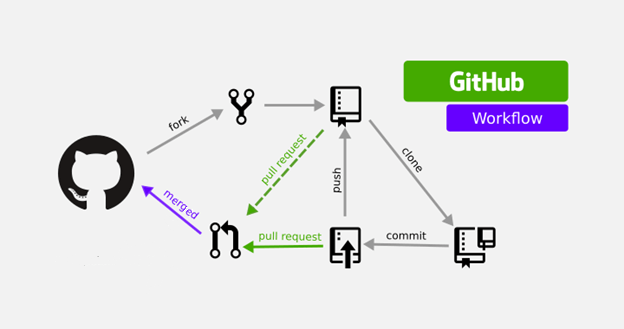
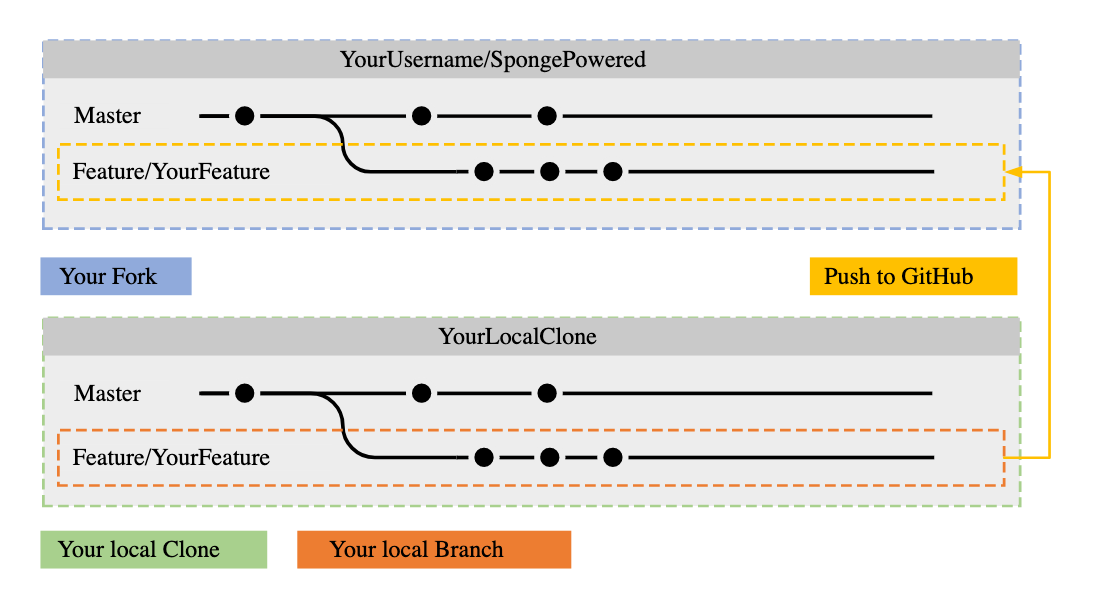
Fork
# GITHUB
Pull Request
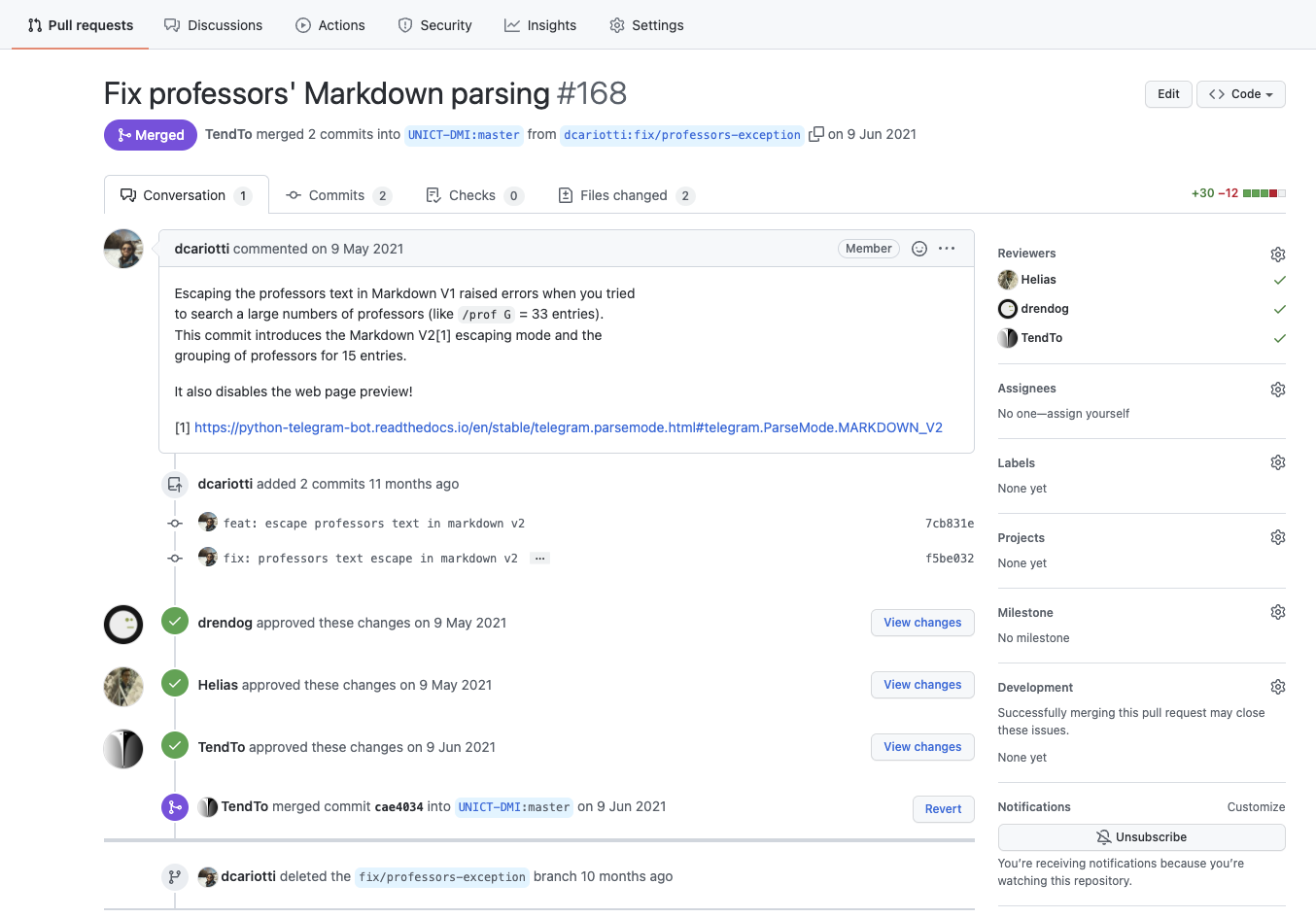
# GITHUB
Pull Request
UNICT Devs
# GITHUB
Pull Request
...others open source communities...
# GITHUB
Pull Request
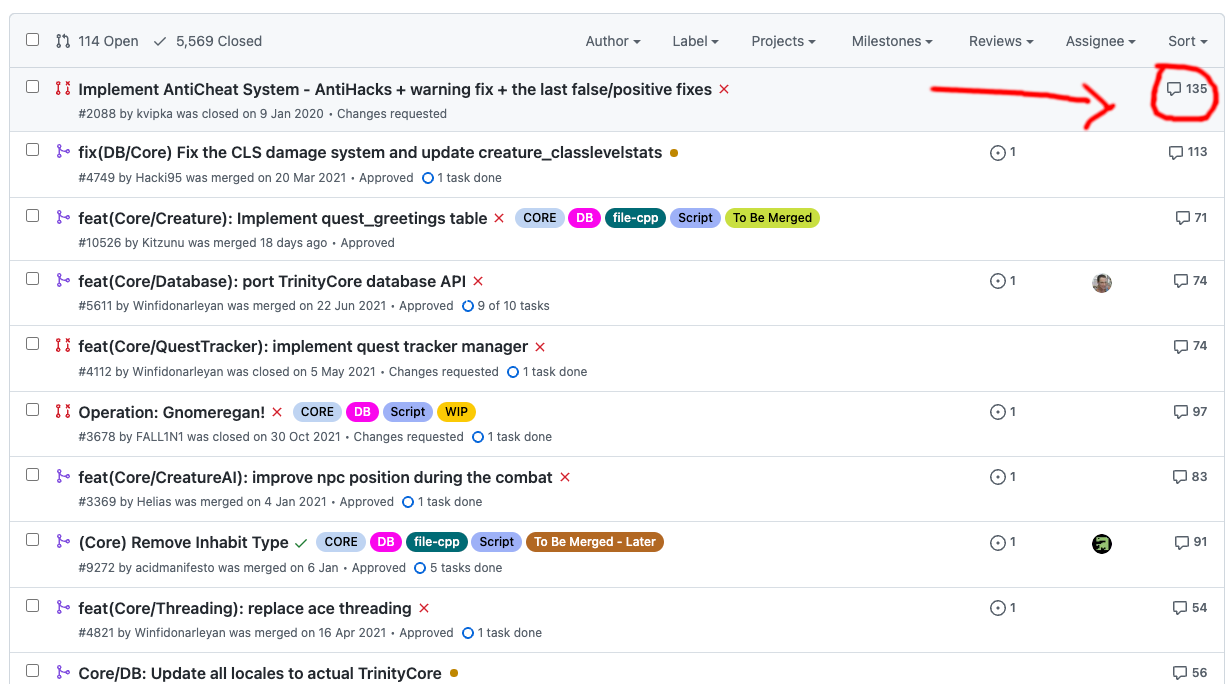
# GITHUB
Pull Request
# GITHUB
GitHub - Main or Master branch?
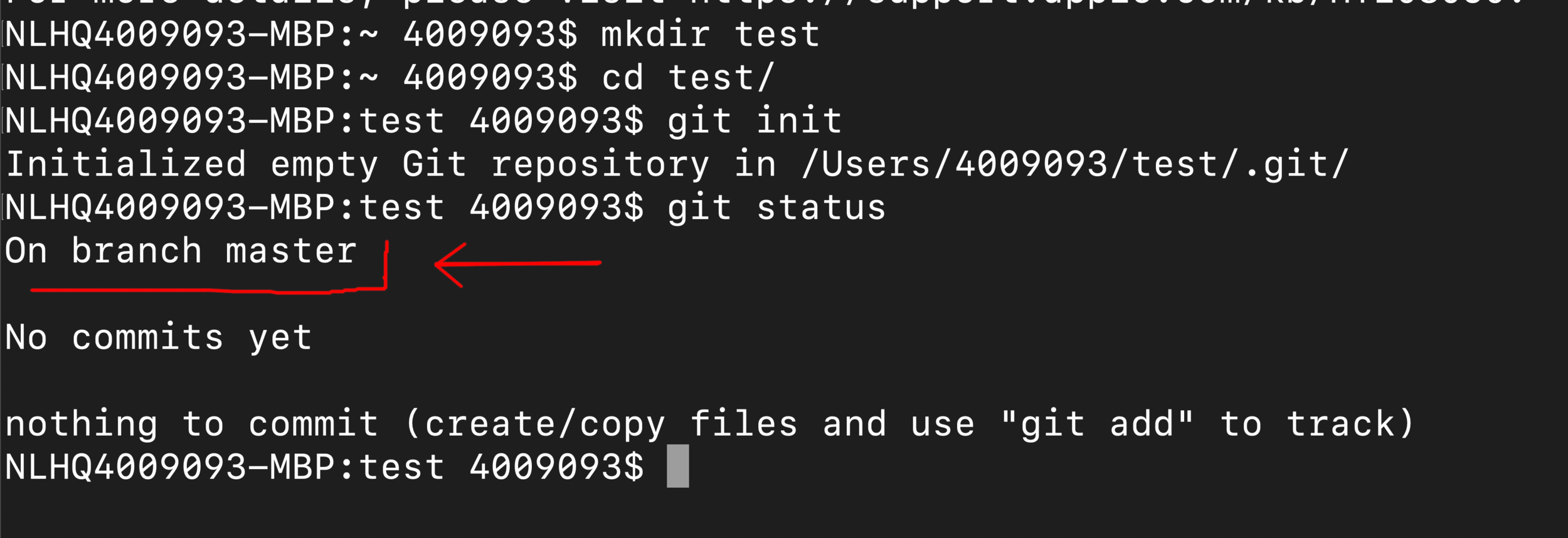
# GITHUB
GitHub - Main or Master branch?


# GITHUB
GitHub - Main or Master branch?

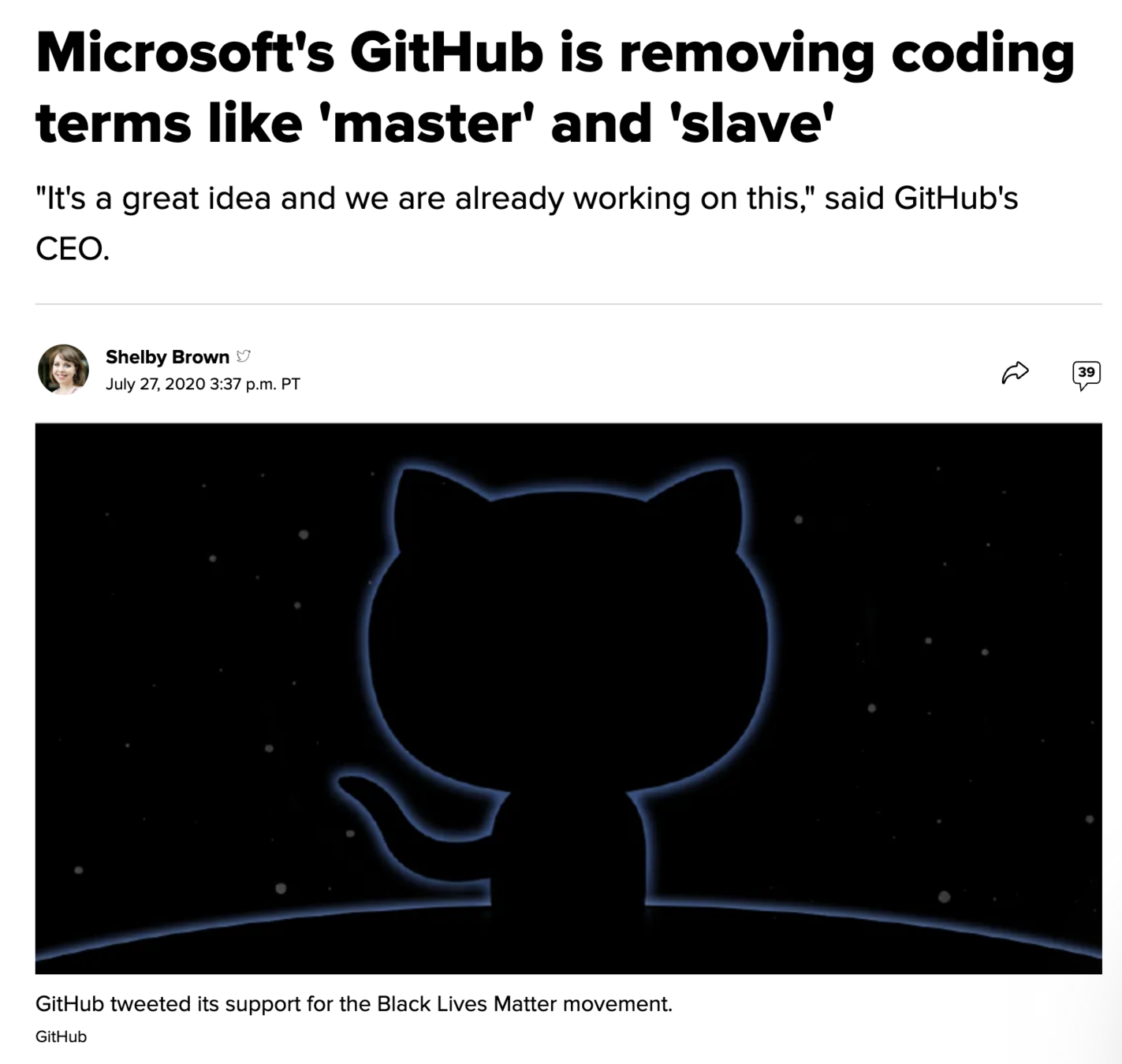
# GITHUB
GitHub - Main or Master branch?
# GITHUB
GitHub - Main or Master branch?


# GITHUB


Ban GitHub for russian developers
# GITHUB
GitHub, do not ban us
https://github.com/1995parham/github-do-not-ban-us

# GITHUB
Github in freedom
https://github.blog/2021-01-05-advancing-developer-freedom-github-is-fully-available-in-iran/

OPEN SOURCE
Opensource
Let's explore some opensource community



OPEN SOURCE
OPEN SOURCE
"Se tu hai una mela, e io ho una mela, e ce le scambiamo, allora tu ed io abbiamo sempre una mela ciascuno. Ma se tu hai un'idea, ed io ho un'idea, e ce le scambiamo, allora abbiamo entrambi due idee"
~ George Bernard Shaw

OPEN SOURCE
Microsoft & open source



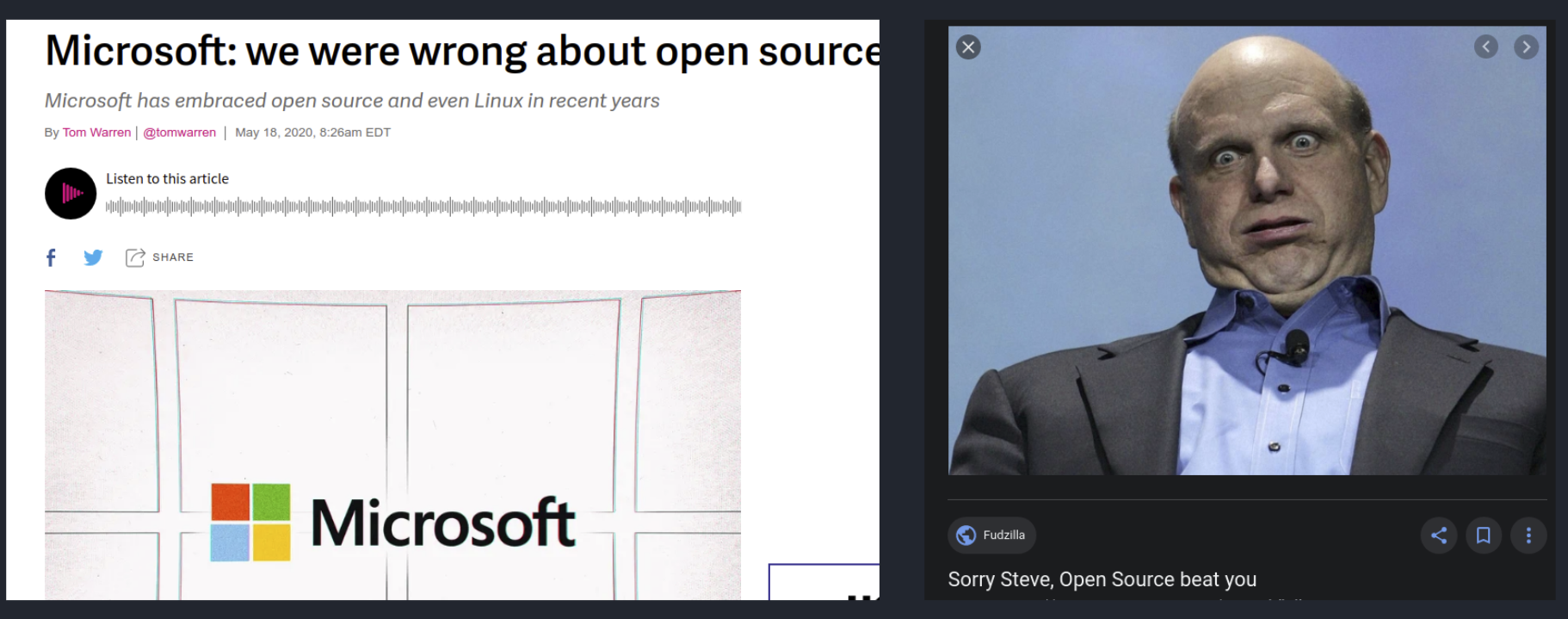

OPEN SOURCE
Microsoft & open source






OPEN SOURCE
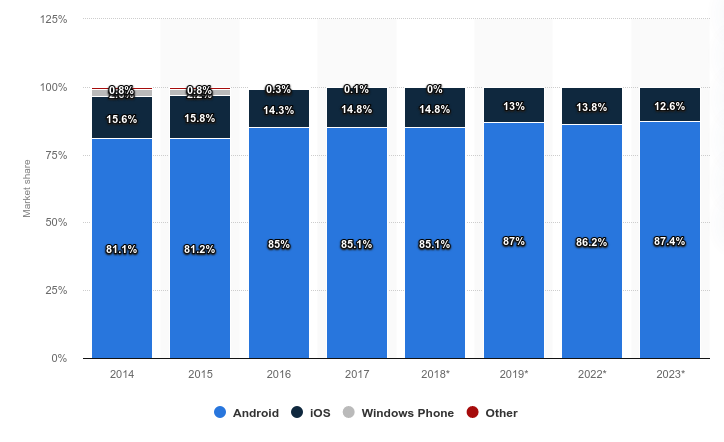
Android

OPEN SOURCE
BSD




OPEN SOURCE
Software licenses
https://choosealicense.com/licenses/
OPEN SOURCE
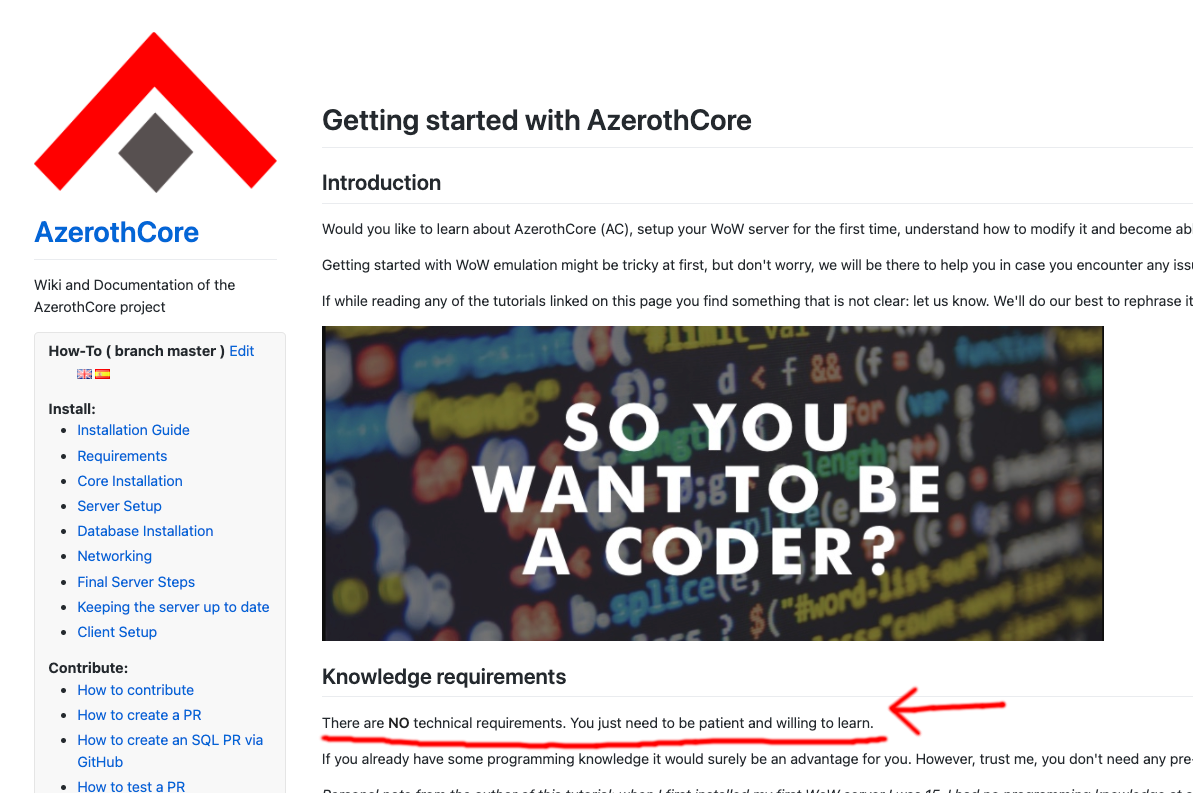
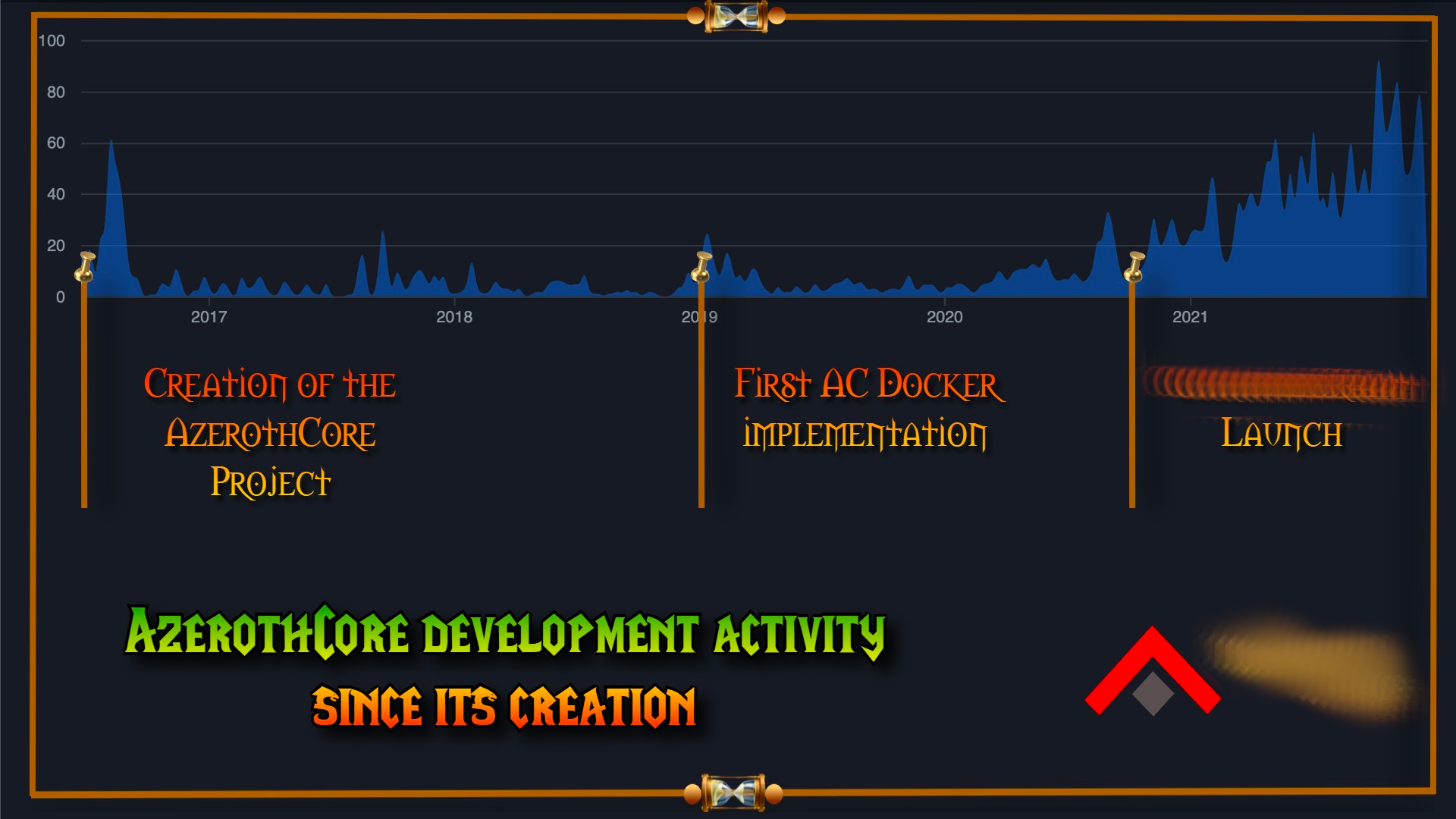
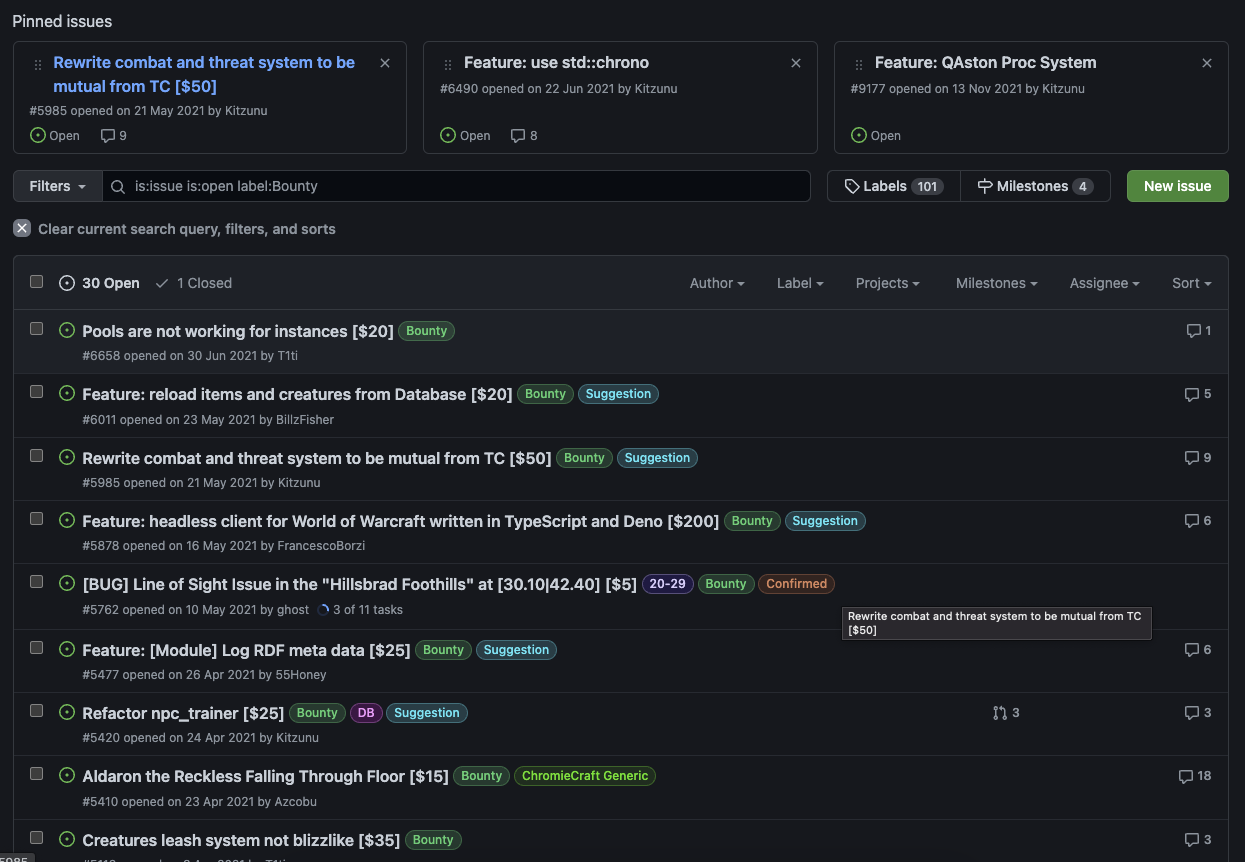
AzerothCore


OPEN SOURCE
OpenSource communities











OPEN SOURCE
Manage open source communities

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZSFDm3UYkeE
OPEN SOURCE
Why should I care?



OPEN SOURCE
Opensource & monetization
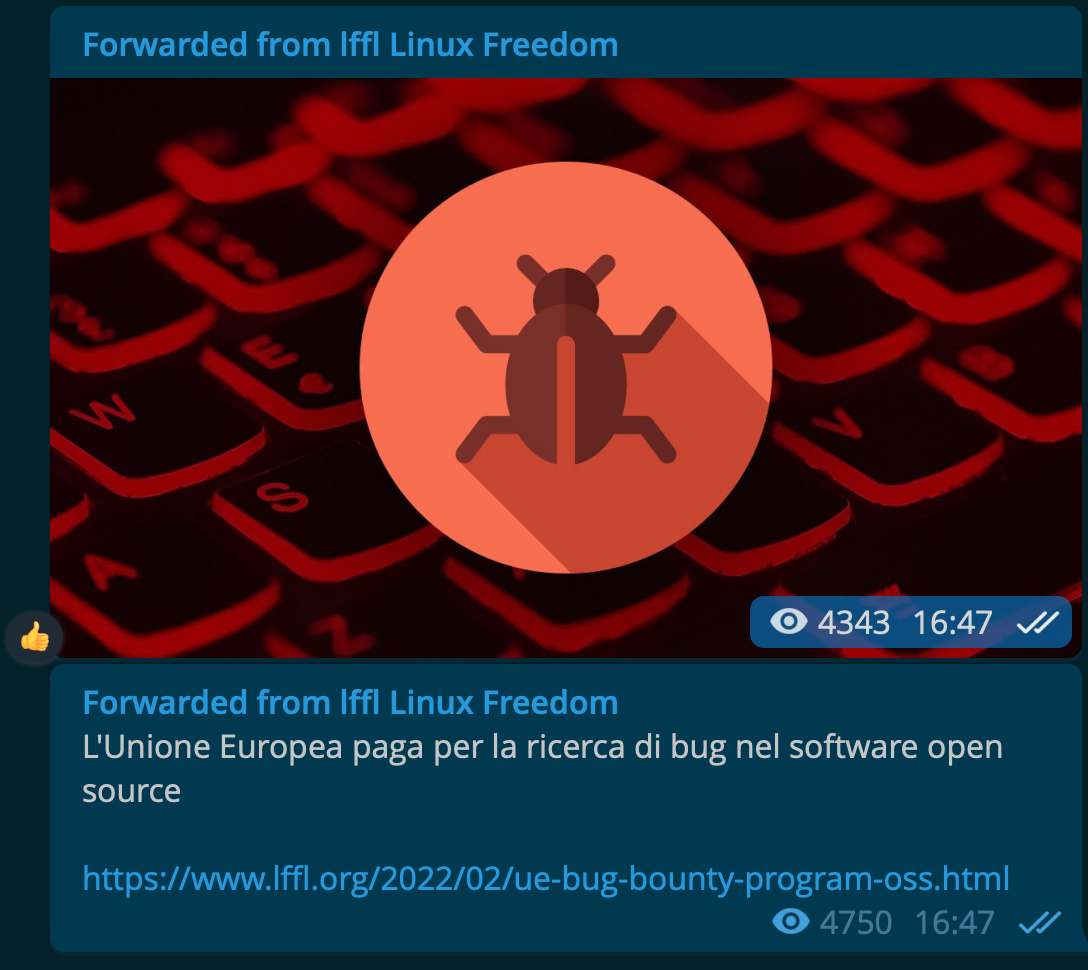

OPEN SOURCE
"Se tu hai una mela, e io ho una mela, e ce le scambiamo, allora tu ed io abbiamo sempre una mela ciascuno. Ma se tu hai un'idea, ed io ho un'idea, e ce le scambiamo, allora abbiamo entrambi due idee"
~ George Bernard Shaw

OPEN SOURCE
Informatico
ingegnere-informatico

DMI_Bot
Sfotted DIEEI


Spotted DMI Bot
OPEN SOURCE
UNICT Devs

OPEN SOURCE
UNICT Devs Projects



Python

OPEN SOURCE
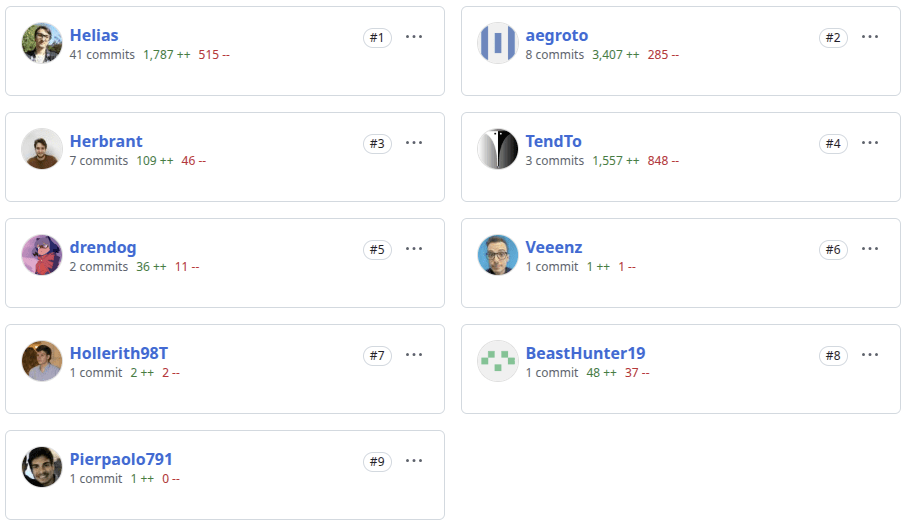
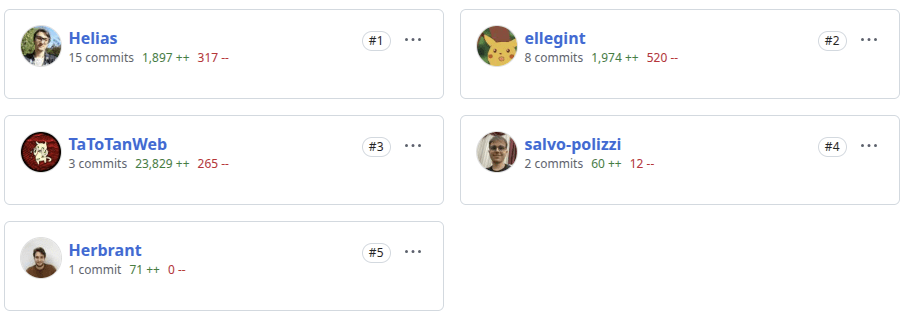
DMI Bot contributors

OPEN SOURCE
SPOTTED DMI BOT

Python

OPEN SOURCE
SPOTTED DMI BOT

OPEN SOURCE
ERSU BOT


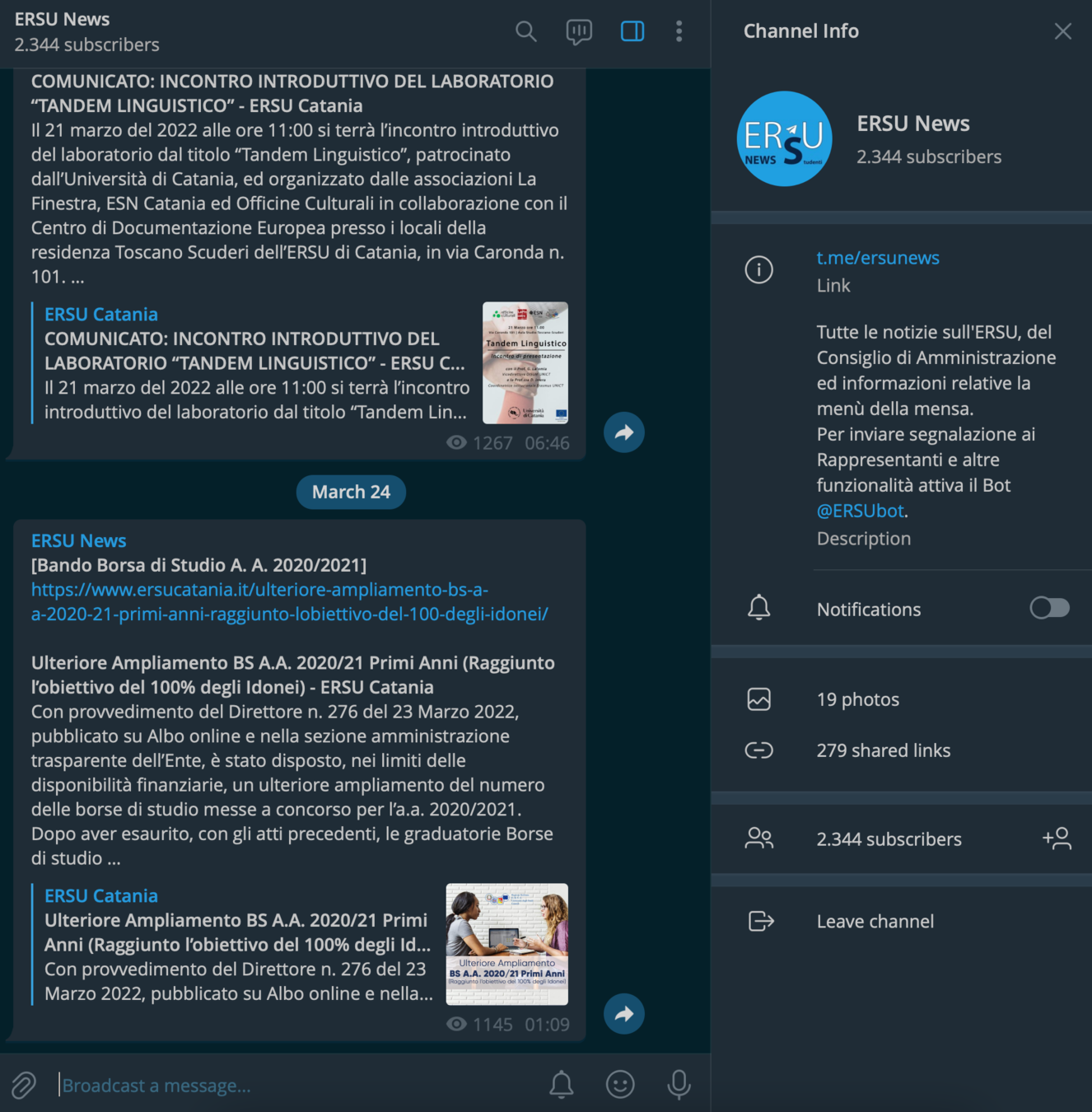



OPEN SOURCE
DMI NEWS

Python


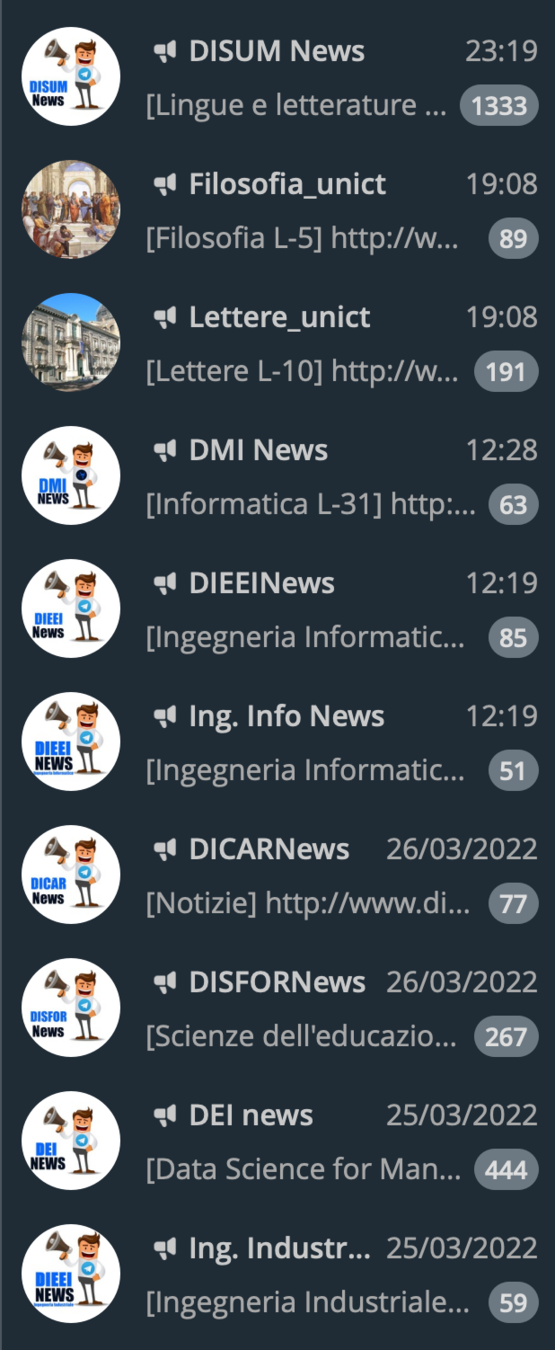
OPEN SOURCE
DMI NEWS


OPEN SOURCE
UNICT list Telegram groups & bots






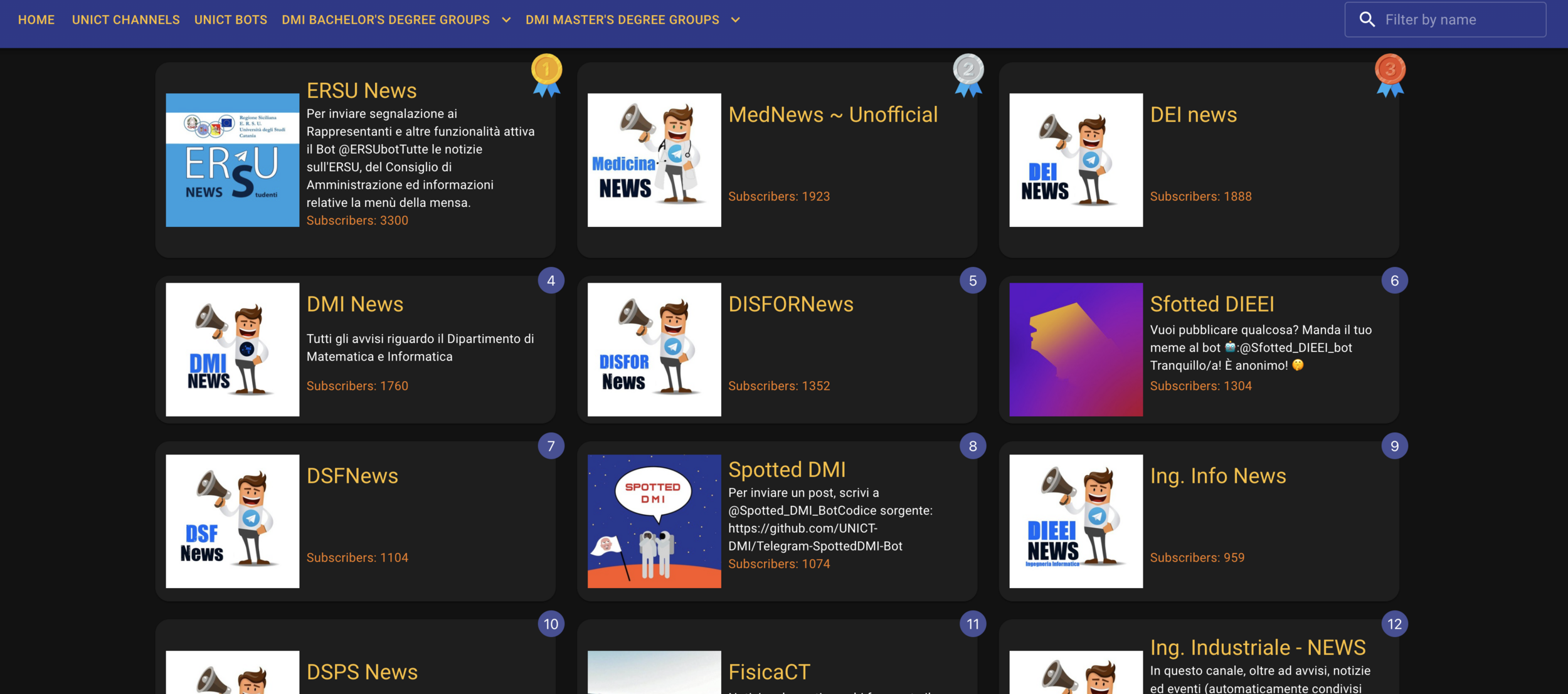
OPEN SOURCE
UNICT list Telegram groups & bots
Contributors




OPEN SOURCE
unict-reservation



OPEN SOURCE
MedBot



Python
OPEN SOURCE
Albo UNICT


Python



OPEN SOURCE
UNICT Bookmarket bot


Python


OPEN SOURCE
Studium Bot


Python

OPEN SOURCE
Open job DMI UNICT




https://open-job-dmi.unictdev.org/
https://t.me/OpenJobDMI

OPEN SOURCE
Saturday Morning Snippets


OPEN SOURCE
Santini Generator


OPEN SOURCE
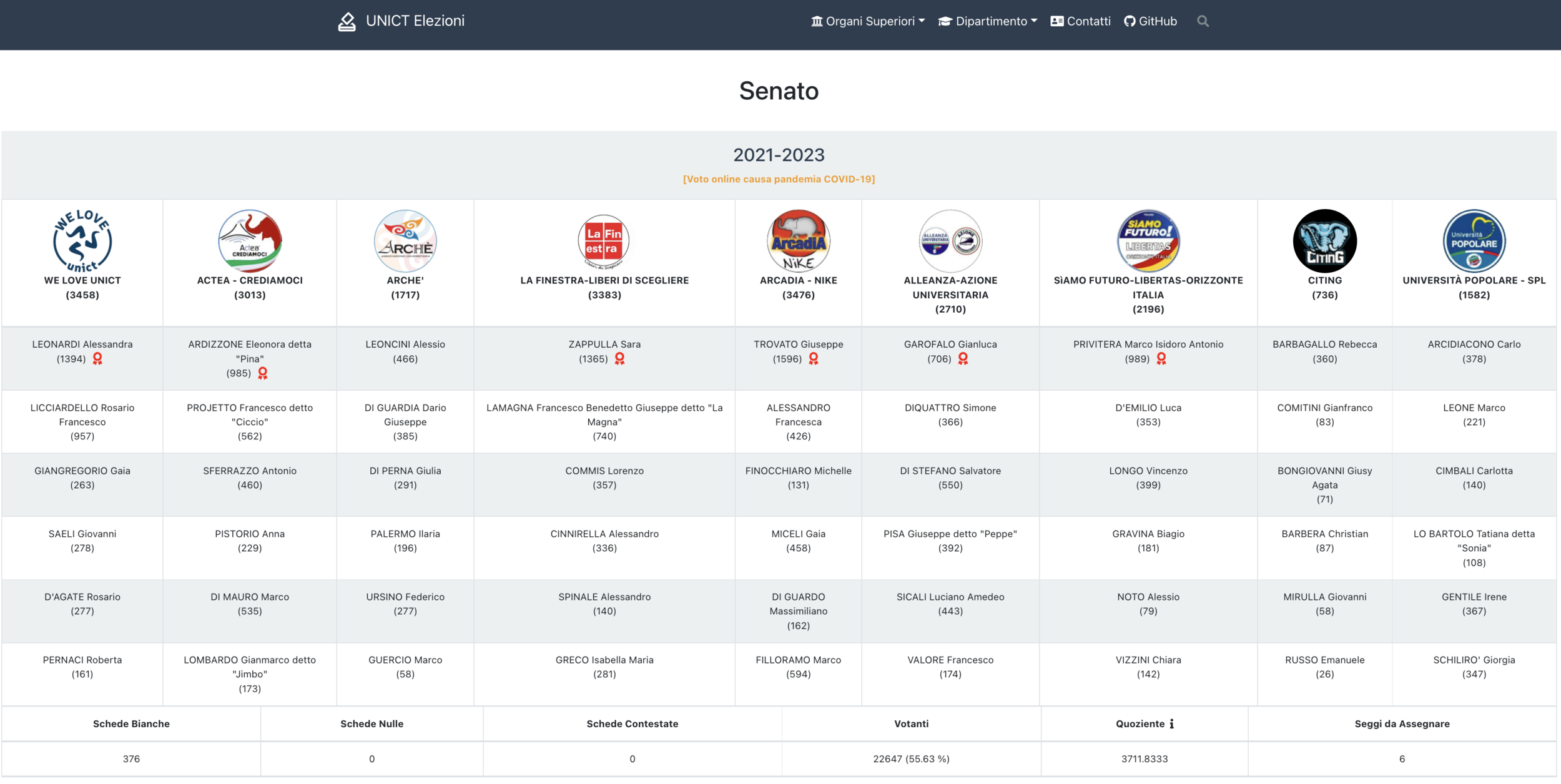
UNICT Elezioni


OPEN SOURCE
UNICT Elezioni

OPEN SOURCE
OPIS - Manager






OPEN SOURCE

OPEN SOURCE
END
Python
Python
A human language

Python
What is Python?
Python is a popular programming language. It was created by Guido van Rossum, and released in 1991.
It is used for:
- web development (server-side)
- software development
- mathematics
- system scripting
Python
How much is it used?
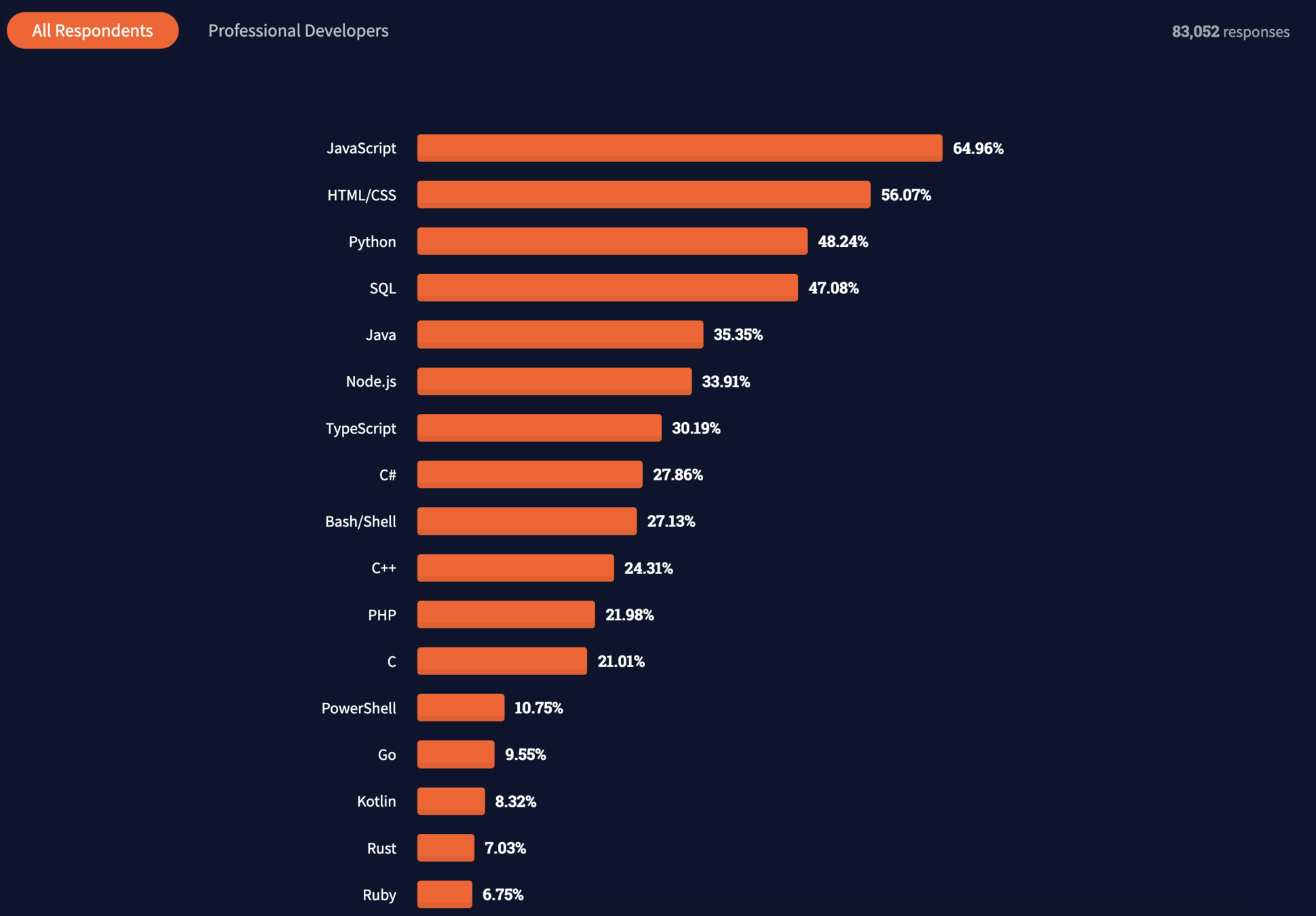
https://insights.stackoverflow.com/survey/2021#most-popular-technologies-language
Python
Download & Install Python
Linux
$ sudo apt install python
Mac OS
$ brew install python
Windows
https://www.python.org/downloads/




Python
Hello World!
print('Hello World!')#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
}


Python
Python style & indentation
if 5 > 2:
print("Five is greater than two!")#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
if (5 > 2) {
cout << "Five is greater than two!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}


Python
Python style & indentation
if 5 > 2:
print("Five is greater than two!")
if 5 > 2:
print("Five is greater than two!")

if 5 > 2:
print("Five is greater than two!")
if 5 > 2:
print("Five is greater than two!")
Python
Case style
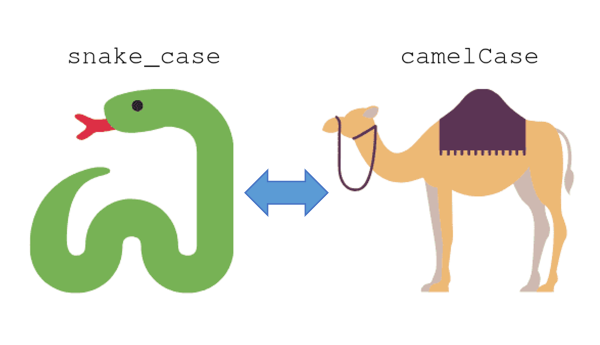


Python
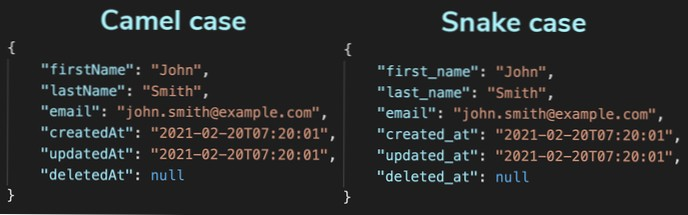
Case style


Python
Comments
# This is a comment
print("OpenSource ❤️") # This is another comment

"""
Multiple comments in
multiple lines
"""
print("Linux is an excellent operative system")Python
Python variables and types
x = 4
print(type(x))
x = "Sally"
print(type(x))

<class 'int'>
<class 'str'>x = str(3) # x will be '3'
y = int(3) # y will be 3
z = float(3) # z will be 3.0Python
Ducktyping

Python
Many Values to Multiple Variables
x, y, z = "Orange", "Banana", "Cherry"
print(x) # Orange
print(y) # Banana
print(z) # Cherry
Unpack a Collection
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
x, y, z = fruits
print(x) # apple
print(y) # banana
print(z) # cherry
Python
Scope and functions
x = "awesome"
def myfunc() -> None:
print("Python is " + x)
myfunc()x = "awesome"
def myfunc() -> None:
x = "fantastic"
print("Python is " + x)
myfunc()
print("Python is " + x)
# Python is awesomePython
The global keyword
def myfunc() -> None:
global x
x = "fantastic"
myfunc()
print("Open source is " + x)
# Open source is fantasticx = "awesome"
def myfunc() -> None:
global x
x = "fantastic"
myfunc()
print("Python is " + x) # Python is fantasticPython
Python types
|
Text Type: |
str |
|
Numeric Types: |
int, float, complex |
|
Sequence Types: |
list, tuple, range |
|
Mapping Type: |
dict |
|
Set Types: |
set, frozenset |
|
Boolean Type: |
bool |
|
Binary Types: |
bytes, bytearray, memoryview |
Python
| x = "Hello World" | str |
|---|---|
| x = 20 | int |
| x = 20.5 | float |
| x = 1j | complex |
| x = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] | list |
| x = ("apple", "banana", "cherry") | tuple |
| x = range(6) | range |
| x = {"name" : "John", "age" : 36} | dict |
| x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"} | set |
| x = frozenset({"apple", "banana", "cherry"}) | frozenset |
| x = True | bool |
| x = b"Hello" | bytes |
| x = bytearray(5) | bytearray |
| x = memoryview(bytes(5)) | memoryview |
Python
Strings are arrays
a = "Hello, World!"
print(a[1]) # e
for x in "mock":
print(x)
# m
# o
# c
# ka = "Hello, World!"
print(len(a))txt = "freedom"
print("free" in txt)txt = "freedom"
if "free" in txt:
print('there is!')
if "free" not in txt:
print("there isn't!")
Python
Slicing / Substring
b = "Hello, World!"
print(b[2:5]) # llo
print(b[:5]) # Hello
print(b[2:]) # llo, World!
print(b[-5:-2]) # orlb[:]Python
Operators
x in y # x is in the object y
x not in y
x is y # id(x) == id(y)
x is not y
x and y # x && y
x or y # x || y
not(x < 5) # !(x < 5)
id magics
>>> x = 10
>>> y = 10
>>> id(x)
11760968
>>> id(y)
11760968
>>> a = 300
>>> b = 300
>>> id(a)
140601663305712
>>> id(b)
140601663306832
Python
Range & short loop
thislist = ["apple", "linux", "microsoft"]
[print(x) for x in thislist]thislist = ["apple", "linux", "microsoft"]
for i in range(len(thislist)):
print(thislist[i])Python
Short loop
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "kiwi", "mango"]
newlist = []
for x in fruits:
if "a" in x:
newlist.append(x)
print(newlist)fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "kiwi", "mango"]
newlist = [x for x in fruits if "a" in x]
print(newlist)newlist = [expression for item in iterable if condition == True]
Python
ternary operator
'identical' if x == y else 'not identical'x == y ? 'identical' : 'not identical'


Python
Functions and types
def sum(a, b):
return a + bdef sum(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + bfrom typing import Union
def sum(a: Union[int, float], b: Union[int, float]) -> Union[int, float]:
return a + bPython
Functions and multiple types
from typing import Union
from typing import Tuple
def sum(a: Union[int, float], b: Union[int, float]) -> Tuple[int, float]:
return a + b, b + a
x, y = sum(a, b)
from typing import Union
from typing import Tuple
def sum(a: Union[int, float], b: Union[int, float]) -> Tuple[Union[int, float], Union[int, float]]:
return a + b, b + a
x, y = sum(a, b)
print(sum(3,4))
print(sum(3.0,4.0))
print(sum(3,4.0))
print(sum(3.0,4))
from typing import Union
from typing import Tuple
def sum(a: int, b: int) -> Tuple[int, int]:
return a + b, b + a
x, y = sum(a, b)

Python
List and types
def my_magic_func(arr: list) -> list:
# my magic code
return arrfrom typing import List
def my_magic_func(arr: List[str]) -> List[str]:
# my magic code
return arr
Python
Are types necessary?
https://www.reddit.com/r/Python/comments/5nb0si/why_optional_type_hinting_in_python_is_not_that/
Does the Python interpreter check types?
def sum(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + bsum(3.0, 3) # 6.0
type(sum(3.0, 3)) # floatPython
try - except
try:
print(x)
except:
print("An exception occurred")print(x)
try:
print(x)
except NameError:
print("Variable x is not defined")
except:
print("Something else went wrong")
Python
for - else
for x in range(6):
print(x)
else:
print("Finally finished!")Print all numbers from 0 to 5, and print a message when the loop has ended:
for x in range(6):
if x == 3: break
print(x)
else:
print("Finally finished!")If the loop breaks, the else block is not executed.
Python
Classes & Objects
class MyClass:
x = 5
p1 = MyClass()
print(p1.x)class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def myfunc(self):
print("Hello my name is " + self.name)
p1 = Person("Helias", 26)
p1.myfunc()Python
Classes & Objects
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self, fname, age, year):
super().__init__(fname, age)
self.graduationyear = year
x = Student("Lorenzo", 23, 2021)Python
private attributes and methods
class P:
def __init__(self, name, alias):
self.name = name # public
self.__alias = alias # private
x = P(name='Alessio', alias='Admin di Spotted')
x.alias
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
AttributeError: P instance has no attribute 'alias'
x._P__alias
'Admin di Spotted'
Python
pip - the pyhton package manager
$ pip install python-telegram-bot

$ pip install -r requirements.txt
$ pip install -r requirements_dev.txt
Python
virtual environment
$ pip install virtualenv
$ virtualenv myenv
$ source myenv/bin/activate
$ python --version
Python 3.9.10
$ deactivate
$ python --version
Python 2.7
Unit test
Unit test
Software testing


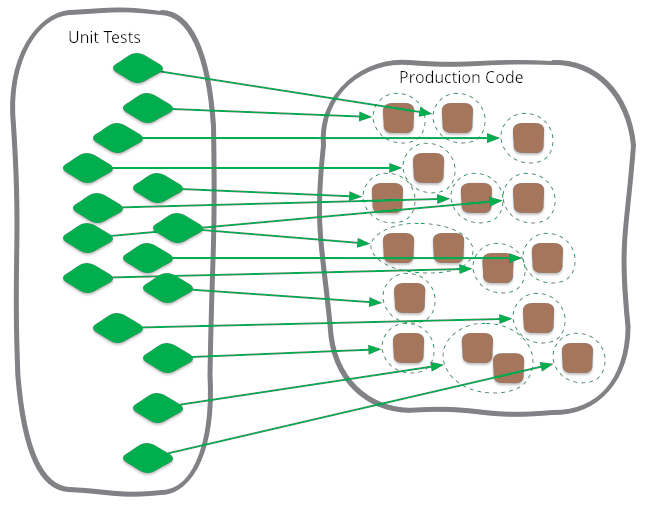
Unit test
def sum(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + bdef test_sum() -> None:
assert sum(3,5) == 8
assert type(sum(3,5)) is intUnit test
Unit test
# example.py
from random import random
def a() -> bool:
return random() > 0.5
def b() -> int:
is_a = a()
if is_a:
...
return 10
else:
...
return 20
Unit test

$ pip install pytest
Unit test

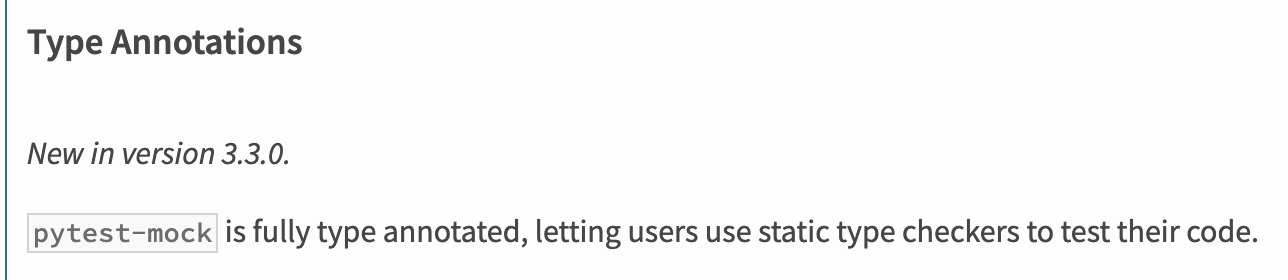
$ pip install pytest-mock
Unit test
Mock
def a() -> bool:
return random() > 0.5
from pytest_mock import MockerFixture
import example
def test_a_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.4
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is False
Unit test
Spy
def a() -> bool:
return random() > 0.5
from pytest_mock import MockerFixture
import example
def test_a_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.4
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "random")
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is False
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_random_return
Unit test
all tests "a" cases
from pytest_mock import MockerFixture
import example
def test_a_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.4
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "random")
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is False
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_random_return
def test_a_2(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.6
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "random")
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is True
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_random_return
Unit test
test "b" case 1
def b() -> int:
is_a = a()
if is_a:
...
return 10
else:
...
return 20
def test_b_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_a_return = True
mocker.patch(__name__ + '.example.a', return_value=mock_a_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "a")
# act
res = example.b()
# assert
assert res == 10
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_a_returnUnit test
from pytest_mock import MockerFixture
import example
def test_a_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.4
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "random")
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is False
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_random_return
def test_a_2(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.6
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "random")
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is True
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_random_return
def test_b_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_a_return = True
mocker.patch(__name__ + '.example.a', return_value=mock_a_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "a")
# act
res = example.b()
# assert
assert res == 10
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_a_return
def test_b_2(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_a_return = False
mocker.patch(__name__ + '.example.a', return_value=mock_a_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "a")
# act
res = example.b()
# assert
assert res == 20
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_a_return
Unit test
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("x", [0, 1])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("y", [2, 3])
def test_foo(x, y):
pass
from typing import List
import pytest
from pytest_mock import MockerFixture
import example
tests: List[dict] = [
{ "mock_value": 0.4, "mock_function": "random", "spy_count": 1, "res": example.a, "expected_res": False },
{ "mock_value": 0.6, "mock_function": "random", "spy_count": 1, "res": example.a, "expected_res": True },
{ "mock_value": True, "mock_function": "a", "spy_count": 1, "res": example.b, "expected_res": 10 },
{ "mock_value": False, "mock_function": "a", "spy_count": 1, "res": example.b, "expected_res": 20 },
]
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test", tests)
def test_generic(mocker: MockerFixture, test: dict) -> None:
# arrange
mocker.patch.object(example, test["mock_function"], return_value=test["mock_value"])
spy = mocker.spy(example, test["mock_function"])
# act
res = test["res"]()
# assert
assert res is test["expected_res"]
assert spy.call_count == test["spy_count"]
assert spy.spy_return == test["mock_value"]
test parametrization
x=0 => y=2, y=3
x=1 => y=2, y=3
4 test casesUnit test
Stub
def test_stub(mocker):
def foo(on_something):
on_something('foo', 'bar')
stub = mocker.stub(name='on_something_stub')
foo(stub)
stub.assert_called_once_with('foo', 'bar')
The stub is a mock object that accepts any arguments and is useful to test callbacks.
Unit test
code coverage

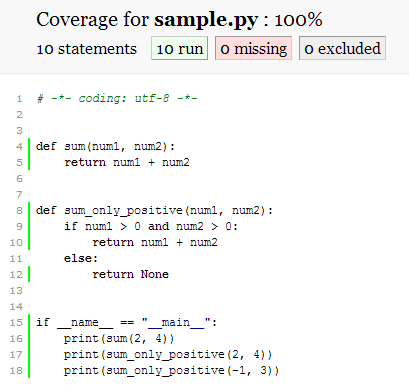
Unit test
code coverage
$ pip install pytest-cov

$ pytest test_sample.py --cov=example --cov-report=html
Unit test
code coverage
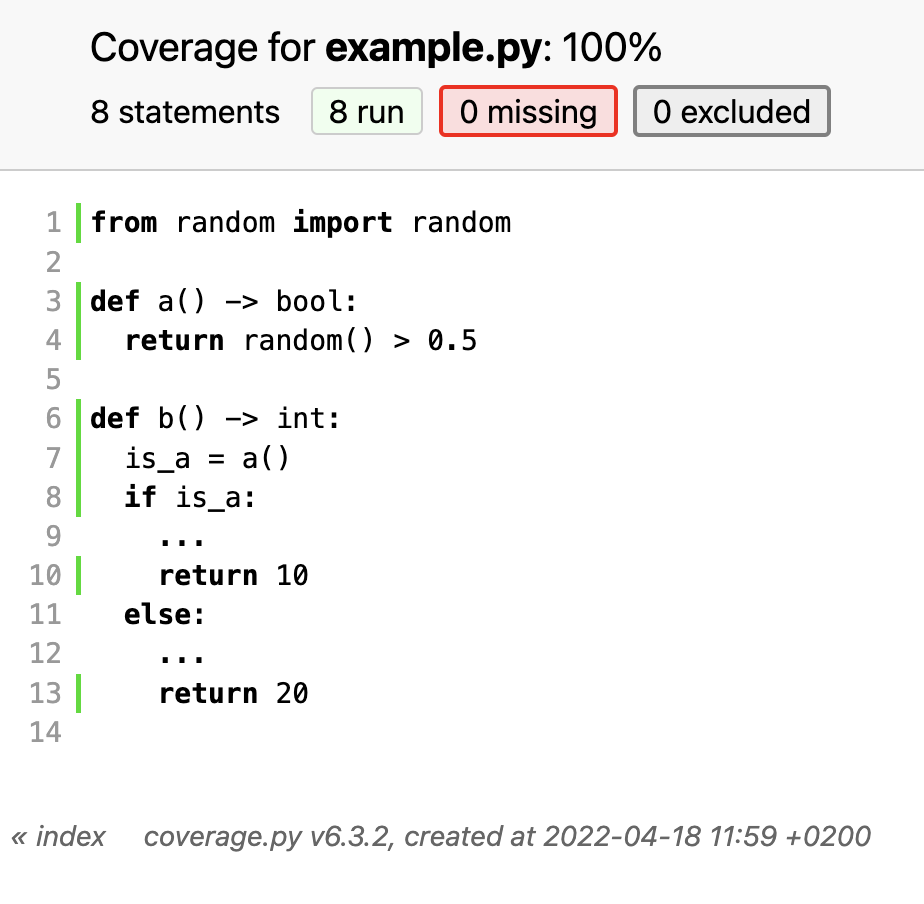
Unit test
Unit Test
PROs
- long-term maintenance
- safer and easier refactoring
- quality assurance
- error detection
CONs
- time-consuming
- hard to write
- Not all errors can be detected later different integration bugs may appear.
Unit test
Unit test
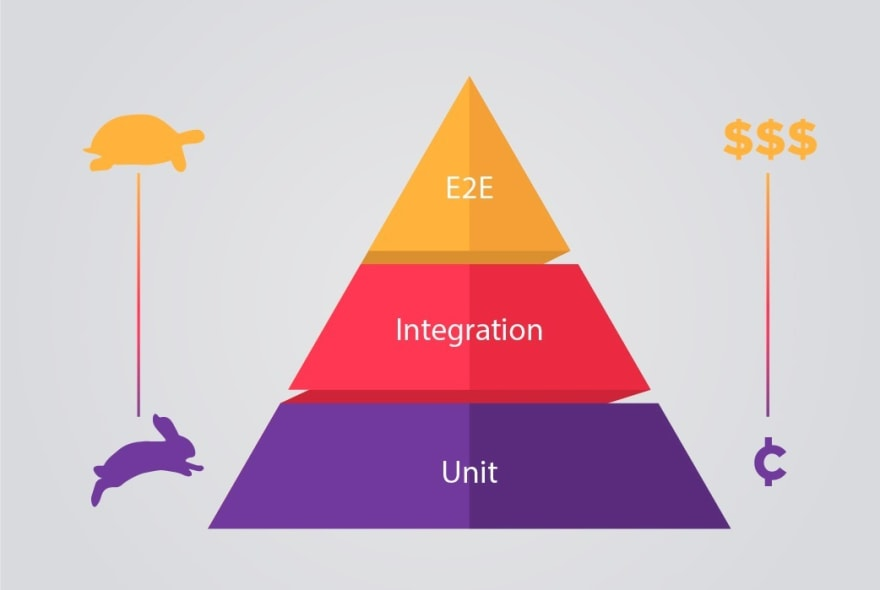
Unit, integration & end-to-end test
Unit test
Integration tests
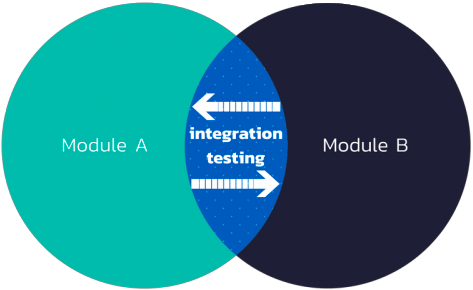
Unit test
End-to-end tests

Unit test
End-to-end tests






Unit test
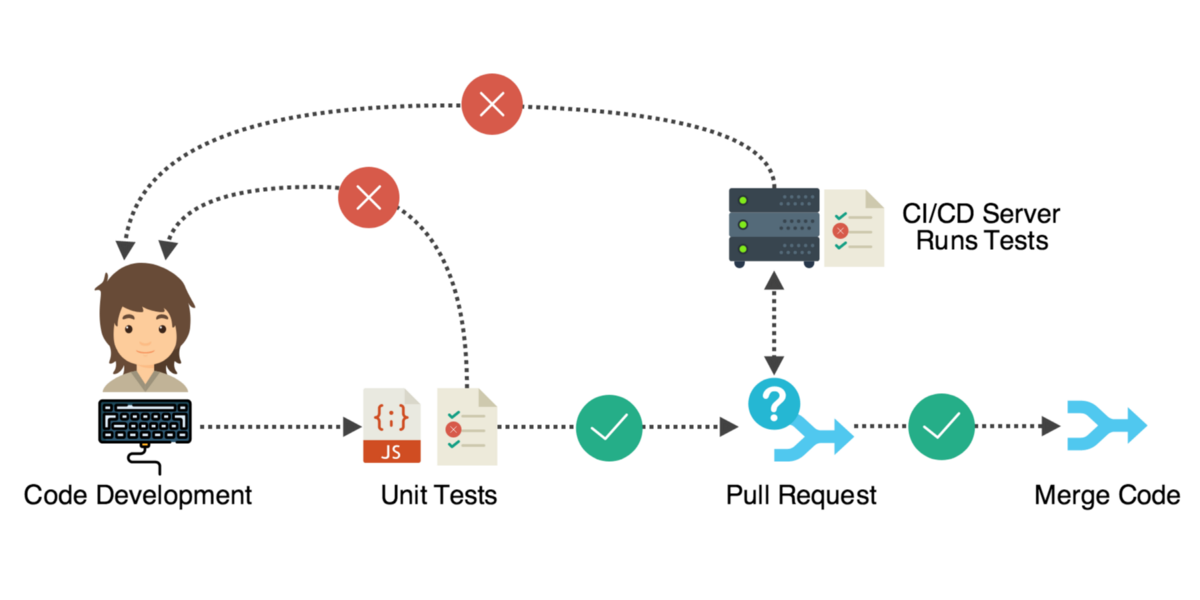
Pipeline & software testing

Unit test
Design Pattern
- Che cos'è un Design Pattern?
- Quanto sono importanti i Design Pattern?
Unit test
Pattern: 'mbare pattern

Unit test
Pattern: Arrange Act Assert (AAA)


Unit test
Pattern: Arrange Act Assert (AAA)

from pytest_mock import MockerFixture
import example
def test_a_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.4
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "random")
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is False
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_random_return
Unit test
Pattern: Arrange Assert Act Assert (AAAA)
from pytest_mock import MockerFixture
import example
def test_a_1(mocker: MockerFixture) -> None:
# arrange
mock_random_return = 0.4
mocker.patch.object(example, "random", return_value=mock_random_return)
spy = mocker.spy(example, "random")
# assert
... # verify the initial conditions
# act
res = example.a()
# assert
assert res is False
assert spy.call_count == 1
assert spy.spy_return == mock_random_return
Unit test
Pattern: Test Driven Development (TDD)
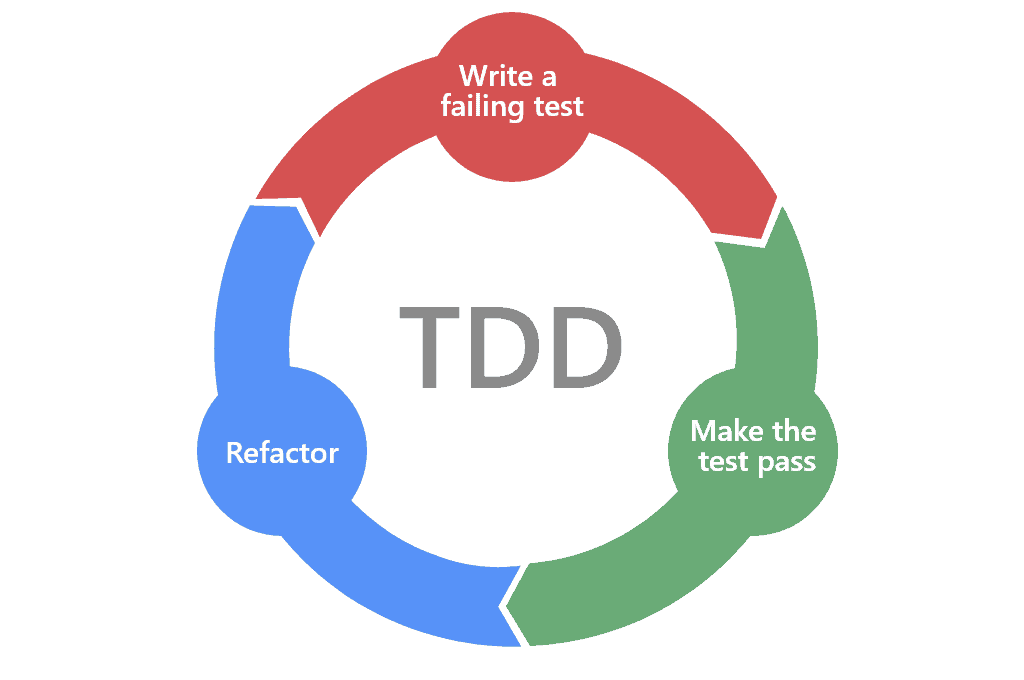

Unit test
Pattern: Behavior Driven Development (BDD)

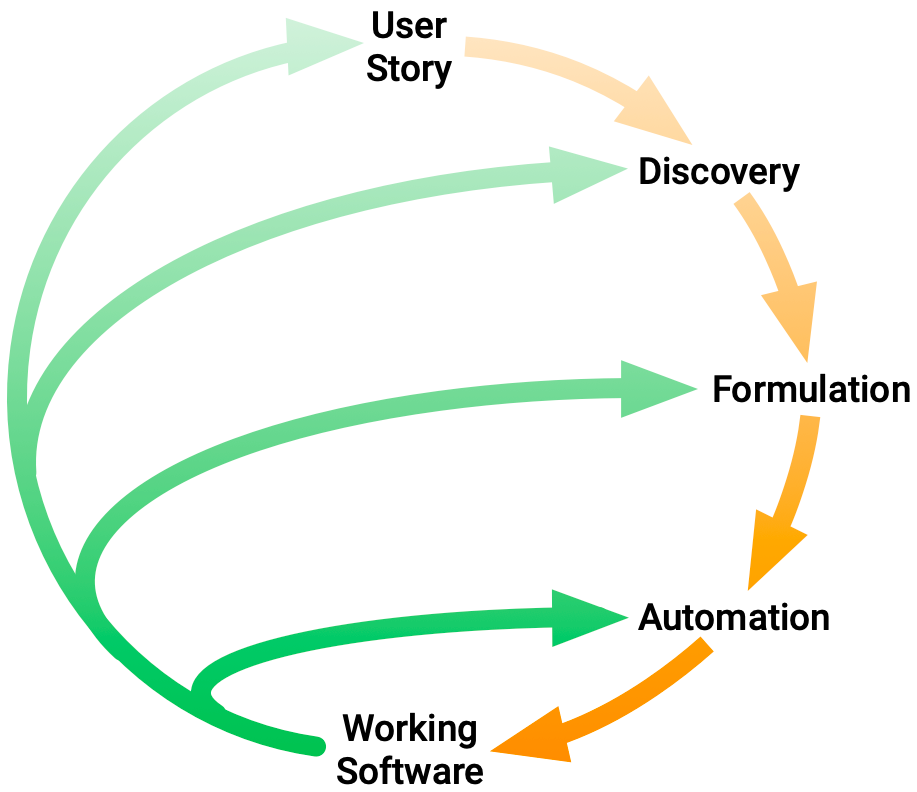
Unit test
Pattern: Behavior Driven Development (BDD)

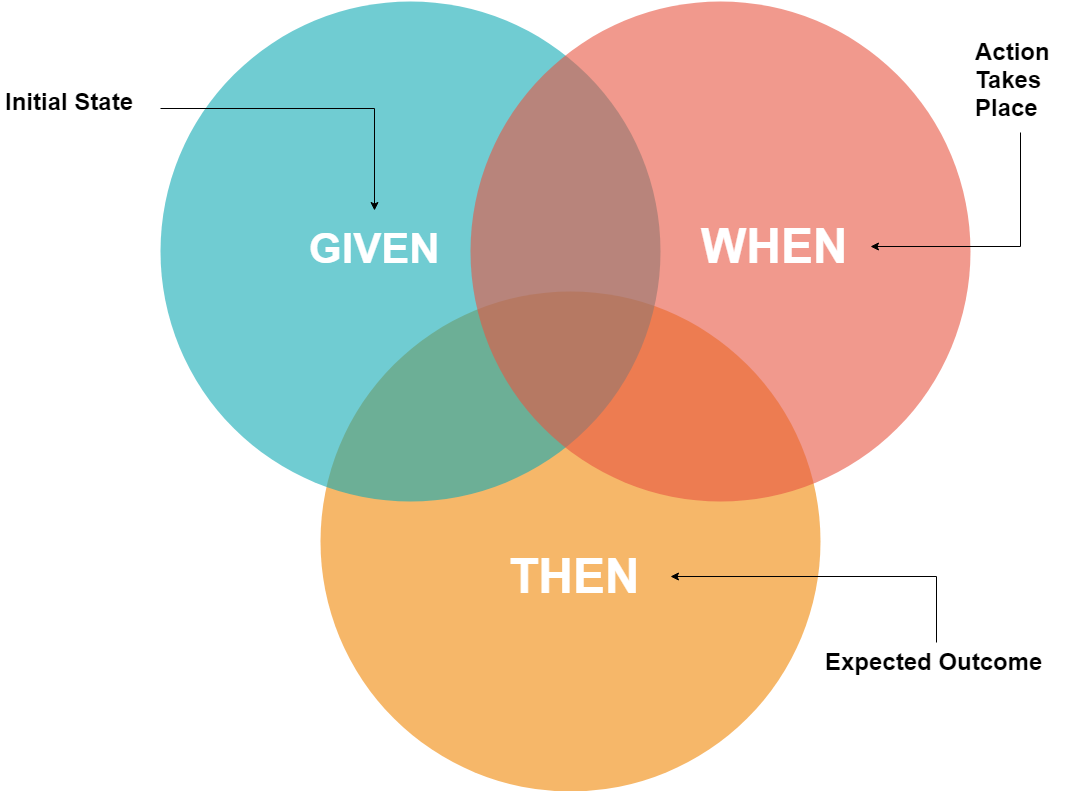
Unit test
Pattern: Page Object
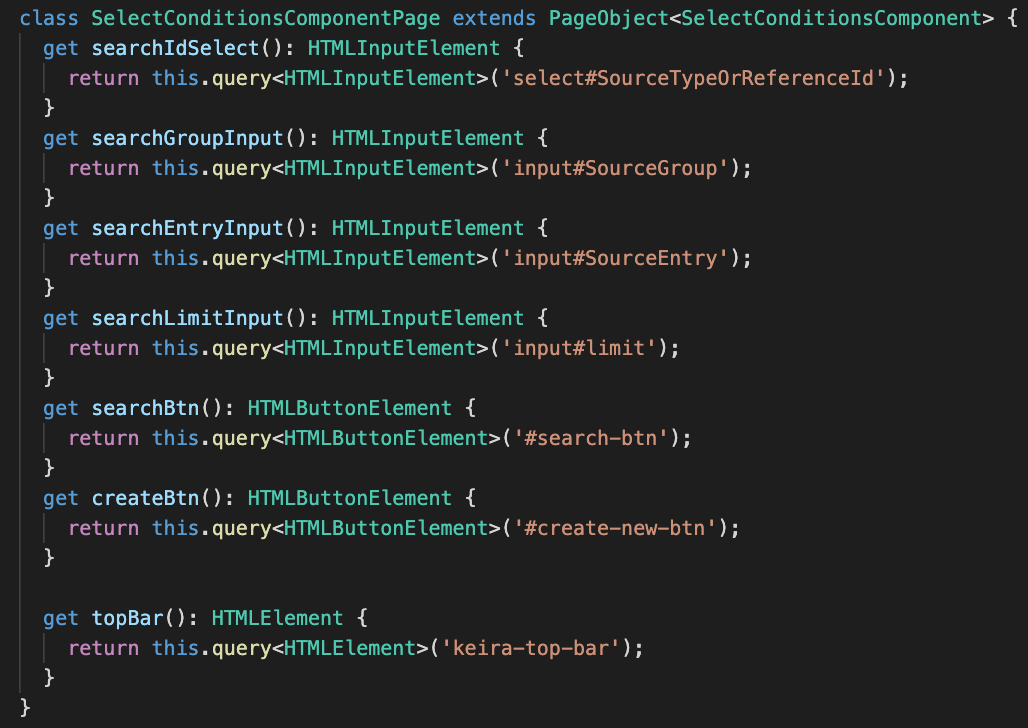
Unit test
Pattern: Page Object
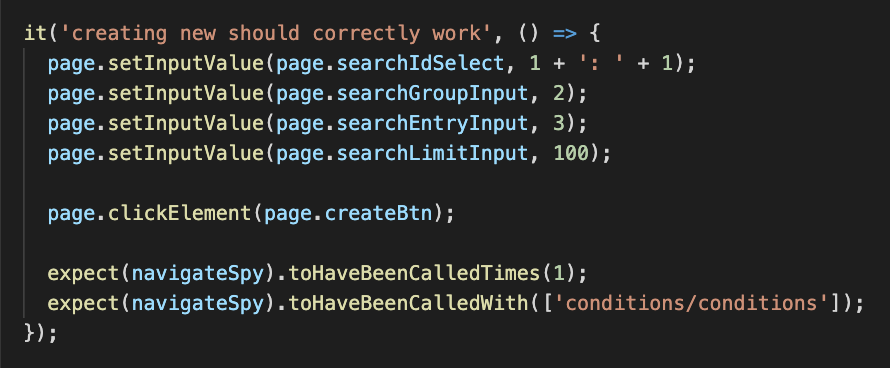
CI/CDContinuous
Integration
Continuous
Delivery
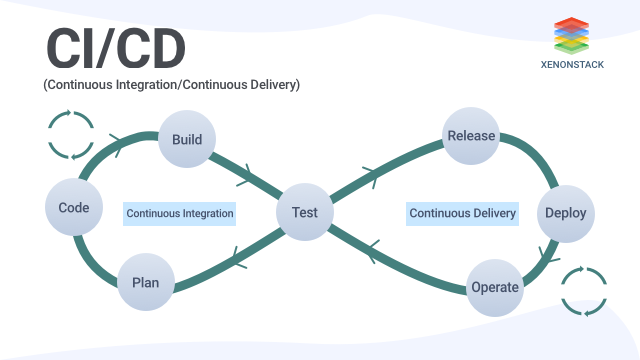
# CI/CDPipeline

Pipeline -> CI / CD

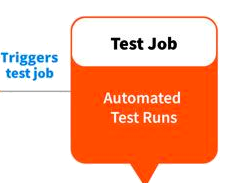

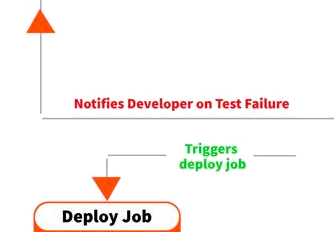
# CI/CDPipeline -> CI / CD
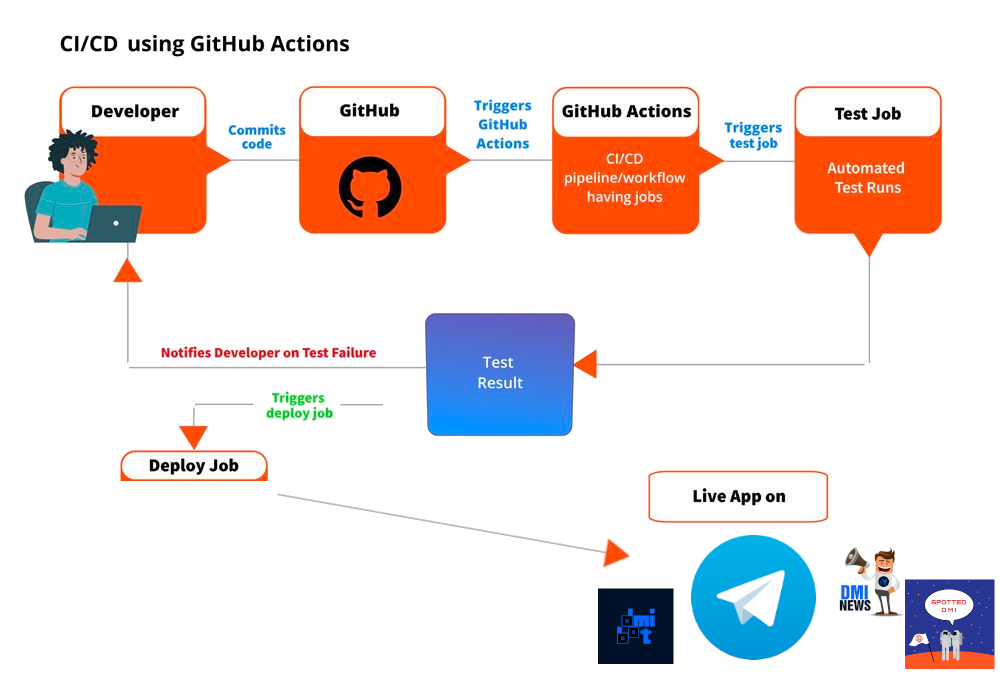
# CI/CDPipeline tools
# CI/CD


Github Action
# CI/CD

2018
Hello World
# CI/CDname: Hello-World
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
hello-world-job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Hello World
run: echo 'Hello World'
Hello World (C++)
# CI/CDname: build-hello-world
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
build-hello-world:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: install g++
run: sudo apt install -y g++
- name: check build
run: |
g++ hello_world.cpp -o hello_world
./hello_world
Release
# CI/CDname: release-hello-world
on:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
build-hello-world:
permissions: write-all
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: compile and run
run: g++ hello_world.cpp -o hello_world_linux
- name: Create Release
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: >-
gh release create ${{ github.ref_name }}
"hello_world_linux"
--generate-notes
--title "Version ${{ github.ref_name }}"Release - cross-platform
# CI/CDname: release-hello-world
on:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
create-release:
permissions: write-all
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Create Release
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: gh release create ${{ github.ref_name }} --generate-notes --title "Version ${{ github.ref_name }}"
build-hello-world:
needs: create-release
permissions: write-all
strategy:
matrix:
include:
- os: ubuntu-latest
file_name: hello_world_linux
- os: macos-latest
file_name: hello_world_mac
- os: windows-latest
file_name: hello_world_windows.exe
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
name: ${{ matrix.os }}
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: compile
run: g++ hello_world.cpp -o ${{ matrix.file_name }}
- name: Update Release
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: gh release upload ${{ github.ref_name }} "${{ matrix.file_name}}"
pipeline checks
# CI/CDname: build-hello-world
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
build-hello-world:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: install g++
run: sudo apt install -y g++
- name: check build
run: |
g++ hello_world.cpp -o hello_world
./hello_world
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x;
cout << x << endl;
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
return 0;
}pipeline checks
# CI/CD#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int* p = nullptr;
cout << *p << endl;
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
return 0;
}
Linter cppcheck
# CI/CDname: build-hello-world
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
build-hello-world:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: install g++
run: sudo apt install -y g++ cppcheck
- name: run cppcheck
run: |
cppcheck hello_world.cpp --output-file=report.txt
if [ -s report.txt ]; then # if file is not empty
cat report.txt
exit 1 # let github action fails
fi
- name: check build
run: |
g++ hello_world.cpp -o hello_world
./hello_world
Pylint & Pytest
# CI/CDname: CI
on:
push:
branches: [main]
paths-ignore:
- "README.md"
- "docs/**"
pull_request:
branches: [main]
paths-ignore:
- "README.md"
- "docs/**"
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python 3.10.0
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: 3.10.0
- name: Install dependencies for requirements and testing
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
if [ -f requirements.txt ]; then pip install -r requirements.txt; fi
if [ -f requirements_dev.txt ]; then pip install -r requirements_dev.txt; fi
- name: Lint with pylint
run: pylint src
- name: Test with pytest
run: pytest --cov src tests/ --cov-fail-under=75Reusable workflows
# CI/CDname: Create and publish a Docker image
on:
workflow_call:
inputs:
repo_ref: # "author/repository_name" or ${{ github.repository }}
required: true
type: string
env:
REGISTRY: ghcr.io
IMAGE_NAME: ${{ inputs.repo_ref }}
jobs:
build-and-push-image:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
packages: write
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Log in to the Container registry
uses: docker/login-action@f054a8b539a109f9f41c372932f1ae047eff08c9
with:
registry: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
username: ${{ github.actor }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Extract metadata (tags, labels) for Docker
id: meta
uses: docker/metadata-action@98669ae865ea3cffbcbaa878cf57c20bbf1c6c38
with:
images: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}
- name: Build and push Docker image
uses: docker/build-push-action@ad44023a93711e3deb337508980b4b5e9bcdc5dc
with:
context: .
push: true
tags: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
labels: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.labels }}Reusable workflows
# CI/CDname: Create and publish a Docker image
on:
push:
branches:
- 'main'
jobs:
build:
uses: unict-dmi/reusable-workflows/.github/workflows/docker.yml@main
with:
repo_ref: ${{ github.repository }}Secrets token
# CI/CDname: Telegram-Secret-Token
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
hello-world-job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Telegram Notify
run: >-
curl -s --data-urlencode "text=Hello World ✅"
"https://api.telegram.org/bot${{ secrets.MY_SECRET_TOKEN }}/sendMessage?chat_id=1044003630" > /dev/nullSecrets token
# CI/CD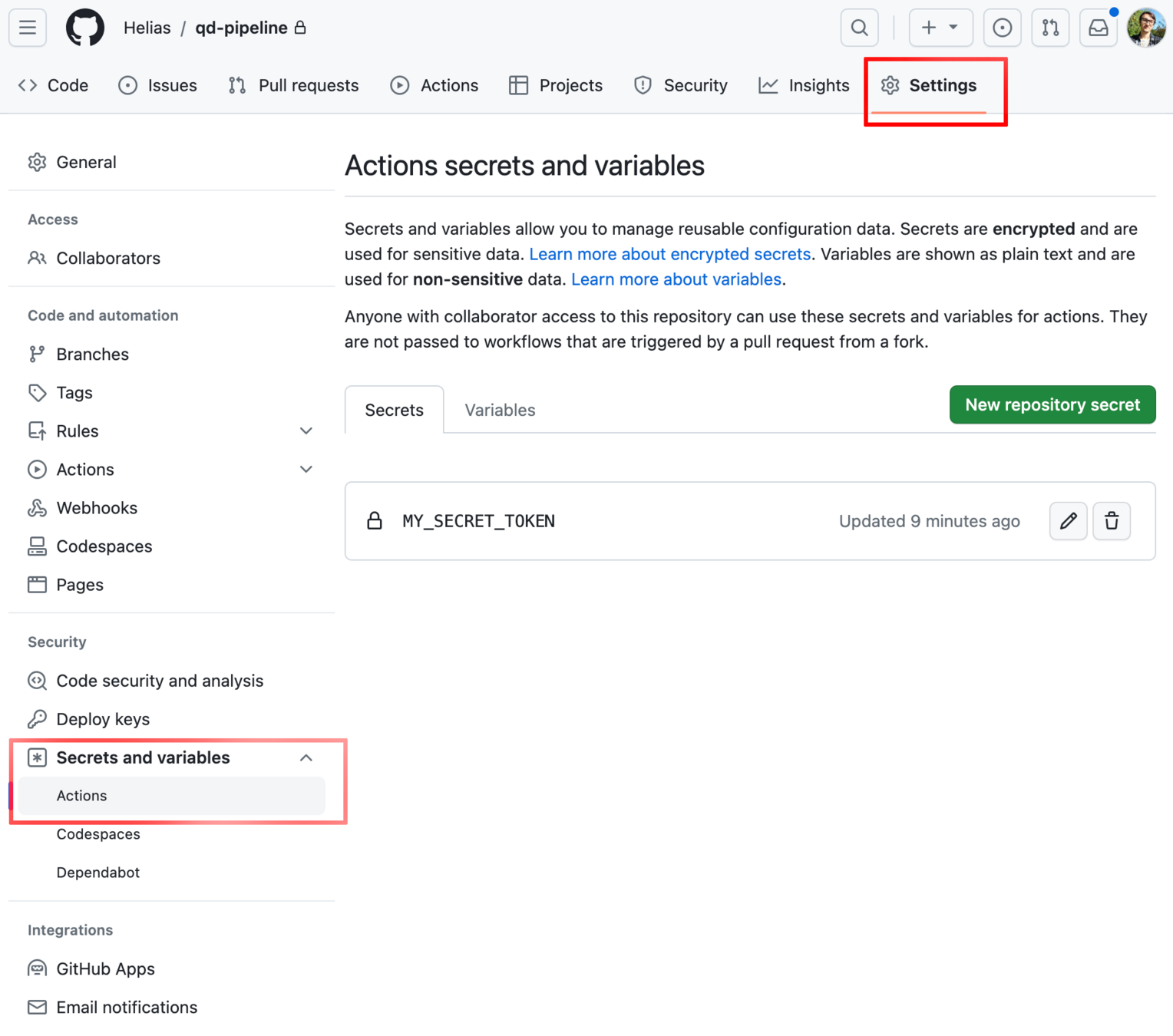
Github Pages
# CI/CD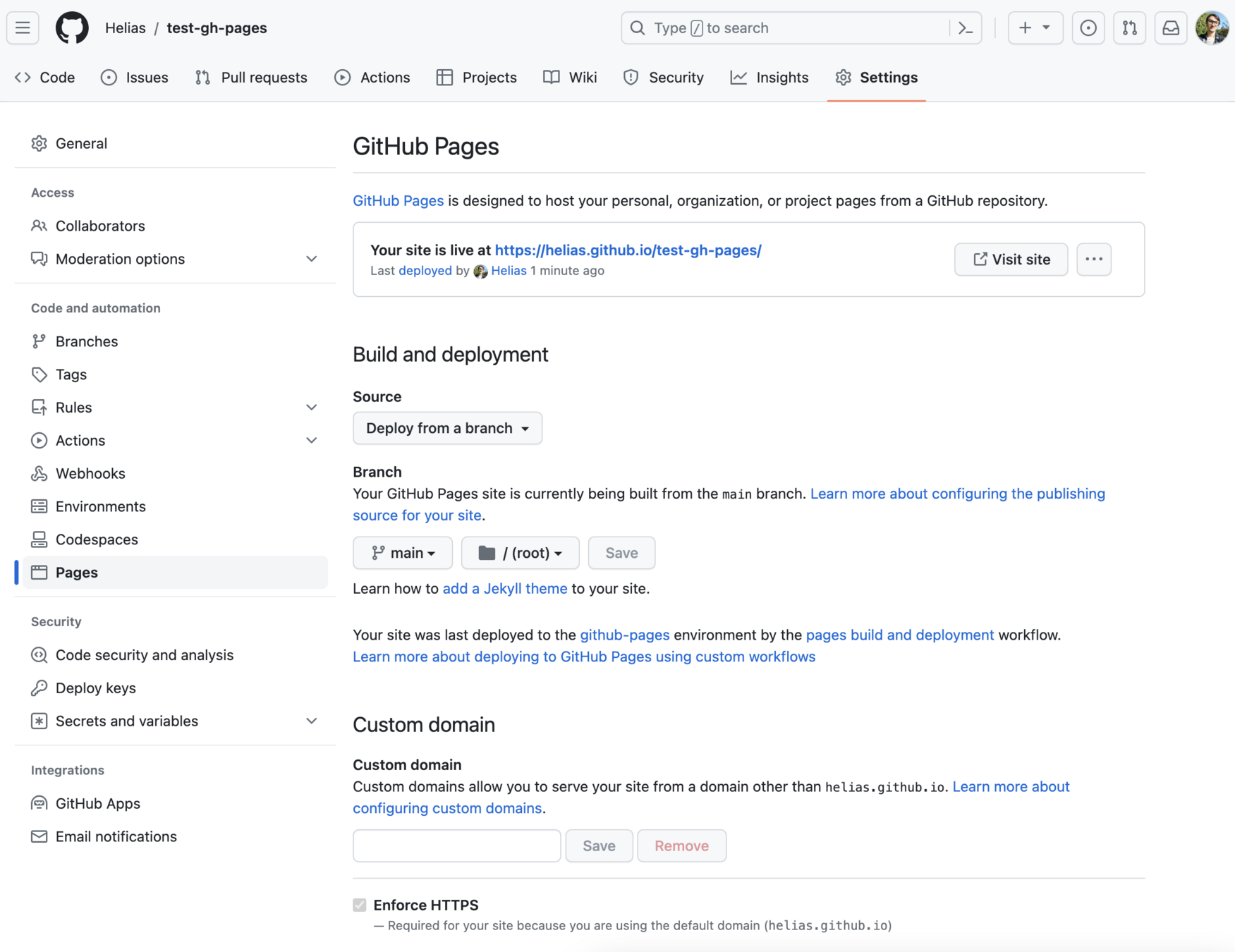
# CI/CD#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int SafeDivide(int a, int b) {
cout << "a: " << a << endl;
cout << "b: " << b << endl;
if (b == 0) {
return 0; // Return 0 if division by zero
}
return a / b;
}
int main() {
int a, b;
cout << "Enter a: ";
cin >> a;
cout << "Enter b: ";
cin >> b;
cout << SafeDivide(a, b) << endl;
return 0;
}
example.cpp
Unit Test example
# CI/CD#include <gtest/gtest.h>
#include "math_utils.h"
TEST(MathUtilsTest, HandlesZeroDivision) {
EXPECT_EQ(SafeDivide(10, 0), 0);
}
TEST(MathUtilsTest, HandlesNormalDivision) {
EXPECT_EQ(SafeDivide(10, 2), 5);
}
#include "math_utils.h"
int SafeDivide(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
return 0; // Return 0 if division by zero
}
return a / b;
}
#pragma once
int SafeDivide(int a, int b);
src/math_utils.cpp
src/math_utils.h
test / math_utils_test.cpp
Fuzz test example
# CI/CD#include <cstdint>
#include <cstddef>
#include "math_utils.h"
extern "C" int LLVMFuzzerTestOneInput(const uint8_t* data, size_t size) {
if (size < 8) return 0;
int a = *(reinterpret_cast<const int*>(data));
int b = *(reinterpret_cast<const int*>(data + 4));
SafeDivide(a, b);
return 0;
}
Fuzz test example
# CI/CD$ ./fuzz_math_utils
==1453512==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: FPE on unknown address
AddressSanitizer can not provide additional info.
SUMMARY: AddressSanitizer: FPE (build/fuzz_math_utils+0x1418d4) (BuildId: b39d1e6b5479d39aaee3a49ef227df07d8e95b48) in SafeDivide(int, int)
==1453512==ABORTING
MS: 5 CrossOver-InsertRepeatedBytes-ChangeByte-ShuffleBytes-ChangeBinInt-; base unit: adc83b19e793491b1c6ea0fd8b46cd9f32e592fc
0x0,0x0,0x0,0x80,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xca,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xf
crash-123456789......
Fuzz test example
# CI/CD$ hexdump crash-123456789......
0000000 0000 8000 ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff
0000010 ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff
0000020 ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff ffff 00ff
0000030 0000 a300
0000034
HEX signed -> Decimal
80000000 = -2147483648
ffffffff = -1
$ hexdump -v -e '"%d, "' -e '8/1 "0x%02x, " "\n"' ./crash-123456789
-2147483648, -1, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x80, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff, [....]
Fuzz test example
# CI/CDname: fuzz-test-example
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
fuzz-test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: install g++
run: sudo apt install -y g++
- name: run build, test and fuzz test
run: |
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=clang++
cmake --build . -- -j$(nproc)
./math_utils_test
timeout 30 ./fuzz_math_utils || echo "Fuzz test crashed or timed out"
if ls crash-* 1> /dev/null 2>&1; then
hexdump -v -e '"%d, "' -e '8/1 "0x%02x, " "\n"' ./crash-*
exit 1 # let github action fails
fi
echo "Build, test and fuzz test completed successfully"
Fuzz test example - binary
# CI/CDBIN DEC MAX (bit length)
1 = 2^0 * 1 = 1 2^1-1 = 1
10 = 2^1 * 1 + 2^0 * 0 = 2
100 = 2^2 * 1 + 2^1 * 0 + 2^0 * 0 = 4
11 = 2^1 * 1 + 2^0 * 1 = 3 2^2-1 = 3
111 = 2^2 * 1 + 2^1 * 1 + 2^0 * 1 = 7 2^3-1 = 7
1000 = 2^3 * 1 ... = 8
1111 = 2^3 * 1 ... = 15 2^4-1 = 15
Fuzz test example - binary signed
# CI/CD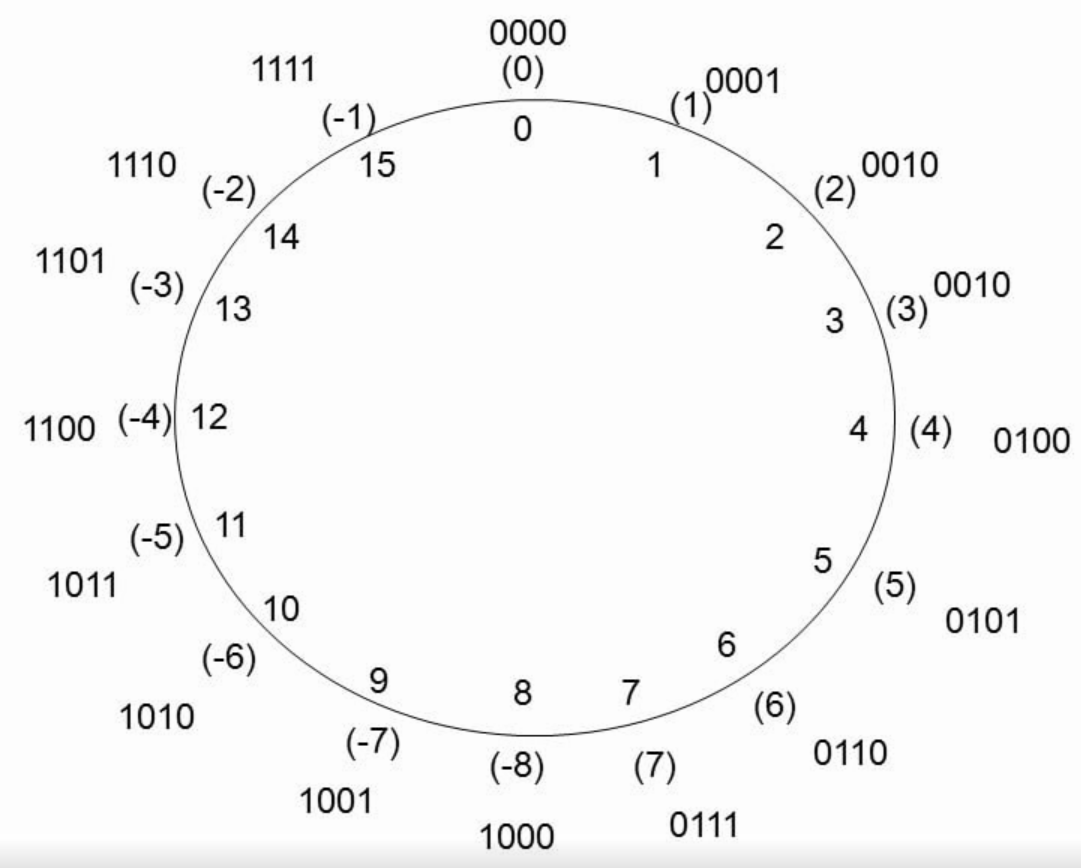
4 bit
0000 = 0
0001 = 1
...
0111 = 7
1000 = -8
32 bit (int32)
00..00 = 0
00..01 = 1
...
01..11 = 2147483647
10..00 = -2147483648
-2147483648 / -1 = ????
= 2147483648
-8 / -1 = ????
= 8
# CI/CD#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int SafeDivide(int a, int b) {
cout << "a: " << a << endl;
cout << "b: " << b << endl;
if (b == 0) {
return 0; // Return 0 if division by zero
}
if (a == -2147483648 && b < 0) {
return 2147483647; // Handle overflow case
}
return a / b;
}
int main() {
int a, b;
cout << "Enter a: ";
cin >> a;
cout << "Enter b: ";
cin >> b;
cout << SafeDivide(a, b) << endl;
return 0;
}
example_workaround.cpp
SOLID
SOLID principles
Code quality and best practices
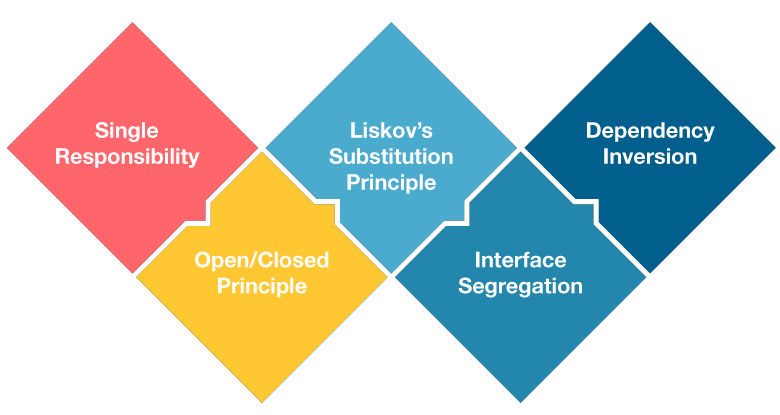
Strongly inspired by:
https://towardsdatascience.com/solid-coding-in-python-1281392a6a94
https://www.pythontutorial.net/python-oop/python-liskov-substitution-principle/
https://testdriven.io/blog/clean-code-python/
https://gist.github.com/dmmeteo/f630fa04c7a79d3c132b9e9e5d037bfd
SOLID
SOLID - The Single-responsibility principle (SRP)
“A class should have one, and only one, reason to exist”
import numpy as np
def math_operations(list_):
# Compute Average
print(f"the mean is {np.mean(list_)}")
# Compute Max
print(f"the max is {np.max(list_)}")
math_operations(list_ = [1,2,3,4,5])
# the mean is 3.0
# the max is 5
❌ Bad code ❌
def get_mean(list_: list[int]) -> None:
'''Compute Mean'''
print(f"the mean is {np.mean(list_)}")
def get_max(list_: list[int]) -> None:
'''Compute Max'''
print(f"the max is {np.max(list_)}")
def main(list_: list[int]) -> None:
# Compute Average
get_mean(list_)
# Compute Max
get_max(list_)
main([1,2,3,4,5])
# the mean is 3.0
# the max is 5✅ Good code ✅
SOLID - The Open–closed principle (OCP)
“Software entities … should be open for extension but closed for modification”
class Animal:
def __init__(self, name: str):
self.name = name
def get_name(self) -> str:
pass
animals = [
Animal('lion'),
Animal('mouse')
]
def animal_sound(animals: list):
for animal in animals:
if animal.name == 'lion':
print('roar')
elif animal.name == 'mouse':
print('squeak')
animal_sound(animals)❌ Bad code ❌
class Animal:
def __init__(self, name: str):
self.name = name
def get_name(self) -> str:
pass
def make_sound(self) -> None:
pass
class Lion(Animal):
def make_sound(self) -> str:
return 'roar'
class Mouse(Animal):
def make_sound(self) -> str:
return 'squeak'
def animal_sound(animals: list) -> None:
for animal in animals:
print(animal.make_sound())
animal_sound(animals)
✅ Good code ✅
SOLID
SOLID - The Liskov substitution principle (LSP)
“Functions that use pointers or references to base classes must be able to use objects of derived classes without knowing it”
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Notification(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def notify(self, message, email):
pass
class Email(Notification):
def notify(self, message, email):
print(f'Send {message} to {email}')
class SMS(Notification):
def notify(self, message, phone):
print(f'Send {message} to {phone}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
notification = SMS()
notification.notify('Hello', 'john@test.com')❌ Bad code ❌
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Notification(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def notify(self, message: str) -> None:
pass
class Email(Notification):
def __init__(self, email: str):
self.email = email
def notify(self, message: str) -> None:
print(f'Send "{message}" to {self.email}')
class SMS(Notification):
def __init__(self, phone: str):
self.phone = phone
def notify(self, message: str) -> None:
print(f'Send "{message}" to {self.phone}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
notification = SMS('+3912345678')
notification.notify('Hello')
notification = Email('stefano.borzi@phd.unict.it')
notification.notify('Hello')
✅ Good code ✅
SOLID
SOLID - The Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
“Many client-specific interfaces are better than one general-purpose interface”
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Mammals(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def swim():
print("Can Swim")
@abstractmethod
def walk():
print("Can Walk")
class Human(Mammals):
def swim():
print("Humans can swim")
def walk():
print("Humans can walk")
class Whale(Mammals):
def swim():
print("Whales can swim")
Human.swim() # Humans can swim
Human.walk() # Humans can walk
Whale.swim() # Whales can swim
Whale.walk() # Can Walk❌ Bad code ❌
✅ Good code ✅
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Walker(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def walk() -> None:
print("Can Walk")
class Swimmer(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def swim() -> None:
print("Can Swim")
class Human(Walker, Swimmer):
def walk() -> None:
print("Humans can walk")
def swim() -> None:
print("Humans can swim")
class Whale(Swimmer):
def swim() -> None:
print("Whales can swim")
if __name__ == "__main__":
Human.walk() # Humans can walk
Human.swim() # Humans can swim
Whale.swim() # Whales can swim
Whale.walk() # ❌❌❌❌❌SOLID
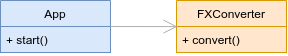
SOLID - The Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
“Abstractions should not depend on details. Details should depend on abstraction. High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions”
class FXConverter:
def convert(self, from_curr, to_curr, amount):
print(
f'{amount} {from_curr} = {amount * 1.2} {to_curr}'
)
return amount * 1.2
class App:
def start(self):
converter = FXConverter()
converter.convert('EUR', 'USD', 100)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = App()
app.start()❌ Bad code ❌
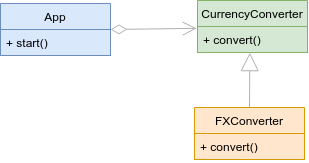
from abc import ABC
class CurrencyConverter(ABC):
def convert(self, from_curr: str, to_curr: str, amount: float) -> None:
pass
class FXConverter(CurrencyConverter):
def convert(self, from_curr: str, to_curr: str, amount: float) -> float:
print('Converting currency using FX API')
print(
f'{amount} {from_curr} = {amount * 1.2} {to_curr}'
)
return amount * 2
class App:
def __init__(self, converter: CurrencyConverter):
self.converter = converter
def start(self) -> None:
self.converter.convert('EUR', 'USD', 100)
if __name__ == '__main__':
converter = FXConverter()
app = App(converter)
app.start()
✅ Good code ✅
SOLID
SOLID - The Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
“Abstractions should not depend on details. Details should depend on abstraction. High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions”
❌ Bad code ❌
✅ Good code ✅
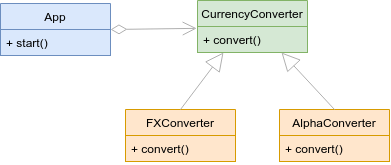
SOLID
DRY - Don't Repeat Yourself
Quality Code
text1 = 1
text2 = 2
text3 = 3
text4 = 4
text5 = 5
print(f"Number: {text1}")
print(f"Number: {text2}")
print(f"Number: {text3}")
print(f"Number: {text4}")
print(f"Number: {text5}")
❌ Bad code ❌
✅ Good code ✅
texts = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
for i in range(len(texts)):
print(f"Number: {texts[i]}")KISS - Keep It Simple Stupid
Quality Code
f = lambda x: 1 if x <= 1 else x * f(x - 1)
❌ Bad code ❌
✅ Good code ✅
def factorial(number: int) -> int:
if number <= 1:
return 1
return number * factorial(number - 1)SoC - Separation Of Concerns
Quality Code
# calculator.py
class Calculator():
def sum(num1: int | float, num2: int | float) -> int | float:
return num1 + num2
def convert_to_float(num: int) -> float:
return float(num)
❌ Bad code ❌
✅ Good code ✅
# calculator.py
class Calculator():
def sum(num1: int | float, num2: int | float) -> int | float:
return num1 + num2
# helpers.py
def convert_to_float(num: int) -> float:
return float(num)
Clean Code
Quality Code
# ❌ This is bad ❌
c = 5
d = 12
# ✅ This is good ✅
city_counter = 5
elapsed_time_in_days = 12Use descriptive/intention-revealing names
Use pronounceable names
from datetime import datetime
# ❌ This is bad ❌
genyyyymmddhhmmss = datetime.strptime('04/27/95 07:14:22', '%m/%d/%y %H:%M:%S')
# ✅ This is good ✅
generation_datetime = datetime.strptime('04/27/95 07:14:22', '%m/%d/%y %H:%M:%S')Avoid using ambiguous abbreviations
# ❌ This is bad ❌
fna = 'Bob'
cre_tmstp = 1621535852
# ✅ This is good ✅
first_name = 'Bob'
creation_timestamp = 1621535852Always use the same vocabulary
# ❌ This is bad ❌
client_first_name = 'Bob'
customer_last_name = 'Smith'
# ✅ This is good ✅
client_first_name = 'Bob'
client_last_name = 'Smith'Clean Code
Quality Code
import random
# ❌ This is bad ❌
def roll():
return random.randint(0, 36) # what is 36 supposed to represent?
# ✅ This is good ✅
ROULETTE_POCKET_COUNT = 36
def roll() -> float:
return random.randint(0, ROULETTE_POCKET_COUNT)Don't use "magic numbers"
# ❌ This is bad ❌
class Person:
def __init__(self, person_first_name, person_last_name, person_age):
self.person_first_name = person_first_name
self.person_last_name = person_last_name
self.person_age = person_age
# ✅ This is good ✅
class Person:
def __init__(self, first_name: str, last_name: str, age: int):
self.first_name = first_name
self.last_name = last_name
self.age = ageDon't add redundant context
Clean Code
Quality Code
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# This variable stores the average of list of numbers.
average = sum(numbers) / len(numbers)
print(average)
Don't add noise comments

Readable code doesn't need comments
Clean Code
Quality Code
# ❌ This is bad ❌
def get_name(): pass
def fetch_age(): pass
# ✅ This is good ✅
def get_name() -> None: pass
def get_age() -> None: passDo not use different words for the same concept
Functions should only perform a single task
# ❌ This is bad ❌
def fetch_and_display_personnel():
data = # ...
for person in data:
print(person)
# ✅ This is good ✅
def fetch_personnel():
return # ...
def display_personnel(data: str) -> None:
for person in data:
print(person)Clean Code
Quality Code
# ❌ This is bad ❌
def render_blog_post(title, author, created_timestamp, updated_timestamp, content):
# ...
render_blog_post("Clean code", "Nik Tomazic", 1622148362, 1622148362, "...")
# ✅ This is good ✅
class BlogPost:
def __init__(self, title, author, created_timestamp, updated_timestamp, content):
self.title = title
self.author = author
self.created_timestamp = created_timestamp
self.updated_timestamp = updated_timestamp
self.content = content
blog_post1 = BlogPost("Clean code", "Nik Tomazic", 1622148362, 1622148362, "...")
def render_blog_post(blog_post):
# ...
render_blog_post(blog_post1)Keep your arguments at a minimum
Clean Code
Quality Code
# ❌ This is bad ❌
text = "This is a cool blog post."
def transform(text, uppercase):
if uppercase:
return text.upper()
else:
return text.lower()
uppercase_text = transform(text, True)
lowercase_text = transform(text, False)
# ✅ This is good ✅
text = "This is a cool blog post."
def uppercase(text: str) -> str:
return text.upper()
def lowercase(text: str) -> str:
return text.lower()
uppercase_text = uppercase(text)
lowercase_text = lowercase(text)Don't use flags in functions
MiscDebugging, utilities,
tools

# DebuggingDebugging

# DebuggingDebugging
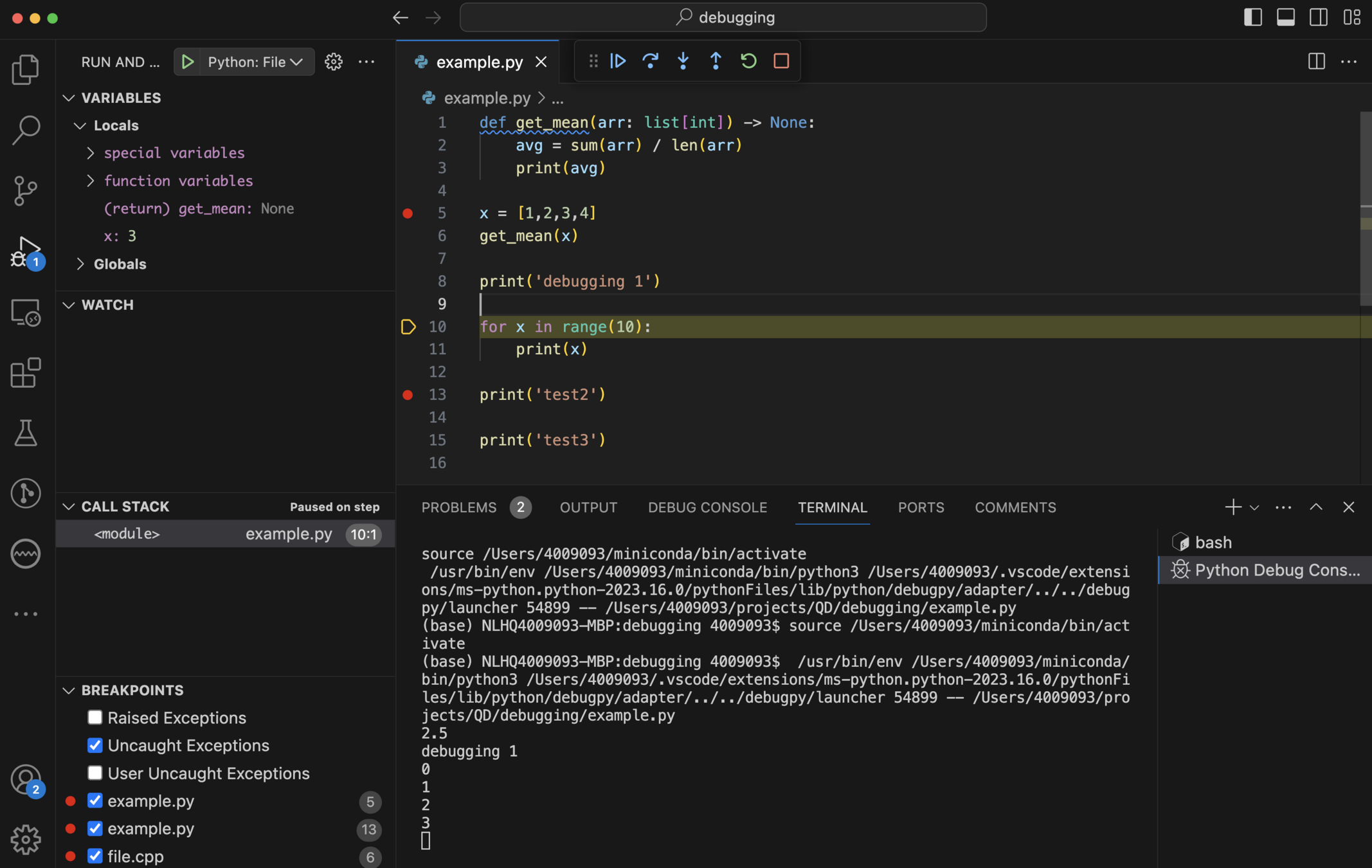
def get_mean(arr: list[int]) -> None:
avg = sum(arr) / len(arr)
print(avg)
x = [1,2,3,4]
get_mean(x)
print('debugging 1')
for x in range(10):
print('test2: ', x)
print(x)
print('test3')
# DebuggingDebugging - VScode + Python
# DebuggingDebugging (JavaScript)
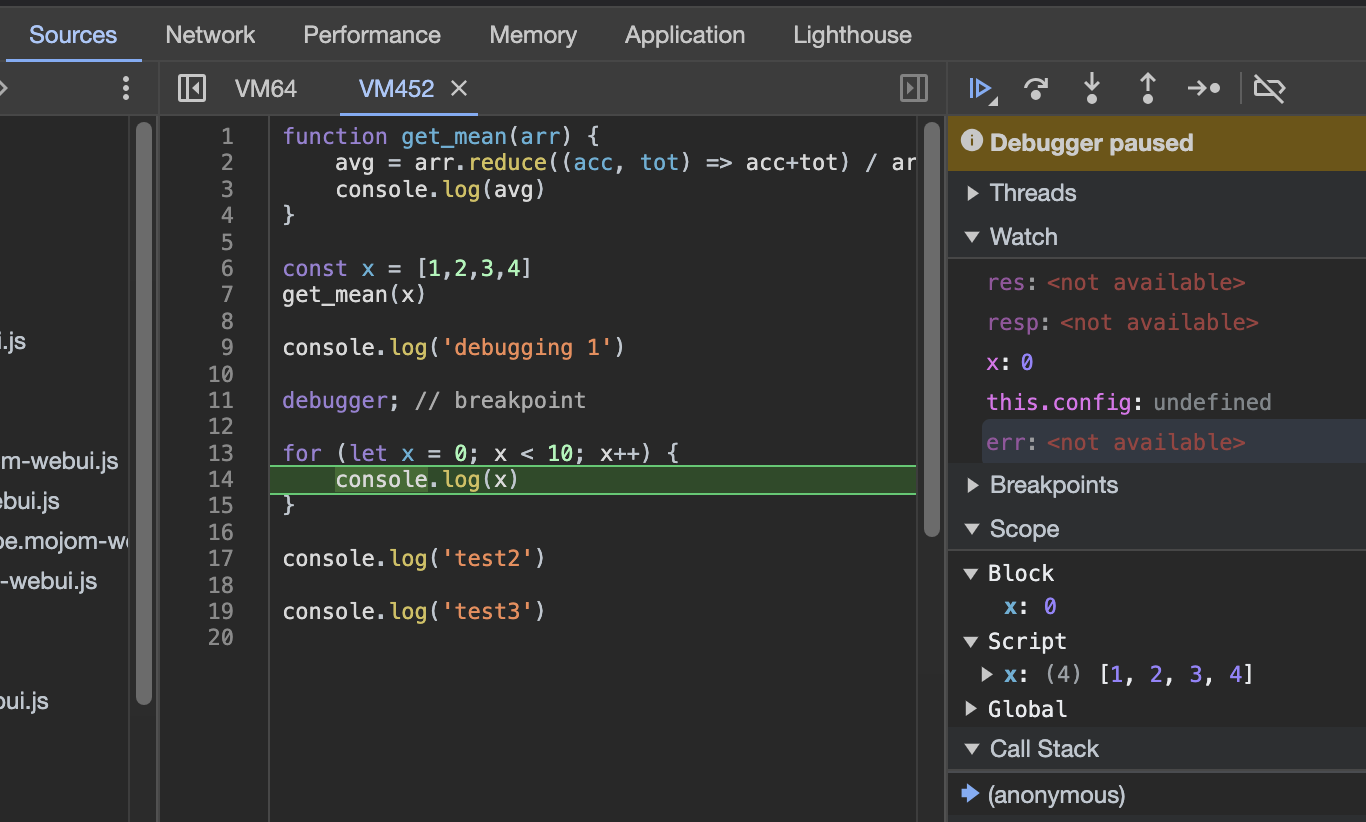
function get_mean(arr) {
avg = arr.reduce((acc, tot) => acc+tot) / arr.length
console.log(avg)
}
const x = [1,2,3,4]
get_mean(x)
console.log('debugging 1')
for (let x = 0; x < 10; x++) {
console.log(x)
}
console.log('test2')
console.log('test3')
# DebuggingDebugging (JavaScript)
# ToolsTools: auto-formatter
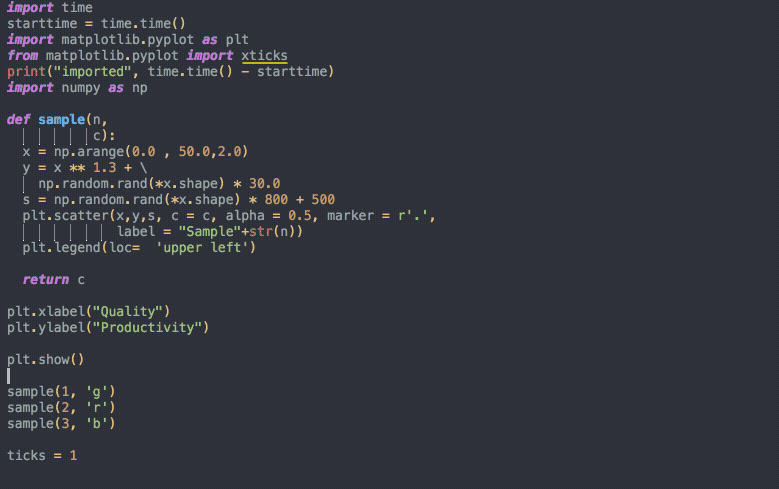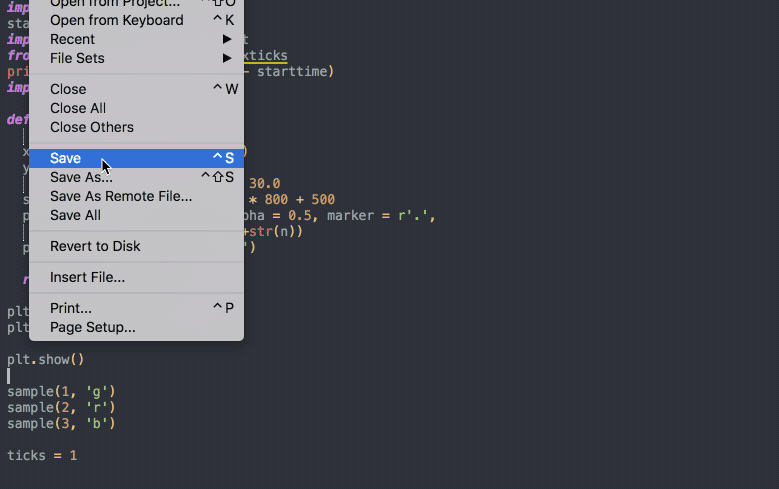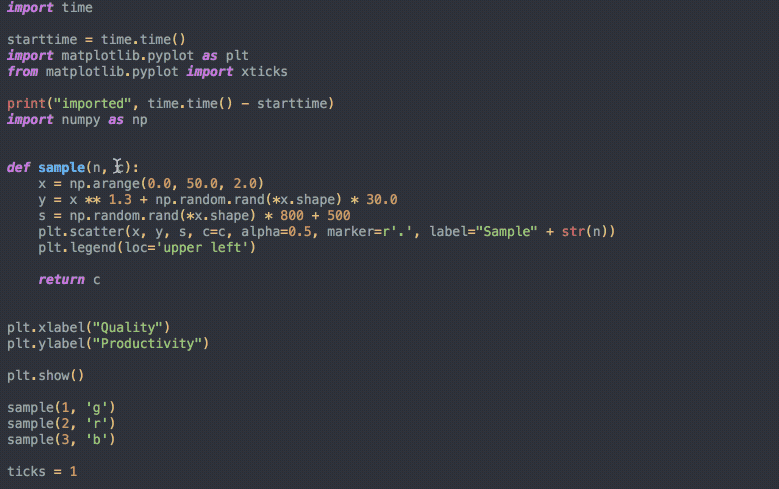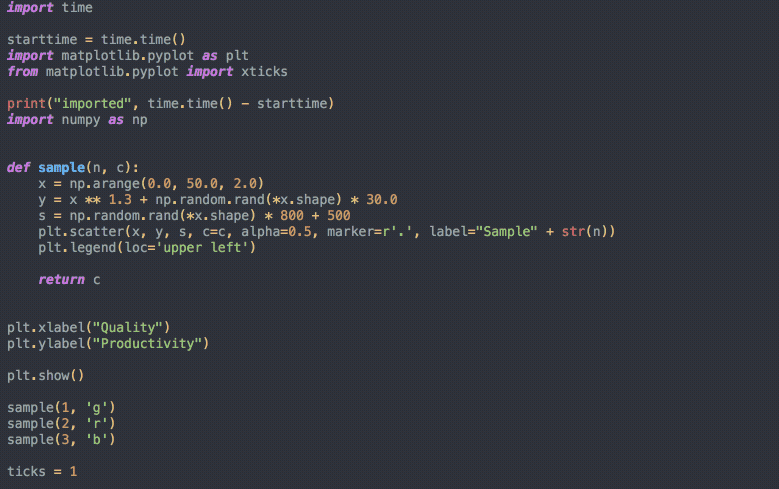
# ToolsTools: auto-formatter (Python)

YAPF

$ sudo apt install black isort
VScode settings
"[python]": {
"editor.defaultFormatter": "ms-python.black-formatter",
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.organizeImports": "explicit"
}
},
"isort.args": ["--profile", "black"]# Tools
VScode plugins
# ToolsTools: auto-formatter (C++)
clang-format
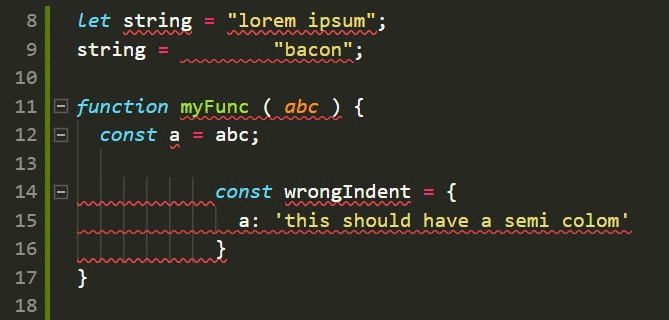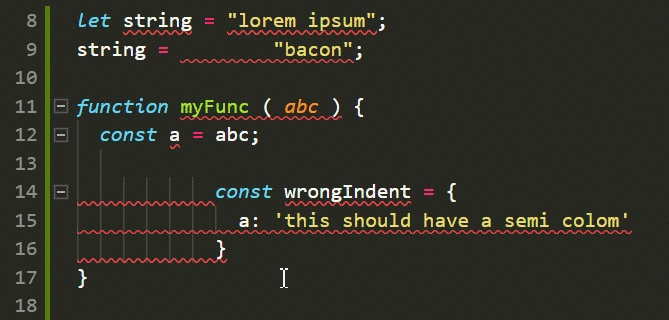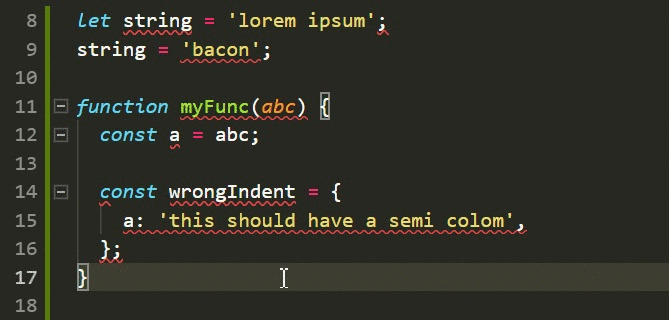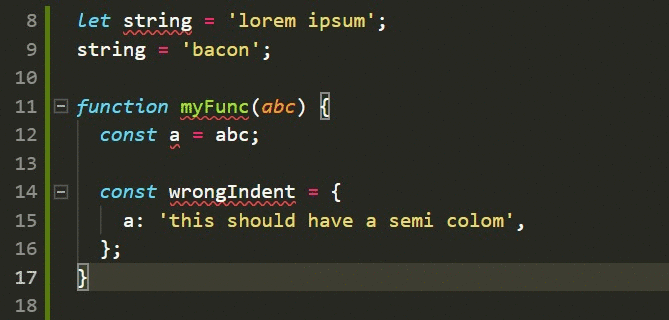
# ToolsTools: auto-formatter (Javascript)
Quality Development
By Stefano Borzì
Quality Development
- 294


