Classification
c17hawke
- Sunny Chandra
In machine learning and statistics, classification is -
the problem of identifying to which of a set of categories (sub-populations) a new observation belongs,
on the basis of a training set of data containing observations (or instances) whose category membership is known.
-Wikipedia
Our Story
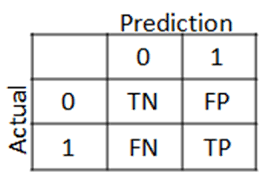
Confusion Matrix
c17hawke
T | N
T | P
F | N
F | P
0 | 0'
1 | 1'
1 | 0'
0 | 1'
0'
0
1
1'
Actual class
Predicted or Guessed
c17hawke
| Actual | Guessed | Interpretation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TN | T | N | Guessed (-ve) and True |
| FP | F | P | Guessed (+ve) but False |
| FN | F | N | Guessed (-ve) but False |
| TP | T | P | Guessed (+ve) and True |
c17hawke
Any Questions ??
Understanding Classification Graphically
Toy dataset
| x | y | label |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 1 | - |
| 3 | 3 | + |
| 3 | 2 | + |
| 2 | 3 | + |
x
y
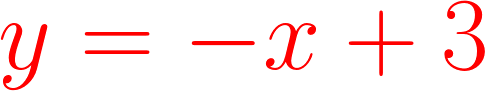
| x | y | label |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 1 | - |
| 3 | 3 | + |
| 3 | 2 | + |
| 2 | 3 | + |
| - | + | |
|---|---|---|
| - | 3 | 0 |
| + | 0 | 3 |
Confusion
Matrix

y
x
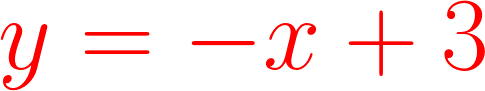
PERFECT CLASSIFIER
Graphical analysis

y
x
Any Questions ??
| x | y | label |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 1 | + |
| 3 | 3 | + |
| 3 | 2 | - |
| 2 | 3 | + |
Classification Errors

y
x
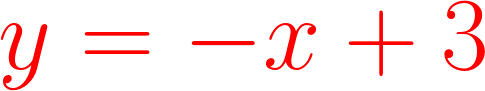
| x | y | label |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 1 | + |
| 3 | 3 | + |
| 3 | 2 | - |
| 2 | 3 | + |
| - | + | |
|---|---|---|
| - | 2 | 1 |
| + | 1 | 2 |
Confusion
Matrix
FN
FP

y
x
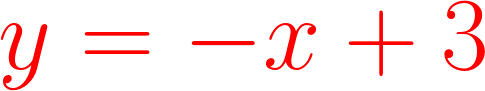
Any Questions ??
More Example ->
| x | y | label |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 0 | - |
| 1 | 1 | - |
| 3 | 3 | + |
| -3 | -3 | + |
| 3 | -3 | + |
| - | + | |
|---|---|---|
| - | 3 | 0 |
| + | 0 | 3 |
Confusion
Matrix

y
x
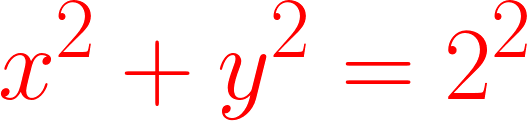

y
x
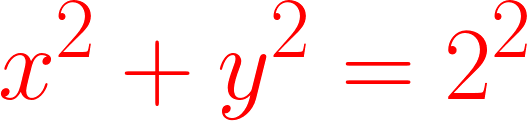
Let's do some calculations
Any Questions ??
More examples -
| x | y | z | label |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | - |
| 1 | 0 | 2 | - |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| 3 | 3 | 4 | + |
| -3 | -3 | 3 | + |
| 3 | -3 | 2 | + |
dataset with 3 features
3D-View
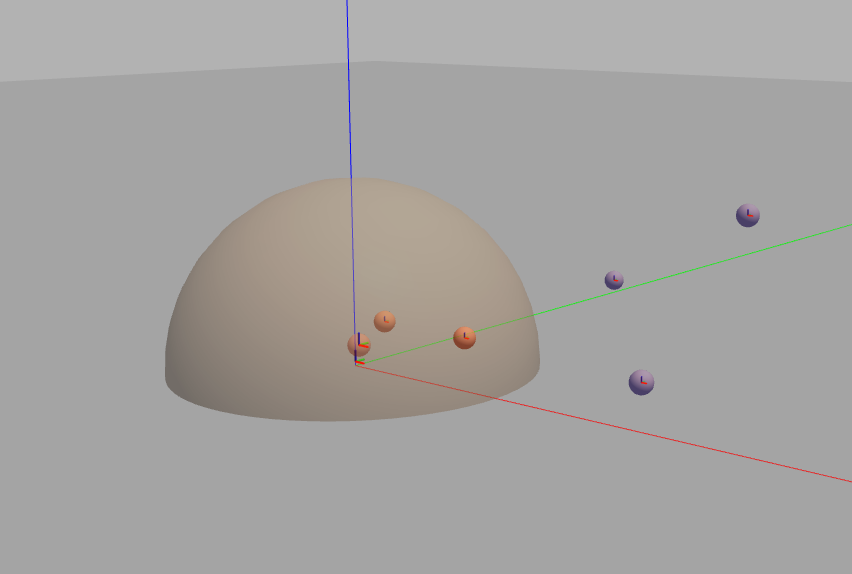
So what we have learned till now?
Classification
In classification, models are nothing but graphs ( line, curve, surface, etc) that separates two or more classes.

x
y
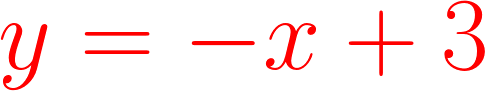
Regression
In Regression, models are nothing but graphs ( line, curve, surface, etc) that fits through the datapoints.

x
y
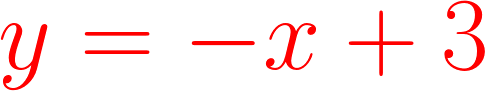
I hope that was fun?:D
Example
MNIST dataset
The MNIST database (Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology database)
is a large database of handwritten digits.
c17hawke
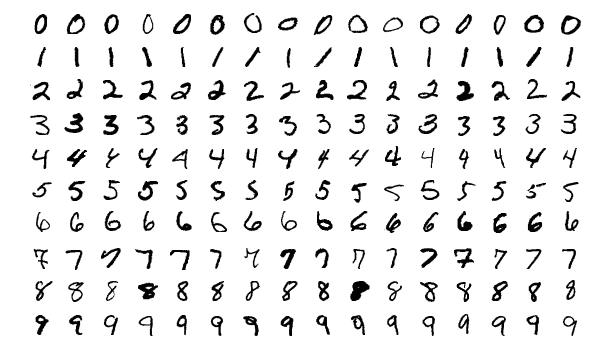
Example 1
MNIST dataset-
let's say we have 10,000 data point (handwritten text) in the Training set
Our task -
detect whether a no. is 5 or not
- hence Positive => detected 5
- and Negative => not a 5
Note:
Total no. of 5s are 1000 => other digits are 9000 in total
c17hawke
Evaluation or Performance Measures
c17hawke
1. Accuracy
accuracy =
TP + TN
TP + TN + FP + FN
c17hawke
2. Precision
Precision =
How many are actually 5 ?
Out of nos. classified as 5
=
TP
TP + FP
c17hawke
3. Recall
Recall =
How many are classified as 5 ?
Out of nos. that are actually 5
=
TP
TP + FN
c17hawke
Case 1
when no. of 5s (i.e. P's ) = 1000
no. of other digits are (i.e. N's) = 9000
T | N
T | P
F | N
F | P
0 | 0'
1 | 1'
1 | 0'
0 | 1'
0'
0
1
1'
Actual data
Predicted or Guessed
9000
1000
0
0
Precision = ?
Accuracy = ?
Recall = ?
FIND
c17hawke
Precision =
TP
TP + FP
Recall =
TP
TP + FN
accuracy =
TP + TN
TP + TN + FP + FN
c17hawke
Case 2
when no. of 5s (i.e. P's ) = 1000
no. of other digits are (i.e. N's) = 9000
T | N
T | P
F | N
F | P
0 | 0'
1 | 1'
1 | 0'
0 | 1'
0'
0
1
1'
Actual data
Predicted or Guessed
0
0
9000
1000
Precision = ?
Accuracy = ?
Recall = ?
FIND
c17hawke
Precision =
TP
TP + FP
Recall =
TP
TP + FN
accuracy =
TP + TN
TP + TN + FP + FN
c17hawke
Observation -
- Accuracy can be misleading in case of classification
- It's not always great to calculate Precision and Recall every time. So we can go for -->
c17hawke
4. F1 Score
- Its harmonic mean of Precision and Recall.
- It gives equal importance to both values.
- It can only result in high score if both are high.
F1 score =
2
1
Precision
+
Recall
1
c17hawke
It's not always Ok to use F1 score
We need to choose our Performance measurers as per our Problem statement
Examples ->
c17hawke
Example 1
Classify safe videos for kids =>
- P = Animation movie
- N = Adult movie or Offensive content
AIM -
(as low as possible) FP =>
- guessed = animated
- actually= adult
(doesn't affect much) FN =>
- guessed = adult
- actually= animated
=>
Precision >
Recall
Preference -
c17hawke
Precision=
TP
TP + FP
Recall =
TP
TP + FN
Example 2
Shoplifting detection using camera feed at a shopping mall =>
- P = Thief
- N = Not Thief
Precision=
TP
TP + FP
Recall =
TP
TP + FN
AIM -
(doesn't affect much) FP =>
- guessed = Thief
- actually= Not thief
(as low as possible) FN =>
- guessed = Not thief
- actually= Thief
=>
Precision <
Recall
Preference -
c17hawke
Example 3
COVID-19 testing =>
- P = infected
- N = healthy
Precision=
TP
TP + FP
Recall =
TP
TP + FN
AIM -
(as low as possible) FP =>
- guessed = infected
- actually= healthy
(as low as possible) FN =>
- guessed = healthy
- actually= infected
=>
both should be high
Preference -
c17hawke
go for high f1 score
USUALLY -
when precision is high => Recall will be low
and vice a versa
This is nothing but Precision-Recall Tradeoff
c17hawke
F scores
F =
x
β
x
precision
+
recall
α ∈ [0, 1]
F =
1
1
x
precision
+
1
x
recall
(1 - α)
α
α
precision
recall
(1 + β )
β
2
2
x
β ∈ [0, +∞]
F =
2
1
precision
+
1
recall
1
More Stuff
Precision | Positive Predictive value(PPV)
Recall | Sensitivity |Hit rate |
True Positive rate (TPR)
specificity|selectivity |
True negative rate (TNR)
False negative rate (FNR)
False positive rate (FPR)
P = TP + FN
N = TN + FP
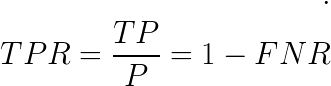
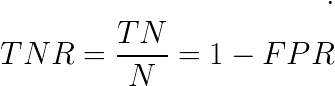
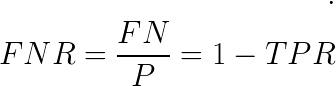
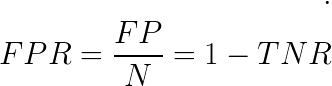
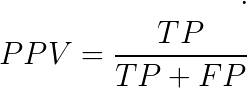
| TN | FP |
| FN | TP |
P(1)
N(0)
Actual
Predicted
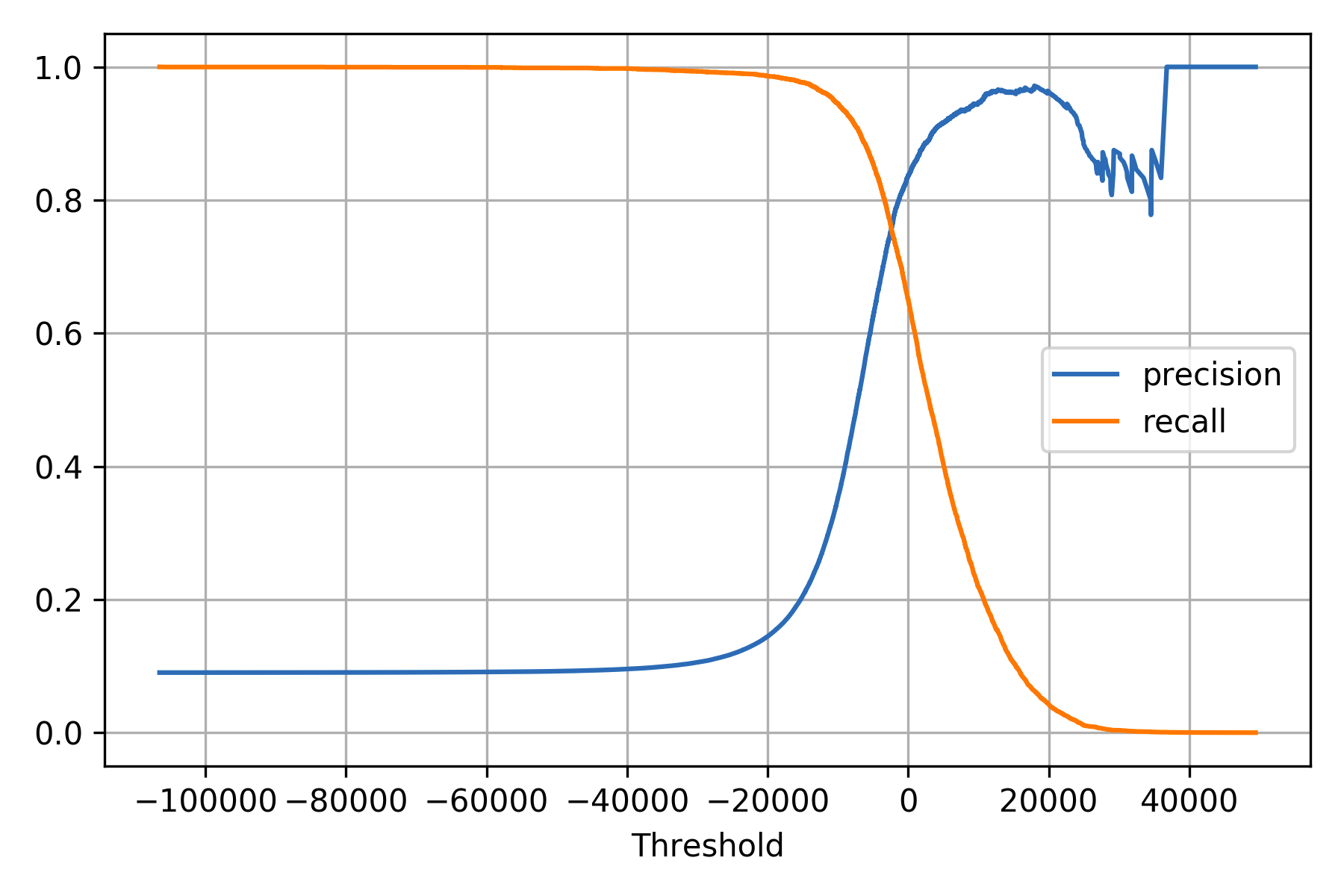
Precision and Recall vs Decision threshold curve
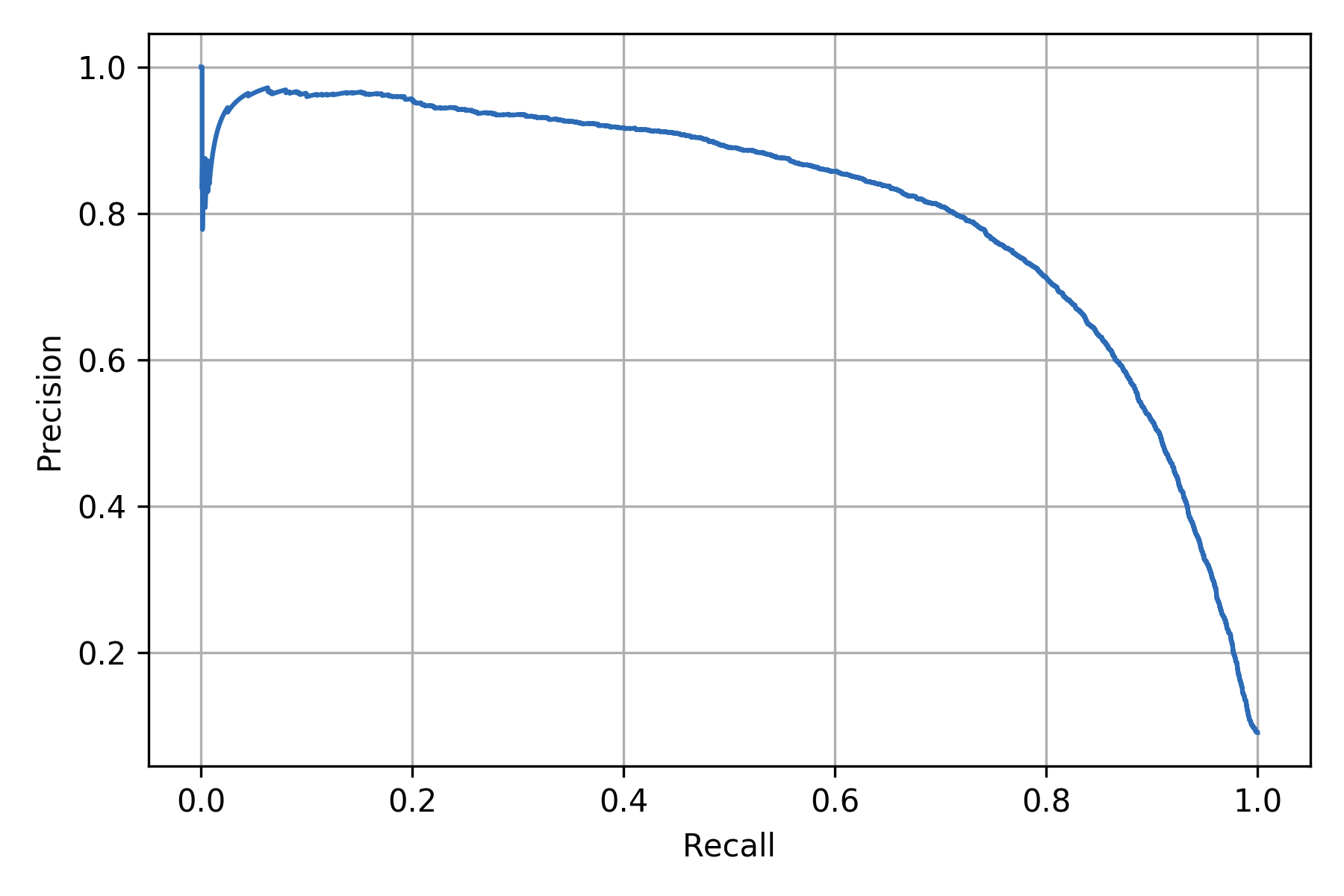
Precision vs Recall curve
ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristics) curve
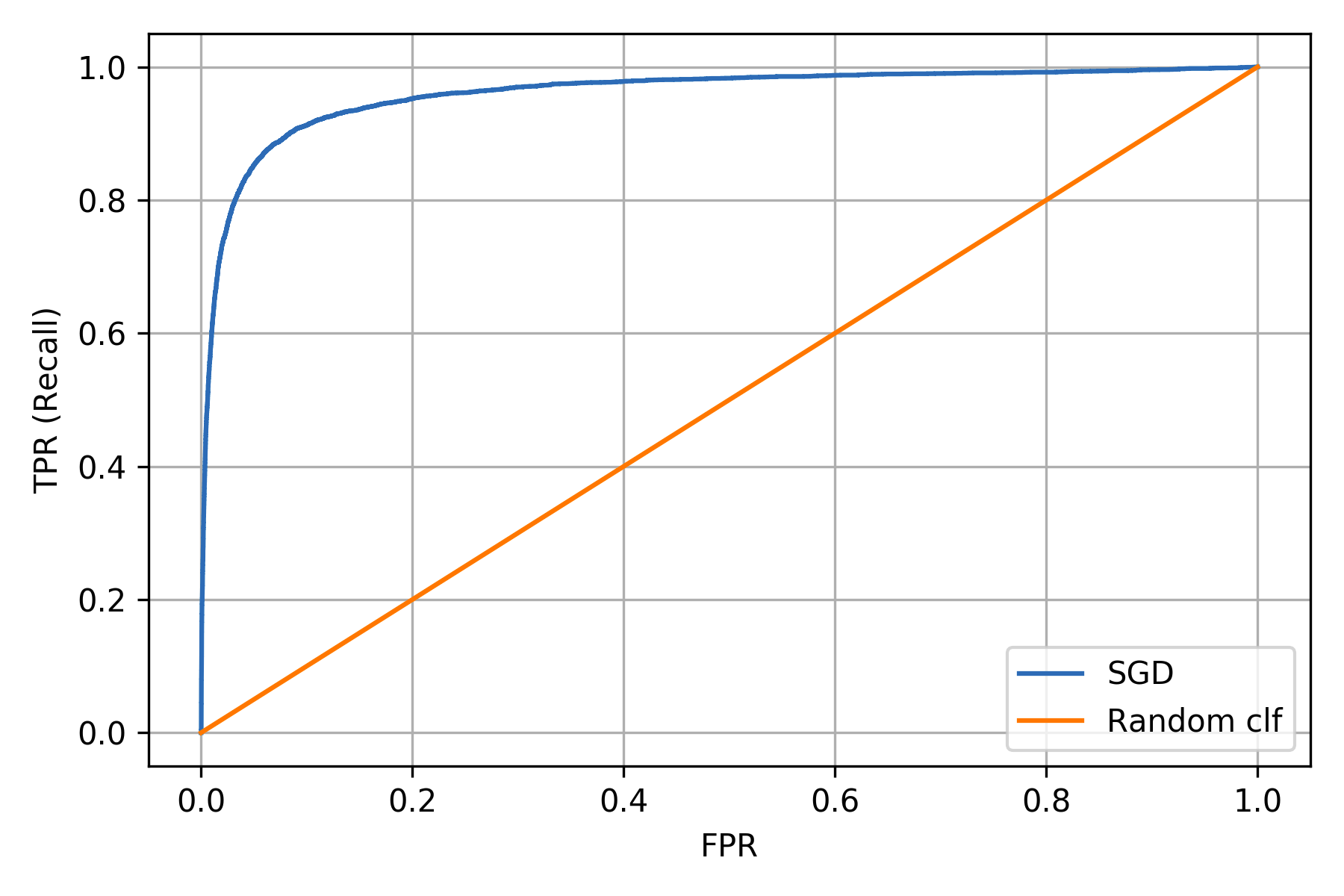
Comparing ROC curve of two models
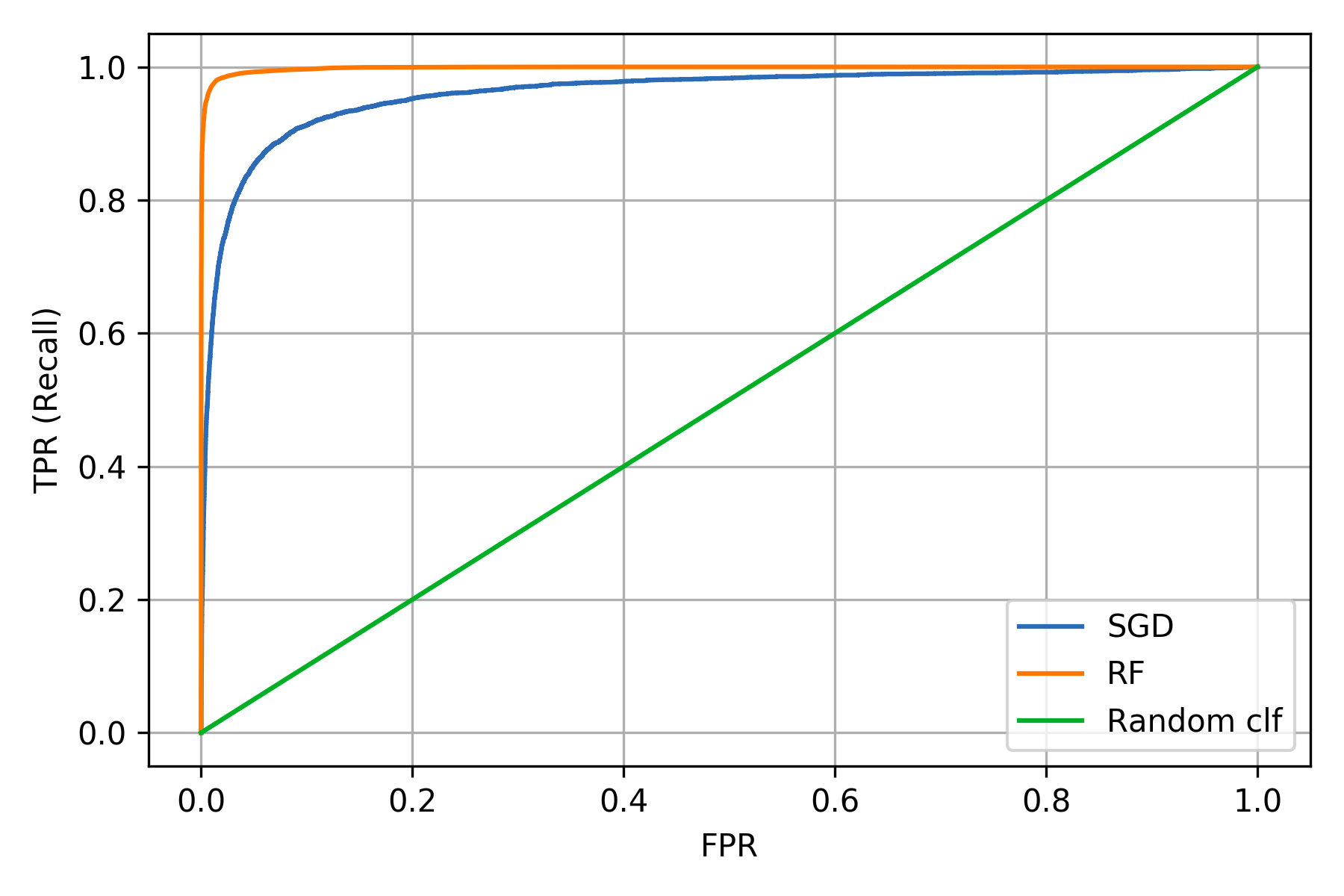
Multi-class Classification aka Multinomial Classification
- Algos that can handle multi-class -
- SGD, Random Forest, Naive Bias, etc.
- Algos which are strictly Binary classifiers -
- Logistic Regression, SVM classifier.
Strategies to make binary classifier work for Multi classification
- OvR (One-vs-Rest) Strategy aka One-vs-All
- based on the highest decision score
- OvO (One-vs-One) Strategy
- make the pairwise binary classifier
- for N classes you'll train = N x (N-1) classifiers
- It is faster as you need to train only a chunk of data at a time.
References -
Classification v2.0
By Sunny
Classification v2.0
This is my presentation on Classification topic in ML
- 758



