M.V.C.

Yeah, you know me
M.V.C.
MVC stands for Model View Controller.
This is used for... Let's go back to Day 1... our favorite thing... separation of concerns.

MVC is one of the most used Software Architectural Design patterns.
Let's Talk Pokémon

User

Controller

View
public class PokemonModel
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string UsName { get; set; }
public string JpName { get; set; }
public string Type1 { get; set; }
public string Type2 { get; set; }
public int Rate { get; set; }
public string Image { get; set; }
}
public class PokemonViewModel
{
public List<PokemonModel> Pokemons { get; set; }
}
Model
Model
The Model is used to Notify and Update the Controller

No, Model does not refer to Gigi Hadid. #sorrynotsorry
This is data the application is built upon (M C) and, how the data is managed (C M).
public class PokemonModel
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string UsName { get; set; }
public string JpName { get; set; }
public string Type1 { get; set; }
public string Type2 { get; set; }
public int Rate { get; set; }
public string Image { get; set; }
}
public class PokemonViewModel
{
public List<PokemonModel> Pokemons { get; set; }
}
Notice the User in the previous slide does NOT interaction with the Model. This is back end data.
View
The View is how Users interact with the application. It is the User Interface that sends input to the Controller and Updates the View.
- Battled and Pokémon got to low health
- Throw the Pokéball
- Pokéball wiggles
- Pokémon breaks free (sorry!)

(Grookey won FYI)
In each of the steps above the User performs and action, the controller updates the View, and the User decides what to do next.
Controller
This is the bad boy on the block.

All the Pokemon ever!
The Controller works with the View and the Model to control the flow of data back and forth.
It takes User Input from the View, manipulates with coded rules, and passes it to the Model.
Think of it like this cartridge. It knows every Pokémon in the game, how they evolve, where to find them, etc.
It works with the User and the Data (Model) to gather and report back that info. Neat huh?
Ok, ok
You want a more tech example and no Pokémon? (heathen)

Example:
- User logs into the application through the login button.
- Credentials are passed to the Controller, which passed it to the Model for authentication.
- The Model passes the authenticated information back to the Controller.
- The controller sees if it is Valid or Invalid and sends instructions to the View to present the appropriate information.
...What?
Maybe a pic will help.
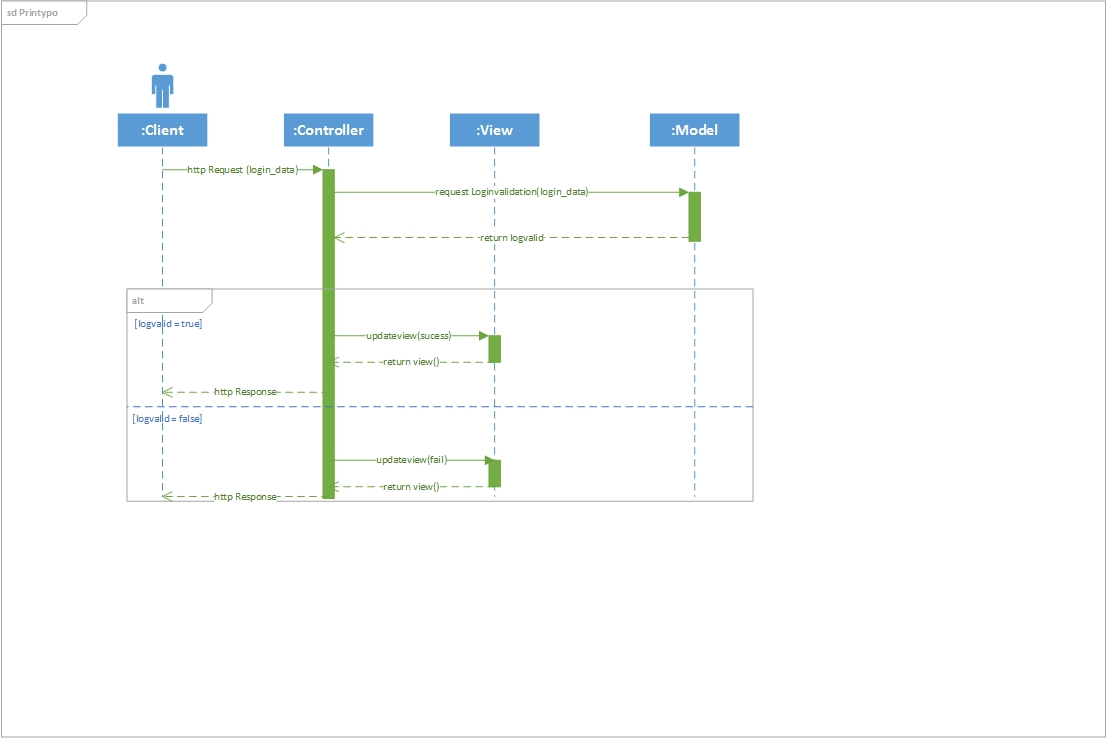
A bit of Spaced Repetition
- The Model is used to Notify and Update the Controller
- The View sends input to the Controller and Updates the View.
- The Controller works with the View and the Model to control the flow of data back and forth.
Ok, now with Leon's Code

Don't worry - we got this!
{
"name": "todolist-review-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon server.js",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"dotenv": "^8.2.0",
"ejs": "^3.1.6",
"express": "^4.17.1",
"mongodb": "^3.6.5",
"mongoose": "^5.12.3",
"nodemon": "^2.0.7"
}
}Let's gooooooooooo
This might not be where you begin coding but it gives us a starting point as to what is going on.
Highlights are important!
"dependencies": {
"dotenv": "^8.2.0",
"ejs": "^3.1.6",
"express": "^4.17.1",
"mongodb": "^3.6.5",
"mongoose": "^5.12.3",
"nodemon": "^2.0.7"
}- These are what is needed to ensure everything runs smoothly.
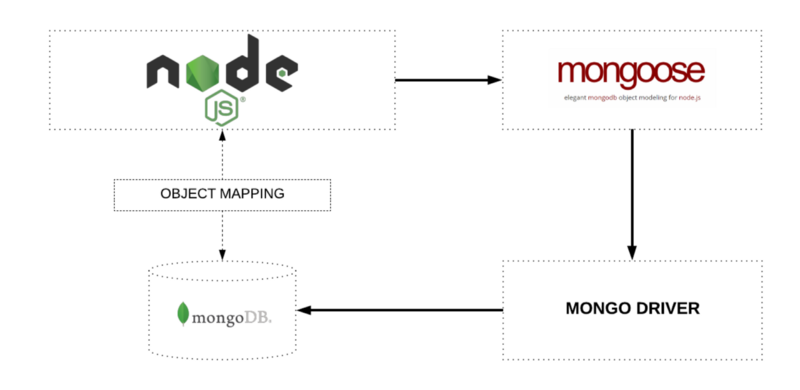
- *New* Mongoose - Object Data Modeling (ODM) library for MongoDB and Node.js.
- Manages relationships between data
- Provides schema validation
- Translates objects in code and the representation of those objects in MongoDB.
Highlights are important 2!
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon server.js",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
}- nodemon is a tool that automatically restarts the node application when file changes in the directory are detected.
- Save -> Restart

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Create A Todo List By Clicking The Button Below</h1>
<a href="/todos"> New Todo List</a>
</body>
</html>views > *.ejs
index.ejs
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Todos</h1>
<ul>
<% todos.forEach( el => { %>
<li class='todoItem' data-id='<%=el._id%>'>
<span class='<%= el.completed === true ? 'completed' : 'not'%>'><%= el.todo %></span>
<span class='del'> Delete </span>
</li>
<% }) %>
</ul>
<h2>Things left to do: <%= left %></h2>
<form action="/todos/createTodo" method='POST'>
<input type="text" placeholder="Enter Todo Item" name='todoItem'>
<input type="submit">
</form>
<script src="js/main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>todos.ejs
Remember: The view is the UI (HTML and CSS
- The User clicks to create a 'New ToDo List'
- The router hears the click and sends it to the Controller.
- The Controller sends the information to the Model.
- The Model returns the data it has to the Controller.
- The Controller presents the information to the User. In this case, asking the User to Enter ToDo Item.
models > Todo.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose')
const TodoSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
todo: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
completed: {
type: Boolean,
required: true,
}
})
module.exports = mongoose.model('Todo', TodoSchema)Remember: The Model is used to Notify and Update the Controller
We know Mongoose manages relationships between data, provides schema validation and translates objects in code and the representation of those objects in MongoDB.
- The ToDo is transferring data to and from the Controller.
- The ToDo list items.
- If the List Item is completed or not.
const Todo = require('../models/Todo')
module.exports = {
getTodos: async (req,res)=>{
try{
const todoItems = await Todo.find()
const itemsLeft = await Todo.countDocuments({completed: false})
res.render('todos.ejs', {todos: todoItems, left: itemsLeft})
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}
},
createTodo: async (req, res)=>{
try{
await Todo.create({todo: req.body.todoItem, completed: false})
console.log('Todo has been added!')
res.redirect('/todos')
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}
},
markComplete: async (req, res)=>{
try{
await Todo.findOneAndUpdate({_id:req.body.todoIdFromJSFile},{
completed: true
})
console.log('Marked Complete')
res.json('Marked Complete')
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}
},
markIncomplete: async (req, res)=>{
try{
await Todo.findOneAndUpdate({_id:req.body.todoIdFromJSFile},{
completed: false
})
console.log('Marked Incomplete')
res.json('Marked Incomplete')
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}
},
deleteTodo: async (req, res)=>{
console.log(req.body.todoIdFromJSFile)
try{
await Todo.findOneAndDelete({_id:req.body.todoIdFromJSFile})
console.log('Deleted Todo')
res.json('Deleted It')
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}
}
} controllers> *.js
todos.js
module.exports = {
getIndex: (req,res)=>{
res.render('index.ejs')
}
}home.js
Remember: The Controller works with the View and the Model to control the flow of data back and forth.
markComplete: async (req, res)=>{
try{
await Todo.findOneAndUpdate({_id:req.body.todoIdFromJSFile},{
completed: true
})
console.log('Marked Complete')
res.json('Marked Complete')
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}
},
deleteTodo: async (req, res)=>{
console.log(req.body.todoIdFromJSFile)
try{
await Todo.findOneAndDelete({_id:req.body.todoIdFromJSFile})
console.log('Deleted Todo')
res.json('Deleted It')
}catch(err){
console.log(err)
}Ok, that was a lot of code
A little imagination please...
- The User interacts with the View and sends data to the Model.
- The Model then sends this information the the Controller.
- The controller runs it's methods to gather information from the Database. Does the list exist? Is it completed?
- The data is returned to the Model, then the View.
Super basic explanation incoming!
Seriously...it was better with Pokémon


Any
Questions?
YO MVC
By susurrate
YO MVC
- 91