Algorithms

Backpack
problem



(Knapsacks problem)


Definition






The first time it was mentioned
The 0/1 Knapsack Problem was first formally introduced in the context of optimization and combinatorial problems by Richard Karp in his 1972 paper titled "Reducibility Among Combinatorial Problems", published in the journal SIAM Journal on Computing. This paper is famous for presenting a set of 21 NP-complete problems, and the 0/1 Knapsack Problem was one of the problems included in this classification.





1-0 Backpack Problem
We have n items, each one of them has a value vi and a weight wi, and we want to determine which items to take without exceeding the maximum weight k while having a total value that is as big as possible, you are asked to return their total value.


Dynamic Programming
Tabulation
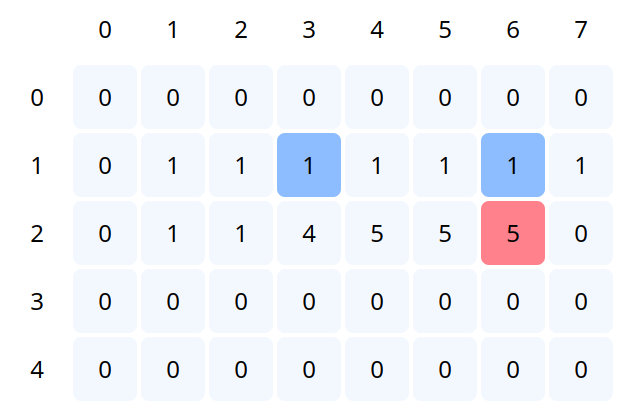


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?

const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


const val = [1, 4, 5, 7]; // The value of all available items const wt = [1, 3, 4, 5]; // The weights of available items const W = 7; // The maximum weight we can carry in our collection const N = val.length; const DP = new Array(N + 1); for (let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++) { DP[i] = new Array(W + 1); for (let j = 0; j < W + 1; j++) { DP[i][j] = 0; } } for (let i = 0; i <= N; i++) { for (let j = 0; j <= W; j++) { if (i === 0 || j === 0) { /* If we have no items or maximum weight we can take in collection is 0 then the total weight in our collection is 0 */ DP[i][0] = 0; } else if (wt[i - 1] <= j) { // take the current item in our collection const A = val[i - 1] + DP[i - 1][j - wt[i - 1]]; const B = DP[i - 1][j]; /* find the maximum of these two values and take which gives us a greater weight */ if (A > B) { DP[i][j] = A; } else { DP[i][j] = B; } } else { // leave the current item from our collection DP[i][j] = DP[i - 1][j]; } } }
How it works?


Dynamic Programming
Memorization



actual
item
remaining
capacity
Recursive definition














def knapsack(values, weights, k, i=0): if i == len(values): return 0 elif k < 0: return float('-inf') else: return max(values[i]+ knapsack(values, weights, k-weights[i], i+1), knapsack(values, weights, k, i+1))
How it works?
(recursive)
1. check the trivial case
2. check if the capacity is negative
3. return the recursive definition (select between max values)



def knapsack(values, weights, k, i=0, lookup=None): lookup = {} if lookup is None else lookup if (i , k) in lookup: return lookup[( i, k)] if i == len(values): return 0 elif k < 0: return float('-inf') else: lookup[(i , k)]=max(values[i]+ knapsack(values, weights, k-weights[i], i+1, lookup), knapsack(values, weights, k, i+1, lookup)) return lookup[(i, k)]
How it works?
(DP memorization)
1. adding a parameter lookup
2. initializing the lookup
3. checking if we already solved the actual subproblem
4. storing the result in the lookup



Fractional Backpack Problem
- Items: Each item is assigned a weight and a value.
- Knapsack Capacity: This is the maximum weight that the knapsack can accommodate.
- Solution: Portions of items may be taken. If an item exceeds the weight limit, only a fraction can be carried.
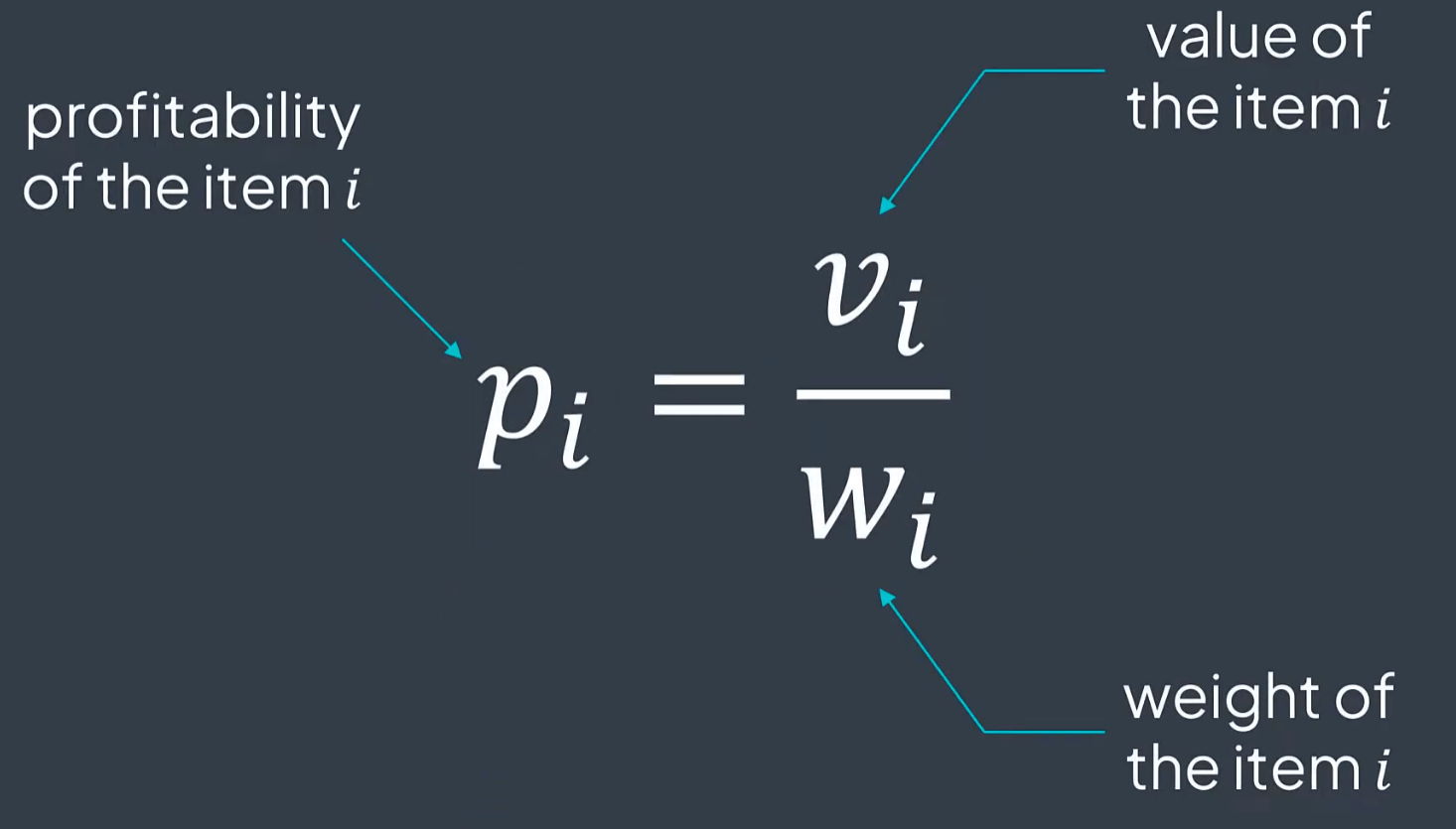













Fractional Backpack Problem


Fractional Backpack Problem







Fractional Backpack Problem







Fractional Backpack Problem








Fractional Backpack Problem

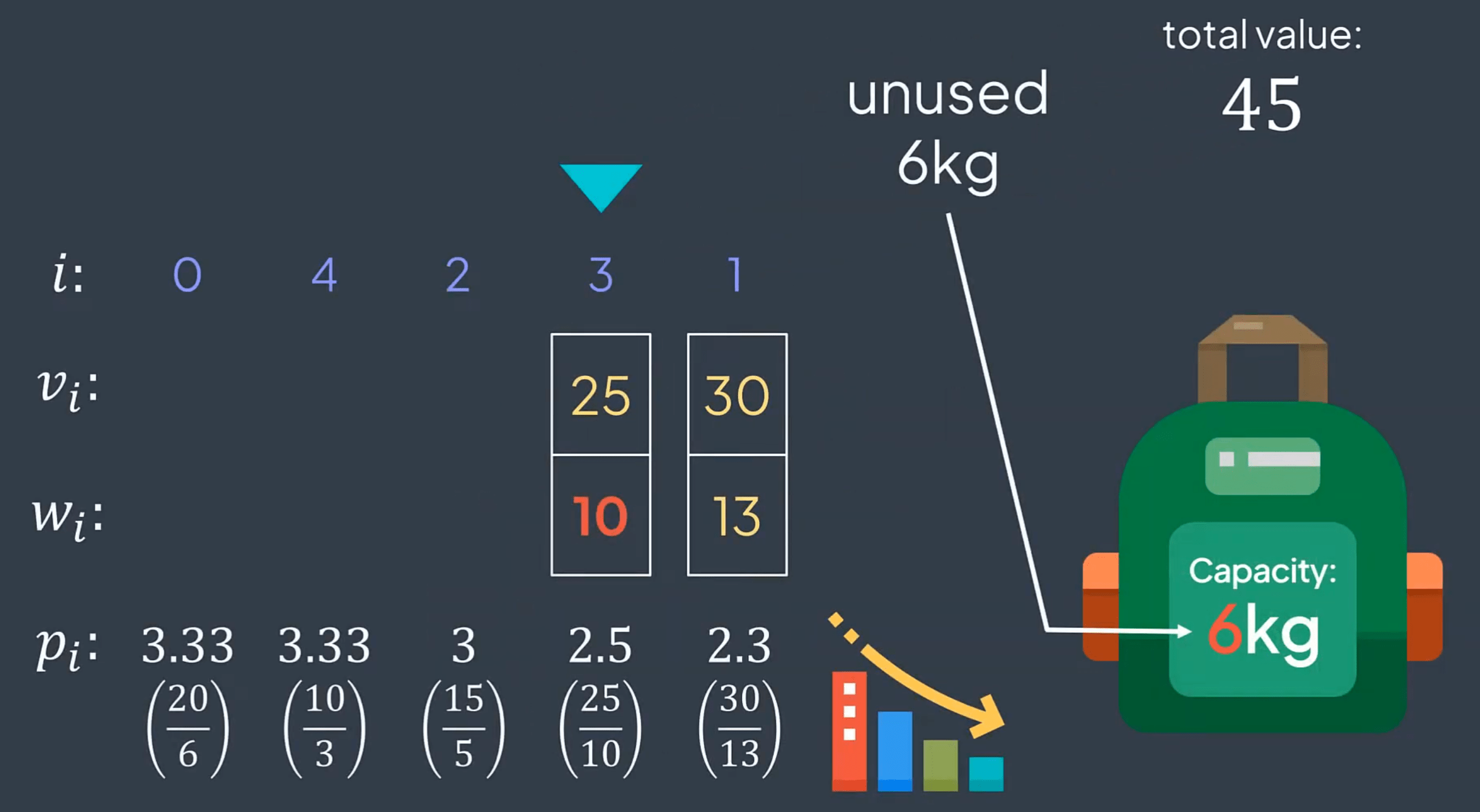









Fractional Backpack Problem
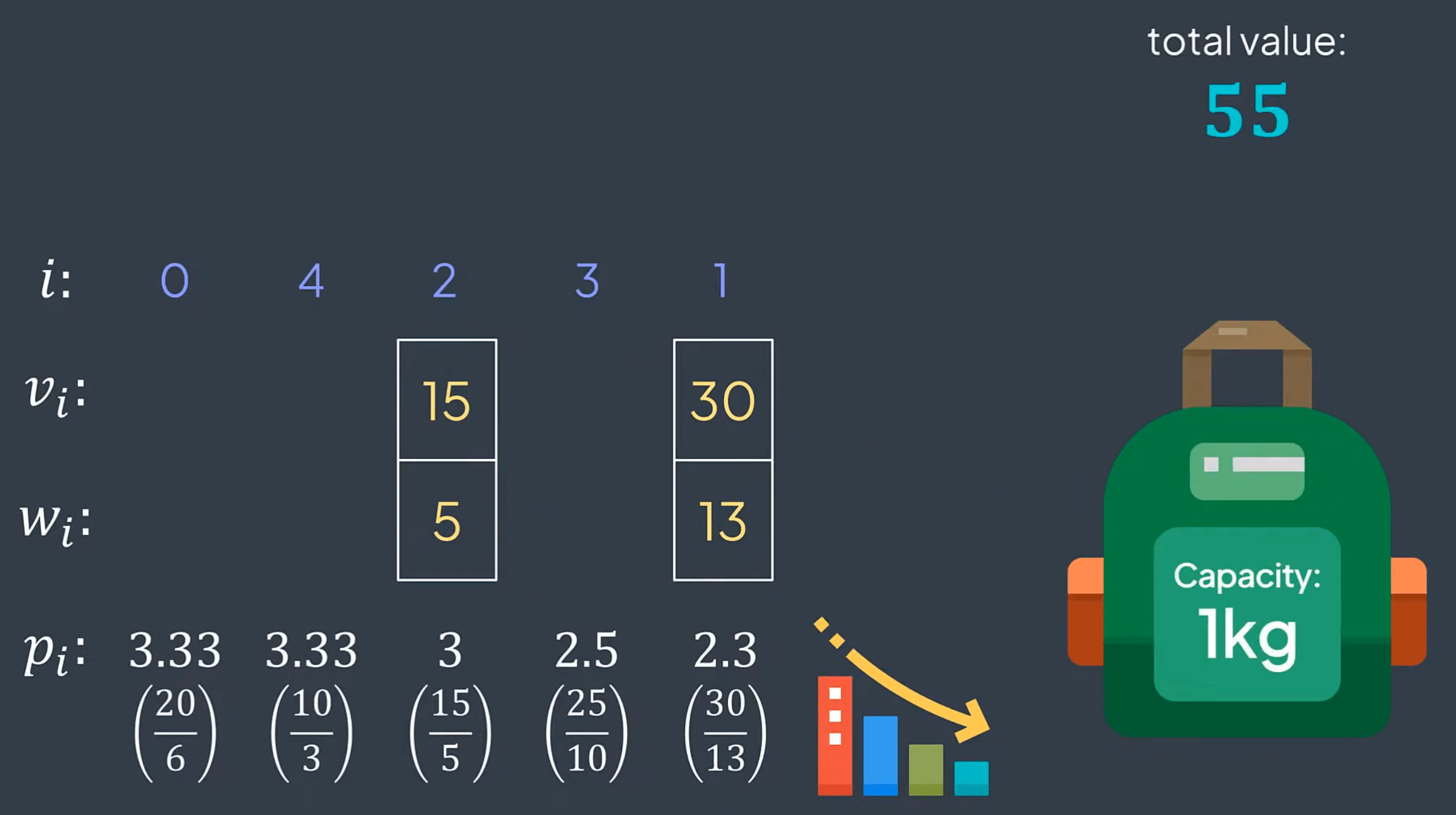










Fractional Backpack Problem
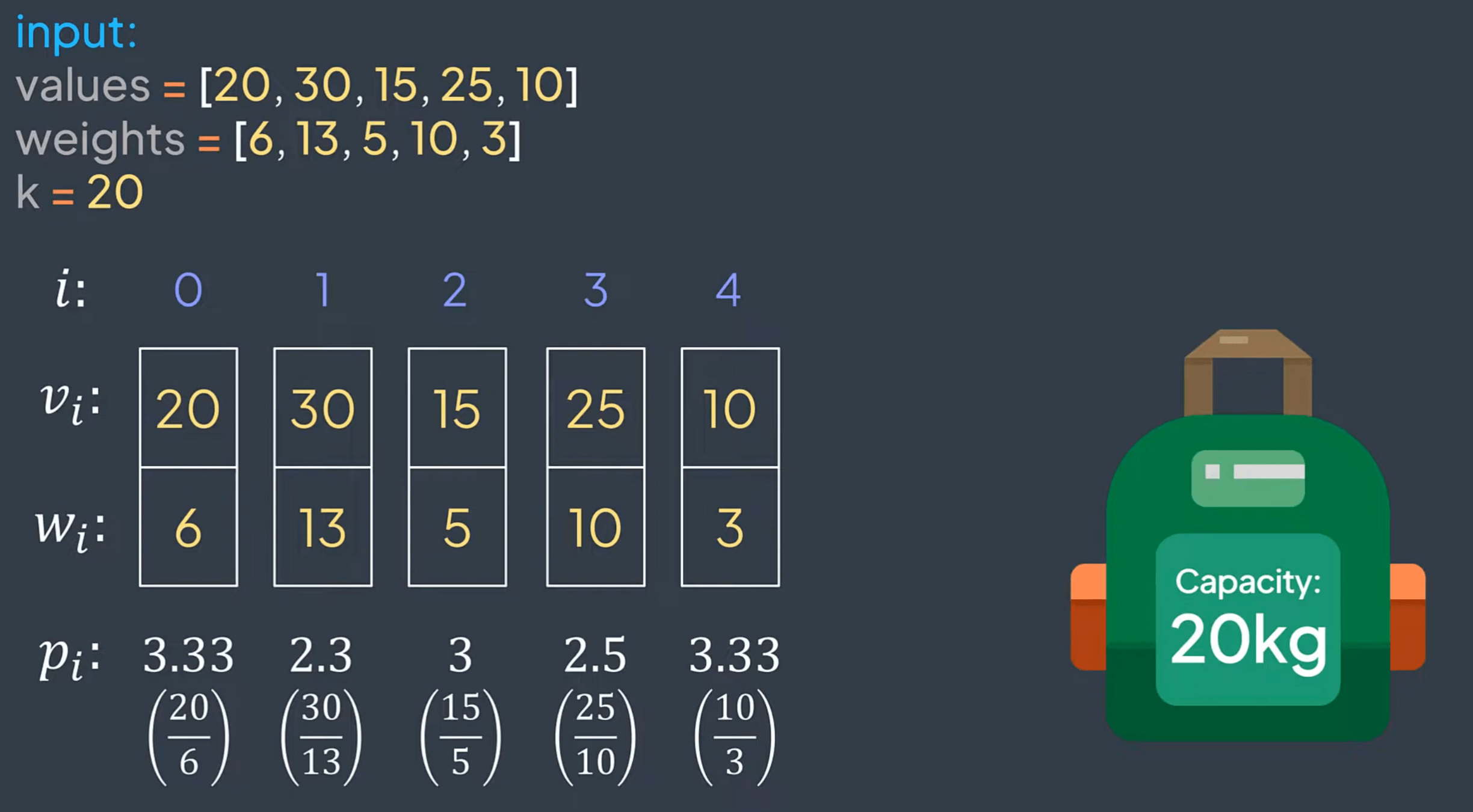
We have n items, each with a value vi and a weight wi. Our goal is to determine which items to take without exceeding the maximum weight k. You are asked to return their total value while maximizing the overall value. We are not required to take the entire item; we can take a fraction of it.


Definition





Don't take item i
Take the whole item i
Take 30% of the item i

Fractional Backpack Problem
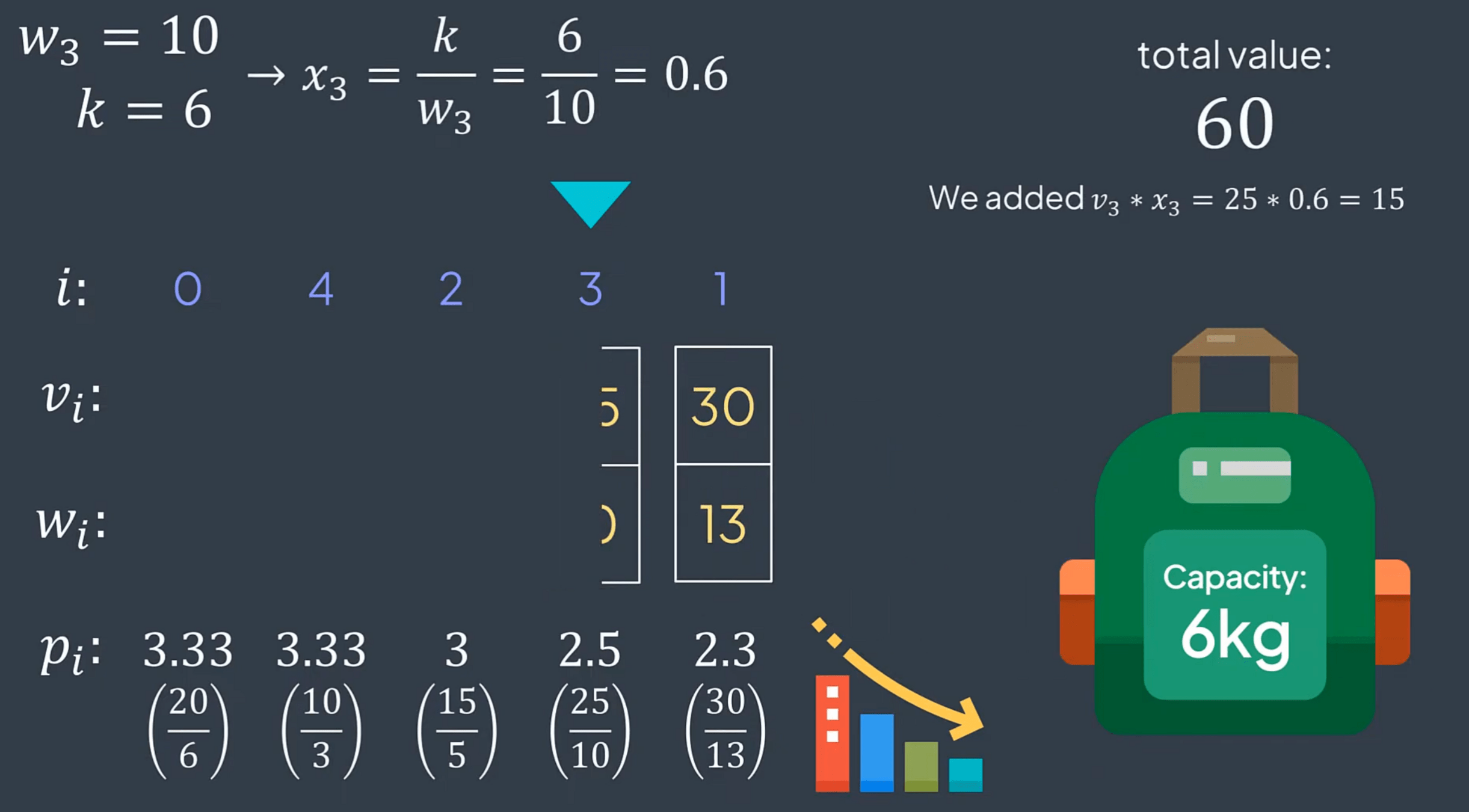



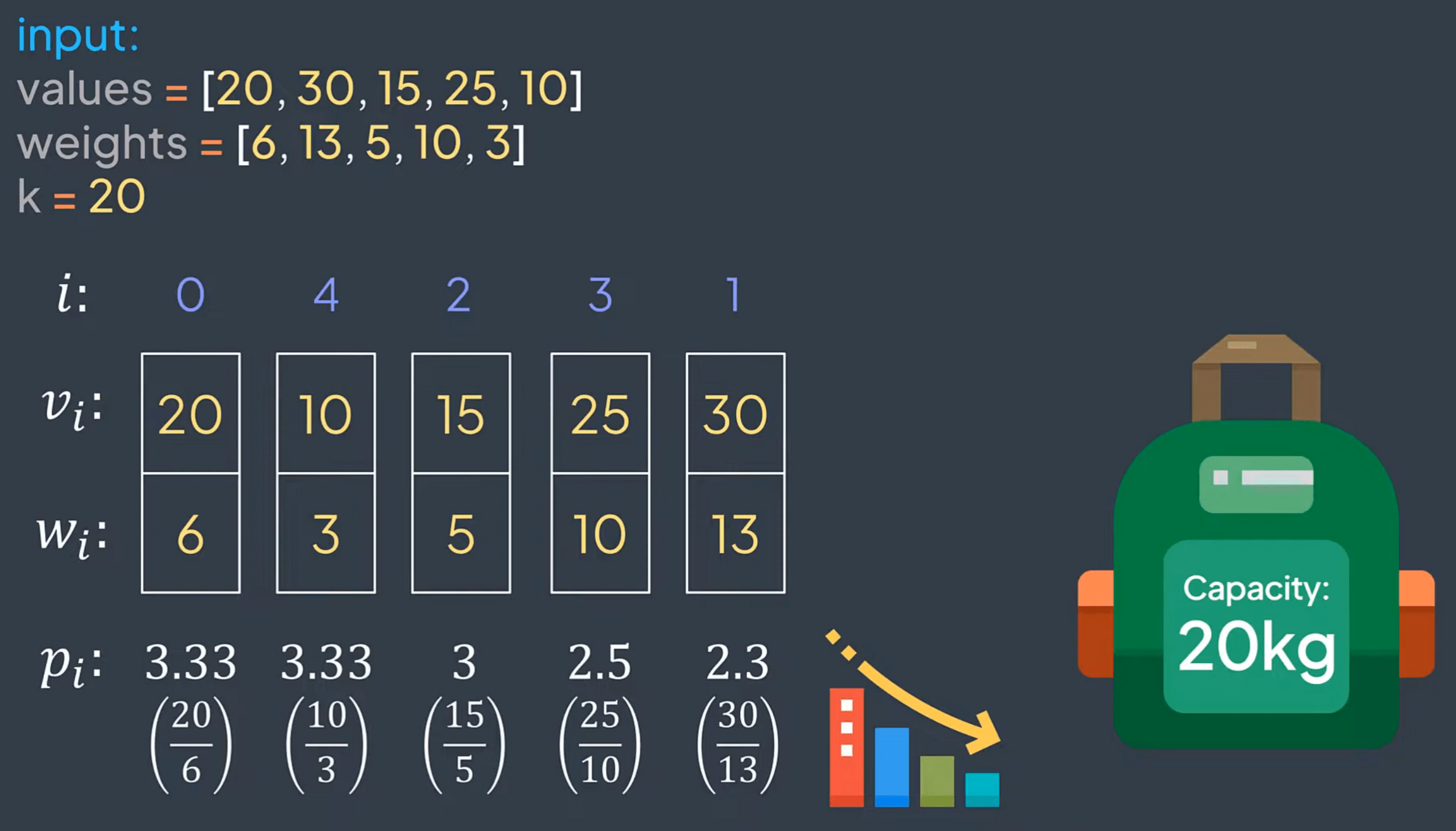
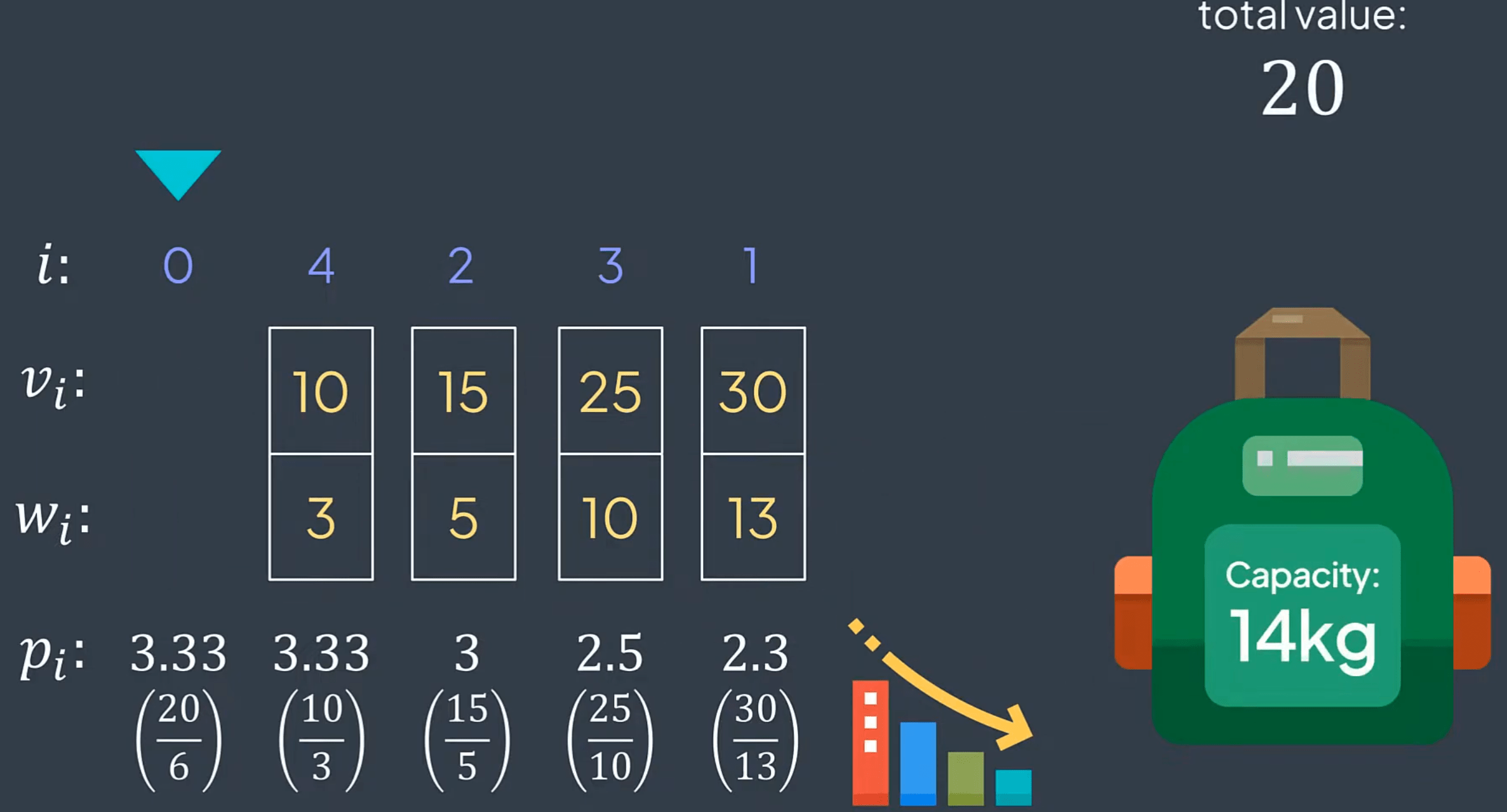
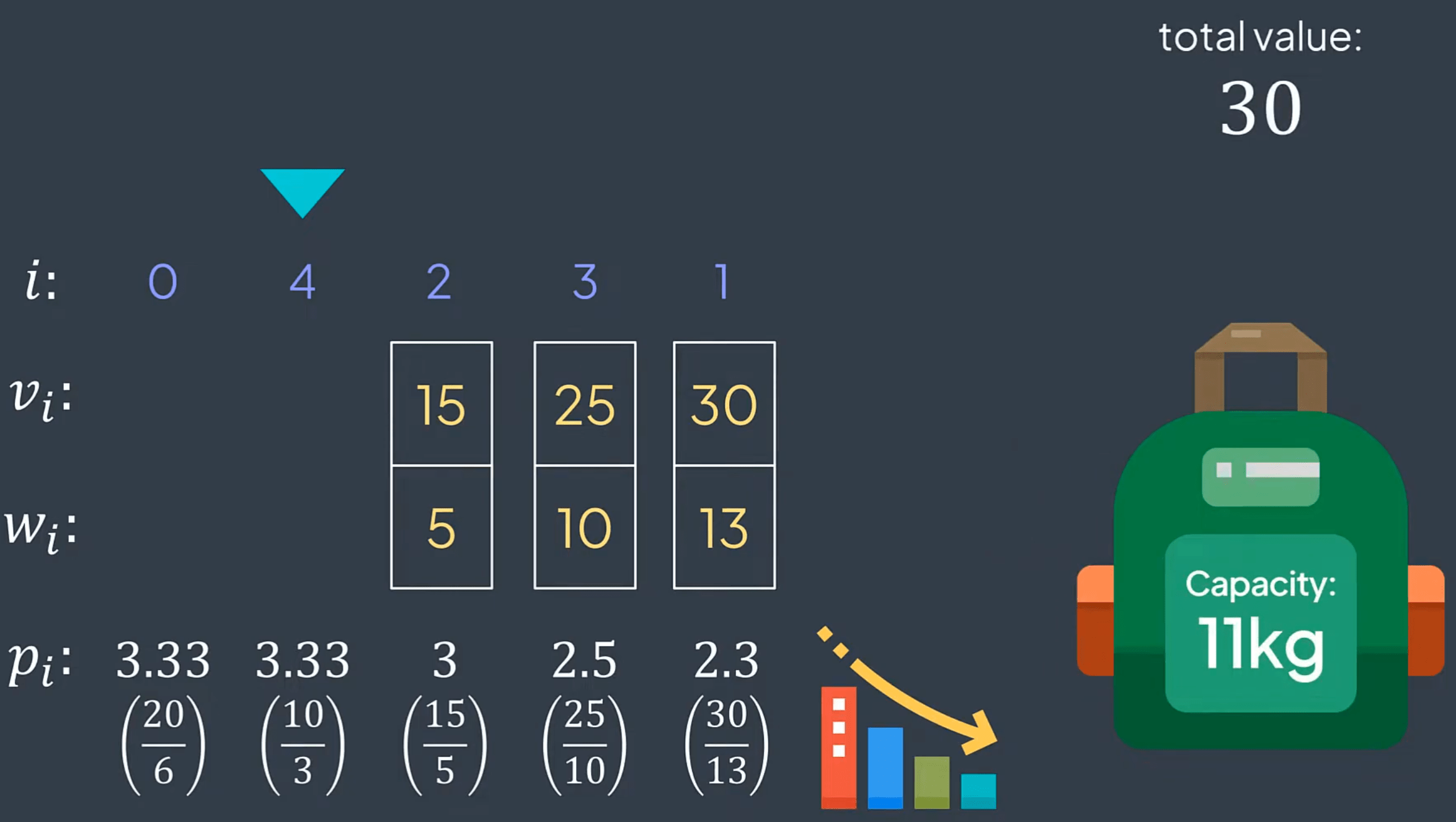
def fractional_knapsack(values, weights, k):
items = list(range(len(values))) #0(n)
items.sort(key=lambda i: values[i]/weights[i], reverse=True)#0(nlogn)
total_value = 0
for i in items: #n
if weights[i] <= k:
total_value += values[i] #0(1)
k -= weights[i]
else:
xi=k/weights[i]
total_value += values[i]*xi
break
return total_value

Complexity
The first time it was mentioned





THANK YOU!
Time for kahoot'it!

谢谢







Knapsacks problem
By Sebastian Yesid Tabares Amaya
Knapsacks problem
- 212



