Stacks
Tarun Luthra




Agenda

What you will learn?
-
Basics of Stacks
-
Implementation
-
Examples


Stacks
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the principle of Last In First Out (LIFO). This means the last element inserted inside the stack is removed first.
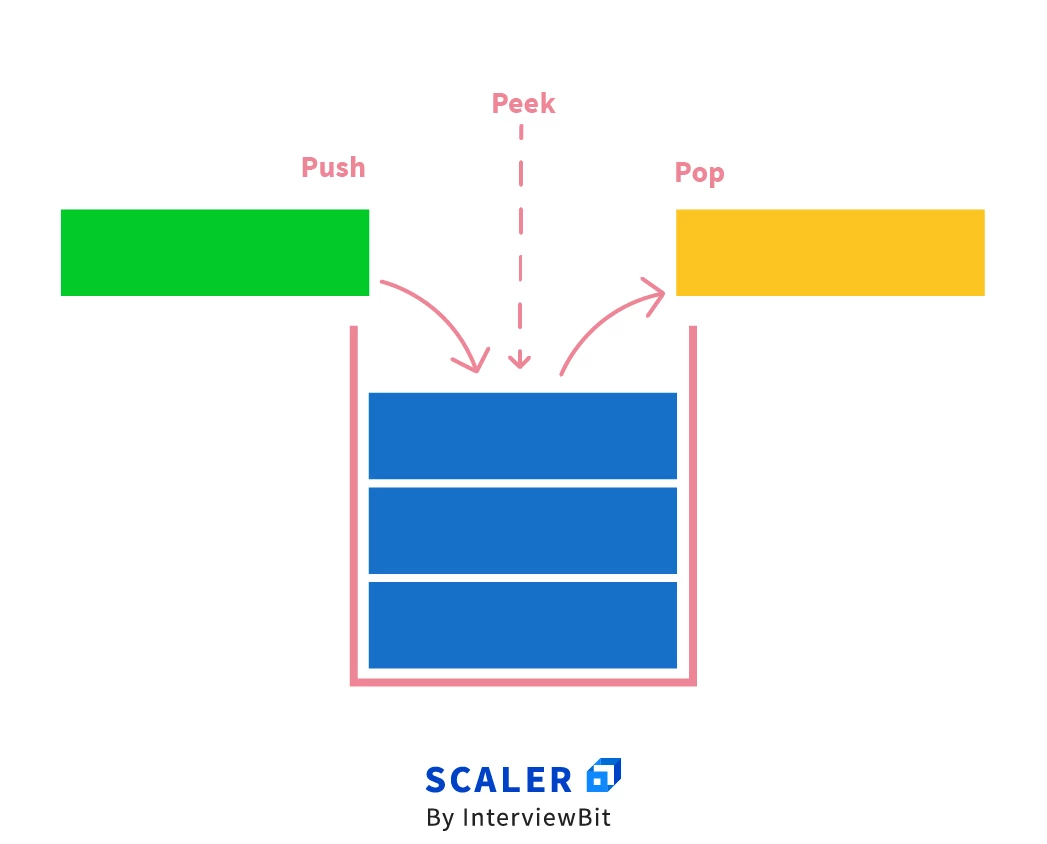





Operations on Stacks



- push(x)
Operations on Stacks


Operations on Stacks

- push(x)
: insert x at the top


Operations on Stacks

- push(x)
- pop()
: insert x at the top


Operations on Stacks

- push(x)
- pop()
: insert x at the top
: delete the top element


Operations on Stacks

- push(x)
- pop()
- top()
: insert x at the top
: delete the top element


Operations on Stacks

- push(x)
- pop()
- top()
: insert x at the top
: delete the top element
: return the top element


Operations on Stacks

- push(x)
- pop()
- top()
- size()
: insert x at the top
: delete the top element
: return the top element
: return no of elements


Can we iterate over a stack ? 🧐


Not without removing the data.
Can we iterate over a stack ? 🧐


Example 👨💻


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8
9


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8
9


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8
9


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8
9


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8
9


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8
Peek at the top


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8
Peek at the top
Read 8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20
8


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
20


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
Peek at the top


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
Peek at the top
Read 40


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
25


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
25


- push(40)
- push(20)
- push(8)
- push(9)
- pop()
- top()
- pop()
- pop()
- top()
- push(25)
Perform these operations
40
25


What would happen if you use pop() or top() on an empty stack ? 🧐


What would happen if you use pop() or top() on an empty stack ? 🧐


What would happen if you use pop() or top() on an empty stack ? 🧐
Accessing pop() or top() method on an empty stack will lead to an
Error


What would happen if you use pop() or top() on an empty stack ? 🧐
Accessing pop() or top() method on an empty stack will lead to an
Stack Underflow Error


Implementation 👨💻


Stack Implementation using Dynamic Arrays 👨💻


Stack Implementation using Dynamic Arrays 👨💻
class Stack {
ArrayList<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
void push(int x) {
l.add(x);
}
void pop() {
l.remove(l.size() - 1);
}
int top() {
return l.get(l.size() - 1);
}
int size() {
return l.size();
}
}class Stack:
l = []
def push(self, x):
self.l.append(x)
def pop(self):
self.l.pop()
def top(self):
return self.l[-1]
def size(self):
return len(self.l)

Stack Implementation using Dynamic Arrays 👨💻
class Stack {
ArrayList<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
void push(int x) {
l.add(x);
}
void pop() {
if (l.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
}
l.remove(l.size() - 1);
}
int top() {
if (l.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
return l.get(l.size() - 1);
}
int size() {
return l.size();
}
}class Stack:
l = []
def push(self, x):
self.l.append(x)
def pop(self):
if len(self.l) == 0:
print("Stack is empty")
self.l.pop()
def top(self):
if len(self.l) == 0:
print("Stack is empty")
return self.l[-1]
def size(self):
return len(self.l)

Stack Implementation using Dynamic Arrays 👨💻
class Stack {
ArrayList<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
void push(int x) {
l.add(x);
}
void pop() throws Exception {
if (l.size() == 0) {
throw new Exception("Stack underflow");
}
l.remove(l.size() - 1);
}
int top() throws Exception {
if (l.size() == 0) {
throw new Exception("Stack underflow");
}
return l.get(l.size() - 1);
}
int size() {
return l.size();
}
}class Stack:
l = []
def push(self, x):
self.l.append(x)
def pop(self):
if len(self.l) == 0:
raise Exception("Stack underflow")
self.l.pop()
def top(self):
if len(self.l) == 0:
raise Exception("Stack underflow")
return self.l[-1]
def size(self):
return len(self.l)

Stack Implementation using Linked Lists 👨💻


Stack Implementation using Linked Lists 👨💻


Stack Implementation using Linked Lists 👨💻
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
}
}class Node:
data = 0
next = None
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.next = None

class Stack {
Node head = null;
int s = 0;
void push(int x) {
Node n = new Node(x);
n.next = head;
head = n;
s++;
}
void pop() throws Exception {
if (head == null) {
throw new Exception("Stack underflow error");
}
head = head.next;
s--;
}
int top() throws Exception {
if (head == null) {
throw new Exception("Stack underflow error");
}
return head.data;
}
int size() {
return s;
}
}class Stack:
head = None
s = 0
def push(self, x):
n = Node(x)
n.next = self.head
self.head = n
self.s += 1
def pop(self):
if self.head is None:
raise Exception("Stack underflow error")
self.head = self.head.next
self.s -= 1
def top(self):
if self.head is None:
raise Exception("Stack underflow error")
return self.head.data
def size(self):
return self.s

Stack Libraries
There are ready-made implementations of Stack in most language's libraries/modules. You can find them here :
- Stacks in Python - https://www.scaler.com/topics/stack-in-python/
-
Stacks in Java - https://www.scaler.com/topics/stack-class-in-java/
-
Stacks in C++ - https://www.scaler.com/topics/cpp/stack-in-cpp/
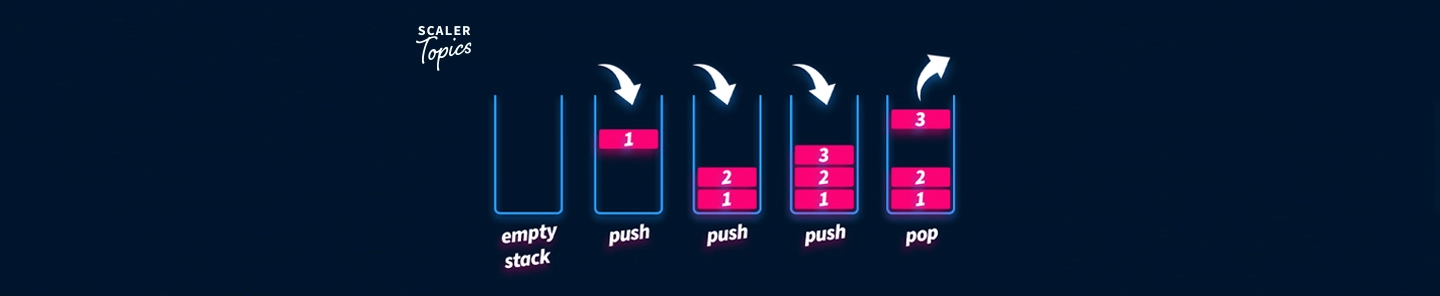


Visualisers
- Stack Visualiser - Array Implementation -https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/StackArray.html
- Stack Visualiser - Linked List Implementation -
https://visualgo.net/en/list?slide=3-5


Codes
- Java LL Implementation :
https://ide.codingminutes.com/?id=ayg - Python LL Implementation :
https://ide.codingminutes.com/?id=ayu - Java Stack ArrayList Implementation :
https://ide.codingminutes.com/?id=ayk - Python Stack List Implementation :
https://ide.codingminutes.com/?id=ayf


Thank you! 👨💻
Stacks Basics
By Tarun Luthra
Stacks Basics
- 195


