Introduction to RxJS
Reactive Extensions for JavaScript
What is RxJS?
A toolbox for creating and handling reactive data streams
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/c4QJzC
Reactive
- Working with (asynchronous) (infinite) data streams
- Everything can be described as a stream of data
- Data is pushed, not pulled
RxJS
- Implementation of Rx for JavaScript
- Provides toolbox to create & handle data streams
- Toolbox provides functional operators
- Developed by Microsoft & open source contributors
- Current versions: 4.1 (stable), 5 (beta)
- License: Apache Licence v2
- Used for example at Netflix and for many Angular 2 internal implementations
What are
data streams?
Image source: http://popkey.co/m/aWG7m-matrix
Data stream
- Observable sequence (= data stream) contains values ordered in time
- Emitted by observables
- Data is pushed into the stream by the Observable once it's available (reactive)
- Can contain three things
- Values (of arbitrary type incl. other observables)
- Error notification
- Completed notification
Marble diagrams
a visual representation of data streams & transformations
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/k97UbB
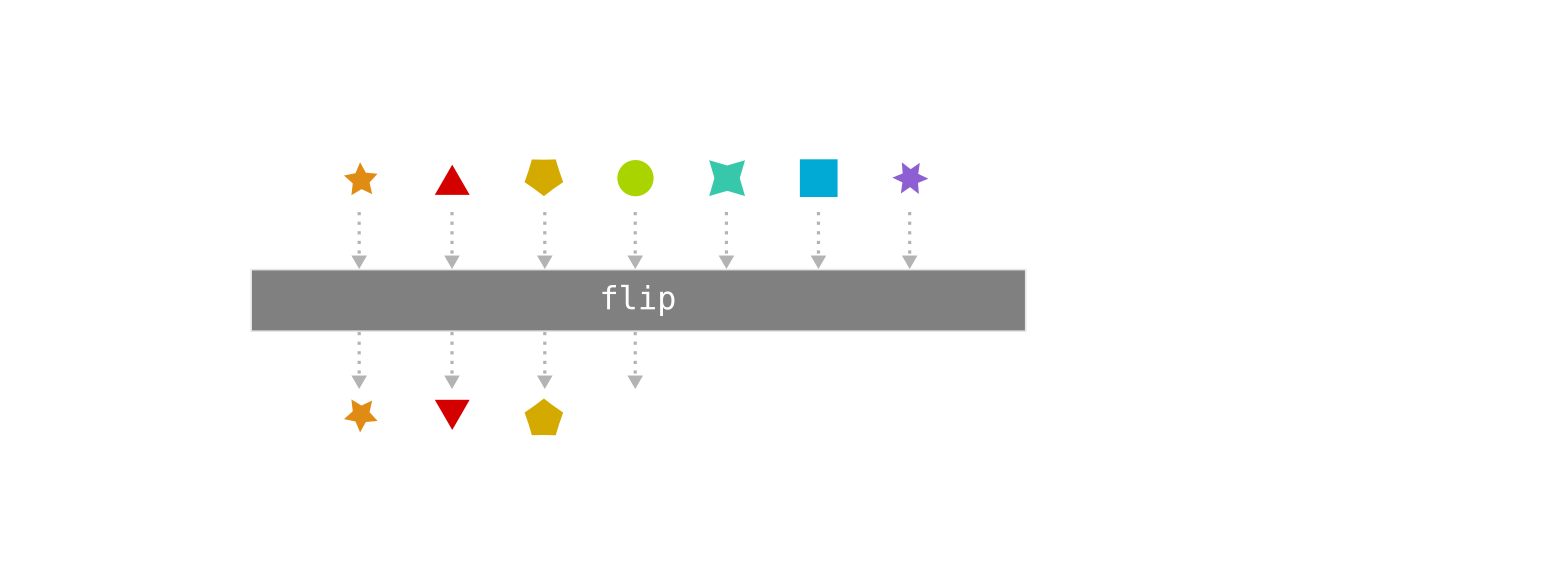
Marble diagrams: Thinking in images
Observable pattern
onNext* (onCompleted|onError)?
API
How to write RxJS code
Observable
- Accepts an observer: an object with `onNext`, `onError` and `onComplete` methods on it
- Can be `subscribe`d to
- Is lazy: does nothing until subscribed to (cold)
- Returns a unsubscribable function on subscription which stops subscription on `unsubscribe()` call
- Values are not shared between subscribers (cold)
- Has a lot of operators defined to manipulate data streams
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/esT1Qa
Observable
import { Observable } from 'rx';
// Contract: Observer needs to implement the following methods
// `onNext`, `onCompleted` and `onError`.
const source = Observable.create((observer) => {
// Yield a single value and complete
observer.next(42);
observer.complete();
// Any cleanup logic might go here.
return () => {
console.log('unsubscribed');
}
});
const subscription = source.subscribe(
(x) => { console.log('next: %s', x); },
(e) => { console.log('error: %s', e); },
() => { console.log('complete'); });
// => next: 42
// => complete
subscription.unsubscribe(); // => unsubscribedImage source: https://flic.kr/p/esT1Qa
Observer
- Can be subscribed to Observables
- Receives emissions & notification from the Observables
import { Subscriber } from 'rxjs/Subscriber';
const subscriber = Subscriber.create(
function next(x) {
console.log('Next: %s', x);
},
function error(err) {
console.log('Error: %s', err);
},
function complete() {
console.log('Completed');
}
);
// Usage
Observable
.interval(1000)
.take(3)
.subscribe(subscriber);Image source: https://flic.kr/p/esT1Qa
Subject
- Inherits from both, Observable and Observer
- Can be used as a proxy in between Observable(s) and Observer(s) to multiplex data streams
import { Observable, Subject } from 'rx';
// Emit a value every second.
const source = Observable.interval(1000);
const subject = new Subject();
const subSource = source.subscribe(subject);
const subSubject1 = subject.subscribe(
(x) => { console.log('Value published to observer #1: ' + x); },
(e) => { console.log('onError: ' + e.message); },
() => { console.log('onCompleted'); });
const subSubject2 = subject.subscribe(
(x) => { console.log('Value published to observer #2: ' + x); },
(e) => { console.log('onError: ' + e.message); },
() => { console.log('onCompleted'); });
setTimeout(function () {
// Clean up
subject.onCompleted();
subSubject1.dispose();
subSubject2.dispose();
}, 5000);
// Value published to observer #1: 0
// Value published to observer #2: 0
// Value published to observer #1: 1
// Value published to observer #2: 1
// Value published to observer #1: 2
// Value published to observer #2: 2
// Value published to observer #1: 3
// Value published to observer #2: 3
// onCompleted
// onCompletedImage source: https://flic.kr/p/esT1Qa
Subject
-
ReplaySubject
Stores all values that it has published and replays them on each new subscription -
BehaviourSubject
Same as `ReplaySubject`, but only repeats the last value -
AsyncSubject
Stores last value and replays it only after the source has completed.
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/esT1Qa
Scheduler
- Controls when subscriptions start and when notifications are sent to Observers
- Will not go into details, but:
- Can be used to simplify testing of async code
- RxJS provides a `TestScheduler` that allows to create, publish and subscribe to sequences in emulated time, e.g. transform a 5 day task into a 2 min task, while maintaining the correct time scale
- Further read
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/biWKFi
Hot vs. cold Observables
- DVD (cold): Observers watch independently
- Live performance (hot): Observers watch together, if you're late, you'll miss parts of the show
- Live performance recorded (hot): Even if you're late you can go back in time and re-watch what you've missed
- Live performance with lazy artists (hot): Artists won't play until somebody is there to watch
Analogy: (Live) Band performance
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/q6jVxA
Hot vs. cold Observables
-
Cold = Observables are lazy
- Observables start running on subscription (default)
- Hot = Observables are non-lazy
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/q6jVxA
Let's get
our hands dirty
Image source: https://flic.kr/p/4YphW4
Create Observables from
- Any list-like objects
- Intervals
- Promises
- Events
- ... many more
Any list-like objects
import { Observable } from 'rx';
const source = Observable.of('RxJs', 'is', 'awesome');
const subscription = source.subscribe(
(x) => console.log(x),
(e) => console.error(e),
() => console.log('completed')
);
// RxJs
// is
// awesome
// completedIntervals
import { Observable } from 'rx';
const source = Observable.interval(1000)
.timestamp() // add current timestamp
.take(3); // take only the first three items of the Observable
const subscription = source.subscribe(
(x) => console.log(x),
(e) => console.error(e),
() => console.log('completed')
);
// Object {value: 0, timestamp: 1463409084511}
// Object {value: 1, timestamp: 1463409085512}
// Object {value: 2, timestamp: 1463409086513}
// completedPromises
import { Observable } from 'rx';
const promiseFn = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('Promise started');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Promise resolved');
resolve(42);
}, 1000);
console.log('Promise in flight');
});
};
const source = Observable.fromPromise(promiseFn);
const subscription = source.subscribe(
(x) => console.log(x),
(e) => console.error(e),
() => console.log('completed')
);
// Promise started
// Promise in flight
// Promise resolved
// 42
// completedEvents
import { Observable } from 'rx';
const source = Observable.fromEvent(document, 'mousemove')
.map(event => `Cursor at: ${event.clientX}, ${event.clientY}`)
.first(5);
const subscription = source.subscribe(
(x) => console.log(x),
(e) => console.error(e),
() => console.log('completed')
);
// Cursor at: 20, 170
// Cursor at: 53, 156
// Cursor at: 82, 146
// Cursor at: 111, 135
// Cursor at: 125, 131
// completed
Modify data streams with
- concat
- pluck
- bufferCount
- bufferTime
- debounce
- distinctUntilChanged
- ... many more
Example #1
Task:
- Asynchronous search via AJAX
- Don't search on each keypress
- Don't search twice if result is same
- Cache results
Debounced search with cached results
Example #2
Task:
- Asynchronous call to some node like method
- If call does not succeed try N more times
(Bonus: with increasing time interval)
Async call with N retries
Example #3
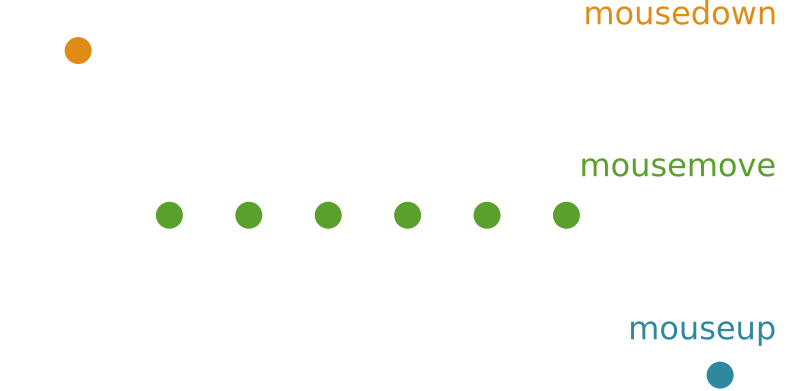
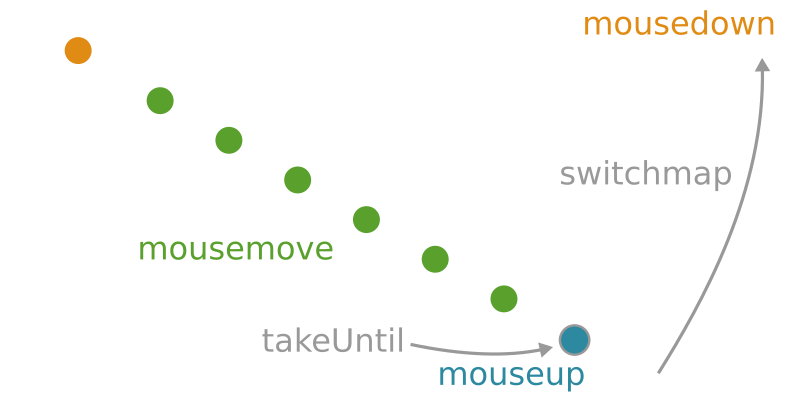
Task:
- On mousedown activate drag-mode for element
- On mousemove move element to current mouse cursor position
- On mouseup deactivate drag-mode again
Drag & Drop
Drag & Drop
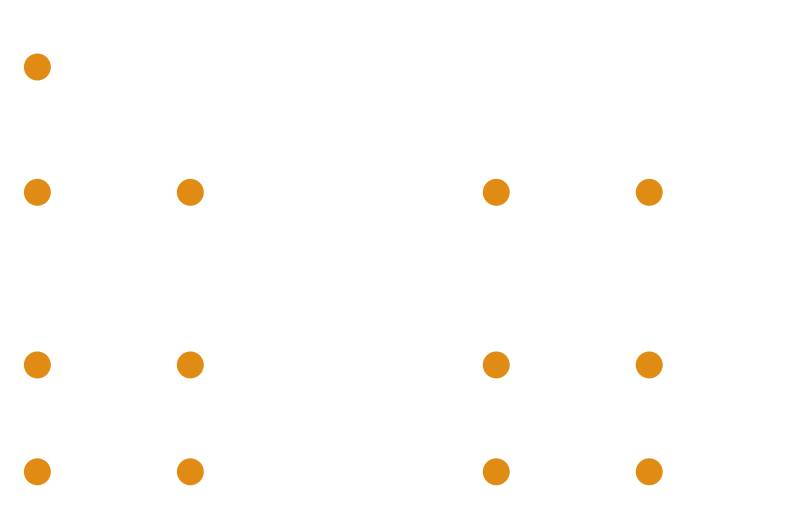
Independent Observables
Drag & Drop
How to compose Observables?
Drag & Drop

Composed Observable
Demo #4
Task:
- Use Observables to escape callback hell
Escape callback hell
References
Angular 2 Workshop 10
By Tarun Sharma
Angular 2 Workshop 10
- 1,034



