COPD & Training
Dimitris Dervas, G.P.
COPD patients
less time walking,
walk at a lower intensity than their healthy counterparts,
most do not meet current recommendations for levels of physical activity
Spruit MA, Pitta F, McAuley E, ZuWallack RL, Nici L. Pulmonary Rehabilitation and Physical Activity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015 Oct 15;192(8):924–33.
this association was confirmed in a 5-year longitudinal observational study that showed that
a decline in physical activity
was associated with
a decline in health status in patients with COPD
COPD
Spruit MA, Pitta F, McAuley E, ZuWallack RL, Nici L. Pulmonary Rehabilitation and Physical Activity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015 Oct 15;192(8):924–33.
Lower physical activity:
- are associated with a higher risk of an exacerbation-related hospitalization
- increase the risk of all-cause mortality in patients with COPD after controlling for relevant confounding factors
- over time also predicts mortality
Spruit MA, Pitta F, McAuley E, ZuWallack RL, Nici L. Pulmonary Rehabilitation and Physical Activity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015 Oct 15;192(8):924–33.
COPD
no direct effect on the physiologic derangements in
lung function
greatest improvements in
- dyspnea,
- exercise tolerance, and
- health-related quality of life
of any intervention available for patients with chronic respiratory disease.
It also decreases subsequent healthcare use, especially when provided following an exacerbation of COPD
pulmonary rehabilitation
| n | Frequency | AET | Intensity | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Breyer et al (2010) |
n=60 CT=30 AET=30 |
3/wk for 3months and 6months |
Nordic Walking | 75% maxHR | ↑6MWD, ↓BORG, ↓HADS anxiety, ↓SF 36 |
| McNamara et al. (2013) | n= 53 CT: 15 AET land based: 20 AET water based: 18 |
3/wk for 8 wks | Exercise in water and on land | 3 to 5 modified Borg scale | ↑6MWT, ↓CRDQ, ↑incremental shuttle walk distance |
| Gottlieb (2011) | n=42 AET: 22 CT: 20 |
2/wk for 7 weeks | 90-minute endurance training, |
16–17 Borg scale | ↑6MWT, ↔MRC, ↑SGRQ |
| Ozdemir (2010) | n: 50 AET: 25 CT: 25 |
3/wk for 4 weeks | water-based pulmonary rehabilitation for 35 minutes | ↔6MWT, ↔Spirometry, ↑CRDQ, ↑HAD Scale |
Aerobic
AET versus control
S/MG/W: maximum sets per muscle group per week, WRpeak: maximum work rate, AET: aerobic endurance training, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, VEpeak: maximum minute ventilation, SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire, 6MWD: 6-min walk distance, PST: progressive strength training, CPET: cardiopulmonary exercise test, ADL: activities of daily living, CRDQ: Chronic Respiratory Disease, MRC: breathlessness scale, HADS: Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale,
1. Breyer M-K, Breyer-Kohansal R, Funk G-C, Dornhofer N, Spruit MA, Wouters EF, et al. Nordic Walking improves daily physical activities in COPD: a randomised controlled trial. Respiratory Research. 2010;11:112. 2. McNamara RJ, McKeough ZJ, McKenzie DK, Alison JA. Water-based exercise in COPD with physical comorbidities: a randomised controlled trial. Eur Respir J. 2013 Jun;41(6):1284–91. 3. Gottlieb V, Lyngsø AM, Nybo B, Frølich A, Backer V. Pulmonary rehabilitation for moderate COPD (GOLD 2)--does it have an effect? COPD. 2011 Oct;8(5):380–6. 4. Özdemi̇r EP, Solak Ö, Fi̇dan F, Demi̇rdal ÜS, Evci̇k D, Ünlü M, et al. The Effect of Water-Based Pulmonary Rehabilitation on Anxiety and Quality of Life in Chronic Pulmonary Obstructive Disease Patients. Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci. 2010;30(3):880–7.
| n | Time | RT | Intensity | Outcome | Secondary Outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Casaburi et al 2004 |
24 COPD 12 RT and 12 Controls |
3d/week for 10 weeks |
RT: 5 exercises Dose: 9 S/MG/W |
60–80% 1RM | ↑FEV1 | ↓TLC ↓DLCO |
|
Clark et al. 2000 |
43 COPD 26 RT and 17 Controls |
2d/week for 12 weeks |
8 exercises Dose: 6 S/MG/W |
70% 1RM | ↑VEpeak | ↑VTpeak |
|
Hoff et al. 2007 |
12 COPD 6 RT and 6 Controls |
3d/week for 8 weeks |
leg press Dose: 12 S/W |
5 repetitions | ↑FEV1 ↓VEpeak |
↑Mechanical efficiency |
|
Kongsgaard et al. 2004 |
14 COPD 9 RT and 9 Controls |
2d/week for 12 weeks |
3 exercises (leg) Dose: 8 S/MG/W |
80% 1RM | ↓FEV1 ↔FVC ↓VE |
↔RV ↓FRC ↓TLC ↓DLCO |
|
Simpmson et al. (1992) 2006 |
34 COPD 17 RT and 17 Controls |
3d/week for 8 weeks |
3 exercises Dose: 3 S/MG/W |
50–85% 1RM | ↑FEV1 | ↔PI |
Resistance Training
RT versus control
S/MG/W: maximum sets per muscle group per week, WRpeak: maximum work rate, AET: aerobic endurance training, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, VEpeak: maximum minute ventilation, SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire, 6MWD: 6-min walk distance, PST: progressive strength training
Strasser B, Siebert U, Schobersberger W. Effects of resistance training on respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2013 Mar;17(1):217–26.
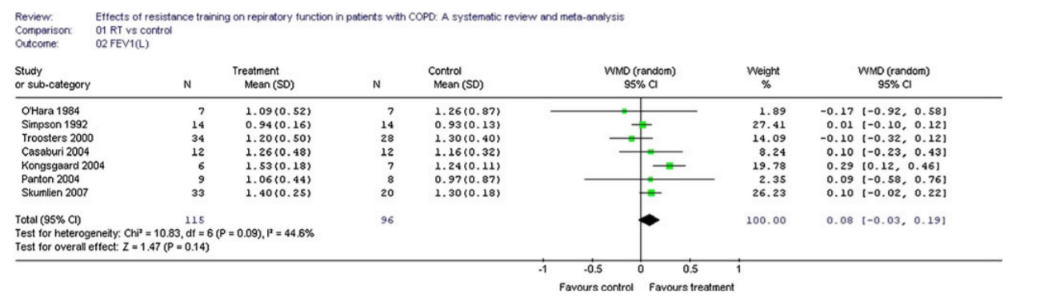
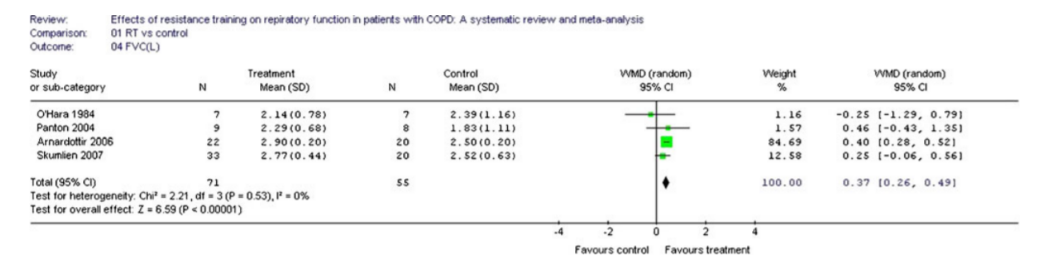
Resistance Training
RT versus control
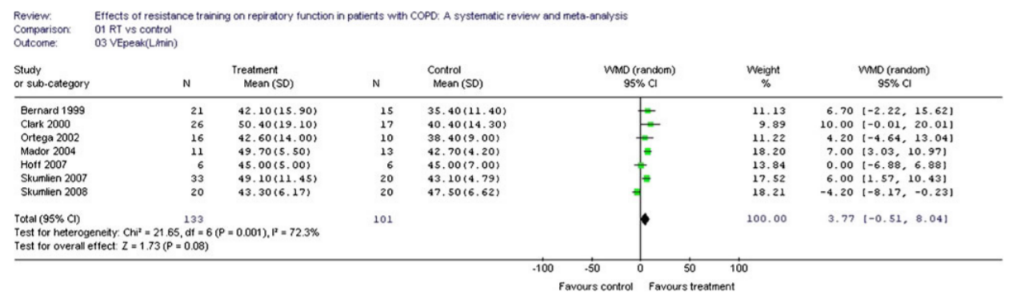
VEpeak
FEV1
FVC
Strasser B, Siebert U, Schobersberger W. Effects of resistance training on respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2013 Mar;17(1):217–26.
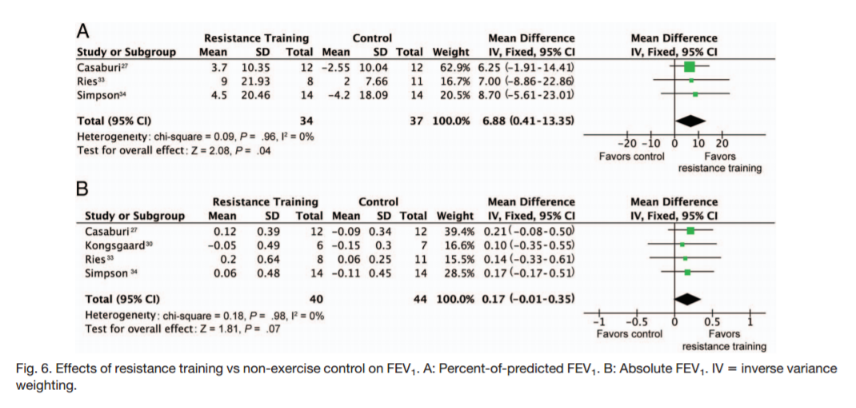
Resistance Training
RT versus control
FEV1
Liao W-H, Chen J-W, Chen X, Lin L, Yan H-Y, Zhou Y-Q, et al. Impact of Resistance Training in Subjects With COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir Care. 2015 Aug;60(8):1130–45.
| paper | n | Exercise | RT | AET | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vonbank et al (2012) | 36 COPD 12 RT + AET 12 AET 12 PST |
2/wk for 12 weeks |
8 muscle groups; 2-4 sets, 8-15 repetitions until fatigue; increasing weight load during the training period | Cycle ergometer training of increasing intensity and time intensity of 60% of VO2peak |
↑HRQoL ↑CPET ↑muscle strength (PST) |
| Dourado et al (2009) | 51 COPD 11 RT 13 AET 11 RT + AET |
3/wk for 12 weeks |
60-min 7 exercises 50%-80% of 1 RM, 3 sets of 12 repetitions; workload was adjusted to 1 RM every 3 wk | 30-min walking at self-determined intensity and 30 min of low intensity RT with a high number of repetitions at low workload |
↔HRQoL ↔walking distance ↑ muscle strength |
| Skumlien et al. (2008) | 40 COPD 20 RT 20 AET |
2/wk for 12 weeks |
RT: 5 exercises Intensity: 15RM Dose: 4 S/MG/W |
AET: 70% WRpeak Dose: 60 min/week |
↓FEV1 with RT ↓FVC with RT ↑VEpeak with RT ↔IC70 |
| Normandin et al(2002) | 40 COPD 20 RT 20 AET |
2/wk for 8 weeks |
low-intensity calisthenics 30-min duration - major muscle groups using free weights and calisthenics; 8-10 repetitions no progression in workload |
high-intensity, lower-extremity endurance training - 30 min of ergometer cycling and treadmill walking intensity 4 and 7 on the Borg 10-point scale |
↔HRQoL ↔ADL ↔CPET |
Resistance Training
RT versus AET
S/MG/W: maximum sets per muscle group per week, WRpeak: maximum work rate, AET: aerobic endurance training, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, VEpeak: maximum minute ventilation, SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire, 6MWD: 6-min walk distance, PST: progressive strength training, CPET: cardiopulmonary exercise test, ADL: activities of daily living
Iepsen UW, Jørgensen KJ, Ringbaek T, Hansen H, Skrubbeltrang C, Lange P. A Systematic Review of Resistance Training Versus Endurance Training in COPD. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2015 Jun;35(3):163–72.
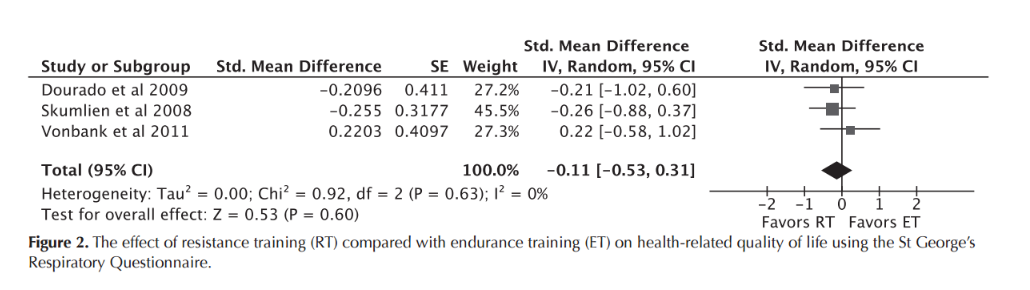
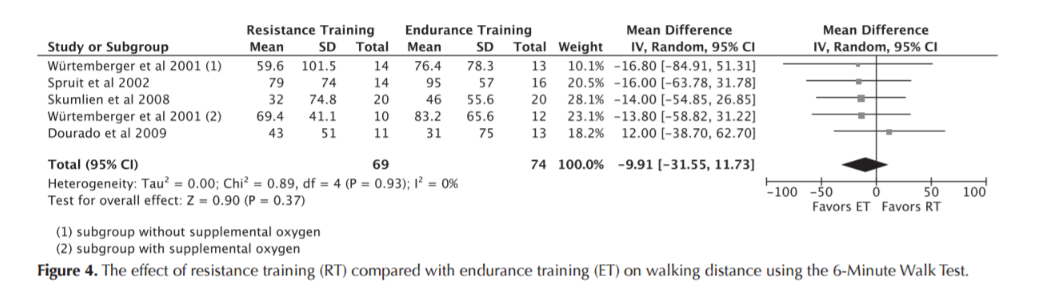
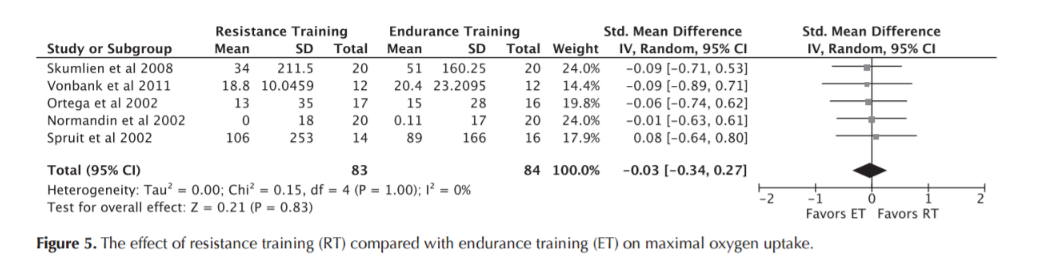
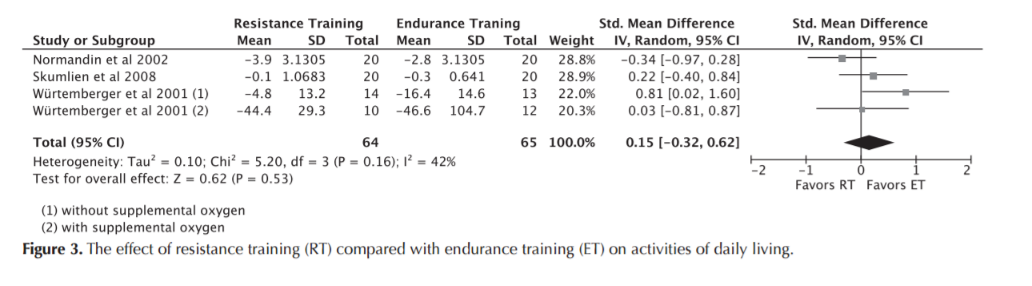
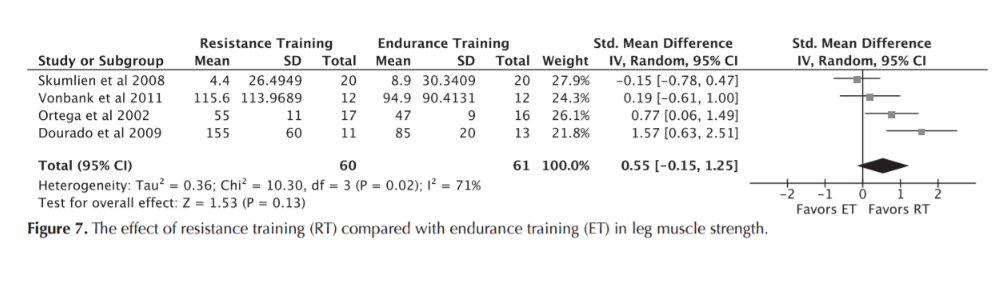
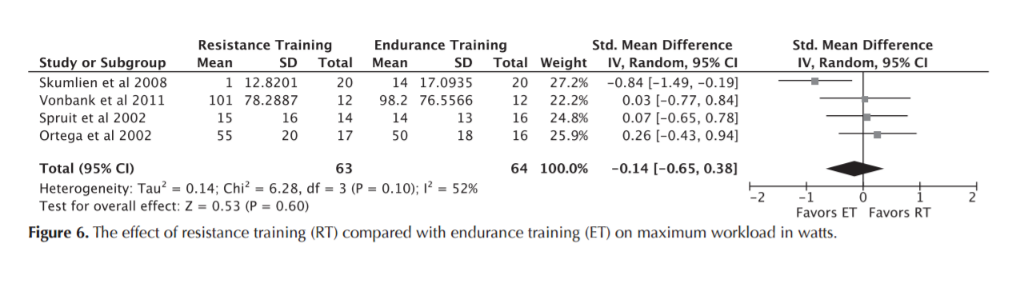
Resistance Training
RT versus AET
St George
6MWT
Max O2 uptake
daily activities
max Workload
leg muscle strength
Iepsen UW, Jørgensen KJ, Ringbaek T, Hansen H, Skrubbeltrang C, Lange P. A Systematic Review of Resistance Training Versus Endurance Training in COPD. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2015 Jun;35(3):163–72.
↔
RT
AET
↔
AET
↔
| n | Frequency | RT | AET | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troosters et al.(2000) | 70 COPD 37 RT and 33 controls |
3/wk for 24 weeks |
RT: 60% 1RM Dose: 9 S/MG/W |
AET: 60–80% WRpeak | ↔FEV1 |
| Skumlien et al. (2007) | 60 COPD 40 RT and 20 controls |
3/wk for 4 weeks |
RT: 5 exercises Intensity: 10–15RM Dose: 6–9 S/MG/W |
AET: 64–83% WRpeak Dose: 90 min/week |
↑FVC ↑FEV1 ↑VEpeak ↔IC |
Mixed Training
RT + AET versus Control
S/MG/W: maximum sets per muscle group per week, WRpeak: maximum work rate, AET: aerobic endurance training, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, VEpeak: maximum minute ventilation, SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire, 6MWD: 6-min walk distance
Strasser B, Siebert U, Schobersberger W. Effects of resistance training on respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2013 Mar;17(1):217–26.
| n | Frequency | RT | AET | Outcome | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bernard et al. (1999) | 45 COPD 26 RT and 19 controls |
3/wk for 12 weeks |
RT: 4 exercises 60–80% 1RM Dose: 9 S/MG/W |
AET: 80% WRpeak Dose: 90 min/week |
↑ muscle strength and mass ↔ exercise capacity or quality of life |
| Mador et al. (2004) | 32 COPD 15 RT and 17 controls |
3/wk for 8 weeks |
RT: 4 exercises 60% 1RM Dose: 9 S/MG/W |
AET: 50% WRpeak Dose: 60 min/week |
↑VEpeak with combined RT+AET |
| Panton et al (2004) | 17 COPD 9 RT and 8 controls |
2 /wk for 12 weeks |
RT: 12 exercises Intensity: 10–15RM Dose: 6 S/MG/W |
AET: 50–70% HRR Dose: 60 min/week |
↓FEV1 with RT ↔FVC with RT |
| Pereira et al (2010) | 50 COPD 25 RT + AET 25 AET |
3/wk for 10 weeks |
RT: 5 exercises, 10 wk, 2 sets/6–12 reps, load of 50–70% 1RM | AET: , 60–70% of reserve heart rate, 30–60 min/session, cycle ergometer | ↑SGRQ with RT ↑SF-36 with RT |
| Phillips et al (2006) | RT + AET: 10 AET: 9 |
2/wk for 8 weeks |
RT: 5 exercises, 50% 1RM, increased by 5%–10% as tolerated when 10 repetitions of an exercise were successful completed |
AET: 3 MET, 20–40 min/session, Monark arm ergometer and motor-driven treadmill |
↑Muscle strength with RT ↑functional fitness with RT |
Mixed Training
RT + AET versus AET
S/MG/W: maximum sets per muscle group per week, WRpeak: maximum work rate, AET: aerobic endurance training, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, VEpeak: maximum minute ventilation, SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire, 6MWD: 6-min walk distance
Strasser B, Siebert U, Schobersberger W. Effects of resistance training on respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2013 Mar;17(1):217–26. / Liao W-H, Chen J-W, Chen X, Lin L, Yan H-Y, Zhou Y-Q, et al. Impact of Resistance Training in Subjects With COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir Care. 2015 Aug;60(8):1130–45.
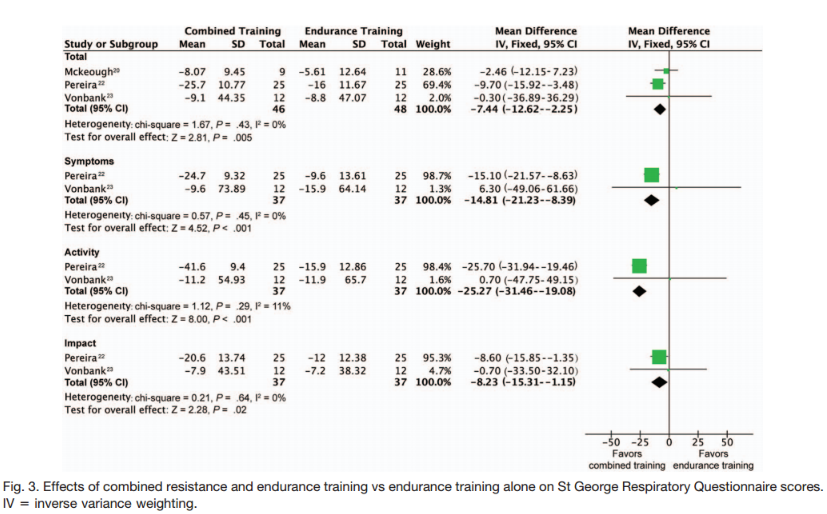
Mixed Training
RT + AET versus AET
St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire
Liao W-H, Chen J-W, Chen X, Lin L, Yan H-Y, Zhou Y-Q, et al. Impact of Resistance Training in Subjects With COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir Care. 2015 Aug;60(8):1130–45.
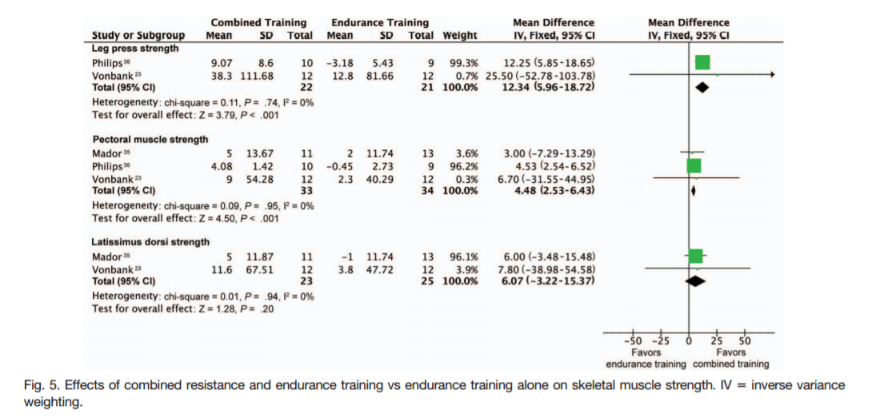
Mixed Training
RT + AET versus AET
Sceletal Muscle Strength
Liao W-H, Chen J-W, Chen X, Lin L, Yan H-Y, Zhou Y-Q, et al. Impact of Resistance Training in Subjects With COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir Care. 2015 Aug;60(8):1130–45.
COPD
By techangel
COPD
- 786



