C# Common Type System
Telerik Academy Alpha
Table of contents
Object, is, as, yield, ref, out
System.Object
C# Types
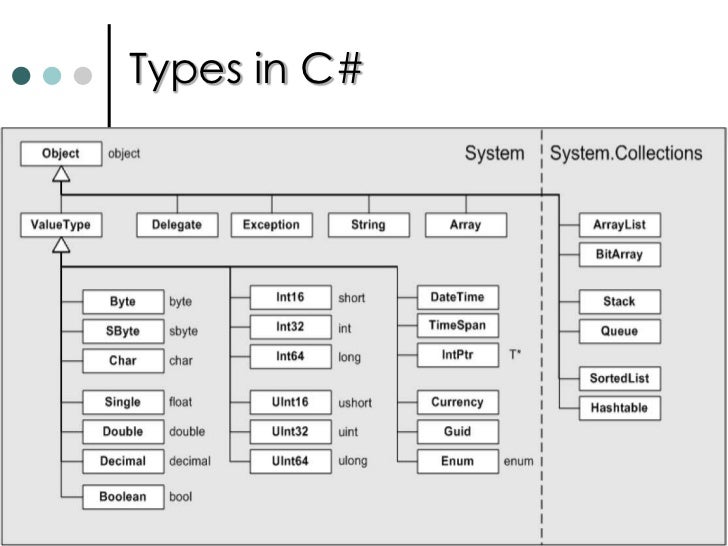
Object class
- Base class for each .NET type
- Inherited by default by all the types created
- Provides a few virtual methods which are useful for certain tasks
- Equals() - compare with other object
- ToString() - represents the object as a string
- GetHashCode() - provides this hash code for algorithms that need quick checks of object equality
- Finalize() - allows an object to try to free resources and perform other cleanup operations
Object class
- Provides protected method which can be used only inside class definition
- MemberwiseClone() - reates a shallow copy of the current object
- Provides two public methods
- static
- ReferenceEquals() - determines whether the specified object instances are the same instance
- instance
- GetType() - gets the type of the current instance.
- static
Override virtual methods
- By default the operator == calls the ReferenceEquals() method
- Compares the addresses for reference types
- Or the binary representation for value types
- The methods Equals(), GetHashCode() should be defined at the same time to be sure that the the two objects are going to be compared correctly
- The same applies for the operators == and !=
- You can override Equals() and use its implementation for == and !=
Type operators
is and as operators
- The is operator
- Checks if an object is an instance of some type
- Polymorphic operation
- 5 is Int
- 5 is object
- 5 is IComparable<int>
- The as operator
- Casts a reference type to another reference type
- Returns null value if it fails
- E.g. if the types are incompatible
Live Demo
Live Demo
yield return
yield return
- The yield return construct in C# simplifies the IEnumerator<T> implementations
- When a yield return statement is reached
- The expression is returned, and the current location in code is retained (for later use)
- When a yield return statement is reached
Populating a temporary list is like downloading the whole video, whereas using yield is like streaming that video.
If you have expensive operation you can stream the data, instead of waiting for the completion
yield return
- Run the example below in Visual Studio because it doesn't work as expected here
ref and out
Passing parameters
- Parameters can be passed in several ways to the methods:
-
in (default)
- Passing value for value types
- Passing heap address for reference types
-
out
- Passed by stack address for both value types and reference types
- The initialization can be done by the called method
-
in (default)
Passing parameters
- Parameters can be passed in several ways to the methods:
-
ref
- Passed by stack address for both value types and reference types
- Initialization can't be done by the called method – access is for read and write
-
ref
Passing parameters
Questions?
[C# OOP] Common Type System
By telerikacademy
[C# OOP] Common Type System
- 1,620



