Methods (Functions)
Telerik Academy Alpha
Table of contents
What are methods?
What are methods?
-
A method is a kind of building block that solves a small problem
-
The Main() you are using to execute your app is a method
-
Also known as functions, procedures, etc.
Declare method
static void PrintLogo() // PrintLogo is the method's name
{
Console.WriteLine("Telerik Academy");
Console.WriteLine("https://telerikacademy.com");
}-
PrintLogo is the method name
-
void is the return type of the method
-
static will be explained in later lectures
-
between { and } is the method body
Declare method
-
When you see something called with () in C# it is a method
-
Methods in C# (Java) could not exist without a class
// class definition
class Program
{
// method definition
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
}Declare method
// class definition
class Program
{
// method definition
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
}-
There must be only one Main() method in a program
-
It is the entry point of your program
Methods Demystified
You have already used them
string myText = "Pesho is attending Alpha every day.";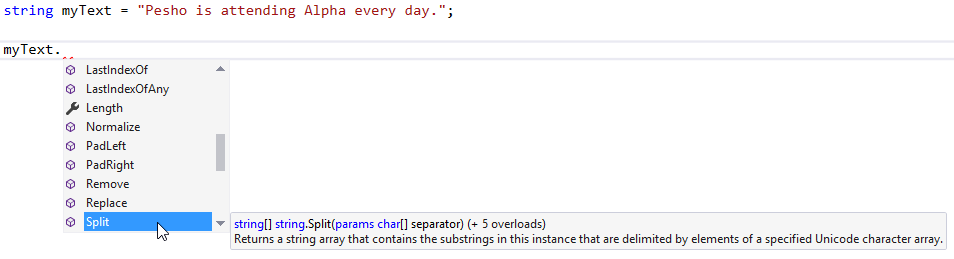
-
All the blue boxes are methods (functions) of the class String
-
The wrench icon means it is a property
-
Properties are just like methods (later in the lectures)
-
Methods parameters
-
Methods could have parameters or not
-
Parameters are passed and the method could use them
-
// Method without parameter
static void PrintMessage()
{
Console.WriteLine("Telerik Academy");
}
// Method WITH parameter
static void PrintMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}Methods parameters
-
There could be many parameters
-
Every parameter should have type and a name
-
// Method with one parameter
static void PrintMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
// Method with two parameters
static void PrintMessage(string message, int number)
{
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}Calling methods
-
Call the method and pass parameters (if any)
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
PrintMessage();
PrintMessage("Telerik Academy passed as parameter");
}
static void PrintMessage()
{
Console.WriteLine("Telerik Academy");
}
static void PrintMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}Methods overloading
-
NOTE: These two methods could exist simultaneously
-
This is called method overloading
-
// Method with one parameter
static void PrintMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
// Method with two parameters
static void PrintMessage(string message, int number)
{
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}Methods overloading
-
There could be multiple methods with the same name
-
but they have to receive different number and/or types of parameters
-
// Method with one parameter
static void PrintMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
// Method with one parameter but the same type
static void PrintMessage(string msg)
{
Console.WriteLine(msg);
}
The same parameter type and number of parameters.
It doesn't matter if the name is different.
Methods overloading
-
There could be multiple methods with the same name
-
but they have to receive different number and/or types of parameters
-
// Method with one parameter
static void PrintSomething(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
// Method with one parameter but from different type
static void PrintSomething(int number)
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}Methods parameters (optional)
-
Some parameters can be declared optional
-
that happens when you set them a default value
-
only the last parameters can be optional
-
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
PrintMessage(); // This will print Telerik Academy
PrintMessage("Hello"); // This will print Hello
}
// Method with optional parameter
static void PrintMessage(string message = "Telerik Academy")
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
}Methods return type
-
Every method could return a value or not
-
void - the method does not return anything. It just makes something
-
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
PrintMessage(); // This will print Telerik Academy
}
static void PrintMessage()
{
Console.WriteLine("Telerik Academy");
}
}Methods return type
-
Every method could return a value or not
-
any type - the method must return object of that type
-
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string upperCaseMessage = UpperCaseLetters("Telerik Academy");
Console.WriteLine(upperCaseMessage); // prints TELERIK ACADEMY
}
// return type string
static string UpperCaseLetters(string message)
{
// ToUpper() is a method of the String class
return message.ToUpper();
}
}Methods return type
-
return keyword exits the method and returns a value
-
if the method is void the return keyword just exits the method
-
anything after return will not be executed
-
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
PrintMessage("TelerikAcademy");
}
static void PrintMessage(string message)
{
return; // anything below this line will not be executed
Console.WriteLine(message); // Unreachable code detected warning
}
}params keyword
-
params - you can specify a method parameter that takes a variable number of arguments
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
PrintMessage("TelerikAcademy", "test");
}
static void PrintMessage(params string[] arr)
{
foreach (var line in arr)
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
}
}params keyword
-
It could be comma-separated list of arguments of the type specified in the parameter declaration
-
It could be an array of arguments of the specified type
-
You also can send no arguments
-
params must be the last parameter passed to the method
Best Practices
Best practices
-
Each method should perform a
single, well-defined task
-
Method’s name should
describe that task
in a clear and non-ambiguous way
-
CalculatePrice(), ReadName()
-
Process(), PrintInfoAndRegisterUser()
-
CalculatePrice(), ReadName()
- In C# the methods are named using PascalCase
Questions?
[C#] Methods
By telerikacademy
[C#] Methods
- 1,165



