cyberattacks

-
What is cyberattacks?
-
Model OSI. Typical cyberattacks.
-
Session Layer. Attacks and methods of protection.
-
Presentation Layer. Attacks and methods of protection.
-
Application Layer. Attacks and methods of protection.
-
Examples.
AGENDA
A cyberattack is any malicious attempt to gain unauthorized access, disrupt, modify, destroy, or steal data or systems within a computer network using digital technology.
It can be:
Active: aimed at altering system resources or affecting their operation (e.g., DDoS, data modification).
Passive: aimed at unauthorized eavesdropping or information gathering without altering resources (e.g., network traffic sniffing, port scanning).
cyberattacks
Model OSI. Typical cyberattacks
Physical
Data Link
Network
Transport
Session
Presentation
Application
SQL Injection, XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), Phishing, Code vulnerabilities, DDoS
Man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM), Data manipulation
Session Hijacking, Sockets port attacks, Improper session termination
SYN Flood, Port Scanning
IP Spoofing, Attacks on routing protocols, MITM
ARP Spoofing, MAC Spoofing, MAC Flooding
Eavesdropping, Sabotage, Signal Jamming
- Session Hijacking - stealing a user's session identifier (token) to gain unauthorized access to their active session. XSS attacks are used to steal session cookies.
- Socket port attacks - attacker joining the connection and can send data that the server interprets as commands, leading to the execution of malicious code on the server). An attacker can intercept data.
Session Layer. Attacks.
- Secure Cookies - using cookie attributes such as Secure (for transmission only over HTTPS) and HttpOnly (to prevent access via JavaScript, protecting against XSS).
- Session Tokens - use of long, randomly generated and unpredictable session identifiers to prevent session hijacking.
- Session Time Limits - set reasonable session expiration times and force logout after a long period of inactivity.
Session Layer. methods of protection
This layer is protected through secure session management.
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) - is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker secretly inserts himself into the middle of a communication between two parties.
Presentation Layer. Attacks.
This level is protected through strong encryption.
Presentation Layer. methods of protection.
- use cryptographic protocol the latest TLS (Transport Layer Security) versions and strong encryption algorithms.
- using HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security)
- using VPN
- be careful with public Wi-Fi
- Injection - injecting malicious data that is executed as commands or database queries: SQL Injection (SQLi), Command Injection, LDAP Injection.
- XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) - injecting client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users to steal sessions or data.
- Broken Access Control - incorrect implementation of access rights, allowing a user to gain unauthorized access to data or functions (IDOR - Insecure Direct Object Reference).
- Incorrect Security Configuration - Open configuration files, use of weak HTTP headers.
- DDoS - destruction of a website or online service by overloading the target server, network resources, or software with a huge amount of traffic.
Application Layer. Attacks.
- Input Validation - all user data must be validated, sanitized and/or shielded.
- CSP (Content Security Policy) - it works as a "whitelist" of content sources that are allowed to load on a page.
- Secure Coding - adhering to secure development standards (e.g. OWASP guidelines) to eliminate logical vulnerabilities and access control errors.
- Web Application Firewall - inbound HTTP traffic filtering, blocking known attack patterns (such as XSS or SQLi) before they reach the application.
- Authentication and Authorization - using multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strict verification of access rights on the server (Broken Access Control).
-
DDoS - Rate Limiting, Blackholing.
Application Layer. methods of protection.
Developer tools -> Validation
Examples
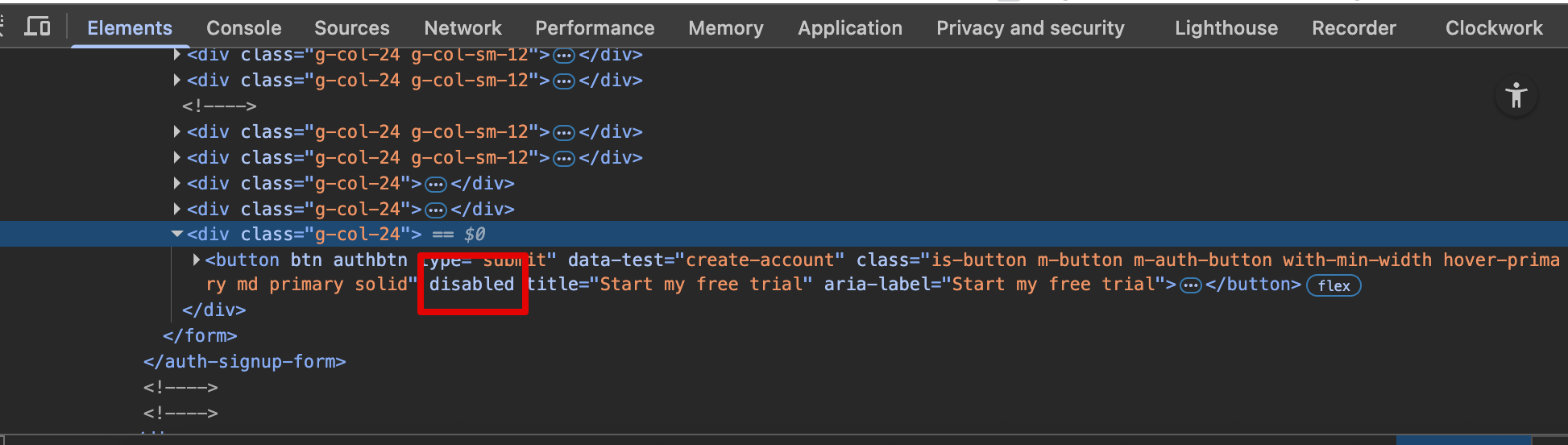
disabled, required, checked
XSS
Examples
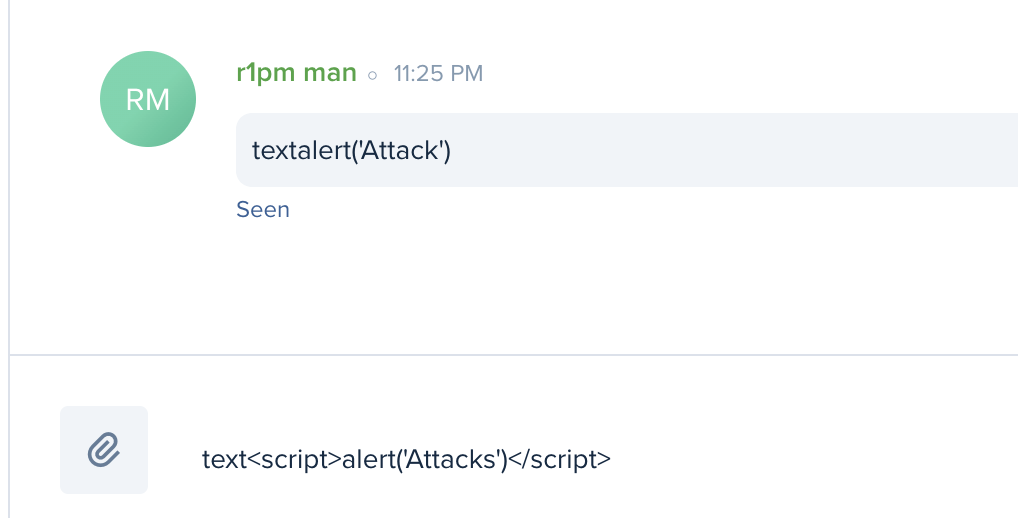
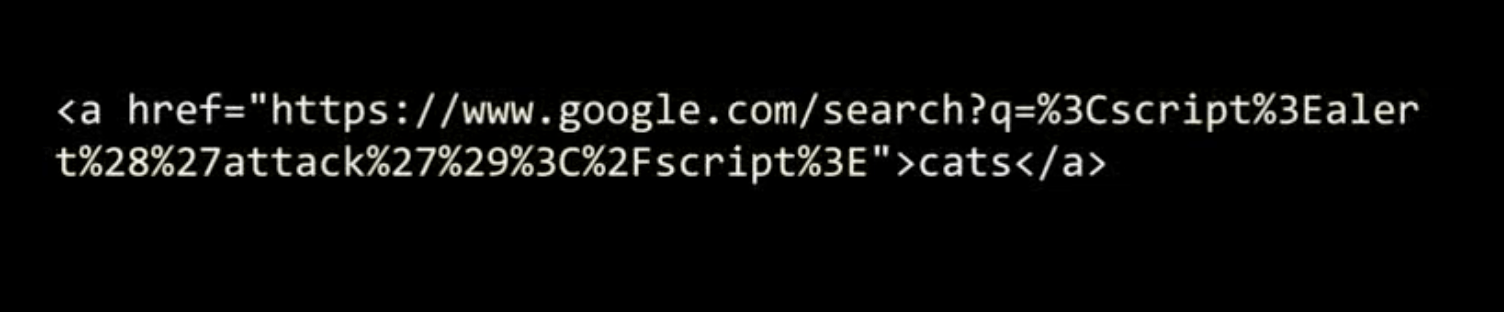
XSS -> Frame
Examples
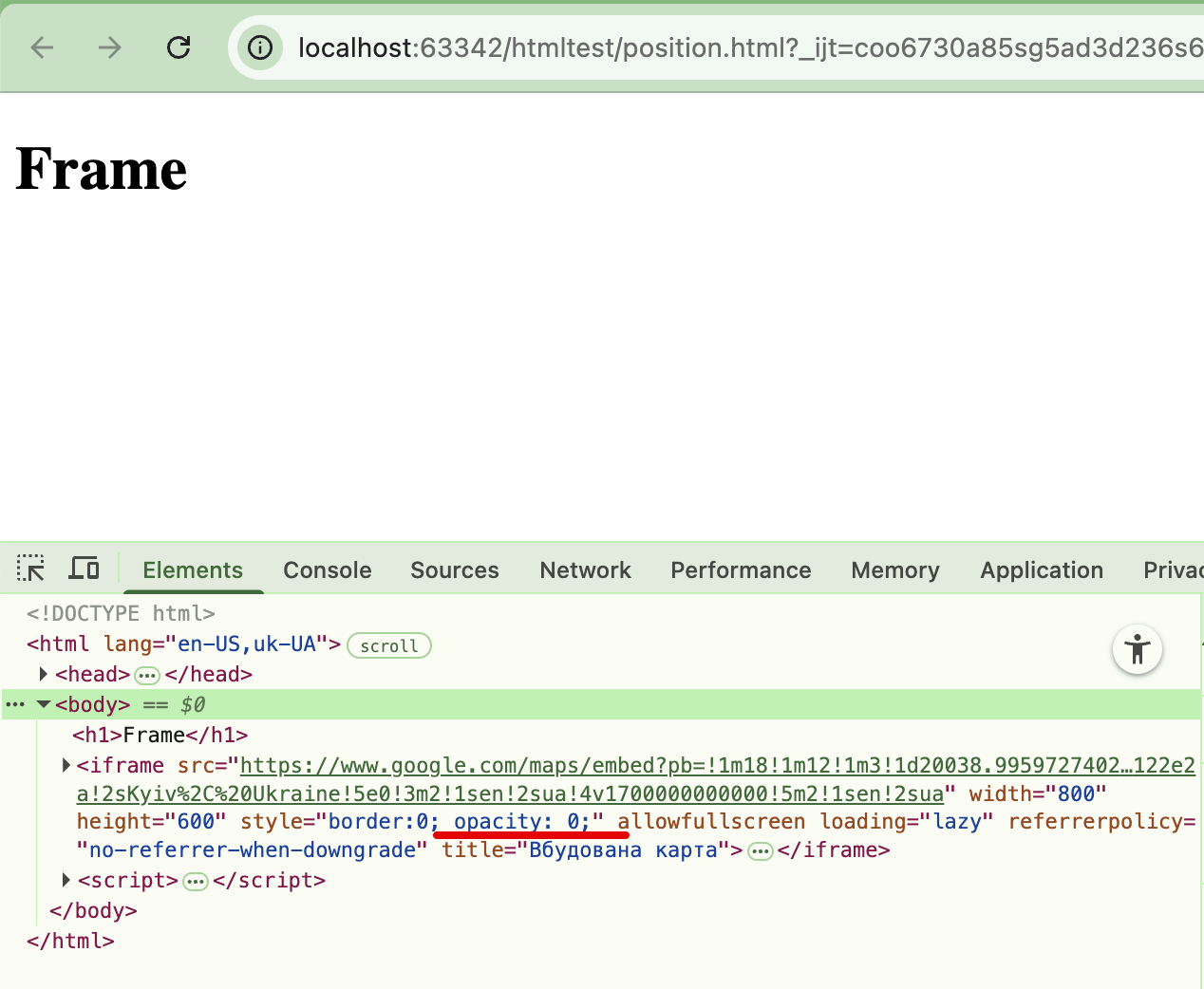
XSS
Examples

<scri<script type="text/javascript">pt>
document.write ('<table width="100%" border="1">');
for (i=1; i<6; i++)
{ document.writeln("<tr>"); for (j=1; j<6; j++)
document.write("<td>" + i + j + "<\/td>"); document.writeln("<\/tr>"); }
document.write ("<\/table> ");
</scri</script>pt>SQL injection
Examples
SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = '${email}';
r1pm@gmail.com'; DELETE FROM users; --
SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = 'r1pm@gmail.com'; DELETE FROM users; --';SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '${username}' AND password = '${password}';
' OR '1' = '1
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = 'ruslan' AND password = '' OR '1' = '1';SE/*comment*/LECT
SeLeCt
Fishing
Examples

Q/A
cyberattacks
By TenantCloud
cyberattacks
- 137



