Alpha & Beta Testing
Software Testing Lifecycle

What are Alpha and Beta Testing?
-
Both are acceptance testing techniques.
-
Used before product release.
-
Goal – gather user feedback and ensure product quality.

2
Alpha Testing
-
Conducted inside the company.
-
Performed by QA team and developers.
-
Uses synthetic scenarios + limited number of users.
-
Goal – detect bugs before the product reaches real users.

3

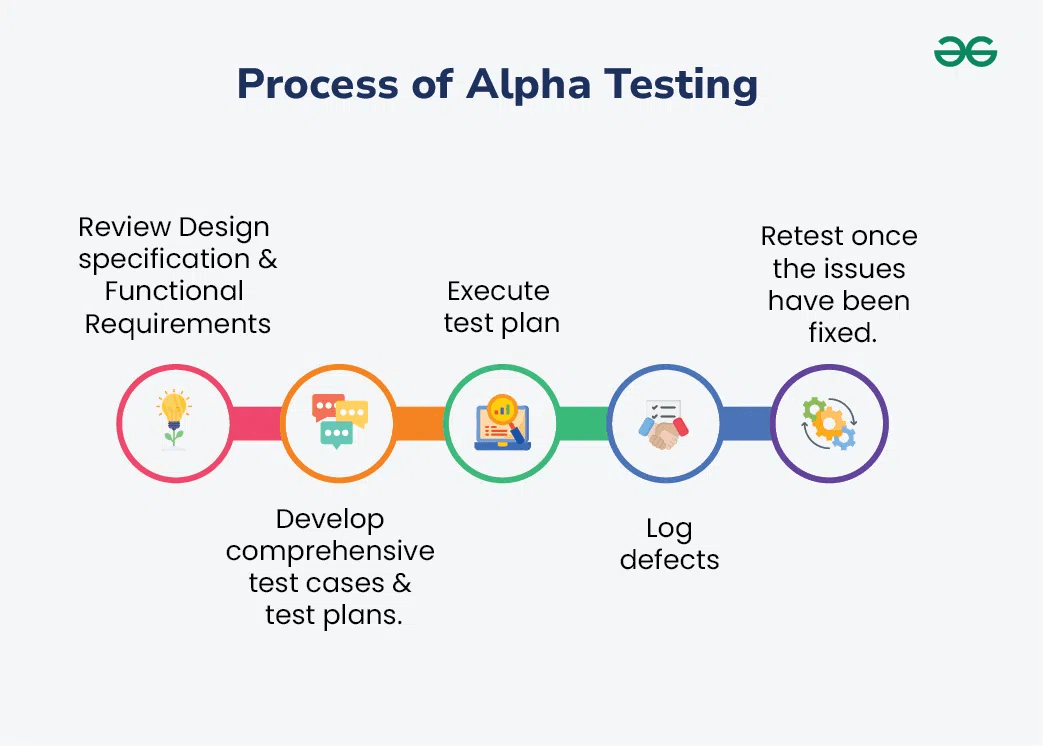
4


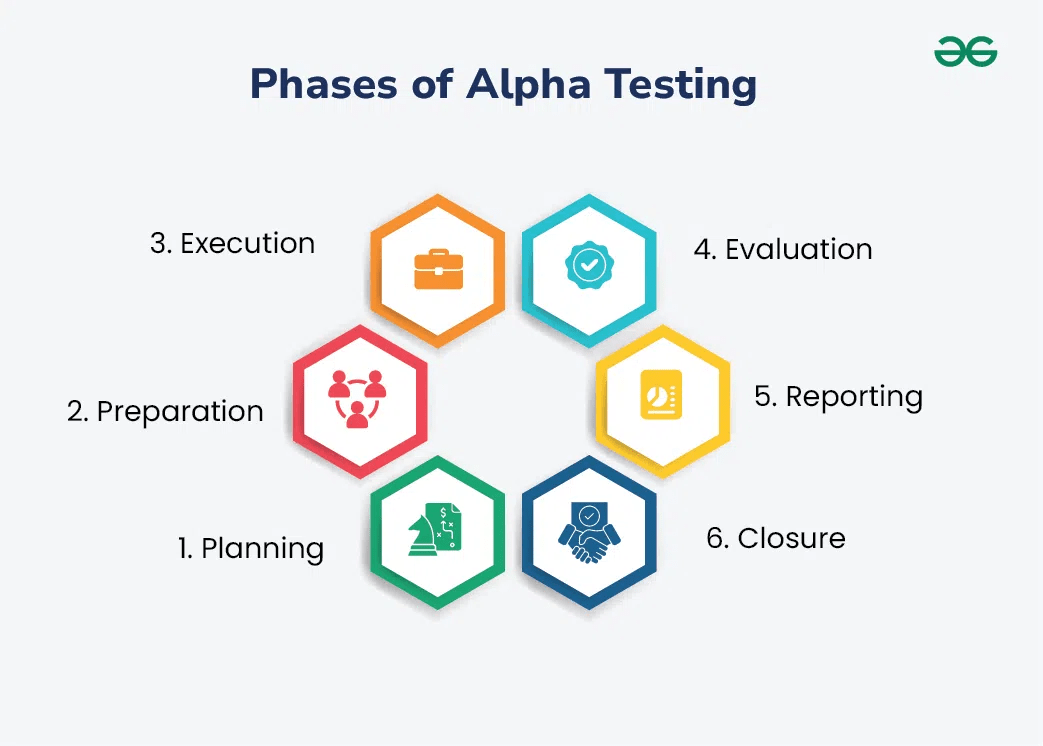
5
Key Points
-
Conducted by developers and testers in a local environment or test link.
-
The goal is to identify and fix bugs, defects, and usability issues before the product becomes publicly available.
-
User involvement is minimal — usually limited to people closely connected with the project, such as those who developed or previously tested the functionality.
-
The testing environment resembles the production one but remains controlled.

6
Beta Testing
-
Conducted by external users.
-
Executed in real-world (production-like) environment.
-
Goal – collect feedback from end-users.
-
Helps to verify if the product is ready for release.

7
Why Beta Testing is Important?
-
Identify issues missed during development.
-
Ensure the product meets expected standards.
-
Test functionality, speed, and responsiveness in real scenarios.
-
Gather insights on usability and features to improve overall experience.

8
Characteristics of Beta Testing
-
Conducted by clients or external users (not company employees).
-
Focus on reliability, security, and stability.
-
Usually applies Black Box Testing.
-
Performed at the user’s location.
-
No lab or dedicated test environment required.

9
Types of Beta Testing
-
Traditional Beta: Product released to target market; feedback collected to improve the product.
-
Public Beta: Product released worldwide via online channels; anyone can provide feedback (e.g., Windows 8 beta).
-
Technical Beta: Product tested internally by employees of the organization.
-
Focused Beta: Released to gather feedback on specific features or functionality.
-
Post-release Beta: Product released to market; feedback collected for future improvements.

10
Tools Used for Beta Testing
-
TestFairy – record user sessions and gather feedback.
-
CenterCode – manage beta programs and tester communities.
-
TryMyUI – usability testing with real users.
-
UserTesting – collect insights on user experience.
-
TestRail – organize and manage test cases.
-
Usersnap – capture in-app feedback and bug reports.
-
Zephyr – test management and reporting.
-
TestFlight – distribute iOS apps for beta testing.

11
Advantages of Beta Testing
-
Reduces product failure risk through customer validation.
-
Tests post-launch infrastructure in real conditions.
-
Improves product quality based on user feedback.
-
Cost-effective compared to other feedback methods.
-
Builds customer goodwill and increases satisfaction.

12
Disadvantages of Beta Testing
-
Hard to track errors as testing environments vary per user.
-
Possibility of duplicate bugs being reported.
-
Limited control over the real-time test environment.
-
Time-consuming due to involvement of real users, delaying overall feedback.
-
Testers need sufficient knowledge of the product; otherwise, testing may be ineffective.

13
Comparison

| Criterion | Alpha Testing 🧪 | Beta Testing 👥 |
|---|---|---|
| Performed by | QA + Dev team | Real users |
| Environment | Controlled | Production |
| Main goal | Find defects | Collect feedback |
| When performed | Before beta phase | Before release |
| Technique Used | White box and black box testing | Black-box testing |
| Execution | May require a long execution cycle | a few weeks |
Advantages

Alpha Testing:
✔ Bugs detected earlier
✔ Controlled environment
Beta Testing:
✔ Real user feedback
✔ Detects issues not visible in local testing
Conclusion

-
Alpha → internal testing, focused on bugs.
-
Beta → external testing, focused on user experience.
-
Together they ensure a high-quality release
Alpha & Beta Testing
By TenantCloud
Alpha & Beta Testing
- 131



