ME4262 Term Project

Application of RFID in manufacturing automation or logistics
Tan Guo Xiang
A0086024L
Introduction to RFID
Based on the principles of electromagnetic fields to transfer data.
Tags/Reader combination
Tags containing transmitters store electronic data about the object that it is attached on.
Reader reads the data stored on the tags by emitting a signal of a predetermined frequency.
Introduction to RFID (Continued)
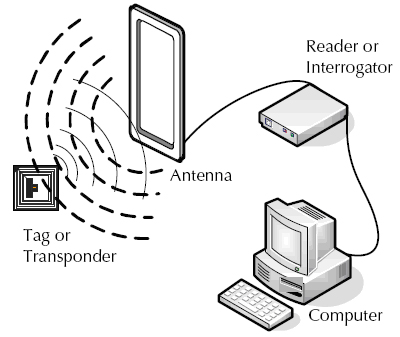
Source: http://www.epc-rfid.info/rfid
Advantages of RFID
No direct line of sight required between tags and readers
Low cost
Multiple tags can be read simultaneously
Long read range
Greatly reduces time spent manually scanning objects
Disadvantages of RFID
Does not work well with objects such as metal and liquid that may disrupt the electromagnetic field.
Not 100% reliable as the reader might miss tags due to disruptions in the radio waves.
Tags can be read by anyone with a reader. Not suitable for storing private or classified imn
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Case Study 1)
How Toyota uses RFID Tags in its paint shop process

Source: http://www.toyota.com
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
Toyota Platn in Derby England manufactures the Avensis and Corolla models.
Bodies entering the paint shop process from the weld shop can be of either models. Specifications of each body has to be known to meet the order's specification.
The read/write RFID tags are employed on the dollies which the bodies sit on. The tags contain specification about the body that it is carrying allowing it to be transfer to readers along the production line.
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
The data stored in the RFID tags can easily be transfer to another carrier if required. During the under body paint process where the body is lifted up by a carrier, the RFID tag on the dolly transfer the information to the carrier allowing continuous monitoring of each body.
The reverse happens when the body is returned to the dolly by the carrier.
The RFID tags used can withstand up to 216 Degree Celsius allowing the RFID tags to follow the body into the ovens to bake the paint.
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
The data stored in the RFID tags can easily be transfer to another carrier if required. During the under body paint process where the body is lifted up by a carrier, the RFID tag on the dolly transfer the information to the carrier allowing continuous monitoring of each body.
The reverse happens when the body is returned to the dolly by the carrier.
The RFID tags used can withstand up to 216 Degree Celsius allowing the RFID tags to follow the body into the ovens to bake the paint.
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
Tags storing the color and build specification of the body help to assist operators in ensuring that the body enters the right station during the top coat spray process.
Finally, the RFID tags help operators to schedule the bodies into the assembly line by reading the information stored on it.
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
Tags storing the color and build specification of the body help to assist operators in ensuring that the body enters the right station during the top coat spray process.
Finally, the RFID tags help operators to schedule the bodies into the assembly line by reading the information stored on it.
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Case Study 2)
How Toyota automated the delivery of parts and sub assemblies using a RFID based Traffic Control System.
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
Toyota Manufacturing in Kentucky Georgetown
Manufactures the Camry, Avalon and Venza models
500,000 vehicles a year with more than 1.8 million parts
Uses 22 automatic guided tuggers and automatic guide carts
Tuggers deliver raw material to stamping robots while the carts carry the parts along the production line
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
RFID tags carrying the coordinates of its location on the production floor are embedded in the floor throughout the production line.
The automatic guided carts are equipped with an RFID tag readers that reads the current coordinates and sends it to a central traffic control system.
The traffic control system monitors the location of all the carts in real time and is able to use the information to control and guide all the automatic units.
Applications of RFID in Automotive (Continued)
When two carts have paths that intercept, the traffic control system is able to determine that through the coordinates pick up from the RFID tags. The system then sends a command giving one cart the right of way in order to avoid any collision.
References
What is RFID? Retrieved from http://www.epc-rfid.info/rfid.
Radio Frequency Identification. Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio-frequency_identification.
RFID applications in manufacturing. Retrieved from http://mmt-inst.com/RFID%20applications%20in%20manufacturing%20_Draft%207_.pdf.
Beyond the tag: Finding RFID value in manufacturing. Retrieved from http://www.reliableplant.com/Read/8161/tag-rfid-manufacturing.
RFID in Toyota's paint shop process. Retrieved from http://www.x-check.co.uk/toyota.php.
How Toyota automated the delivery of parts and subassemblies. (October 01, 2012). Retrieved from http://www.mmh.com/article/how_toyota_automated_the_delivery_of_parts_and_subassemblies.
ME4262 Term Paper
By tgxworld
ME4262 Term Paper
- 1,979



