Link Cut Tree
LCT 能做什麼?
動態樹問題
給你一座森林
然後加邊、刪邊
過程保證是森林
可能會有一些詢問
LCT 可以做到每次操作均攤 \(O(logN)\)
各種樹上問題
樹鏈剖分能解決的 LCT 也能做,而且通常比較不需要思考,寫起來也比較簡單(?
大概就跟看到區間問題無腦亂砸線段樹差不多
Splay
一種平衡二元樹
他可以轉
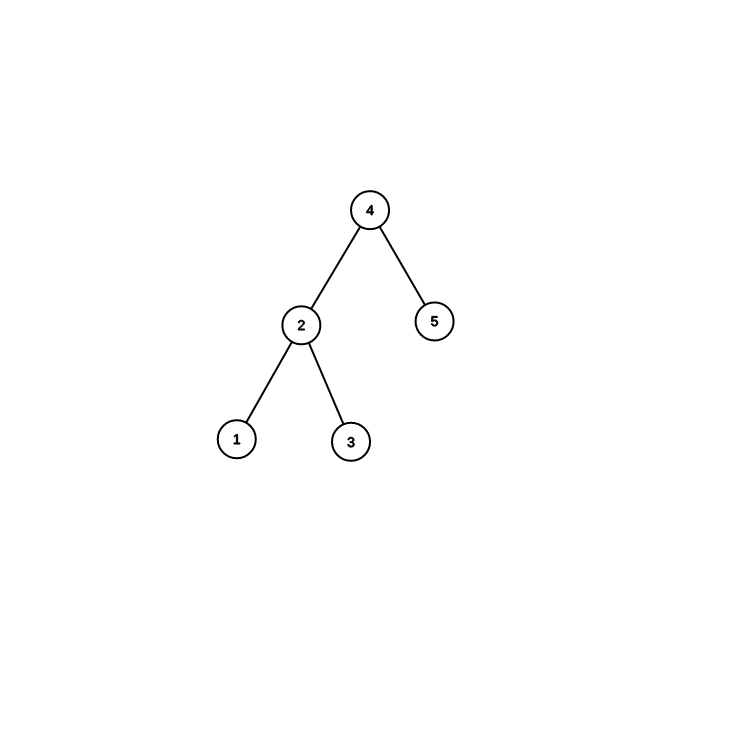
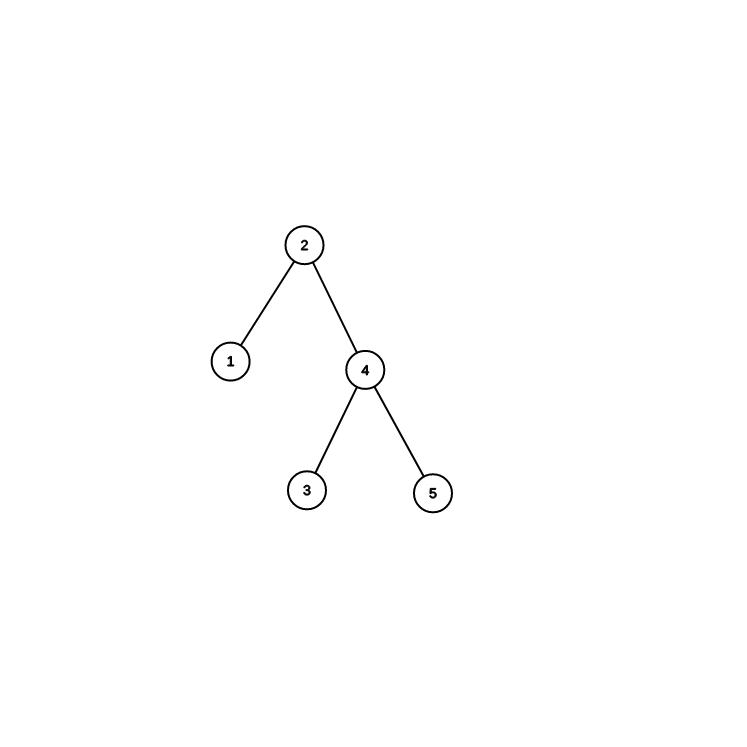
轉動 : 把自己的深度變淺1,同時維持中序遍歷順序不變
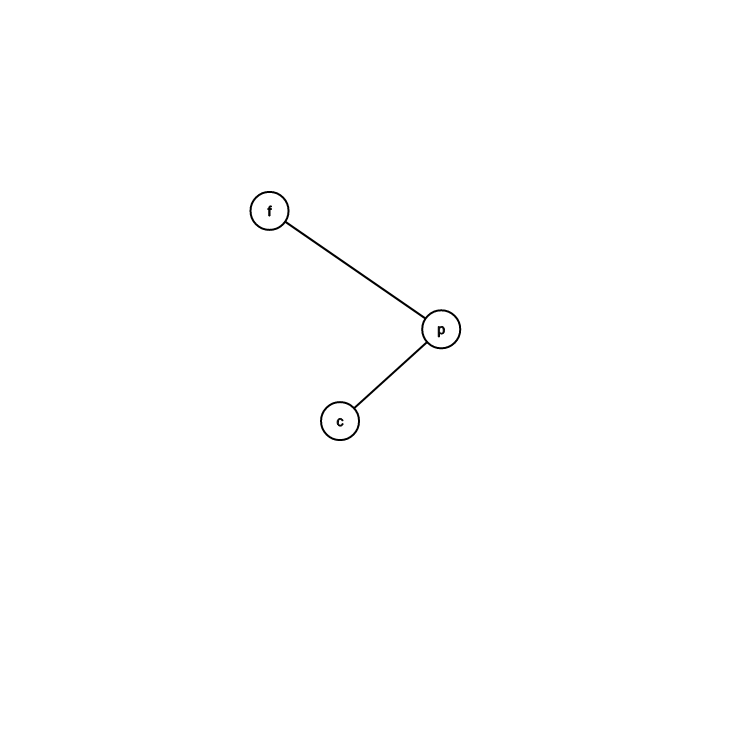
轉法
目前位置是 \(p\)
假設 \(p\) 是左兒子
\(f\) 是 \(p\) 的爸爸
\(c\) 是 \(p\) 的右兒子
\(p\) 的爸爸變 \(f\) 的爸爸
\(f\) 成為 \(p\) 的右兒子
\(c\) 變成 \(f\) 的左兒子
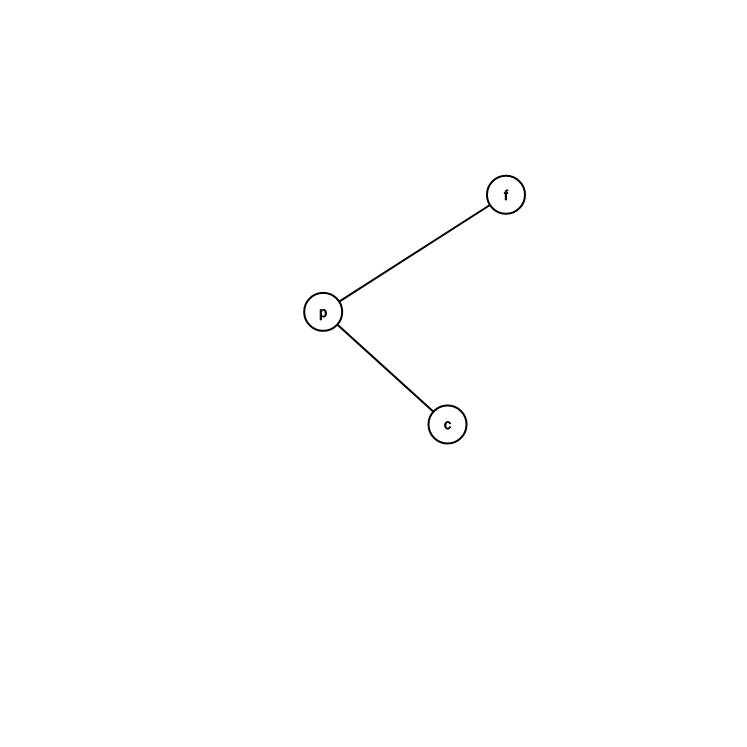
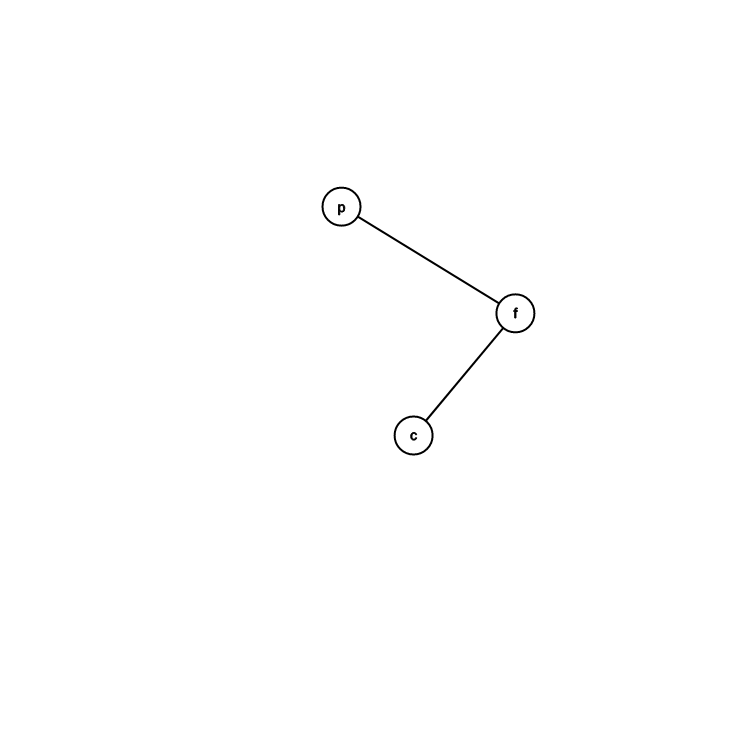
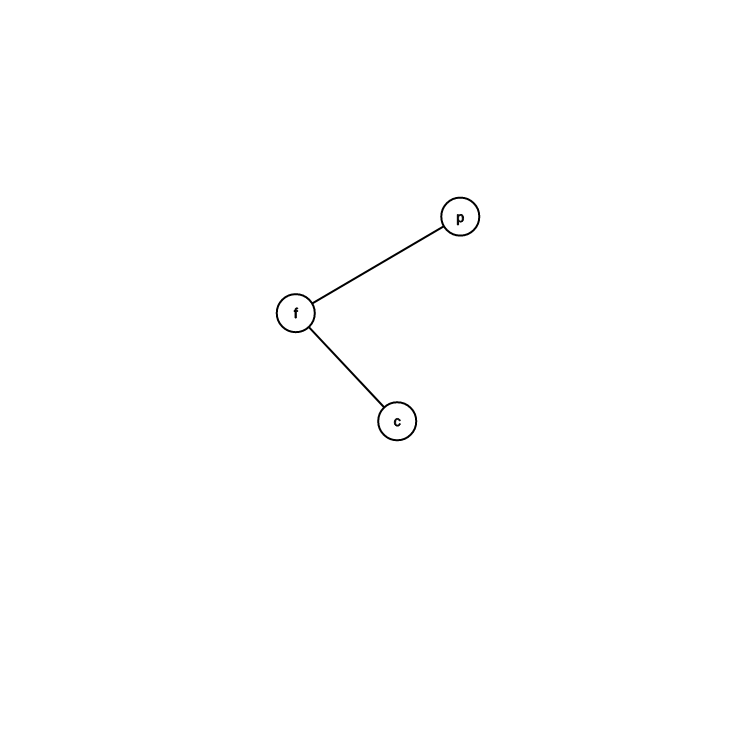
轉法
目前位置是 \(p\)
假設 \(p\) 是右兒子
\(f\) 是 \(p\) 的爸爸
\(c\) 是 \(p\) 的左兒子
\(p\) 的爸爸變 \(f\) 的爸爸
\(f\) 成為 \(p\) 的左兒子
\(c\) 變成 \(f\) 的右兒子
扣可能長這樣吧
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
array<int, 100004> S, F;
array<array<int, 2>, 100004> C;
void pull(int p){
S[p] = S[lc] + S[rc] + 1;
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(F[f]) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}Splay
把一個點轉到變成根
爆搜所有情況
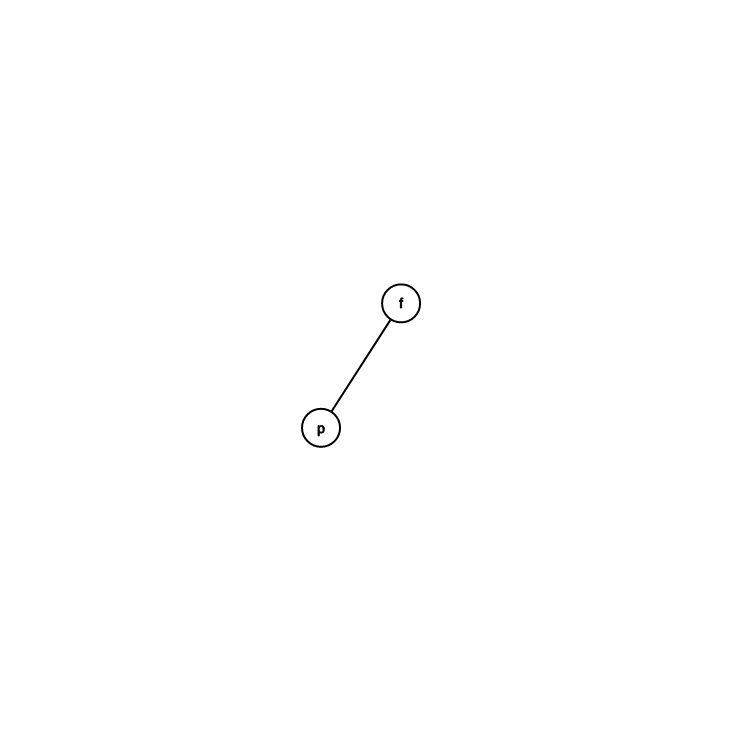
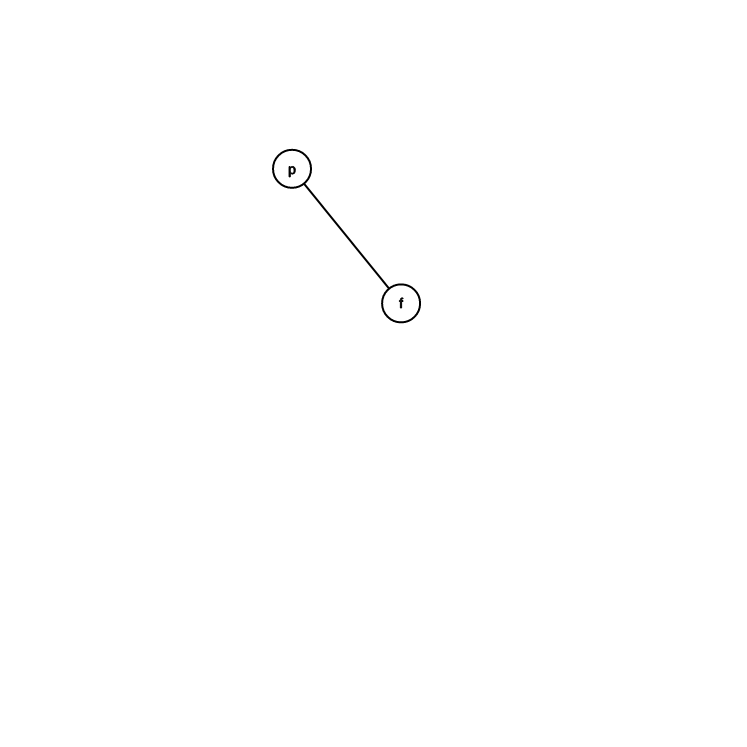
轉 \(p\)
爸爸就是根
爆搜所有情況
跟爸爸同邊
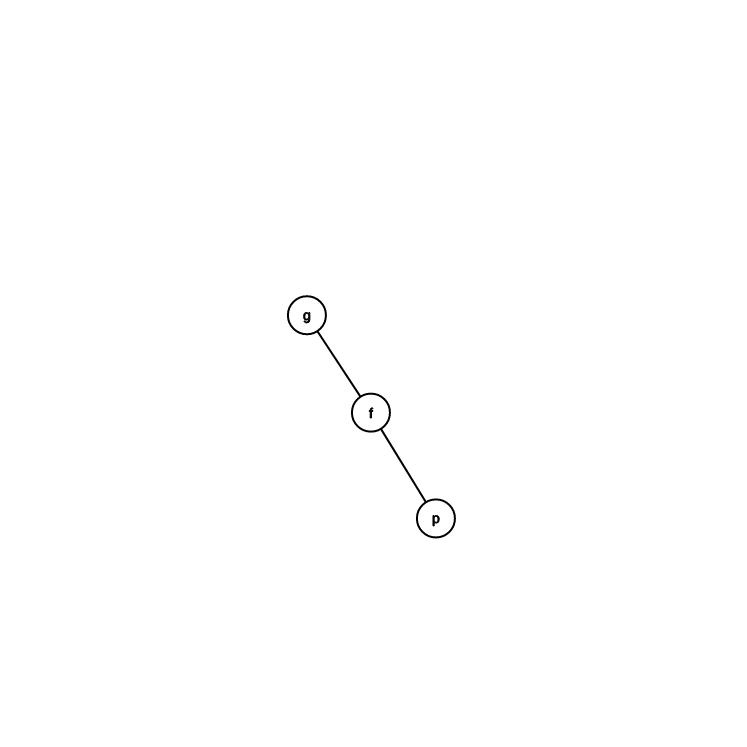
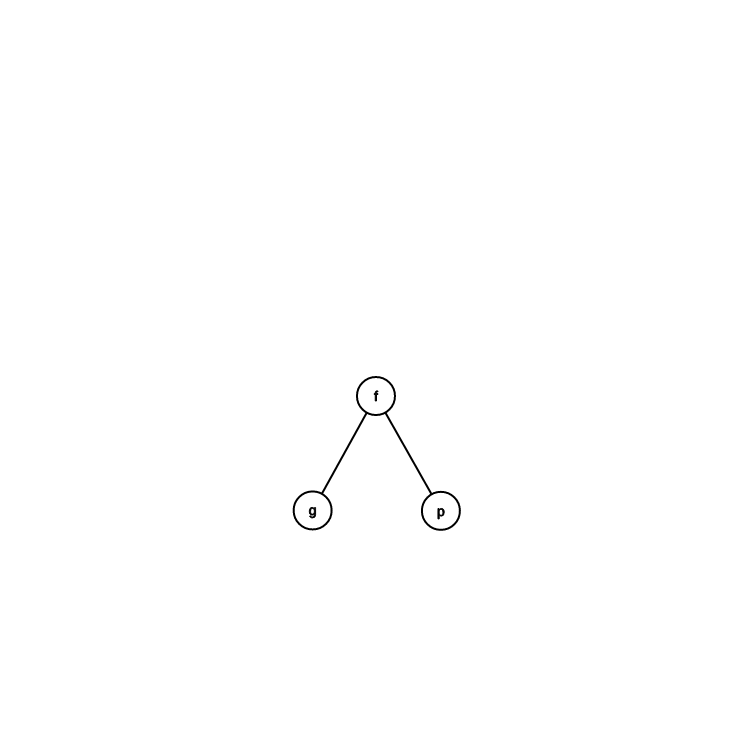
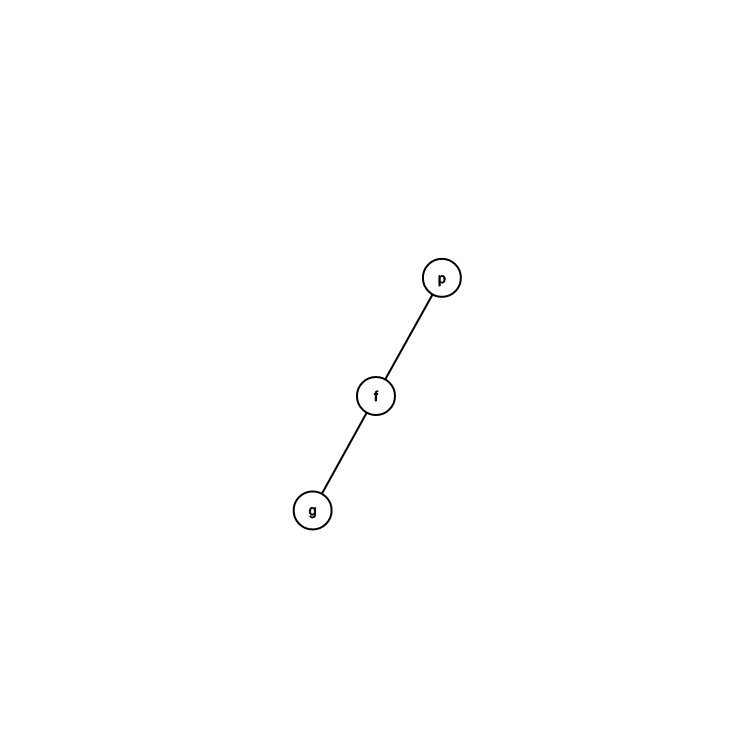
轉 \(f\)
轉 \(p\)
爆搜所有情況
跟爸爸不同邊
轉 \(p\)
轉 \(p\)
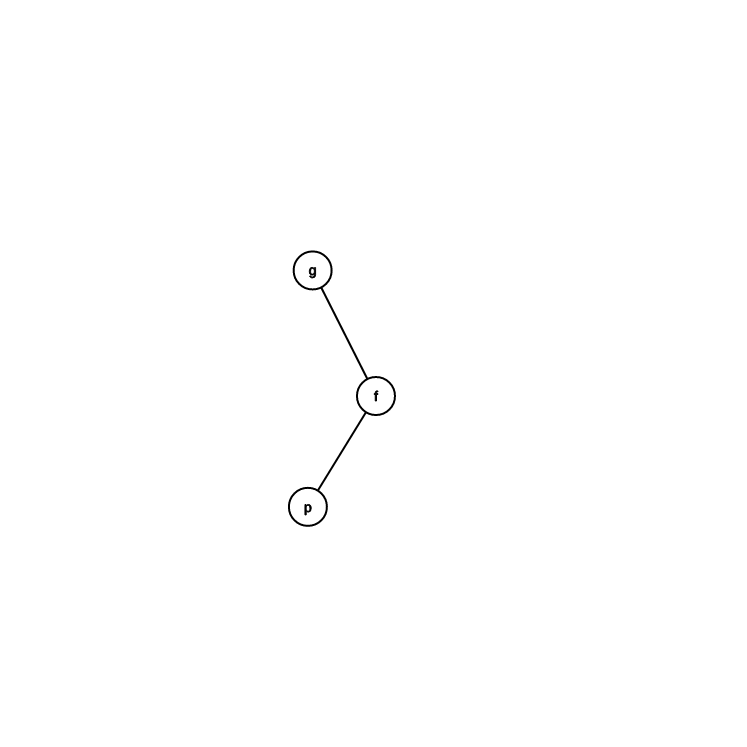
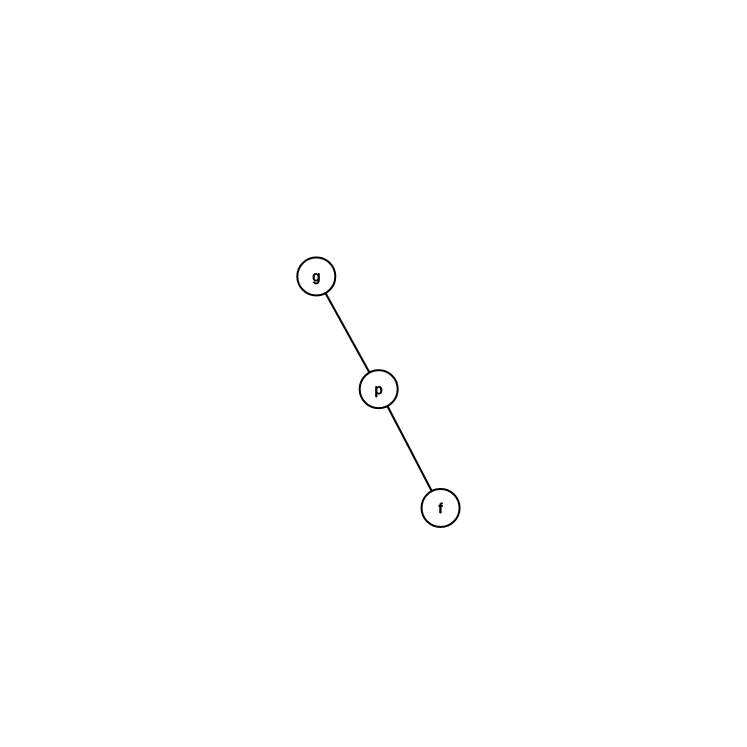
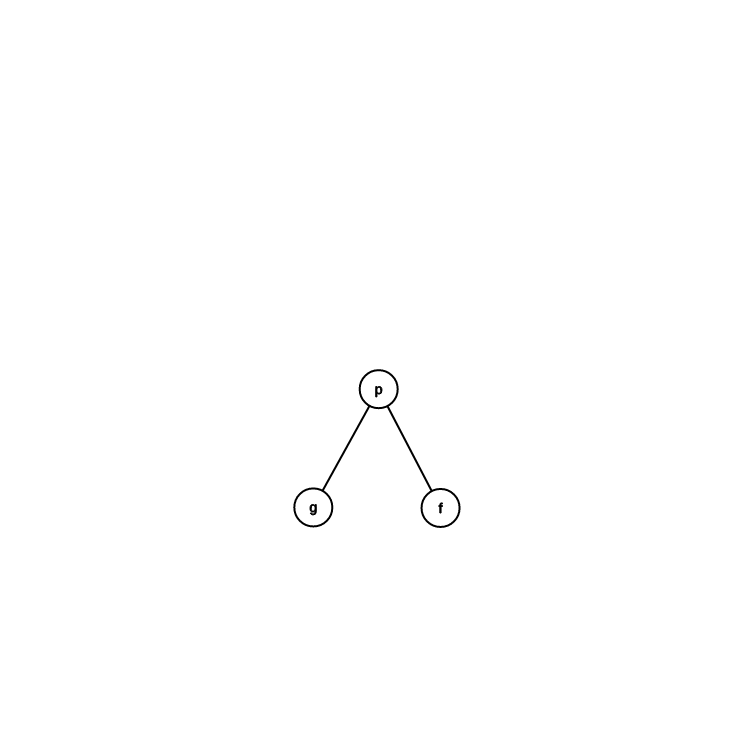
關於他的扣
void splay(int p){
for(int f = F[p]; f; turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(F[f]) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}Splay 的功能
rank(p) : 查 p 在 splay 的中序遍歷中排第幾
find(p, k) : 查 p 所在 splay 中 rank 第 k 的編號
merge(u, v) : 把 u 和 v 兩點所在的兩棵 splay 合併
split(p, k) : 把 p 所在的 splay 從 k 和 k + 1 中間砍斷
相信學過 treap 的大家應該都對這些東西不陌生
然後這4個東西都不會在 LCT 用到
扣
int rank(int p){
splay(p);
return S[lc] + 1;
}
int find(int p, int k){
splay(p);
while(k){
if(k > S[lc] + 1) k -= S[lc] + 1, p = rc;
else if(k <= S[lc]) p = lc;
else return p;
}
return 0;
}
void merge(int u, int v){
if(!S[u] || !S[v] || find(u, 1) == find(v, 1)) return;
u = find(u, S[u]), v = find(v, 1);
splay(u), splay(v);
C[u][1] = v, F[v] = u;
pull(u);
}
void split(int p, int k){
if(!k || !S[p]) return;
p = find(p, k), splay(p);
F[rc] = 0, rc = 0;
pull(p);
}複雜度
可以用勢能證明 splay 的均攤時間是 \(O(logN)\)
勢能證明
有一個通靈出來的勢能函數 \(\phi(x) = log(|x|(x\) 子樹大小\())\)
均攤複雜度 \(=\) 實際複雜度 \(+\) 總勢能變化
splay 複雜度 \(= \ h(x\) 深度\()\) \(+ \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{t(turn次數)}{\phi(p_i) - \phi(p_{i - 1})}\)
\( = h + \phi(p_t) - \phi(p_0)\)
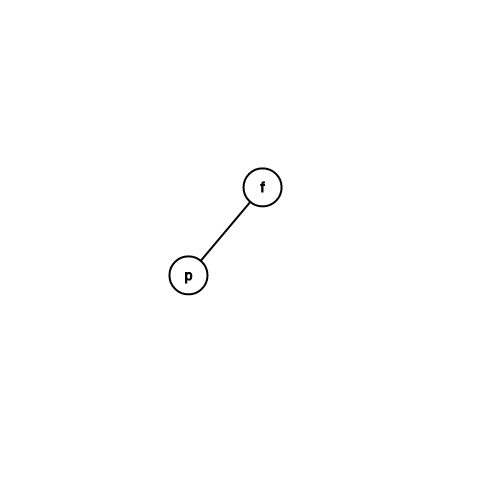
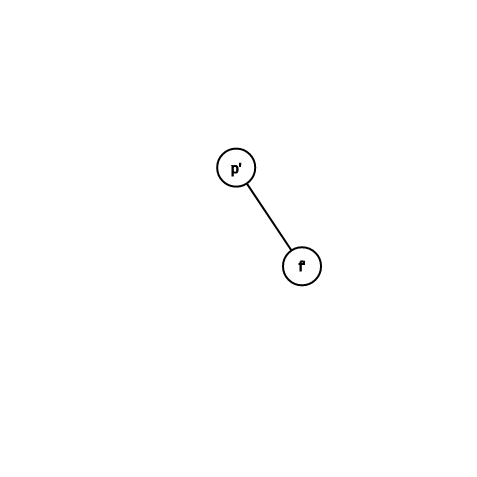
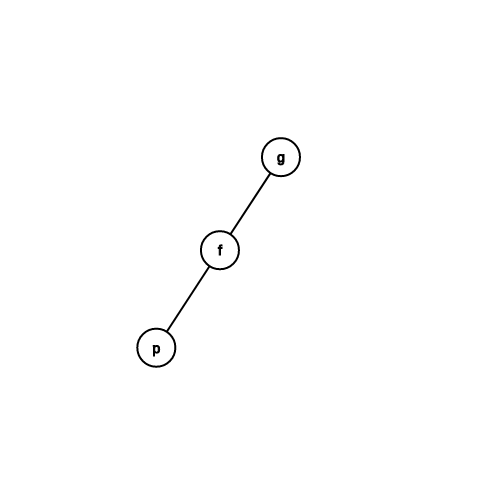
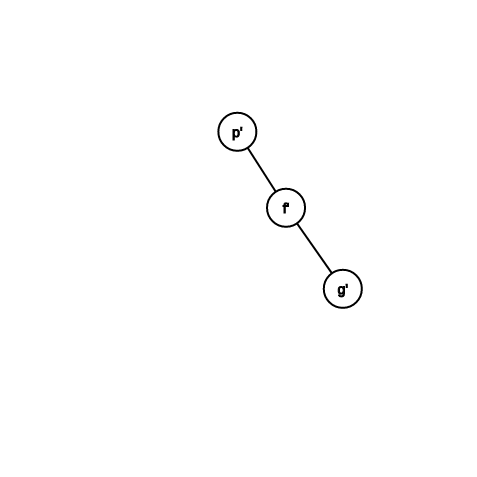
\(1(\)實際時間\() + \phi(p') + \phi(f') - \phi(p) - \phi(f) \\ = 1 + \phi(f') - \phi(p) \ (\phi(f) = \phi(p')) \\ \le 1 + \phi(p') - \phi(p) \ (\phi(f') \le \phi(p'))\)
\(2(\)實際時間\() + \phi(p') + \phi(f') + \phi(g') - \phi(p) - \phi(f) - \phi(g) \\ = 2 + \phi(f') + \phi(g') - \phi(p) - \phi(f) \ (\phi(g) = \phi(p')) \\ \le 2 + \phi(p') + \phi(g') - 2\phi(p) \ (\phi(f') \le \phi(p'), \phi(f) \ge \phi(p)) \\ \le 3\phi(p') - 3\phi(p) \ (log\frac{|g'| + |p|}{2} \ge \frac{log|g'| + log|p|}{2}) \\ \le 3(\phi(p') - \phi(p)))\)
\(2(\)實際時間\() + \phi(p') + \phi(f') + \phi(g') - \phi(p) - \phi(f) - \phi(g) \\ = 2 + \phi(f') + \phi(g') - \phi(p) - \phi(f) \ (\phi(g) = \phi(p')) \\ \le 2 + \phi(f') + \phi(g') - 2\phi(p) \ (\phi(f) \ge \phi(p)) \\ \le 2\phi(p') - 2\phi(p) \ (log\frac{|f'| + |g'|}{2} \ge \frac{log|f'| + log|g'|}{2}) \\ \le 2(\phi(p') - \phi(p))\)
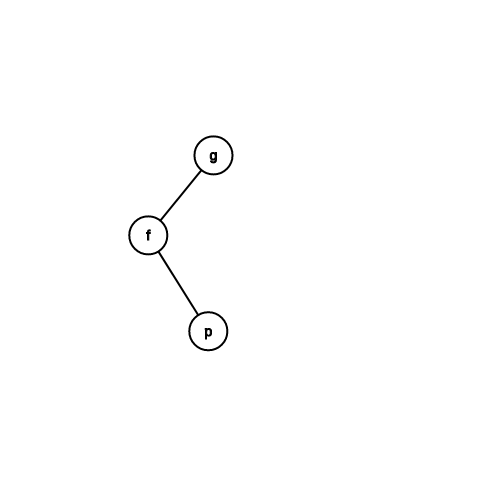
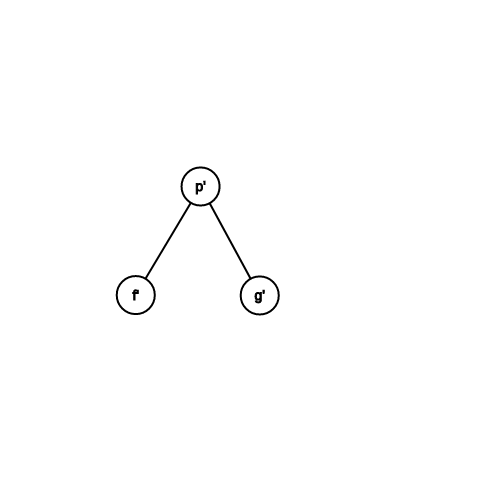
splay 複雜度 \(\le 3(\phi(p_t) - \phi(p_0)) + 1 \\ \le 3logN + 1 \ (\phi(p_t) = logN) \\ \implies O(logN)\)
一棵翻轉懶標 splay
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
array<int, 100004> S, F, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 100004> C;
void pull(int p){
S[p] = S[lc] + S[rc] + 1;
}
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(F[f]) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(F[p]) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; f; turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(F[f]) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}
int rank(int p){
splay(p);
return S[lc] + 1;
}
int find(int p, int k){
splay(p);
while(k){
push(p);
if(k > S[lc] + 1) k -= S[lc] + 1, p = rc;
else if(k <= S[lc]) p = lc;
else return p;
}
return 0;
}
void merge(int u, int v){
if(!S[u] || !S[v] || find(u, 1) == find(v, 1)) return;
u = find(u, S[u]), v = find(v, 1);
splay(u), splay(v);
C[u][1] = v, F[v] = u;
pull(u);
}
void split(int p, int k){
if(!k || !S[p]) return;
p = find(p, k), splay(p);
F[rc] = 0, rc = 0;
pull(p);
}一點小練習
扣
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
array<int, 130004> S, F, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 130004> C;
void pull(int p){
S[p] = S[lc] + S[rc] + 1;
}
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(F[f]) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(F[p]) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; f; turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(F[f]) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}
int find(int p, int k){
splay(p);
while(k){
push(p);
if(k > S[lc] + 1) k -= S[lc] + 1, p = rc;
else if(k <= S[lc]) p = lc;
else return p;
}
return 0;
}
void merge(int u, int v){
if(!S[u] || !S[v] || find(u, 1) == find(v, 1)) return;
u = find(u, S[u]), v = find(v, 1);
splay(u), splay(v);
C[u][1] = v, F[v] = u;
pull(u);
}
void split(int p, int k){
if(!k || !S[p]) return;
p = find(p, k), splay(p);
F[rc] = 0, rc = 0;
pull(p);
}
void build(int l, int r, int f){
if(l > r) return;
int p = (l + r) >> 1;
F[p] = f, C[f][p > f] = p;
build(l, p - 1, p), build(p + 1, r, p);
pull(p);
}
void print(int p){
if(!p) return;
push(p);
print(lc), cout << p << " ", print(rc);
}
signed main(){
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int n, q, l1, r1, l2, r2, a, b, c, d, e;
string t;
cin >> n >> q;
build(1, n, 0);
C[0][1] = 0;
while(q--){
cin >> t >> l1 >> r1;
if(t == "REV"){
a = find(1, l1 - 1), b = find(1, l1), c = find(1, r1 + 1);
split(b, r1), split(b, l1 - 1);
splay(b), rev[b] ^= 1;
merge(a, b), merge(b, c);
}else{
cin >> l2 >> r2;
a = find(1, l1 - 1), b = find(1, l1), c = find(1, r1 + 1), d = find(1, l2), e = find(1, r2 + 1);
split(b, r2), split(b, l2 - 1), split(b, r1), split(b, l1 - 1);
merge(a, d), merge(d, c), merge(c, b), merge(b, e);
}
}
splay(1), print(1), cout << "\n";
return 0;
}LCT
用平衡二元樹表示一棵樹
其實跟樹鏈剖分的鏈用 線段樹/treap 差不多
實鏈剖分
回顧樹鏈剖分
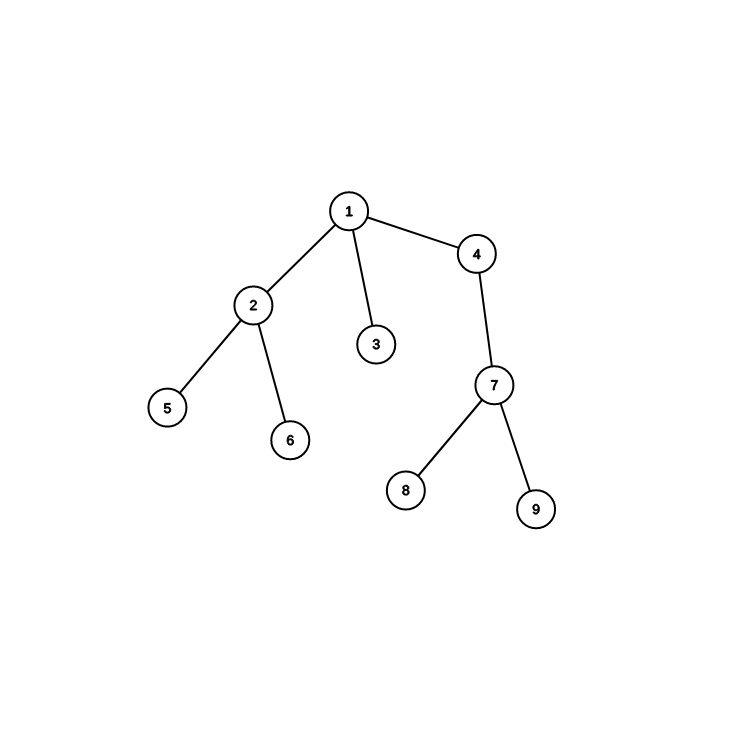
輕 重
實鏈剖分

虛 實
每個點隨便選一條往下的邊當實邊
每一條實鏈都砸一棵平衡二元樹
於是我們砸了 splay
一棵樹
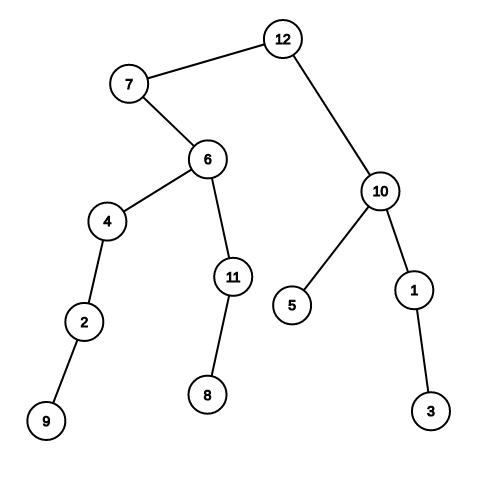
實 虛
被砸了splay 之後的樣子
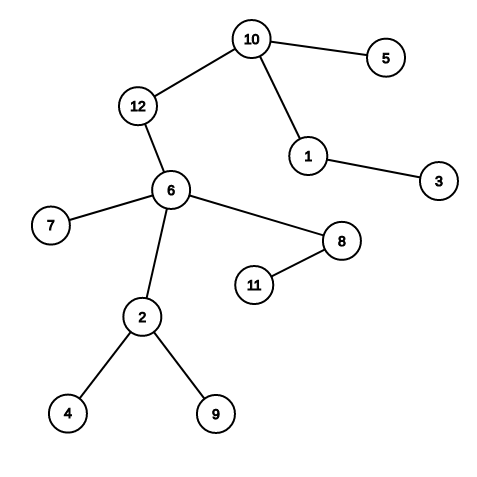
在 splay 中越左邊代表在原樹上越上面
虛邊記父不記子
LCT 最重要的功能
把一個點到樹根中間用實鏈串起來,該點往下都變虛邊


把 2 到根串起來

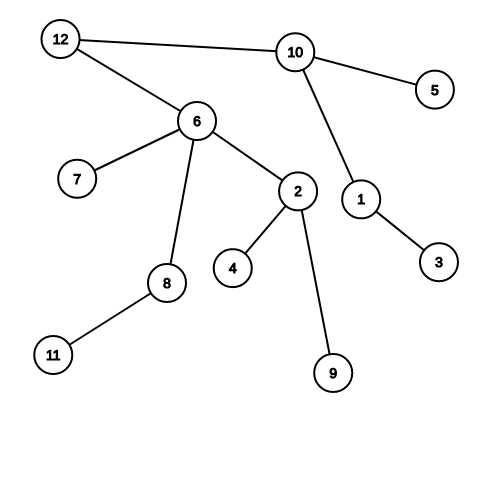
從 splay 的角度看
扣
int kabab(int p){
int c;
for(c = 0; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), rc = c, pull(p);
}
return c;
}回傳 splay 的根
更多功能
把一個點變成根
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p);
rev[p] ^= 1;
}找原樹上的根
int find(int p){
p = kabab(p);
for(; lc; push(p), p = lc);
return p;
}把兩個點接起來
void link(int u, int v){
if(find(u) == find(v)) return;
if(u > v) swap(u, v);
E.insert({u, v});
plant(u), splay(u), F[u] = v;
}把兩個點斷開來
void cut(int u, int v){
if(u > v) swap(u, v);
if(E.find({u, v}) == E.end()) return;
E.erase({u, v});
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
F[C[u][1]] = 0, C[u][1] = 0;
pull(u);
}複雜度
用 splay 做的串串操作均攤 \(O(logN)\)
其他種二元平衡樹可能是 \(O(log^2N)\)
串一次合併的鏈數均攤 \(O(logN)\) 條
把兩條鏈串在一起會發生的事情 :
輕虛邊 \(\to\) 輕實邊 or 重虛邊 \(\to\) 重實邊
輕邊最多遇到 \(logN\) 條
重虛邊 \(\to\) 重實邊 \(=\) 重實邊 \(\to\) 重虛邊
重實邊 \(\to\) 重虛邊 \(=\) 輕虛邊 \(\to\) 輕實邊
砸 splay 的複雜度
複雜度 \( = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{k(串起來的鏈數)}{3(\phi(p_{it}) - \phi(p_{i0})) + 1} \\ \le 3\phi(root) + k \implies O(logN)\)
完整的 LCT
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
array<int, 100004> F, S, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 100004> C;
set<pair<int, int>> E;
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
int root(int p){
return p != C[F[p]][get(p)];
}
void pull(int p){
S[p] = S[lc] + S[rc] + 1;
}
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(!root(f)) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(!root(p)) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; !root(p); turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(!root(f)) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}
int kabab(int p){
int c;
for(c = 0; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), rc = c, pull(p);
}
return c;
}
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p);
rev[p] ^= 1;
}
int find(int p){
p = kabab(p);
for(; lc; push(p), p = lc);
splay(p);
return p;
}
void link(int u, int v){
if(find(u) == find(v)) return;
if(u > v) swap(u, v);
E.insert({u, v});
plant(u), splay(u), F[u] = v;
}
void cut(int u, int v){
if(u > v) swap(u, v);
if(E.find({u, v}) == E.end()) return;
E.erase({u, v});
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
F[v] = 0, C[u][1] = 0;
pull(u);
}題目
扣點中間就會現身了
扣
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
array<int, 100004> F, X, V, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 100004> C;
set<pair<int, int>> E;
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
int root(int p){
return p != C[F[p]][get(p)];
}
void pull(int p){
X[p] = X[lc] ^ X[rc] ^ V[p];
}
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(!root(f)) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(!root(p)) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; !root(p); turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(!root(f)) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}
int kabab(int p){
int c;
for(c = 0; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), rc = c, pull(p);
}
return c;
}
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p);
rev[p] ^= 1;
}
int find(int p){
p = kabab(p);
for(; lc; push(p), p = lc);
return p;
}
void link(int u, int v){
if(find(u) == find(v)) return;
if(u > v) swap(u, v);
E.insert({u, v});
plant(u), splay(u), F[u] = v;
}
void cut(int u, int v){
if(u > v) swap(u, v);
if(E.find({u, v}) == E.end()) return;
E.erase({u, v});
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
F[C[u][1]] = 0, C[u][1] = 0;
pull(u);
}
signed main(){
int n, q, t, x, y;
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> V[i], X[i]= V[i];
while(q--){
cin >> t >> x >> y;
if(t == 1) link(x, y);
else if(t == 2) cut(x, y);
else if(t == 3) splay(x), X[x] ^= V[x] ^ y, V[x] = y;
else{
plant(x), kabab(y), splay(x);
cout << X[x] << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}扣
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int unsigned
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
const int mod = 51061;
array<int, 100004> F, S, A, M, val, sum, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 100004> C;
int add(int a, int b){
return (a + b) % mod;
}
int mul(int a, int b){
return a * b % mod;
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
int root(int p){
return p != C[F[p]][get(p)];
}
void pull(int p){
sum[p] = add(val[p], add(sum[lc], sum[rc]));
S[p] = S[lc] + S[rc] + 1;
}
void push(int p){
sum[lc] = add(mul(sum[lc], M[p]), mul(S[lc], A[p]));
sum[rc] = add(mul(sum[rc], M[p]), mul(S[rc], A[p]));
val[lc] = add(mul(val[lc], M[p]), A[p]);
val[rc] = add(mul(val[rc], M[p]), A[p]);
A[lc] = add(mul(A[lc], M[p]), A[p]);
A[rc] = add(mul(A[rc], M[p]), A[p]);
M[lc] = mul(M[lc], M[p]), M[rc] = mul(M[rc], M[p]);
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
A[p] = 0, M[p] = 1, rev[p] = 0;
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(!root(f)) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(!root(p)) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; !root(p); turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(!root(f)) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}
int kabab(int p){
int c;
for(c = 0; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), rc = c, pull(p);
}
return c;
}
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p);
rev[p] ^= 1;
}
void link(int u, int v){
plant(u), splay(u), F[u] = v;
}
void cut(int u, int v){
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
F[C[u][1]] = 0, C[u][1] = 0;
pull(u);
}
signed main(){
char op;
int n, q, u, v, c;
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) sum[i] = val[i] = S[i] = M[i] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
cin >> u >> v;
link(u, v);
}
while(q--){
cin >> op >> u >> v;
if(op == '+'){
cin >> c;
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
sum[u] = add(sum[u], mul(S[u], c));
val[u] = add(val[u], c);
A[u] = add(A[u], c);
}else if(op == '-'){
cut(u, v);
cin >> u >> v;
link(u, v);
}else if(op == '*'){
cin >> c;
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
sum[u] = mul(sum[u], c);
val[u] = mul(val[u], c);
A[u] = mul(A[u], c), M[u] = mul(M[u], c);
}else{
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
cout << sum[u] << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}這題他媽的有自環
扣
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
struct edge{
int p, x;
};
const int inf = 1 << 30;
array<int, 250004> L, R, F, M, V, rev, in;
array<array<int, 2>, 250004> C;
vector<edge> E;
bool cmp(edge a, edge b){
return a.x < b.x;
}
void pull(int p){
M[p] = min({V[p], M[lc], M[rc]});
}
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
int root(int p){
return p != C[F[p]][0] && p != C[F[p]][1];
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(!root(f)) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(!root(p)) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; !root(p); turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(!root(f)) turn(get(f) == get(p)? f : p);
}
}
int kabab(int p){
int c = 0;
for(; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), rc = c, pull(p);
}
return c;
}
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p);
rev[p] ^= 1;
}
int find(int p){
p = kabab(p);
for(; lc; push(p), p = lc);
return p;
}
void link(int u, int v){
plant(u), splay(u), F[u] = v;
}
void cut(int u, int v){
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
F[C[u][1]] = 0, C[u][1] = 0, pull(u);
}
int query(int p){
splay(p);
for(; p; push(p), p = M[lc] < M[rc]? lc : rc){
if(V[p] == M[p]) return p;
}
return p;
}
signed main(){
int n, m, u, v, w, q, ans = inf, cnt = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i <= n + m; i++) V[i] = M[i] = inf;
for(int i = 0, k = n + 1; i < m; i++, k++){
cin >> u >> v >> w;
L[k] = u, R[k] = v, V[k] = w;
E.pb({k, w});
}
sort(E.begin(), E.end(), cmp);
for(int lp = 0, rp = 0; rp < m; rp++){
auto [p, x] = E[rp];
if(L[p] == R[p]) continue;
if(find(L[p]) == find(R[p])){
plant(L[p]), kabab(R[p]), q = query(L[p]);
cut(L[q], q), cut(R[q], q), in[q] = 0, cnt--;
}
link(L[p], p), link(p, R[p]), in[p] = 1, cnt++;
while(!in[E[lp].p]) lp++;
if(cnt == n - 1) ans = min(ans, E[rp].x - E[lp].x);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}扣
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
#define int long long
using namespace std;
array<int, 100004> F, S, I, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 100004> C;
void pull(int p){
S[p] = S[lc] + S[rc] + 1 + I[p];
}
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
int root(int p){
return p != C[F[p]][0] && p != C[F[p]][1];
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(!root(f)) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(!root(p)) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; !root(p); turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(!root(f)) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}
int kabab(int p){
int c = 0;
for(; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), I[p] += S[rc] - S[c], rc = c, pull(p);
}
return c;
}
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p);
rev[p] ^= 1;
}
void link(int u, int v){
plant(u), splay(u), kabab(v), splay(v), F[u] = v, I[v] += S[u];
}
void cut(int u, int v){
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
F[C[u][1]]= 0, C[u][1] = 0, pull(u);
}
signed main(){
char t;
int n, q, u, v;
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) S[i] = 1;
while(q--){
cin >> t >> u >> v;
if(t == 'A') link(u, v);
else{
cut(u, v);
plant(u), plant(v), splay(u), splay(v);
cout << S[u] * S[v] << "\n";
link(u, v);
}
}
return 0;
}扣
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pb push_back
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
struct edge{
int p, a, b;
};
array<int, 150004> F, M, B, L, R, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 150004> C;
vector<edge> E;
bool cmp(edge a, edge b){
return a.a < b.a;
}
int min(int a, int b){
if(a < 0 || b < 0) return a < 0? b : a;
return a < b? a : b;
}
void pull(int p){
M[p] = max({M[lc], M[rc], B[p]});
}
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
int root(int p){
return p != C[F[p]][0] && p != C[F[p]][1];
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(!root(f)) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
pull(f), pull(p);
}
void update(int p){
if(!root(p)) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; !root(p); turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(!root(f)) turn(get(p) == get(f)? f : p);
}
}
int kabab(int p){
int c = 0;
for(; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), rc = c, pull(p);
}
return c;
}
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p), rev[p] ^= 1;
}
int find(int p){
p = kabab(p);
for(; lc; push(p), p = lc);
return p;
}
void link(int u, int v){
plant(u), splay(u), F[u] = v;
}
void cut(int u, int v){
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
C[u][1] = 0, F[v] = 0, pull(u);
}
int query(int p){
splay(p);
for(; p; push(p), p = M[lc] > M[rc]? lc : rc){
if(M[p] == B[p]) return p;
}
return 0;
}
signed main(){
int n, m, x, y, p, q, t, ans = -1;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = n + 1; i <= n + m; i++){
cin >> x >> y >> p >> q;
L[i] = x, R[i] = y, B[i] = q;
E.pb({i, p, q});
}
sort(E.begin(), E.end(), cmp);
for(auto [p, a, b] : E){
if(L[p] == R[p]) continue;
if(find(L[p]) == find(R[p])){
plant(L[p]), kabab(R[p]), t = query(L[p]);
if(B[t] <= b) continue;
cut(t, L[t]), cut(t, R[t]);
}
link(p, L[p]), link(p, R[p]);
if(find(1) == find(n)){
plant(1), kabab(n), splay(1);
ans = min(ans, a + M[1]);
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}扣
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pb push_back
#define lc C[p][0]
#define rc C[p][1]
using namespace std;
array<int, 300004> F, rev;
array<array<int, 2>, 300004> C;
array<pair<int, int>, 300004> W;
void push(int p){
if(rev[p]) swap(lc, rc);
rev[lc] ^= rev[p], rev[rc] ^= rev[p];
rev[p] = 0;
}
int get(int p){
return p == C[F[p]][1];
}
int root(int p){
return p != C[F[p]][0] && p != C[F[p]][1];
}
void turn(int p){
int f = F[p], g = get(p), c = C[p][!g];
if(!root(f)) C[F[f]][get(f)] = p;
F[p] = F[f], F[f] = p, C[p][!g] = f, C[f][g] = c;
if(c) F[c] = f;
}
void update(int p){
if(!root(p)) update(F[p]);
push(p);
}
void splay(int p){
update(p);
for(int f = F[p]; !root(p); turn(p), f = F[p]){
if(!root(f)) turn(get(f) == get(p)? f : p);
}
}
int kabab(int p){
int c = 0;
for(; p; c = p, p = F[p]){
splay(p), rc = c;
}
return c;
}
void plant(int p){
p = kabab(p);
rev[p] ^= 1;
}
int find(int p){
p = kabab(p);
for(; lc; push(p), p = lc);
return p;
}
void link(int u, int v){
plant(u), splay(u), F[u] = v;
}
void cut(int u, int v){
plant(u), kabab(v), splay(u);
F[v] = C[u][1] = 0;
}
signed main(){
int n, m, p, q, k = 1;
char t;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
cin >> p >> q;
link(p, q);
}
while(m--){
cin >> t >> p;
if(t == 'Q'){
cin >> q;
cout << (find(p) == find(q)? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}else if(t == 'C'){
cin >> q;
W[k++] = {p, q};
cut(p, q);
}else{
auto [a, b] = W[p];
link(a, b);
}
}
return 0;
}扣
嗷嗷待補LCT
By thanksone
LCT
- 831



