{supply chain security}

Introduction
Based on NorthSec 2023 presentations:
- Broken links - Behind the scenes of Supply Chain breaches, by François Proulx
- Abusing GitHub for fun and profit: Actions and Codespaces Security by Magno Logan
Cyber breach where the threat actor is able to target insecure trusted 3rd party software
What is SCS?


Some stats
In 2022, supply chain cyber attacks in the United States impacted 1743 entities (Statista)
Financial losses attributed to software supply chain cyberattacks will jump 76% and cost the global economy almost $81 billion in lost revenue and damages by 2026 (Juniper research)
SLSA
Threat model that aims to identify the weakest links in the developer supply chain
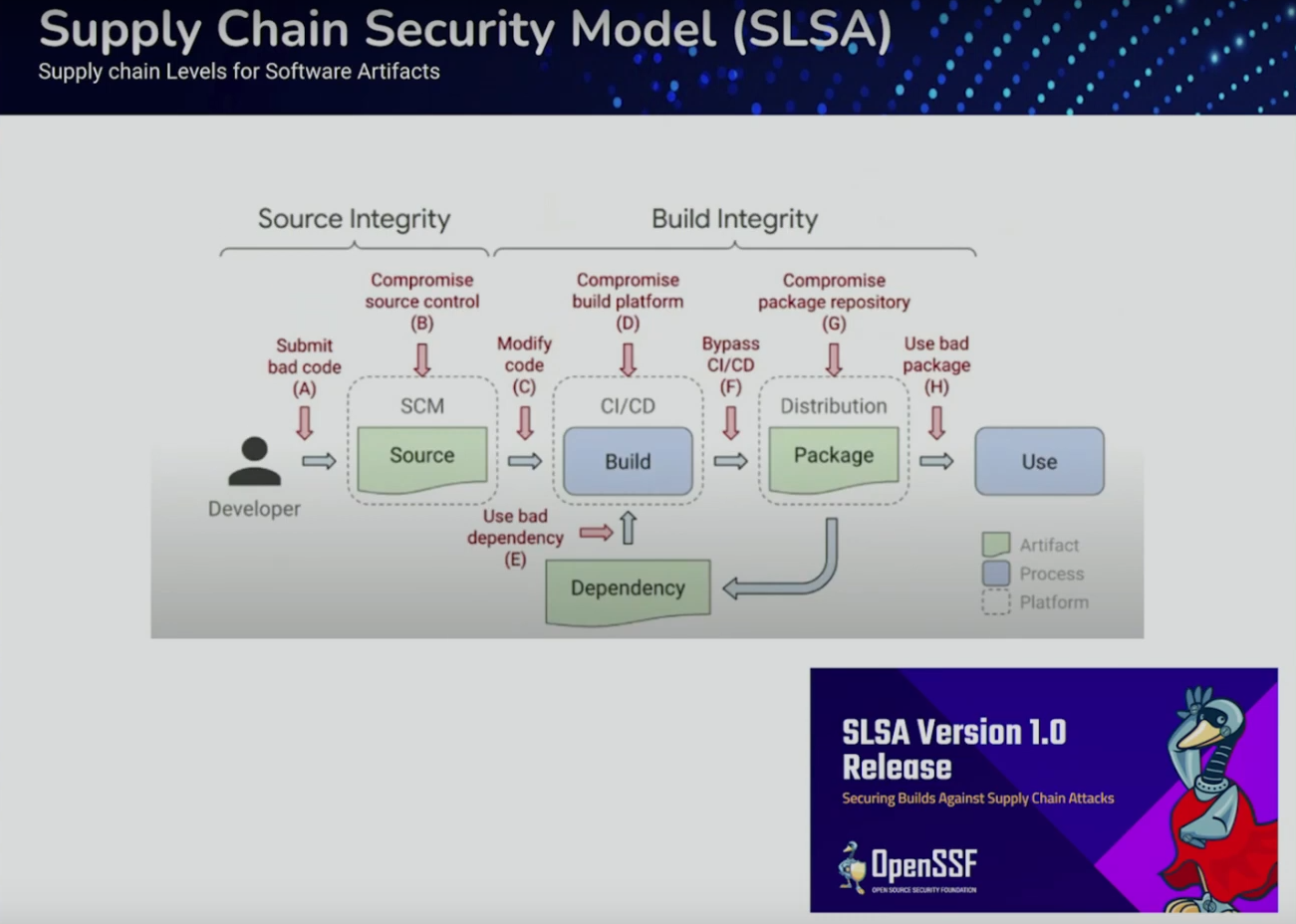
Broken links - Behind the scenes of Supply Chain breaches, by François Proulx

Attack vectors 🔥
Source code compromise 💻
Phishing developers
🔥 Dropbox email phishing pretending to be from CircleCI - November 2022
- stole Github credentials, gained access to private repos and exfiltrated source code
Malicious developers
🔥 Linux kernel experiment - August 2020
- researchers simulated an attack by submitting malicious code to linux kernel
- code review caught most but not all
Build platform compromise 🏗️
Direct compromise
🔥 SolarWinds - December 2020
- attacker compromised build server
- malware modified source files to add backdoor during build step
- reverted modification after build to stay hidden
Build platform compromise 🏗️
Github actions
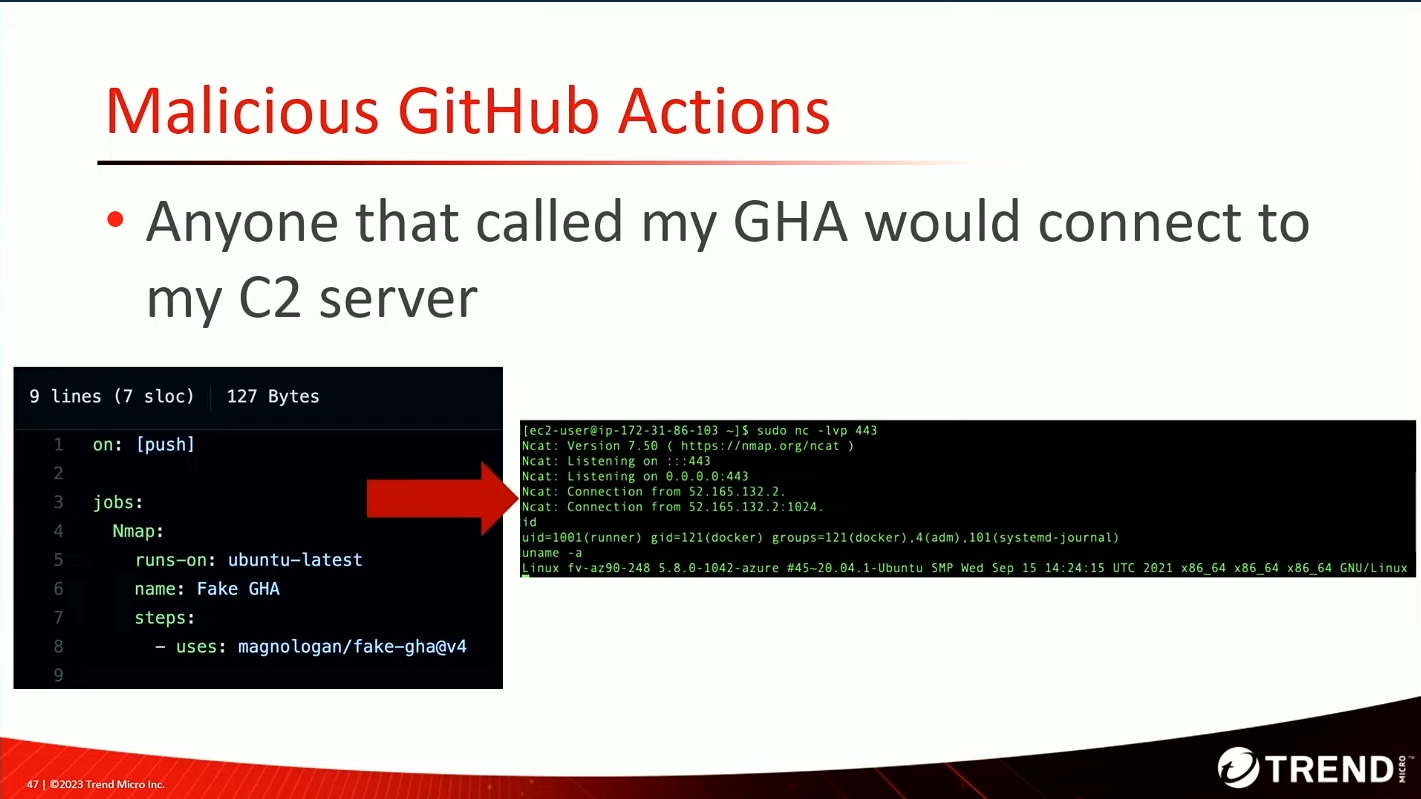
Abusing GitHub for fun and profit: Actions and Codespaces Security by Magno Logan
Dependencies 📦
0 day vulnerabilities
🔥 Log4j December - 2021
- popular Java logging library used everywhere
- had a special documented feature that allowed RCE by logging user controlled data
Dependency confusion
- Some package managers first resolve public repositories instead of private ones with the same name
- Used to trick build system in dowloading malicious public package instead of private legitimate one
Dependencies 📦
Typosquatting
PyPI:
- 🔥 Python `request` package instead of `requests` - August 2020
Npm:
- 🔥Typosquatting campaign targetting node developers - October 2022
- 🔥 Cyber firm Phylum discovered 15 npm packages using typosquatting totalling 1.2 billion downloads per week
- tslbi, tsilb, tlsib -> tslib or crossenv -> cross-env
Docker hub:
- 🔥 In its 2022 report, Sysdig Threat Research Team found thousands of typosquatted docker images hiding cryptominers
Dependencies 📦
Lockfile injection
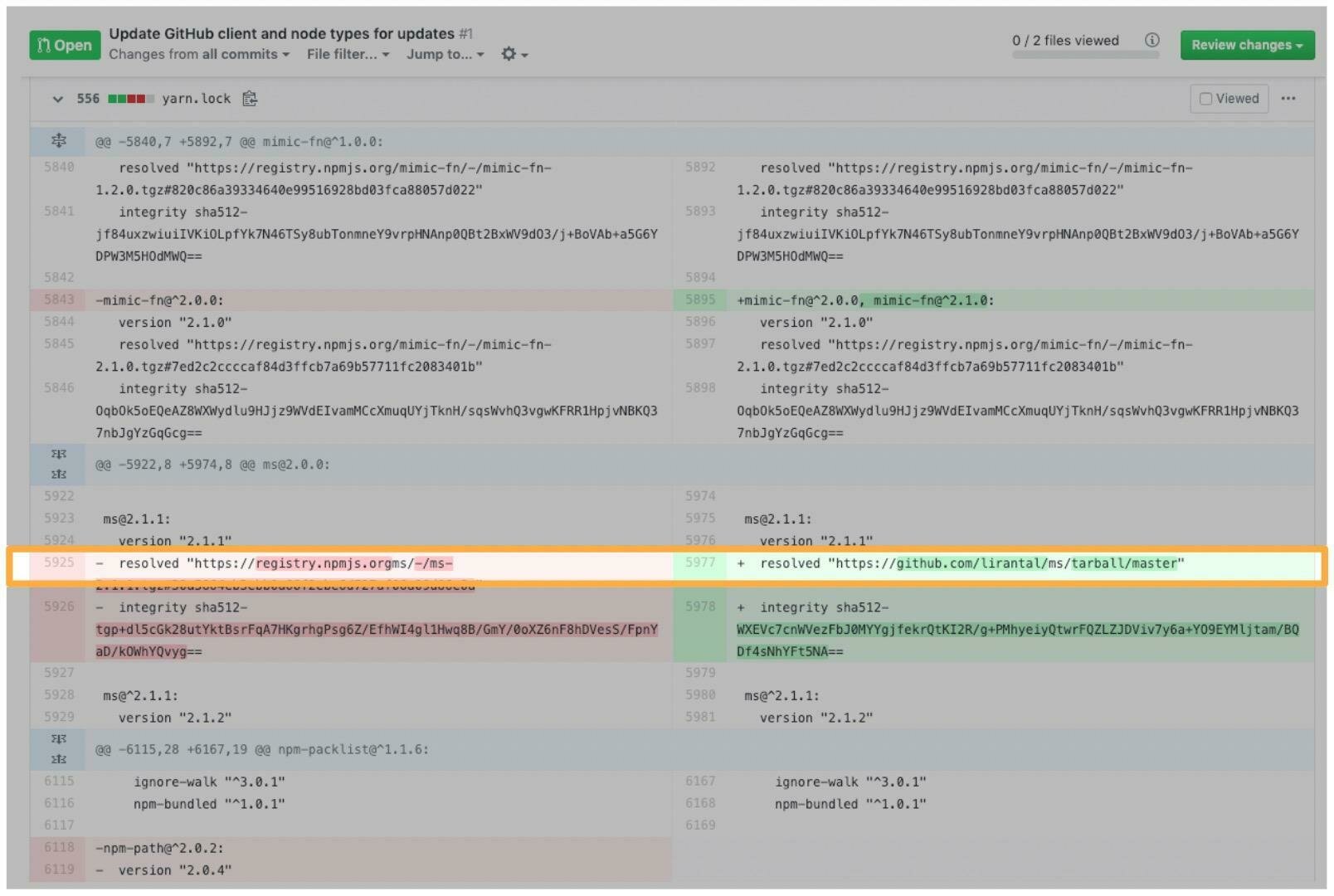
Dependencies 📦
Arbitrary command execution
- npm provides an install lifecycle hook as part of a dependency install process
- 🔥 node-ipc package modified to execute commands that will create files or even wipe hard drives
Hijacked package
- 🔥 October 2021 UA-Parser.js npm package was hijacked and infected with stealing passwords and cookies code and crypto-miner.
IDE plugins 🔌
VSCode plugins:
- 🔥 Theme Darcula dark was stealing basic system information
- 🔥 python-vscode allowed for remote code execution
- 🔥 prettiest java stole credentials or authentication tokens from Discord, Chrome, Opera, Brave Browser and later exfiltrated them using a Discord webhook.
all 3 were downloaded 46,600 times 💀

Mitigations
Low hanging fruits 🍓
- MFA for developers/everyone
- Code source branch protection rules
- Git commit signatures
- SAST, DAST, SAC, security linters
- Scan for leaked secrets, docker images
- Run package managers audits regularly
- Enforce lock files
- Update dependencies at the right cadence with a sane process
- Keep up to date on the latest 0day bombs
Advanced 🧐
- use --ignore-scripts to avoid postinstall scripts
- use lockfile-lint to prevent lockfile injection attack
- use tools like npq which analyzes new packages before installing them and minimizes risk of installing malware
- be more careful about IDE plugins (check reviews, src code)
- only use GH actions from trusted creators, don't run actions from forked repos without reviewing them
Thank you!

Supply chain security
By Thomas Rebaud
Supply chain security
- 279