Program the web using APIs in Javascript
{
name: "Thibaud Arnault", job: "CEO & Co-founder, webshell.io", twitter: "@thibaud_arnault", email: "thibaud.arnault@gmail.com" }
Why?
- API Design & paradigm are too different
- Client side APIs and Server side APIs are hard to mashup
- Authorization is a mess and need server side
- Javascript rules the web
a platform and an API
On top of node.js
- Platform: discover, try and mash up APIs.
- Webshell API: integrate easily all your favorite APIs and script them into your apps.
API Endpoints become Javascript objects
CONSOLE - REPL
WEB API
GET or POST on
http://api.webshell.io/?code=SOME_JAVASCRIPT
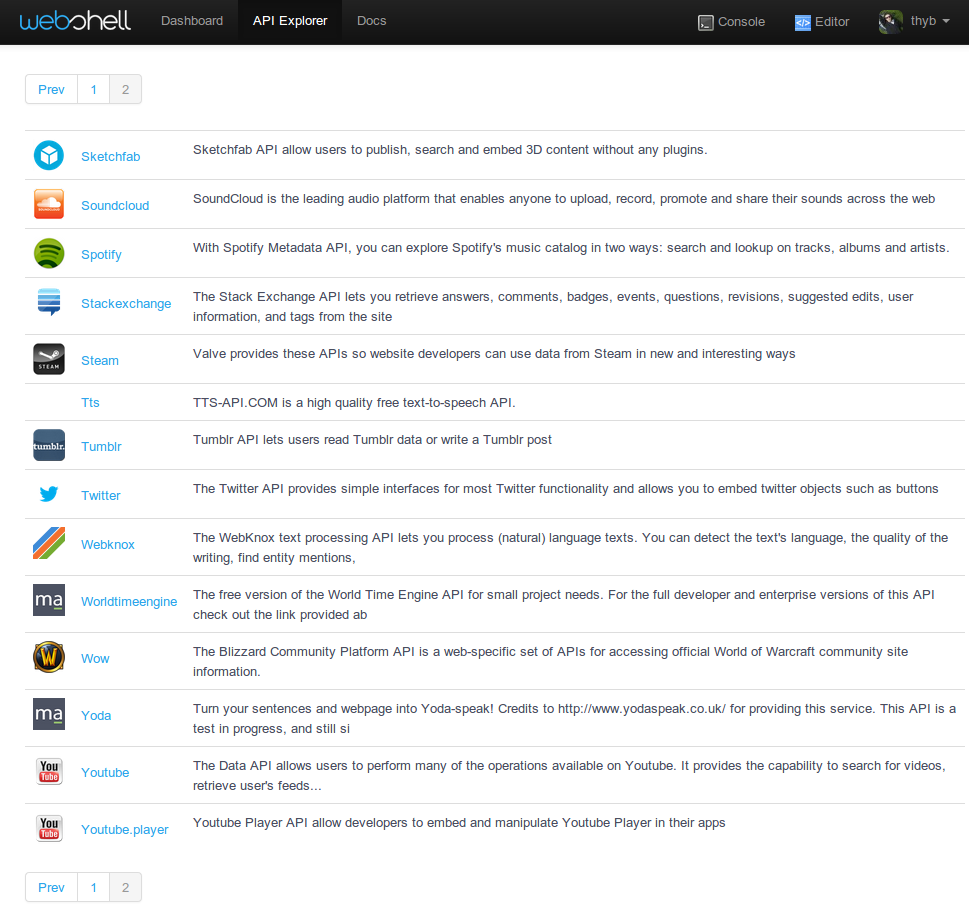
API Explorer
Javascript SDK
Include this one line...
<script type="text/javascript" src="http://api.webshell.io/sdk/js?key={key}"></script>
... and start making API calls in a <script>
wsh.exec({
code: function() {
apis.google.maps();
},
process: function(data, meta) {
$(body).append(meta.view)
}
});
SDK NODE
Std lib
-
Make HTTP request
- Manipulate your Webshell app from the code
- Render views
- Geolocalize your user
- Other various helper/debugging functions
Those are the building blocks.
All APIs on Webshell are made using them.
HTML View
JSON responses include both data and metadata
in these metadata, there is an important optional field: view
The metadata holds a view field that contains:
- HTML markup
- CSS
- Javascript
Allows us to handle client-side APIs such as Google Maps, Youtube player, etc.
template your api data
var hn = get({
url: 'https://news.ycombinator.com/rss',
format: 'xml'
});
render(hn, { view: '<ul>\
<% for (var item in data.rss.channel[0].item) { %>\
<li>\
<a href="<%= data.rss.channel[0].item[item].link[0] %>">\
<%= (parseInt(item) + 1) %>. <%= data.rss.channel[0].item[item].title[0] %>\
</a><br /><span>(<%= data.rss.channel[0].item[item].link[0] %>)</span>\
</li>\
<% } %>\
</ul>' });
exAmples of api with views
var m = apis.google.maps();
m.center('paris');
or
var player = apis.youtube.player('BbkE-qN-jOM');
player.playVideo();
Storage
Each user has a free workspace
-
Store their API scripts
- 3rd party libraries
- assets (img, css, js)
Edit files IN your workspace
Cloud9 Adapted to Webshell
FS Endpoints
All scripts that users make are public at the moment but we're working on private workspaces
To read a file:
http://api.webshell.io/raw/fs/username/path/to/file
or using STD Lib
cat(fs.thyb.helloWorld.sandbox.helloWorld);
Execute script
To access a file using STD Lib you can use fs builtin
fs.username.path.to.file
Execute the file by calling it:
fs.thyb.helloWorld();
or
or
APIs on Webshell
APIs are stored under the @bin account
http://api.webshell.io/raw/fs/bin/facebook/v0.1/facebook
we created the "apis" builtins, a handy shortcut
var apis = fs.bin
You can thus simply do apis.facebook.me();
Examples
Make an application that tells the current weather in your current location
One-liner authorization
All authorization protocols are implemented on Webshell. You can store your API Key on webshell and connect your user easily
apis.facebook.auth(); //connexion with OAuth2
apis.twitter.auth(); //connexion using OAuth1
Using REST APIs
once authorized, you can make calls without passing any token
apis.facebook.me();
or
apis.twitter.search('@webshell_');
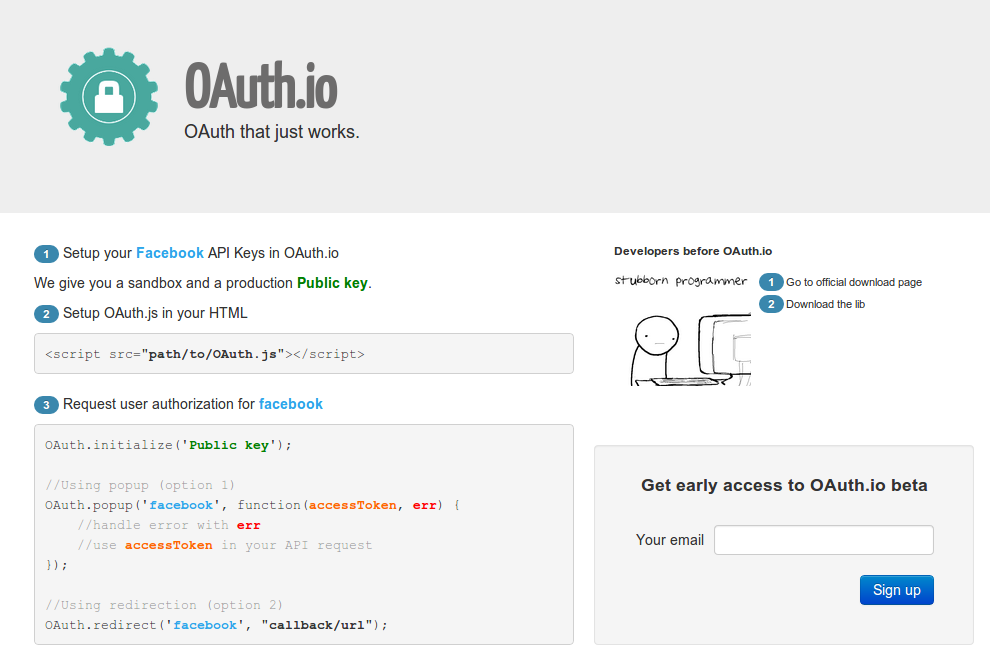
OAuth.io
What's next?
Webshell will be based on OAuth.io for authorization
Webshell views will make use of web components (Shadow DOM, HTML Import, Custom elements ...) cf polymer project
Thanks
Do you have questions ? :-)
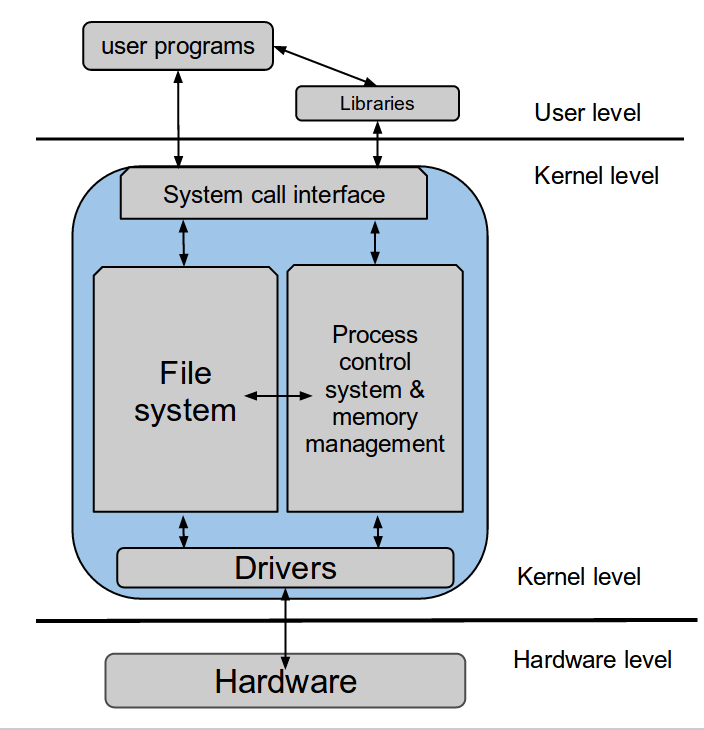
CLASSICal os structure
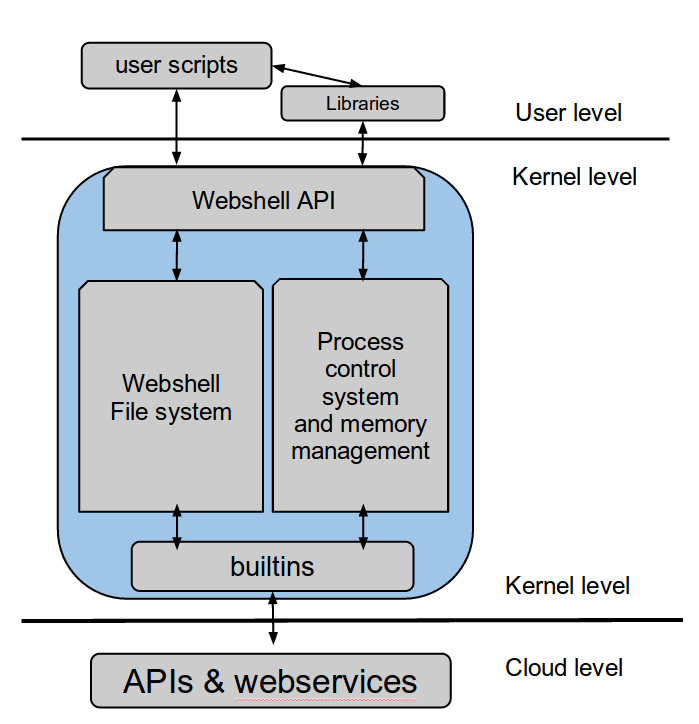
Webshell structure
webshell
By Thibaud Arnault
webshell
- 4,933