The Modern Web & Design Disciplines

Web Design 1 | Spring 2024
Tim McKenna
The Web Spawned A Golden Age for Design
In the 90's, we started to see a merging, diverging, and start of different design disciplines thanks in part of technology and the web boom (and eventual bust.) Design became evermore important to web denizens as the web's capabilities grew from box layout to then moving to CSS and Javascript becoming viable to connect data and interactions.
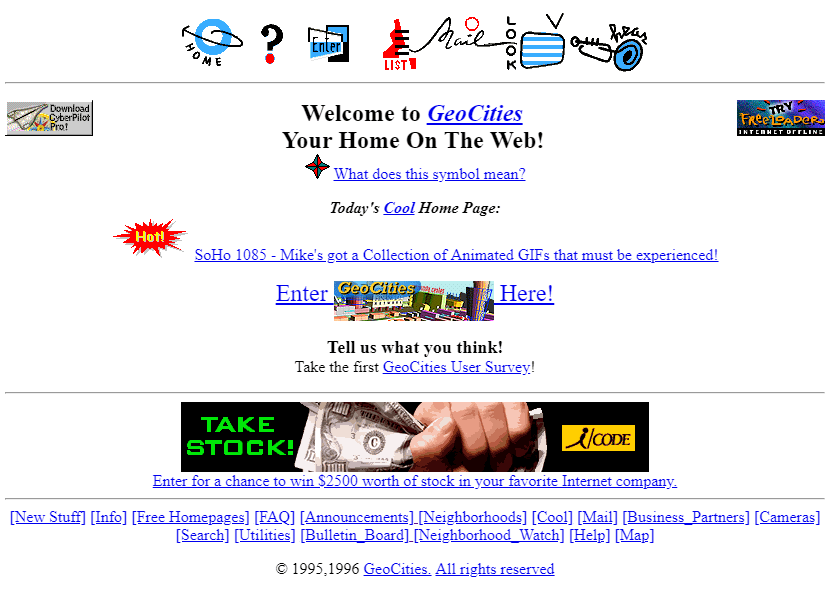
Web Design in Web 1.0
Box Model
Web Design in Web 2.0
CSS
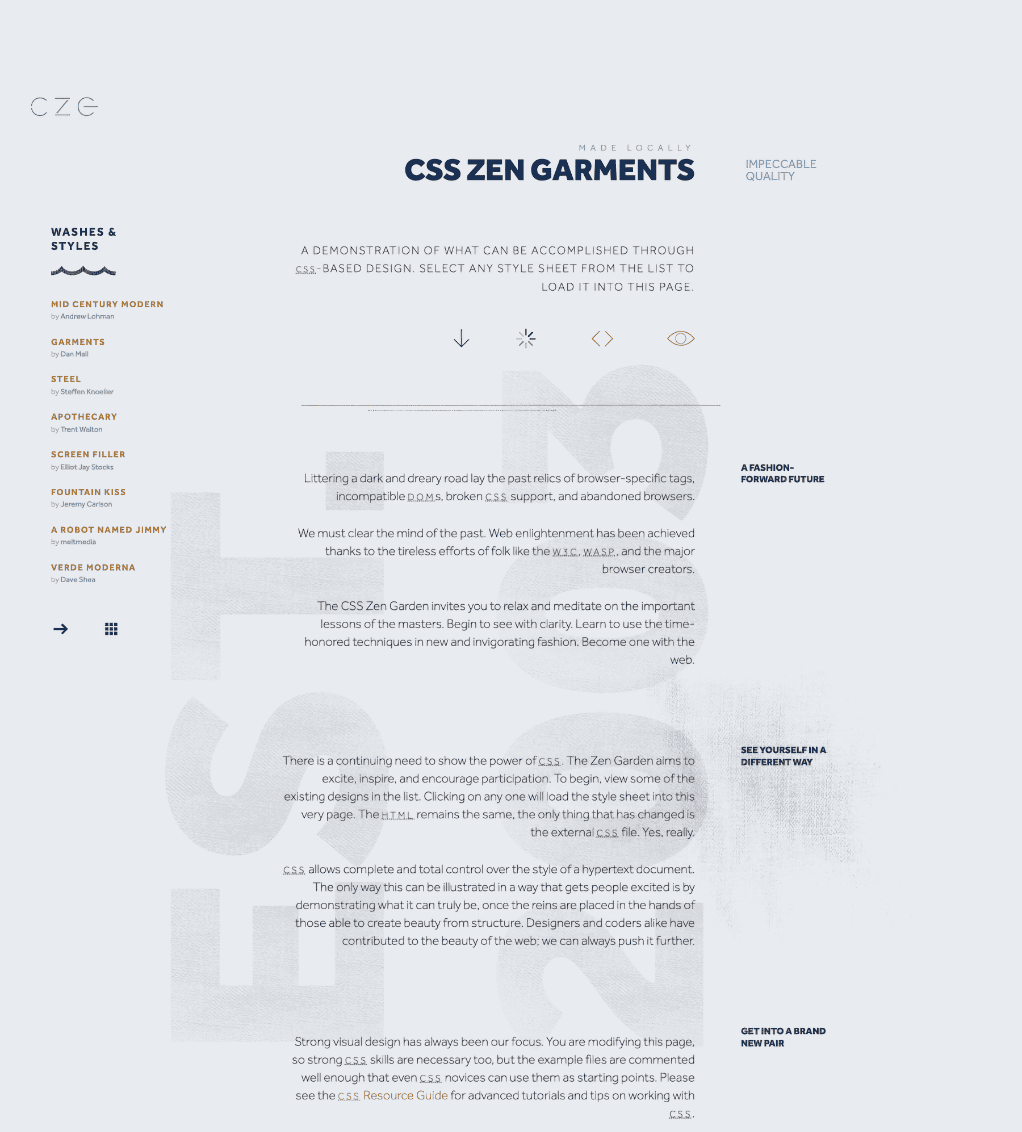
div=header
div=header
div=content
div=sidebar
Web Design in Web 3.0
Real Time Data Transfer and Personalization
HTML in JS
HTML in JS
HTML in JS
HTML in JS
HTML in JS
Design Disciplines
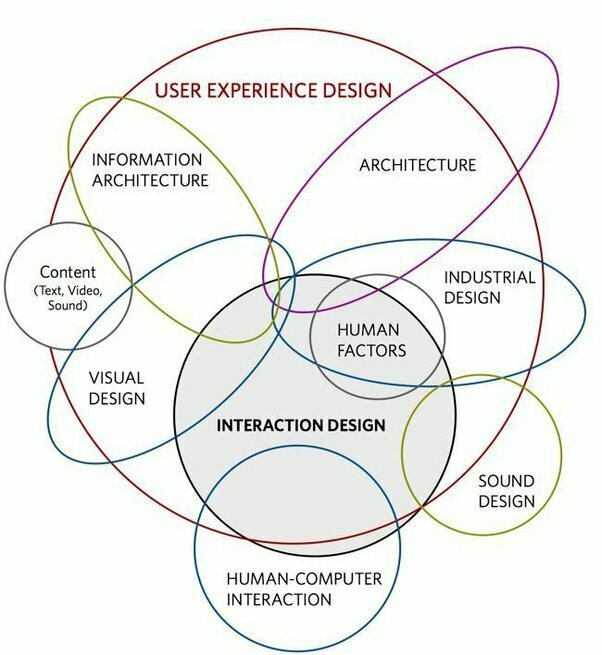
Design disciplines have always had overlaps in various ways and technology development enabled overlapping to occur more frequently and meaningfully.
Visual Designer

The visual designer title is often used interchangeably with the graphic designer/ visual communications, but in reality, visual design is focused exclusively on the look and feel aspects of design — colours, sizes, and placement.
Web Designer

A web designer straddles the world of development and visual design.
A web designer straddles the world of development and visual design.
WEB DESIGN
Interaction Designer

Interaction designers focus on how users interact with products and use principles of good communication to create desired user experiences. For UX designers, the moment of interaction is just a part of the journey that a user goes through when they interact with a product.
WEB DESIGN
UX Designer

UX design focuses on the interaction between real human users and everyday products and services, such as websites, apps, and even coffee machines.
It’s an extremely varied discipline, combining aspects of psychology, business, market research, design, and technology.
WEB DESIGN
UI Designer

A UI designer is someone who designs the graphical user interface of an app, website, or device that a human interacts with. For example, when you access a website or an app on your phone, there's usually a graphical interface that allows you to navigate and achieve your goal.
WEB DESIGN
Industrial Designer

An industrial designer combines artistic and engineering skills to create and develop innovative and functional products. Industrial designers are involved in the design and development process of a wide range of products, including consumer electronics, furniture, appliances, automobiles, medical equipment, and more. Their goal is to enhance the usability, aesthetics, and overall user experience of products, taking into consideration factors such as ergonomics, materials, manufacturing processes, and market demands.
WEB DESIGN
Architectural Designer

The term architectural designer (AD) refers to a building designer who is not a registered architect. ADs work with architects in the process of creating and documenting design projects. ADs receive their OJT (On-Job-Training) experience through this process. Unlike architects, ADs are not required to take the ARE, as they are primarily focused on the design aspect of architecture, and qualifications in related fields often suffice.
WEB DESIGN
Content Designer

The role of content designer is growing in both importance and popularity. Brands are realising just how critical content design is to a successful user experience, and talented writers and designers are taking notice of this impactful and rewarding career path.
WEB DESIGN
Human-Computer Interaction

Human-computer interaction (HCI) is the field of study that focuses on optimizing how users and computers interact by designing interactive computer interfaces that satisfy users’ needs. It is a multidisciplinary subject covering computer science, behavioral sciences, cognitive science, ergonomics, psychology, and design principles.
WEB DESIGN
Human Factors

Human factors (HF) is the study of how people use technology. It involves the interaction of human abilities, expectations, and limitations, with work environments and system design. The term "human factors engineering" (HFE) refers to the application of human factors principles to the design of devices and systems. It is often interchanged with the terms "human engineering," "usability engineering," or "ergonomics."
WEB DESIGN
Sound Designer

Sound design is the art and practice of creating soundtracks for a variety of needs. It involves specifying, acquiring or creating auditory elements using audio production techniques and tools. It is employed in a variety of disciplines including filmmaking, television production, video game development, theatre, sound recording and reproduction, live performance, sound art, post-production, radio, new media and musical instrument development.
WEB DESIGN
Spatial Designer
Spatial design is the design of human environments, particularly interior environments. Working from the inside out, spatial designers think about how spaces feel, how they are organized and how they might enrich the lives of those experiencing them.
Game Designer
Game designers combine their imaginative ideas with a deep understanding of player psychology and game mechanics to create engaging and immersive gaming experiences. They conceptualize game worlds, characters, and storylines, determining the game's objectives, rules, challenges, and rewards. Game designers often work closely with interdisciplinary teams, including artists, programmers, and sound designers, to bring their vision to life.
Computational Designer
A computational designer’s job is to use data-driven processes, like automation, to design better built environments. While architects and engineers traditionally rely on intuition and experience to solve design problems, computational designers can enhance that process through visual programming, thus creating an impact at project as well as company level.
And More Disciplines Grow Each Day...
Sustainability Designer, Accessibility & Inclusivity Designer, Environmental Designer, etc.
YCP Class 3 - The Modern Web & Design Disciplines
By Tim McKenna
YCP Class 3 - The Modern Web & Design Disciplines
- 76


