JavaScript Promises

Motivation
Solution to "callback hell"


Common Promise example
Basics
Use
Create
Flow

Promises
Basics
Basics
What are promises?
Promises are an alternative way to manage your asynchronous code in JavaScript.
Basics
What are promises?
a promise is an object who represents the result of an asynchronous operation.
It is a place holder for a value that will become available in the future.
Implementation status
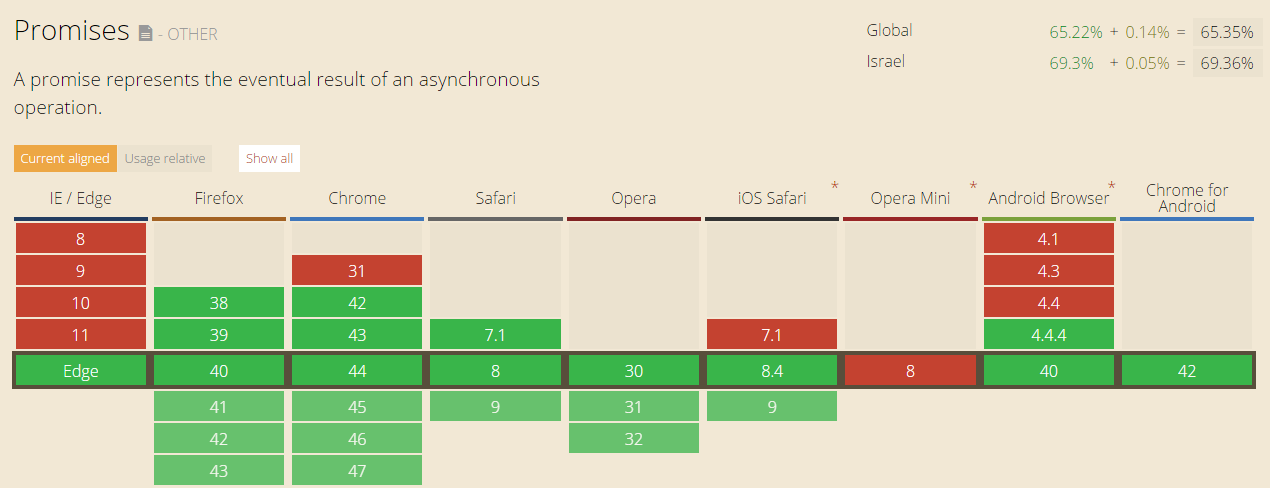
Basics
Spec



Standard Libraries


Full list
Basics
Promises Axiomas
-
Will always be Async
Executed at least on the next tick -
a Promise handler always return another Promise
-
Promises can be used only once
-
a Promise object is "Then-able"
Basics
Promises states
-
PENDING - The initial state of a promise.
-
FULFILLED - a successful operation - returns a Value.
-
REJECTED - a failed operation - throws an exception.
has a 'Reason' property. -
(SETTLED) - means either fulfilled or rejected
Once a promise is settled, it is immutable
and cannot be changed.
Basics
Using
Promises
Promise.prototype.then( )
Use
getUser('userID')
.then(onFulfilled, onRejected)
getUser('userID')
.then(function(userData) {
if(userData) return 'Success!'
else throw new Error('No user data was found...')
//your app logic error, always throw with an Error...
},
function(reason){
//handle DB errors...
})Chaining Promises
Use
"a Promise handler always return another Promise"
therefore it can be chained to other Promises
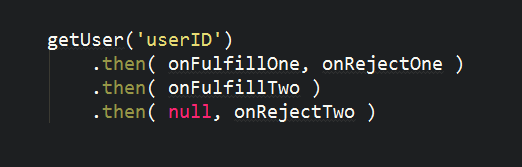
Promise.prototype.catch( )
Use


Creating
Promises
function readFile(filename, enc){
return new Promise(function (fulfill, reject){
fs.readFile(filename, enc, function (err, res){
if (err) reject(err);
else fulfill(res);
});
});
}Create
new Promise( )
var readFile = Promise.promisify(require("fs").readFile);
readFile("myfile.js", "utf8").then(function(contents) {
return eval(contents);
}).then(function(result) {
console.log("The result of evaluating myfile.js", result);
}).catch(SyntaxError, function(e) {
console.log("File had syntax error", e);
//Catch any other error
}).catch(function(e) {
console.log("Error reading file", e);
});Create
Promise.promisify()
var fs = Promise.promisifyAll(require("fs"));
fs.readFileAsync("myfile.js", "utf8").then(function(contents) {
console.log(contents);
}).catch(function(e) {
console.error(e.stack);
});Create
Promise.promisifyAll()
Controll Async Code Flow
fetch('/api/friends')
.then(promisedStep1)
.then(promisedStep2)
.then(promisedStep3)
.then(promisedStep4)
.catch(function (error) {
// Handle any error from all above steps
})Flow
Chaining Promises( )
var items = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
Promise.each(items, function(item) {
return Promise.delay(Math.random() * 2000)
.then(function() {
console.log('async Operation Finished. item:', item);
});
}).then(function(resultsArray) {
console.log('All tasks are done now...',resultsArray);
}).catch(function(error) {
console.dir(error)
});Flow
Promise.each()
Serial iterator over a collection
and then...
var items = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
Promise.map(items,function(item) {
return Promise.delay(Math.random() * 2000)
.then(function() {
console.log('async Operation Finished. item:', item);
});
}, {concurrency: 3}) //adjust concurrency...
.then(function() {
console.log('All tasks are done now...');
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.dir(error)
});Flow
Promise.map()
Parallel iterator over a collection
and then...
Promise.all(pendingItemsArray).then(function (items) {
console.log('All operations are complete!', 'items: ',items);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log('Error: ',error);
});
Flow
Promise.all()
Parallel execution of different async operations
and then...
- input - an array of promises
- output an array of results values
(ordered respectively to the original array order!)
Promise.props(pendingItemsObj).then(function(result) {
console.log('All operations are complete!', 'result: ');
console.dir(result);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log('Error: '.red,error);
})
Flow
Promise.props()
Parallel execution of different async operations
and then...
- input - an Object with promises key/value pairs
- output - an Object of results key/values
(easier to work with results...)
Promise.race(pendingItemsArray).then(function (item) {
console.log('The first operation is complete!', 'first item: ',item);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log('Error: '.red,error);
});Flow
Promise.race()
The .then( ) handler runs after the
first async operation is complete
Promise.some(pendingItemsArray, 2)
.spread(function(first, second) {
console.log('first: ', first, ', ','second: ', second);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log('Error: ',error);
});Flow
Promise.some()
Similar to race()
The .then() handler runs after the (n)th async operation is complete
RX JS Promises Observables 2.x
By tkssharma
RX JS Promises Observables 2.x
Go through these slides to get a strong grip on JavaScript Promises. A way to manage your async JavaScript code.
- 1,073




