Introduction to Version Control with Git and GitHub


Hi, I'm Bolaji Ayodeji
Digital Strategist @Philanthrolab
Technical Writer & Chapter Lead @OSCAFRICA
- Front-end Developer
- Open Source Advocate
Learning Objectives
- What is Version Control
- CVCS vs DVCS
- What is Git
- Version Control with Git (Practical)
- What is GitHub
- Setting up GitHub (Practical)
- Git and GitHub are not the same
- What next?

What is Version Control?
Version Control is:
the process of managing changes to source code or set of files over time.
Version control software keeps track of every modification to the code in a special kind of database.
If a mistake is made, developers can restore and compare earlier versions of the code to help fix the mistake while minimizing disruption to all team members or contributors.


CentralIzed VCS
Distributed VCS
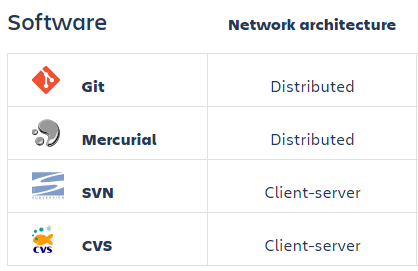
Type of VCS
Benefits of Version Control
-
Backups
-
Preserves efficiency and agility
-
Source Code Management
-
Traceability
-
Branching and Merging
-
Reverting Changes
-
Collaboration
Version control software is an essential part of the every-day of the modern day software developer practices.
Once accustomed to the powerful benefits of version control systems, many developers wouldn't consider working without it even for non-software projects.
What is Git?
By far, Git is the most widely used modern version control system in the world today is. Git is a distributed and actively maintained open source project originally developed in 2005 by Linus Torvalds, the famous creator of the Linux operating system kernel.
Unlike older centralized version control systems such as SVN and CVS, Git is distributed: every developer has the full history of their code repository locally. Git also works well on a wide range of operating systems and IDEs (Integrated Development Environments).
Git is a Free and Open Source Distributed Version Control System
Version control with Git


git init // creates a new git repository
// create a new file (README.md), do something new!
git add README.md or git add * or git add --all
// Proposes this new change and adds it to the index
git status
// check what has been going on in git, see whats staged or not.
git commit -m "commit description"
// tell us what you did and add to HEAD
git push origin master
// push HEAD to the remote repository
git log
// see the repository history
git pull
// grabs the latest directory with updates from the remote repository
git clone <url>
// clone a remote repository to localBranching

git checkout -b <branch name>
// creates a new branch named <branch name> and switches to it
git checkout master
// switch back to the master branch
git branch -d <branch name>
// deletes the branch named <branch name>
git push origin <branch name>
// push your branch to remote repository
git merge <branch name>
// merge <branch name> into master
What is GitHub?

GitHub is a web-based hosting service for version control using Git. It is mostly used for computer code. It offers all of the distributed version control and source code management functionality of Git as well as adding its own features.

GitHub Features
- Repository
- Commits
- Tags
- Pull Request
- Branch
- Code editor
- Issues
- Releases
- Projects
- Organizations/ Teams
GitLab
BitBucket
Cloudforge
Working with Git and GitHub

Create and setup your GitHub account


git config --global user.name "Your username here"
git config --global user.email "your email here"
git config --global color.ui true
git config --global core.editor emacs
git config --listDifferences between Git and GitHub

Git is a revision control system, a tool to manage your source code history.
GitHub is a hosting service for Git repositories.
So they are not the same thing: Git is the tool, GitHub is the service for projects that use Git.
What next?
Useful resources to learn Git and GitHub
Tweet @iambolajiayo
Code
@bolajiayodeji
Write @bolajiayodeji.com

DevOps -Pre Slides
By Tarun Sharma
DevOps -Pre Slides
Introduction to version control, version control systems, Git and GitHub plus practical usage, code, tips, and resources.
- 766



