Columbus AngularJS October Meetup
Forms in AngularJS
Presented By Tom Acree
Transcordia LLC
Source Code
Presentation Example Project
https://github.com/Transcordia/ng-meetup
The source for this presentation is in the "ng-forms" directory
Topics
- Angular Form Components
- Validation
- Customizing Validation
- Directive Controllers
Forms, Again?
- We've All Been Here Before...
- Probably a Million Times...
- With Dozens of Approaches...
What Angular Brings To The Table
- Two-Way Binding
- Validation
- Simple to Use
- Designed for Ajax-driven Single Page Apps
First Example
- user object is added to the scope
- myForm is added to the scope
- myForm has a property firstAndLastName
- See example 1
<form role="form" name="myForm" novalidate="novalidate">
<input type="text" ng-model="user.firstLastName" name="firstLastName"
placeholder="Enter Name">
</form>Key Directives
- form Directive
- This directive is used essentially to expose the FormController
- Form Element Controls/Directives (e.g. <input>)
- Each Form Element has a corresponding directive with its own ngModel directive
- ngModel Directive
- This Directive Exposes the NgModelController and registers it with the FormController
Key Controllers
-
FormController
- Directive Controller created by the form directive
- Primary Responsibility is to monitor the overall validity of the form and whether it is "pristine" or "dirty"
-
NgModelController
- Directive controller created by the ngModel directive
- Provides the API for managing the state between the model value and the form element to which it is associated
- Provides support for rendering the current form value, converting it to the bound model value, tracking validation
Peak under the Covers
<!--
The form directive is created. It is bound to the directive controller FormController
which is injected into its link function. The FormController initializes validation
and pristine state. Finally, myForm--a reference to the FormController--is added
to the scope.
-->
<form role="form" name="myForm" novalidate="novalidate">
<!--
Two directives are created: input directive and ngModel directive. The ngModel
directive requires as an optional controller, the FormController created above,
as well as an NgModelController, both of which are injected into its
link function as an array. The ngModelController is added to the myForm controller
as an attribute named "firstLastName"
-->
<input type="text" ng-model="user.firstLastName" name="firstLastName"
placeholder="Enter Name">
</form>Using the "name" Attribute
- Adding the "name" attribute to the form adds the FormController to the scope by that name
- Adding the "name" attribute to a control with the ngModel directive adds that ngModelController for that control to the FormController
- This is useful if one wants to check the state of the form or control programmatically
Binding Data To Controls
- Controls allow the UI to communicate with model to which it is bound
- This is enabled through the control directives by the ngModel directive
- Some standard out of the box control directives
- input - all its various flavors
- textarea
- select
Input Checkboxes
- Bullet One
- Bullet Two
- Bullet Three
<!-- This example shall bind true or false to user.agreement -->
Agree to terms: <input type="checkbox" ng-model="user.agreement">
<!-- This example shall bind "yes" or "no" to user.agreement -->
Agree to terms: <input type="checkbox" ng-model="user.agreement"
ng-true-value="yes" ng-false-value="no" >- Binds a boolean value
- Or an alternative value if desired
Input Radio Buttons
- To use, just bind to same model property
<input type="radio" ng-model="user.favColor" value="red"> Red <br/>
<input type="radio" ng-model="user.favColor" value="green"> Green <br/>
<input type="radio" ng-model="user.favColor" value="blue"> Blue <br/>Select Control
<!--
Using Select with hard-coded strings binds the hardcoded string to the model.
Note the use of the ngSelected directive to apply the "selected" attribute
through the expression.
-->
<select name="sex" ng-model="user.sex">
<option value="m" ng-selected="user.sex=='m'">Male</option>
<option value="f" ng-selected="user.sex=='f'">Female</option>
</select>ngOptions
- Builds a dynamic list of bindable options for the select control
- Can bind values from the following models:
- Array of primitive values: [1, 2, 3] or ['red', 'blue'...]
- Array of Objects: [{id: 1, color: 'red'}, {id: 2, color: 'green'}, ...]
- Values from an Object: {'red' : 1, 'green' : 2, ...}
- Robust expression language for building options list
NgOptions Initialization
- Problem with array of objects angular compares object values by reference
// controller initialized values
$scope.user.favFood = {name: 'Hamburger', group: 'Meats'};
$scope.formData = {
foods: [
{name: 'Spaghetti', group: 'Grains'},
{name: 'Cereal', group: 'Grains'},
{name: 'Steak', group: 'Meats'},
{name: 'Hamburger', group: 'Meats'},
{name: 'Apple', group: 'Fruits'},
{name: 'Lemon', group: 'Fruits'},
{name: 'Tomato', group: 'Vegetables'},
{name: 'Cucumber', group: 'Vegetables'}
]
};
// $scope.user.favFood does not === $scope.formData.foods[0] - Using the "track by" option in the expression solves this
- Included as of Angular 1.2.x
<select ng-model="user.favFood" id="favFood" name="favFood"
ng-options="food.name for food in formData.foods track by food.id">
<option value="" selected disabled>Please select a food</option>
</select>Form Validation
Built-in Validation Directives
-
required - Value is required
-
pattern - Uses a regular expression to validate the value
-
minlength - Minimum number of characters
-
maxlength - Maximum number of characters
-
min - Minimum numeric value
- max - Maximum numeric value
<input type="number" ng-model="user.age" name="age" min="1" max="120" required>Form Validation State
- FormController - Holds the validation state of the form
-
ngModelController - Holds the validation state of a control
- ngModelController reports this state to the form controller
- Key API Methods:
- ngModelController.$setValidity(validationErrorKey, isValid)
- FormController.$setValidity(validationToken, isValid, control)
These states are applied to both FormController and ngModelController objects
-
$pristine - {boolean} - True if user has not interacted with the control yet.
-
$dirty - {boolean} - True if user has already interacted with the control.
-
$valid - {boolean} - True if there is no error.
- $invalid - {boolean} - True if at least one error on the control.
Form Validation States
Form Validation $error
- Each controller contains an $error object which stores the error state for particular validation directives
// The ngModelController.$error object holds a map each validation on the HTML Element
userForm.age.$error = {
required: false,
min: false,
max: true
}
// The FormController.$error object holds an map of validations, each holding
// the array of ngModelController objects
userForm.$error = {
max: [
// array containing each ngController Object that violates the "max" validation
],
required: [
// array each ngController Object that violates the "required" validation
]
}Validation CSS Styles
- Validation styles are css classes that are applied to the Form Control
- Based on the state of the FormController and ngModelController
- Applied to <form> element by form controller
- Applied to <control> element by ngModelController
Built-in Styles
Styles are empty by default
-
ng-valid - is set if the model is valid.
-
ng-invalid - is set if the model is invalid.
-
ng-pristine - is set if the model is pristine.
- ng-dirty - is set if the model is dirty.
Styles can be combined to give the meaning you desire
Other Useful Directives
- ngShow - shows or hides html based on boolean expression
- ngHide - shows or hides html based on boolean expression
- ngClass - Dynamically set CSS classes based on expression
Custom Validator
- Implemented by adding a parser function to the ngModelController.$parsers array
-
$parsers is an array of functions that are called when the view changes
-
Called during $setViewValue method
-
Each function is called in order passing the output as input to the subsequent function
-
The parser function should test for validity and call ngModel.$setValidity
- If the value is valid, the parsed value should be returned, otherwise, return undefined
-
Form Submission
- Designed for Ajax use
- Use ngClick with a submit button
- Use ngSubmit on form element
- Setting the "action" attribute on the form will submit form the traditional way
Directive Controllers
-
Directive Controllers are used to expose an API to one or more directives in a hierarchy
-
Directive Controllers can have $element--the element of the directive--injected into it.
- This is done because the purpose of this type of controller is to externalize business logic related to implementing the directive, bind events, etc.
- See Controller Bound Directive Example
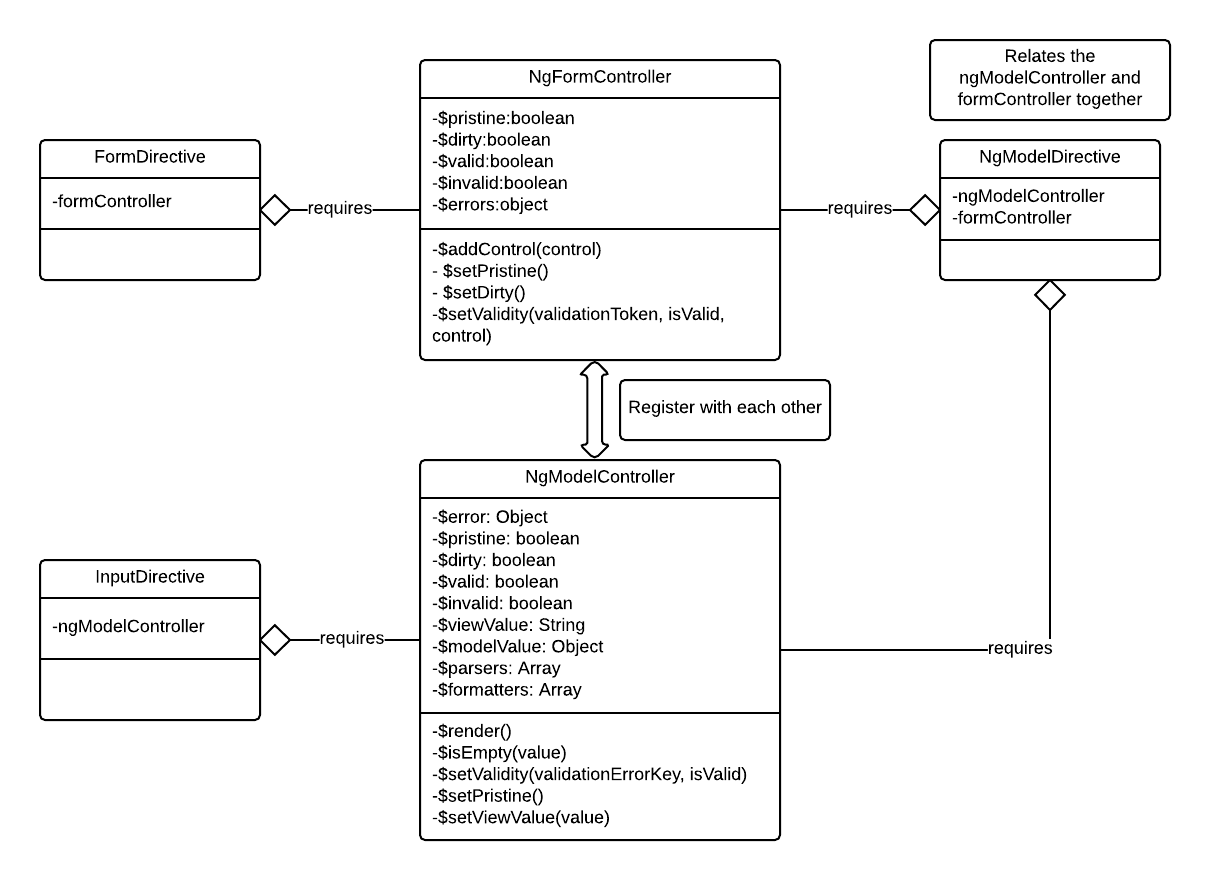
Form/NgModel Object Relationships
Forms in AngularJS
By Tom Acree
Forms in AngularJS
This presentation on AngularJS forms is being presented for the Columbus AngularJS meetup for October, 2014
- 1,274