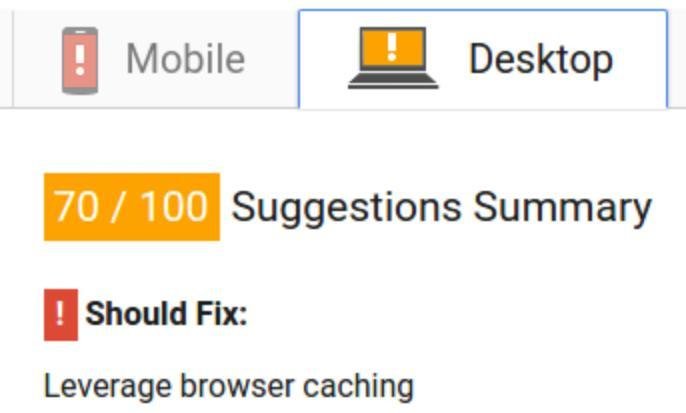
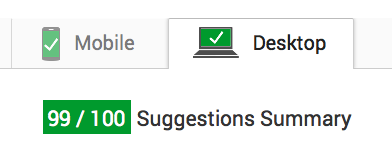
HTTP Caching 101
Why do we care?
The internet is not instant
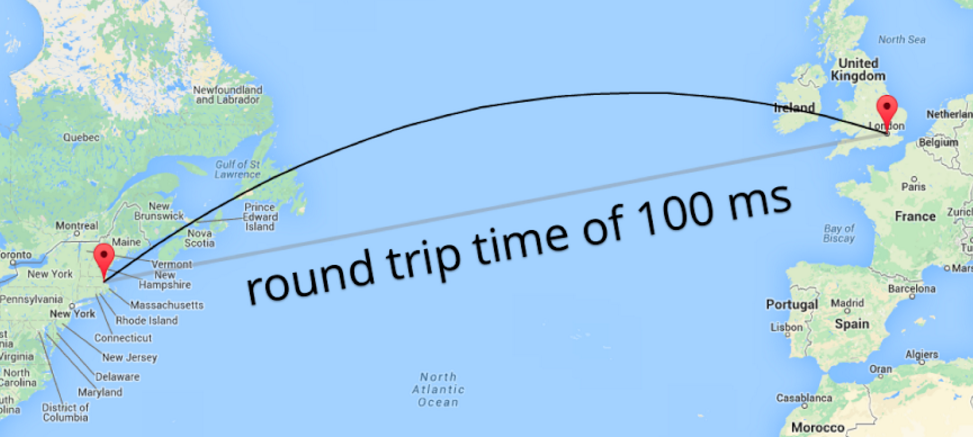
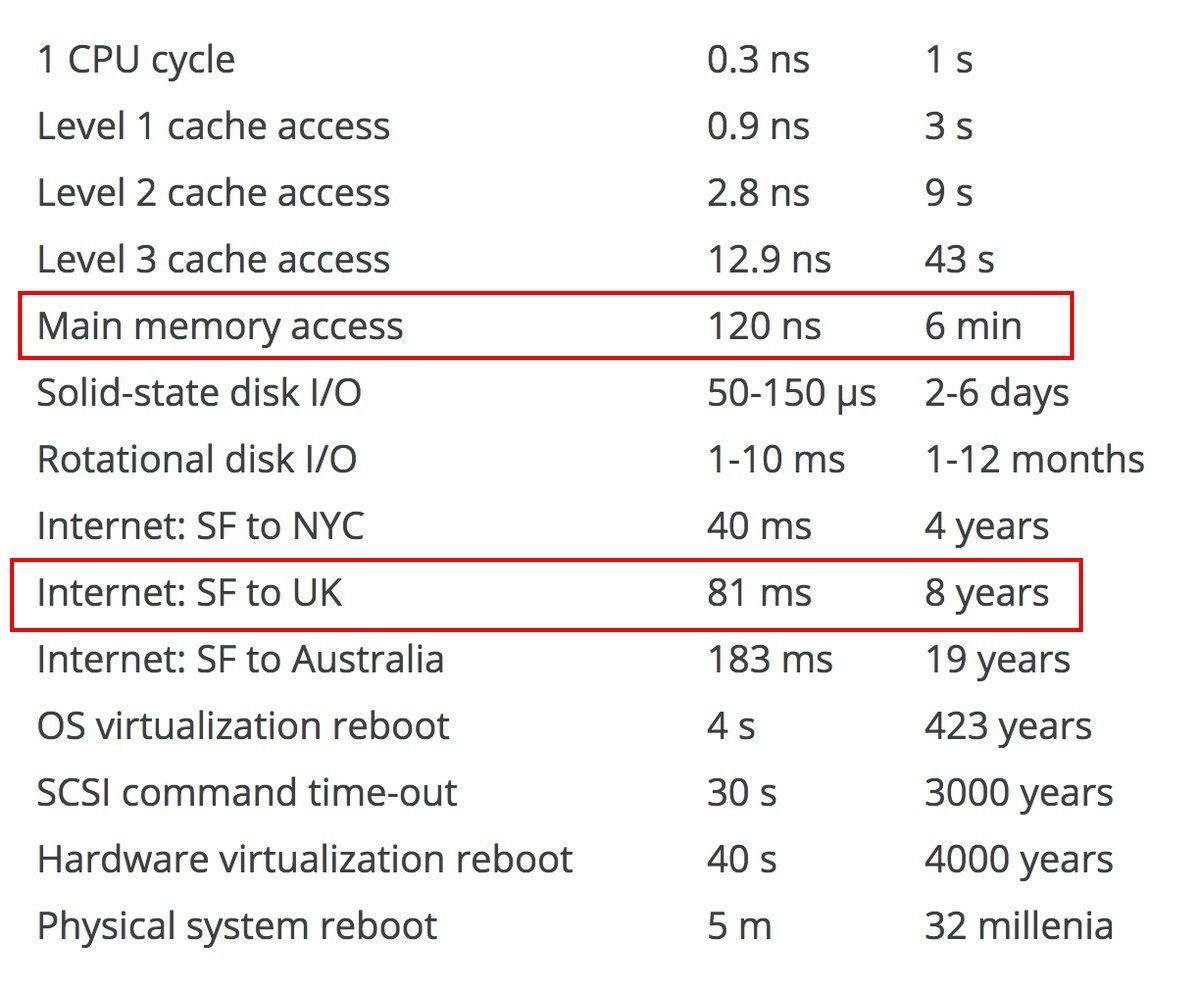
Human time
Without caching
100 ms => 10 years
With caching
120 ns => 6 minutes
How?

What can we cache?
Images
JavaScript
CSS
HTML
Where can we cache?
Browser
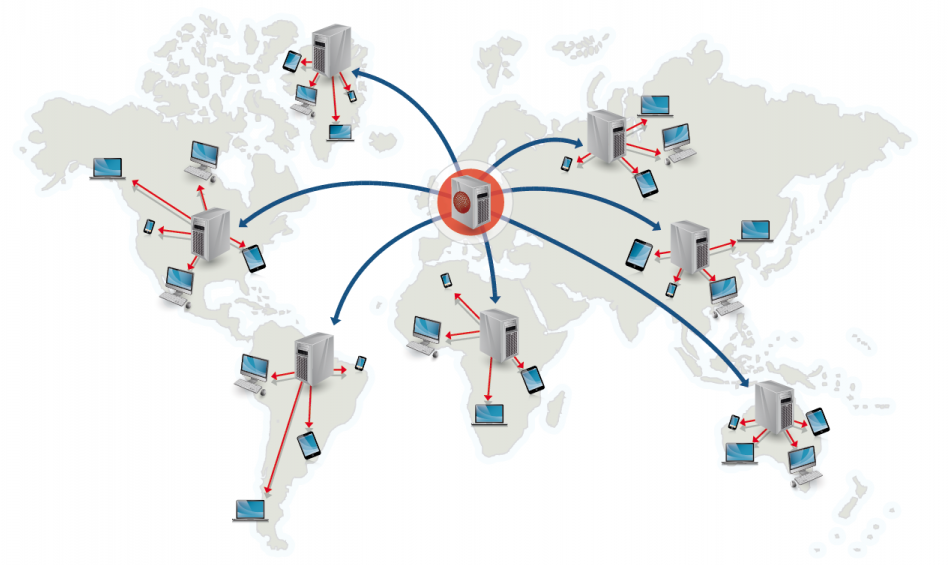
CDN (Content Delivery Network)
Server
Cooking dinner



Browser
CDN
Server
Browser


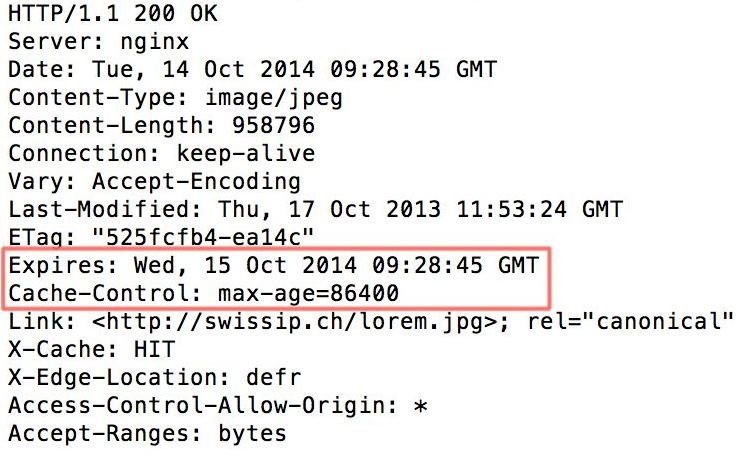
HTTP Response
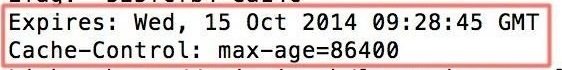
This can be confusing
| Max-age | Expires |
|---|---|
| Relative | Absolute |
| Takes priority | Used if max-age is missing |
Which is better?
No clocks and time zones
No DDOS
Max-age
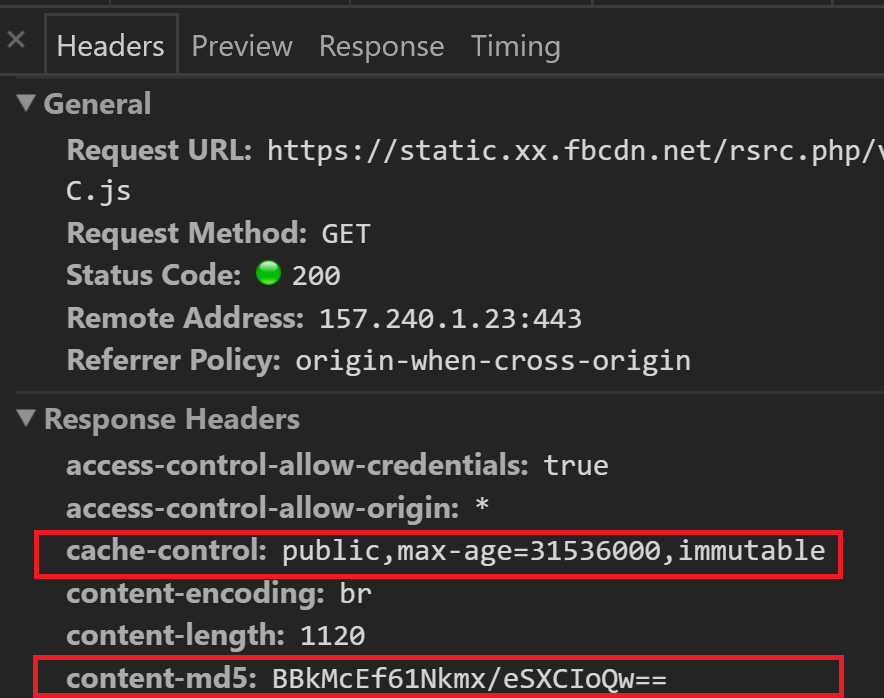
What happens when time runs out?
| E-tag | Last-Modified |
|---|---|
| MD5 hash of file | Date |
Has the file changed?
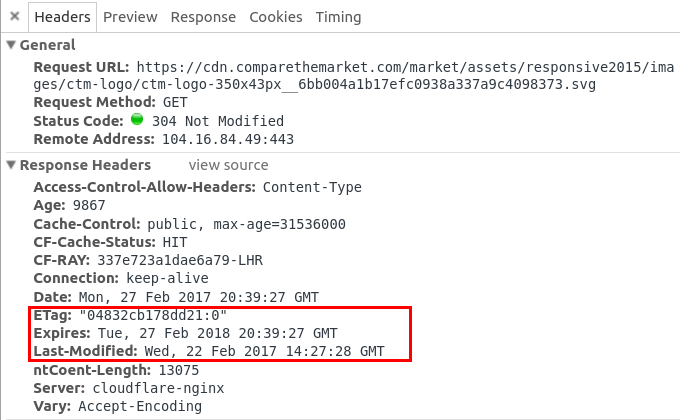
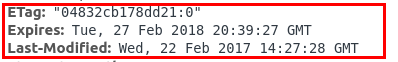


Can I use the cached file?
Has the time in max-age passed?
Cache-control
Expires
Current time < Expires time?
Yes
No
Use cache
Do I need to get a new version?
Yes
No
Use cache
Has it been modified since?
Has the Etag changed?
Get a new version!
Yes
Yes
No
Use cache
Use cache
No
Has the time in max-age passed?
Cache-control
Has the time in max-age passed?
Cache-control
Yes
No
Use cache
Has the Etag changed?
Has the time in max-age passed?
Cache-control
Yes
No
Use cache
Has the Etag changed?
Get a new version!
Yes
No
Use cache
So what happens if we change a file?
Cache-busting

File change => name change
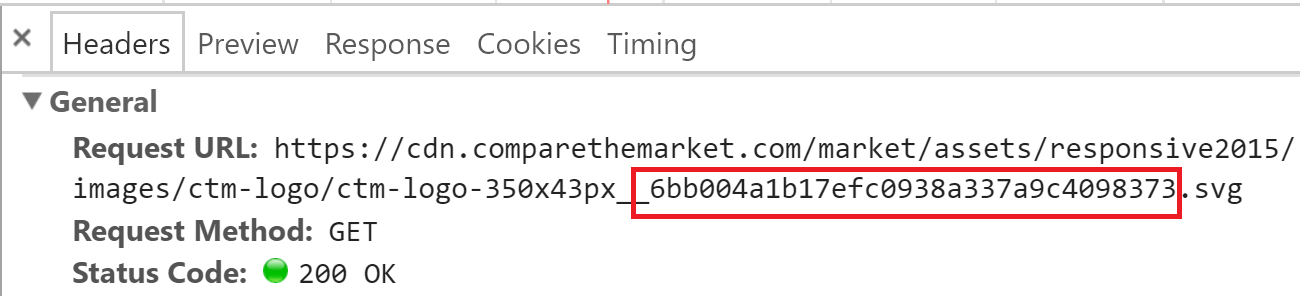
Relies on short-lived HTML
CDN

Server caching

Key points
Bring files closer to users
Browser is best
Generate less
Check your speed
- https://gtmetrix.com
- https://www.webpagetest.org
Thanks!
@thomdane
Caching
By Tom Dane
Caching
- 696



