React.js
Tiago Rodrigues
@trodrigues
JS/Frontend developer at contentful.com

What is React.js?
- A library for creating user interfaces
- Not a framework
- Implements the "view" part of MV*
What is react.js?
- React components describe:
- The structure of the UI
- The behavior of the UI
What is react.js?
- Heavy focus on JS features
- Small API
- Top level API
- Components API
What is react.js?
Why React.js?
- Closer link between view logic and representation
- Components create a virtual representation of the UI (Virtual DOM)
- Promotes a cleaner data flow *
Why React.js?
- What is view logic anyway?
- Fetching data to be rendered
- Preparing data to be rendered
- Handling view event handlers
Why React.js?
- What's the Virtual DOM?
- Your template is not rendered straight into HTML
- Creates an internal tree representation
Why React.js?
- How does it work?
- When something changes the tree nodes are compared
- The actual DOM is only changed if the tree changed
Why React.js?
- Advantages?
- Improves rendering speed *
- Allows rendering to other outputs
Why React.js?
Getting started
- Warning: some ES6 ahead
- Don't panic!
- https://babeljs.io/docs/learn-es2015
Getting started
- https://github.com/trodrigues/react-hot-boilerplate
- npm install
- npm start
- open http://localhost:3000/
- edit src/App.js
- git checkout stepX
- https://github.com/trodrigues/react-hot-boilerplate/branches
Getting started
App.js
// ES6 modules
import React, { Component } from 'react';
// ES6 classes
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>Hello, world.</h1>
);
}
}myfirstcomponent.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
export default class MyFirstComponent extends Component {
render() {
return (
<p>This is my first component</p>
);
}
}Branch: step1
Using our component
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './MyFirstComponent';
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
// This won't really work
return (
<h1>Hello, world.</h1>
<MyFirstComponent />
);
}
}Branch: step1
Using our component
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './MyFirstComponent';
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world.</h1>
<MyFirstComponent />
</div>
);
}
}Branch: step1
What is JSX?
- HTML/XML syntax inside JS
- Transformed into JS
- Just sugar on top of React.DOM
- You can use React.DOM directly
What is JSX?
- You can use HTML attributes
- Exceptions: className, htmlFor
- http://facebook.github.io/react/docs/dom-differences.html
- Event handlers
- declarative, on markup
- delegated
What is JSX?
Event handlers
export default class MyFirstComponent extends Component {
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>Do stuff</button>
);
}
handleClick() {
alert('Stuff is done!');
}
}Branch: step2
Using state
- this.state represents the component state
- When state changes, the component is re-rendered
- For that reason, state should be as small as possible
Using state
- Don't store computed data in state
- Don't store components or markup in state
Using state
Setting state
export default class MyFirstComponent extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = { count: 0 };
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>Clicked {this.state.count} times</p>
<button onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this)}>Do stuff</button>
</div>
);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
});
}
};Branch: step3
Computed data
export default class MyFirstComponent extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
items: [
{label: 'item 1', quantity: 4},
{label: 'item 2', quantity: 3}
]
};
}
render() {
var total = this.state.items.reduce((total, item) => total+item.quantity, 0);
return (
<p>Total: {total}</p>
);
}
};Branch: step4
Generated markup
export default class MyFirstComponent extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
items: [
{label: 'item 1', quantity: 4},
{label: 'item 2', quantity: 3}
]
};
}
render() {
var items = this.state.items.map(item => {
return <li>Item: {item.label}, Quantity: {item.quantity}</li>;
});
return (
<ul>{items}</ul>
);
}
};Branch: step5
Using props
- immutable parameters passed down by parent components
- change when parent component is re-rendered
using props
using props
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import MyFirstComponent from './MyFirstComponent';
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<MyFirstComponent message="hello world" />
);
}
}Branch: step6
using props
import React, { Component } from 'react';
export default class MyFirstComponent extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h1>{this.props.message}</h1>
);
}
};Branch: step6
lifecycle methods
- render
- getInitialState (or constructor)
- getDefaultProps
- componentWillMount
- componentDidMount
- componentWillReceiveProps
- shouldComponentUpdate
- componentWillUpdate
- componentDidUpdate
- componentWillUnmount
Lifecycle methods
Getting data
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const API_URL = 'http://pokeapi.co/';
const API_PATH = API_URL + 'api/v1/';
export default class Pokemon extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {name: '', image: ''};
}
componentDidMount() {...}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.state.name}</h1>
<img src={this.state.image} />
</div>
);
}
};Branch: step7
Getting data
import axios from 'axios';
const API_URL = 'http://pokeapi.co/';
const API_PATH = API_URL + 'api/v1/';
export default class Pokemon extends Component {
constructor(props){...}
componentDidMount() {
axios.get(API_PATH + `pokemon/${this.props.id}/`)
.then(response => {
var name = response.data.name;
axios.get(API_URL + response.data.sprites[0].resource_uri)
.then(response => this.setState({
name: name,
image: API_URL + response.data.image
}));
});
}
render() {...}
};Branch: step7
separating concerns
/* ... */
export default class Pokemon extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {name: '', image: ''};
}
componentDidMount() {
axios.get(API_PATH + `pokemon/${this.props.id}/`)
.then(response => {
var name = response.data.name;
axios.get(API_URL + response.data.sprites[0].resource_uri)
.then(response => this.setState({
name: name,
image: API_URL + response.data.image
}));
});
}
render() {
return (
<PokemonDisplay name={this.state.name} image={this.state.image} />
);
}
};Branch: step8
separating concerns
import React, { Component } from 'react';
export default class PokemonDisplay extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.state.name}</h1>
<img src={this.state.image} />
</div>
);
}
};
Branch: step8
- Higher level components deal with data
- Wrappers for display components
- https://medium.com/@dan_abramov/mixins-are-dead-long-live-higher-order-components-94a0d2f9e750
Higher order components
- Application architecture
- Patterns for dealing with data
- One way data flow
- No official implementation
What is flux?
Components
- Views
- Stores
- Actions
- Dispatcher
Dispatcher
- Usually a singleton
- Listens to actions (events)
- Registers callbacks which respond to actions
Views
- React.js view/controllers
- Get data from Stores
- Use that data to set view state
- Fire Actions with metadata
Stores
- Manage application data and state
- Not a model: can contain many models
- Can contain app state
- Should be concerned with a single domain
- Listen to actions which mutate its data
- Fire change events when state is changed
- Stores listen to each other via waitFor
Stores
var TodoStore = {
__proto__: EventEmitter.prototype,
_todos: [],
getAll: function() {
return this._todos;
},
emitChange: function() {
this.emit('change');
},
addChangeListener: function(callback) {
this.on('change', callback);
}
};
...Stores
...
AppDispatcher.register(function(action) {
switch(action.actionType) {
case TodoConstants.TODO_CREATE:
TodoStore._todos.push(action.text);
TodoStore.emitChange();
break;
}
});Actions
- Simple helper methods
- Trigger events to dispatcher with metadata
Actions
var TodoActions = {
create(text) {
AppDispatcher.dispatch({
actionType: TodoConstants.TODO_CREATE,
text: text
});
}
};Data flow
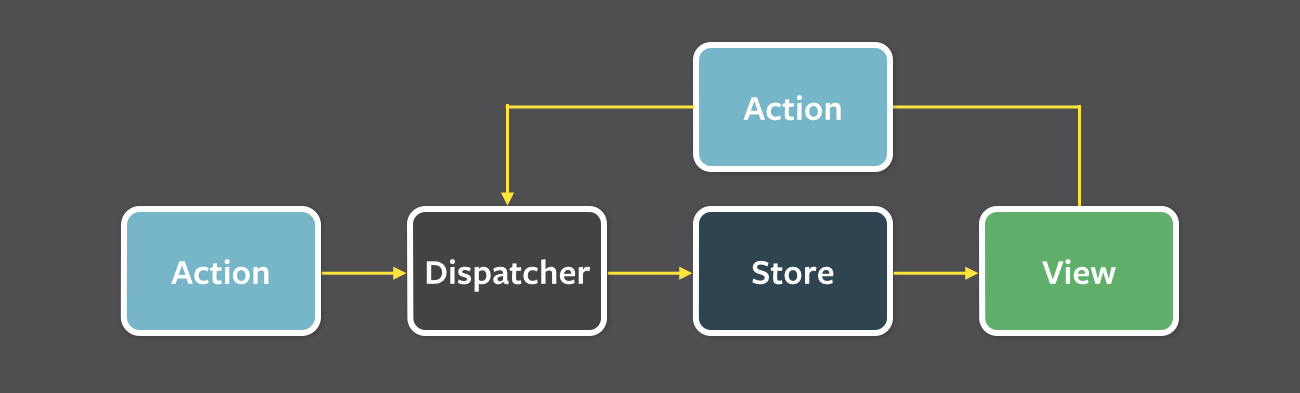
Flux implementations
- http://fluxxor.com/
- https://github.com/acdlite/flummox
- https://goatslacker.github.io/alt/
- https://github.com/kenwheeler/mcfly
- https://github.com/jmreidy/fluxy
- http://deloreanjs.com/
- http://martyjs.org/
- http://www.tuxedojs.org/
- https://github.com/yahoo/fluxible
- https://github.com/elierotenberg/nexus-flux
- https://github.com/spoike/refluxjs
- https://github.com/fdecampredon/rx-flux
Flux implementations
More at:
http://slides.com/trodrigues/flux-implementations
Relay and graphql
- Upcoming framework for data fetching in React
- Allows components to specify their data dependencies in GraphQL
- Relay centralizes and optimizes queries
relay and graphql
- Data is cached and reused efficiently
- Components only get the data they need
- Data passed via props,
- When props change, components re-render
relay and graphql
relay and graphql
react ecosystem
- Reusable shared components
- Good documentation
- Best practices articles
react ecosystem
- react-router / react-router-component
- react-async
- react-grid
- react-dnd
- react-hot-keys
- ...
components
components
Resources
That's all folks!
Thank you!
How does React even
By trodrigues
How does React even
- 1,624


