Introduction to Algorithms(IV)
- Sorting In Linear Time
Ting-Yun Tseng
曾庭筠
2014/09/27
Outline
- Sort Algorithms Review
- Decision-Tree Model
- Lower Bounds for Comparison Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Counting Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Radix Sort
Outline
- Sort Algorithms Review
- Decision-Tree Model
- Lower Bounds for Comparison Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Counting Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Radix Sort
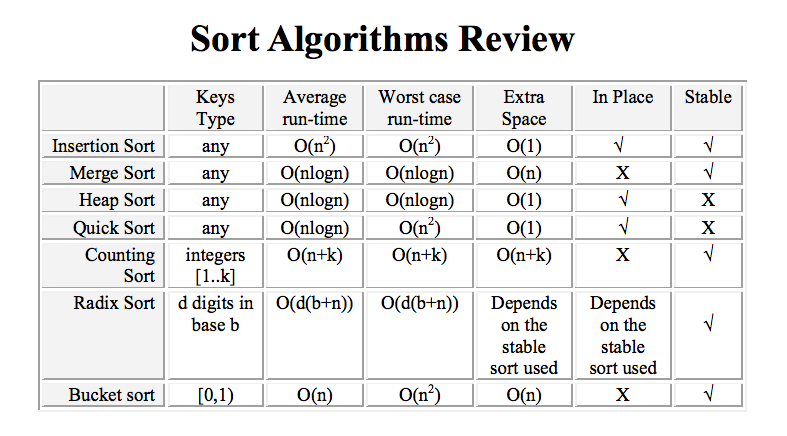
Sort Algorithms Review
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort
- QuickSort
Comparison Sort
- only use comparisons to determine relative order of elements.
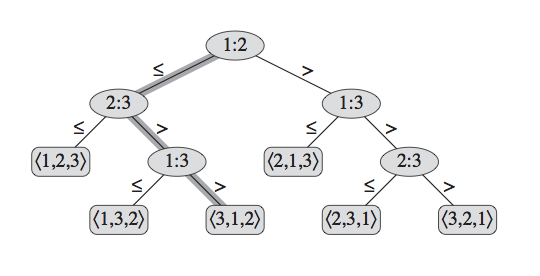
Decision-Tree Model
-
view comparison sorts abstractly in terms of decision trees
-
Control, data movement, and all other aspects of the algorithm are ignored
Hands - On
A = {a1, a2, a3, a4}
Draw the Decision Tree for Merge Sort on A
Outline
- Sort Algorithms Review
- Decision-Tree Model
- Lower Bounds for Comparison Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Counting Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Radix Sort
Lower bound for Comparison Sort
Use decision tree to clarify the meaning of Running Time
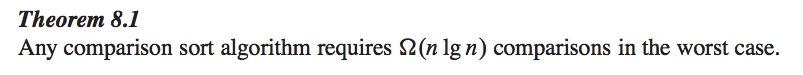
- Running Time = Number Of Comparisons
= Length Of Path
- Worse Case Running Time = Height Of Tree
According to the former theorem...
[Corollary]
- Merge Sort and HeapSort are asymptotically optimal comparison sorts.
- Randomized QuickSort algorithm is asymptotically optimal in expectation.
CAN WE DO BETTER ?
Outline
- Sort Algorithms Review
- Decision-Tree Model
- Lower Bounds for Comparison Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Counting Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Radix Sort
Counting Sort
Input : A[1,2,...n], each A[i] belongs to {1,2,...,k}
Output : B[1,2,....n] = sorting of A

Analysis of Counting Sort
Running Time of Counting Sort = theta(k+n)
- When k = O(n) , Running Time = theta(n)
- When k may larger that O(nlgn) --> use merge sort
**Counting Sort is a stable sorting algorithm
What is stable?
Stable Sorting Algorithm preserves the relative order of equal elements
[***Explanation on white board***]
Q : Which other sorting algorithms are stable?
And which are not?
Answer : Insertion Sort and Merge Sort are stable.
QuickSort is not stable.
Outline
- Sort Algorithms Review
- Decision-Tree Model
- Lower Bounds for Comparison Sort
- Sorting in Linear Time - Counting Sort
-
Sorting in Linear Time - Radix Sort
SUPER SMART ALGORITHM
Radix Sort
Input : A[1,2,...,n], each A[i] has d digits where digit 1 is the lowest-order digit and digit d is the highest-order digit.
Output : A[1',2',...,n'] with A[1']<=...<=A[n']

Analysis of Radix Sort (I)
Decimal digits (Lemma8.3)
- Running Time of Radix Sort = theta(d(k+n)) if stable sort takes theta(k+n) time.
Analysis of Radix Sort (II)
Binary digits (Lemma8.4)
Given n b-bits numbers, and any positive number r>0
- Running Time of Radix Sort = theta((b/r)(n+2^r))
if stable sort takes theta(k+n) time for input in the range(0,k)
Q : Is Radix Sort stable?
A : Yes, it uses stable sort to sort array A on digit i .
Summary
END
Sorting in Linear Time
By tseng0211
Sorting in Linear Time
- 788



