DESPOT/DESPOT-\(\alpha\)
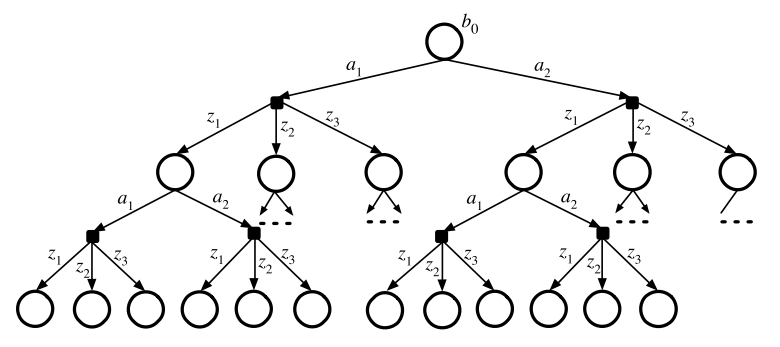
Standard Belief Tree
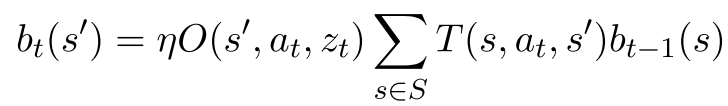
\(\mathcal{O}(|A|^DC^D) \)(|A|^D||Z|^D)
DESPOT
\(\mathcal{O}(K|A|^D)\)
DEterminized Sparse Partially Observable Tree
Sparse: Create subset of possible state trajectories from belief tree via scenarios
Determinized: Scenarios are randomly sampled state trajectories using a deterministic simulative model
Text
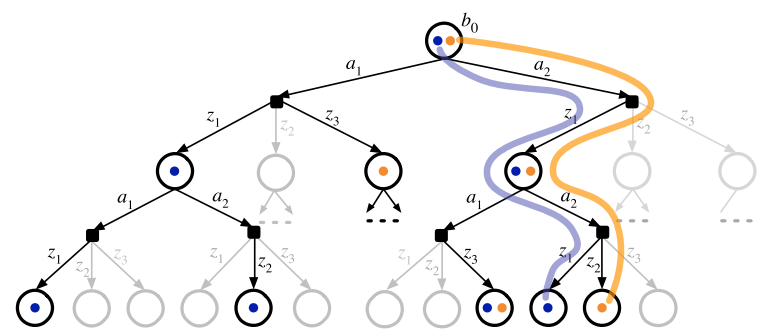
Determinization
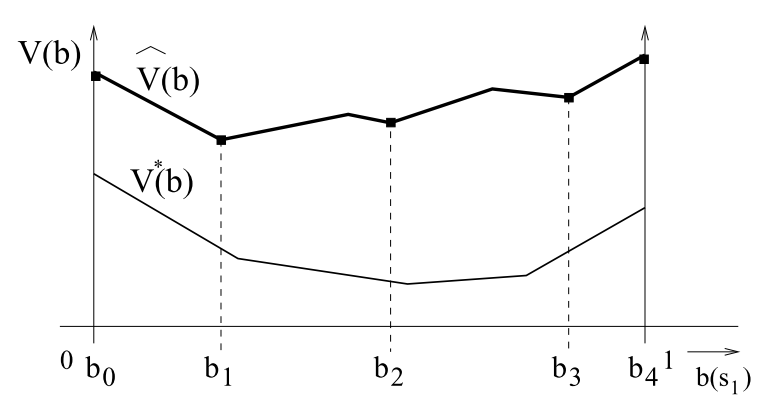
Purpose: Don't want to attribute reward gains or losses due to process noise to the value inherent to a belief state.
Consequence: Possible Overfitting
Empirical policy belief value
Generalizing to any node in the constructed tree, define regularized, weighted, discounted utility (RWDU) as:
Regularize Reward
Belief Node Backup
Start at leaf belief nodes
Move through internal belief nodes
Evaluate best action at root belief node
ARDESPOT
(Anytime Regularized DESPOT)
Construct tree incrementally with belief value bounds heuristics
\(l(b), \mu(b)\) : lower and upper bounds of optimal RWDU at belief node \(b\) \(\rightarrow l(b) \le \nu^*(b) \le \mu(b)\)
\( L_0(b), U(b)\) : lower and upper bounds of non-regularized belief value \(\rightarrow L_0(b) \le \hat{V}^*(b) \le U(b)\)
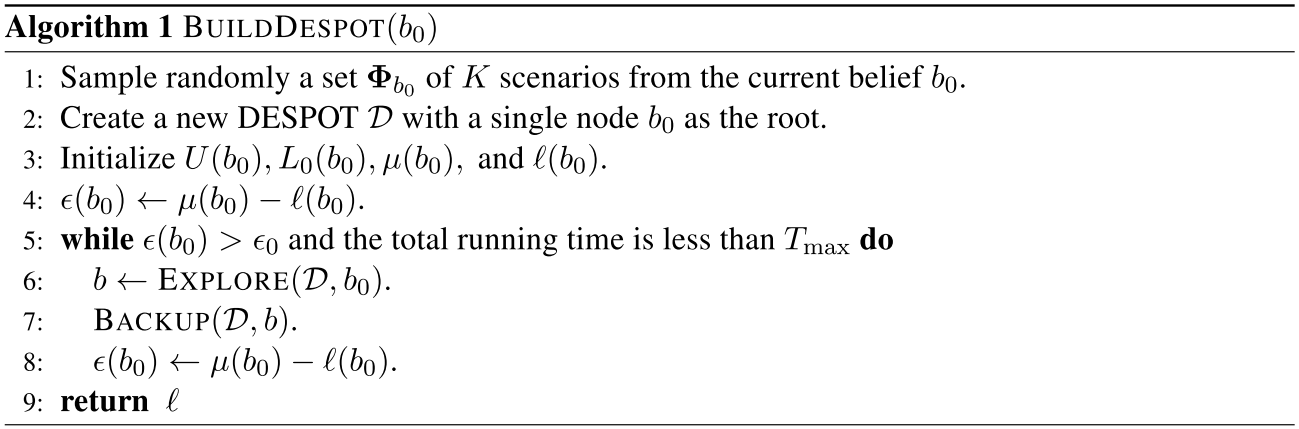
\(\xi\) : Tuning parameter - Desired RWDU bounds contraction rate at root node \(b_0\)
Cease exploration once \(E(b') \le 0 \). Exploration beyond this point yields minimal RWDU bounds contraction

Pruning

Blocked if
Backup
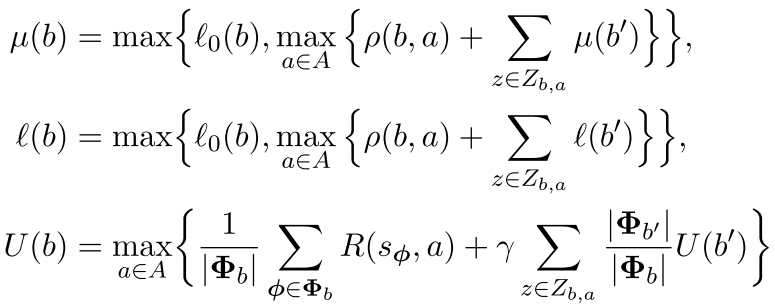
DESPOT-\(\alpha\)
DESPOT with \(\alpha\)-vector update
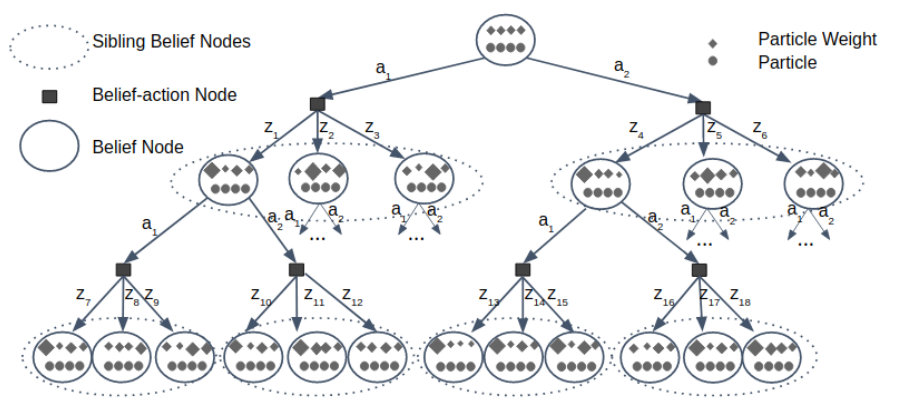
Belief in state determined by weight of representative particle
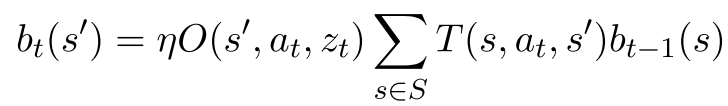

- Using \(C \le K\) scenarios at each belief-action node to generate observation branches
- Re-weighting all particles for each new belief node is computationally costly relative to DESPOT
- Save computation time using parallelizable \(\alpha\)-vectors on sibling nodes
- Sibling nodes share same scenarios with same states just different beliefs over these states
- Assume sibling beliefs are similar in terms of conditional plan that maximizes their values
- Holds for larger observation spaces
Upper bounds maintained with sawtooth approximation

Choose set of grid points to be an arbitrary grid point \(b' \in G\) and \(|S|-1\) extreme points of the belief simplex
Leaf Node
Internal Nodes
Text
DESPOT-(alpha)
By Tyler Becker
DESPOT-(alpha)
- 511



