Java 8 STREAMS
Ümit ÜNAL - n11.com
Java 8 STREAMS
What is a Stream?
- Streams have no storage.
- The design of streams is based on internal iteration.
- Streams are designed to support functional programming.
- Streams support lazy operations.
- Streams can be ordered or unordered.
- Streams cannot be reused.
Java 8 STREAMS
Internal vs. External Iteration
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
int sum = 0;
for (int n : numbers) {
if (n % 2 == 1) {
int square = n * n;
sum = sum + square;
}
}int sum = numbers.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.map(n -> n * n)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);Java 8 STREAMS
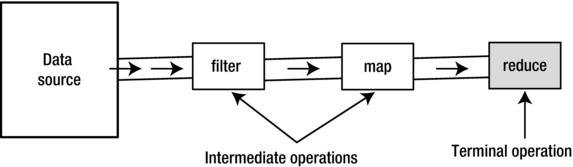
Stream Operations
- Intermediate operations
- Terminal operations
A stream supports two types of operations:
Java 8 STREAMS
Stream Operations
Java 8 STREAMS
Stream Operations
Step by step Stream
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
int sum = numbers.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.map(n -> n * n)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);Java 8 STREAMS
Stream Operations
Step by step Stream
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
int sum = numbers.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.map(n -> n * n)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);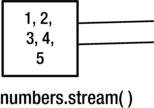
Java 8 STREAMS
Stream Operations
Step by step Stream
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
int sum = numbers.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.map(n -> n * n)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);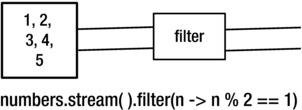
Java 8 STREAMS
Stream Operations
Step by step Stream
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
int sum = numbers.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.map(n -> n * n)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);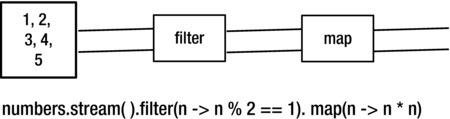
Java 8 STREAMS
Stream Operations
Step by step Stream
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
int sum = numbers.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.map(n -> n * n)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);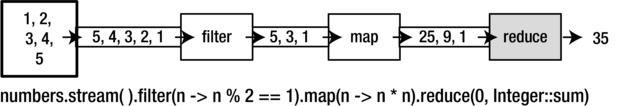
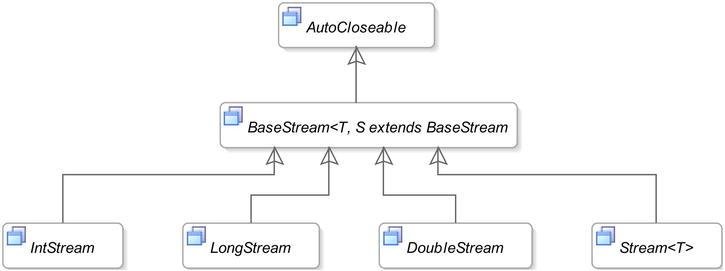
Java 8 STREAMS
Architecture of the Streams API
Java 8 STREAMS
Creating Streams
Streams from Values
<T> Stream<T> of(T t)
<T> Stream<T> of(T...values)
// Creates a stream with one string elements
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("Hello");
// Creates a stream with four strings
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("Ken", "Jeff", "Chris", "Ellen");
// Compute the sum of the squares of all odd integers in the list
int sum = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.map(n -> n * n)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
// Result
Sum = 35
Java 8 STREAMS
Creating Streams
Streams from Values
String[] names = {"Ken", "Jeff", "Chris", "Ellen"};
// Creates a stream of four strings in the names array
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of(names);Java 8 STREAMS
Creating Streams
Streams from Functions
Stream.iterate(1L, n -> n + 2).limit(5)
.forEach(System.out::println);
// Result:
1
3
5
7
9
////////////////////////////////////
Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(5)
.forEach(System.out::println);
// Result:
0.05958352209327644
0.8122226657626394
0.5073323815997652
0.9327951597282766
0.4314430923877808Java 8 STREAMS
Creating Streams
Streams from Arrays
// Creates a stream from an int array with elements 1, 2, and 3
IntStream numbers = Arrays.stream(new int[]{1, 2, 3});
// Creates a stream from a String array with elements "Ken", and "Jeff"
Stream<String> names = Arrays.stream(new String[] {"Ken", "Jeff"});Java 8 STREAMS
Creating Streams
Streams from Collections
// Create and populate a set of strings
Set<String> names = new HashSet<>();
names.add("Ken");
names.add("jeff");
// Create a sequential stream from the set
Stream<String> sequentialStream = names.stream();
// Create a parallel stream from the set
Stream<String> parallelStream = names.parallelStream();Java 8 STREAMS
Creating Streams
Streams from Other Sources
String str = "5 apples and 25 oranges";
str.chars()
.filter(n -> !Character.isDigit((char)n) && !Character.isWhitespace((char)n))
.forEach(n -> System.out.print((char)n));
// Result :
applesandoranges
String str = "Ken,Jeff,Lee";
Pattern.compile(",")
.splitAsStream(str)
.forEach(System.out::println);
// Result :
Ken
Jeff
LeeJava 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Common Stream Operations
Intermediate
- Distinct
- filter
- flatMap
- limit
- map
- peek
- skip
- sorted
Terminal
- allMatch
- anyMatch
- findAny
- findFirst
- noneMatch
- forEach
- reduce
Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Debugging a Stream Pipeline
int sum = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.peek(e -> System.out.println("Taking integer: " + e))
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 1)
.peek(e -> System.out.println("Filtered integer: " + e))
.map(n -> n * n)
.peek(e -> System.out.println("Mapped integer: " + e))
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
//Result:
Taking integer: 1
Filtered integer: 1
Mapped integer: 1
Taking integer: 2
Taking integer: 3
Filtered integer: 3
Mapped integer: 9
Taking integer: 4
Taking integer: 5
Filtered integer: 5
Mapped integer: 25
Sum = 35Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Applying the ForEach Operation
void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action)
void forEachOrdered(Consumer<? super T> action)
Person.persons()
.stream()
.filter(Person::isFemale)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//Result:
(3, Donna, FEMALE, 1962-07-29, 8700.00)
(5, Laynie, FEMALE, 2012-12-13, 0.00)Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Applying the ForEach Operation
// Get the list of persons
List<Person> persons = Person.persons();
// Print the list
System.out.println("Before increasing the income: " + persons);
// Increase the income of females by 10%
persons.stream()
.filter(Person::isFemale)
.forEach(p -> p.setIncome(p.getIncome() * 1.10));
// Print the list again
System.out.println("After increasing the income: " + persons);
Before increasing the income: [(1, Ken, MALE, 1970-05-04, 6000.00),
(2, Jeff, MALE, 1970-07-15, 7100.00),(3, Donna, FEMALE, 1962-07-29, 8700.00),
(4, Chris, MALE, 1993-12-16, 1800.00), (5, Laynie, FEMALE, 2012-12-13, 0.00),
(6, Li, MALE, 2001-05-09, 2400.00)]
After increasing the income: [..(3, Donna, FEMALE, 1962-07-29, 9570.00)..]Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Applying the Map Operation
<R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T,? extends R> mapper)
DoubleStream mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T> mapper)
IntStream mapToInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> mapper)
LongStream mapToLong(ToLongFunction<? super T> mapper)
ToDoubleFunction:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToDoubleFunction<T> {
/**
* Applies this function to the given argument.
*
* @param value the function argument
* @return the function result
*/
double applyAsDouble(T value);
}
You can apply the map operation on a stream using one of the following methods of the Stream<T> interface
Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Applying the Map Operation
IntStream map(IntUnaryOperator mapper)
DoubleStream mapToDouble(IntToDoubleFunction mapper)
LongStream mapToLong(IntToLongFunction mapper)
<U> Stream<U> mapToObj(IntFunction<? extends U> mapper)
IntToDoubleFunction:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface IntToDoubleFunction {
/**
* Applies this function to the given argument.
*
* @param value the function argument
* @return the function result
*/
double applyAsDouble(int value);
}
Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Applying the Map Operation
IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 5).map(n -> n * n)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//Result :
1
4
9
16
25
Person.persons().stream().map(Person::getName)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//Result :
Ken
Jeff
Donna
Chris
Laynie
LiJava 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Flattening Streams
Stream.of(1, 2, 3)
.map(n -> Stream.of(n, n * n))
.forEach(System.out::println);
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@372f7a8d
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@2f92e0f4
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@28a418fcJava 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Flattening Streams
Stream.of(1, 2, 3)
.map(n -> Stream.of(n, n * n))
.forEach(e -> e.forEach(System.out::println));
// Result :
1
1
2
4
3
9Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Flattening Streams
Stream.of(1, 2, 3)
.flatMap(n -> Stream.of(n, n * n))
.forEach(System.out::println);
1
1
2
4
3
9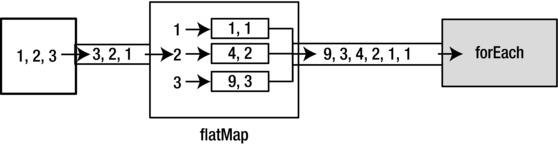
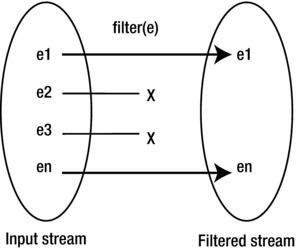
Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Applying the Filter Operation
You can apply a filter operation to a stream using the filter() method of the Stream, IntStream, LongStream, and DoubleStream interfaces. The method accepts an instance of the Predicate interface.
Java 8 STREAMS
Applying Operations on Streams
Applying the Filter Operation
Person.persons()
.stream()
.filter(Person::isFemale)
.map(Person::getName)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//Result :
Donna
Laynie
Person.persons()
.stream()
.filter(p -> p.isMale() && p.getIncome() > 5000.0)
.map(Person::getName)
.forEach(System.out::println);
//Result :
Ken
JeffJava 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
<R> R collect(Supplier<R> supplier, BiConsumer<R,? super T> accumulator,
BiConsumer<R,R> combiner)
<R,A> R collect(Collector<? super T,A,R> collector)Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
// Using a lambda expression
Supplier<ArrayList<String>> supplier = () -> new ArrayList<>();
// Using a constructor reference
Supplier<ArrayList<String>> supplier = ArrayList::new;// Using a lambda expression
BiConsumer<ArrayList<String>, String> accumulator = (list, name) -> list.add(name);
// Using a constructor reference
BiConsumer<ArrayList<String>, String> accumulator = ArrayList::add;
// Using a lambda expression
BiConsumer<ArrayList<String>, ArrayList<String>> combiner =
(list1, list2) -> list1.addAll(list2);
// Using a constructor reference
BiConsumer<ArrayList<String>, ArrayList<String>> combiner = ArrayList::addAll;Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
List<String> names = Person.persons()
.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(ArrayList::new, ArrayList::add, ArrayList::addAll);
System.out.println(names);
[Ken, Jeff, Donna, Chris, Laynie, Li]
Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
List<String> names = Person.persons()
.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(names);
[Ken, Jeff, Donna, Chris, Laynie, Li]Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
Set<String> uniqueNames = Person.persons()
.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(uniqueNames);
[Donna, Ken, Chris, Jeff, Laynie, Li]Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
SortedSet<String> uniqueSortedNames= Person.persons()
.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));
System.out.println(uniqueSortedNames);
[Chris, Donna, Jeff, Ken, Laynie, Li]Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
List<String> sortedName = Person.persons()
.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedName);
[Chris, Donna, Jeff, Ken, Laynie, Li]Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
long count = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("Person count: " + count);
Person count: 6
Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data Using Collectors
long count = Person.persons()
.stream()
.count();
System.out.println("Persons count: " + count);
Persons count: 6Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Summary Statistics
- DoubleSummaryStatistics
- LongSummaryStatistics
- IntSummaryStatistics
Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Summary Statistics
DoubleSummaryStatistics incomeStats =
Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Person::getIncome));
System.out.println(incomeStats);
DoubleSummaryStatistics{count=6, sum=26000.000000, min=0.000000,
average=4333.333333, max=8700.000000}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Summary Statistics
DoubleSummaryStatistics stats = new DoubleSummaryStatistics();
stats.accept(100.0);
stats.accept(500.0);
stats.accept(400.0);
// Get stats
long count = stats.getCount();
double sum = stats.getSum();
double min = stats.getMin();
double avg = stats.getAverage();
double max = stats.getMax();
count=3, sum=1000.00, min=100.00, average=500.00, max=333.33Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data in Maps
toMap(Function<? super T,? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T,? extends U> valueMapper)
toMap(Function<? super T,? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T,? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction)Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data in Maps
Map<Long,String> idToNameMap = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getId, Person::getName));
System.out.println(idToNameMap);
{1=Ken, 2=Jeff, 3=Donna, 4=Chris, 5=Laynie, 6=Li}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data in Maps
Map<Person.Gender,String> genderToNamesMap = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getGender, Person::getName));
The code throws the following runtime exception. java.lang.IllegalStateException: Duplicate key Ken
Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data in Maps
Map<Person.Gender,String> genderToNamesMap = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
Person::getGender,
Person::getName,
(oldValue, newValue) -> String.join(", ", oldValue, newValue)
));
System.out.println(genderToNamesMap);
{FEMALE=Donna, Laynie, MALE=Ken, Jeff, Chris, Li}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Collecting Data in Maps
Map<Person.Gender, Long> countByGender = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getGender, p -> 1L,
(oldCount, newCount) -> oldCount++));
System.out.println(countByGender);
{MALE=4, FEMALE=2}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Joining Strings Using Collectors
joining()
joining(CharSequence delimiter)
joining(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence prefix, CharSequence suffix)Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Joining Strings Using Collectors
String names = persons.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println("Joined names: " + names);
Joined names: KenJeffDonnaChrisLaynieLiJava 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Joining Strings Using Collectors
String delimitedNames = persons.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
System.out.println("Joined, delimited names: " + delimitedNames);
Joined, delimited names: Ken, Jeff, Donna, Chris, Laynie, Li
Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Joining Strings Using Collectors
String prefixedNames = persons.stream()
.map(Person::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", ", "Hello ", ". Goodbye."));
System.out.println(prefixedNames);
Hello Ken, Jeff, Donna, Chris, Laynie, Li. Goodbye.
Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Grouping Data
groupingBy(Function<? super T,? extends K> classifier)
groupingBy(Function<? super T,? extends K> classifier,
Collector<? super T,A,D> downstream)
groupingBy(Function<? super T,? extends K> classifier,
Supplier<M> mapFactory,
Collector<? super T,A,D> downstream)Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Grouping Data
Map<Person.Gender, List<Person>> personsByGender =
Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getGender));
System.out.println(personsByGender);
// Result
{FEMALE=[(3, Donna, FEMALE, 1962-07-29, 8700.00),
(5, Laynie, FEMALE, 2012-12-13, 0.00)],
MALE=[(1, Ken, MALE, 1970-05-04, 6000.00),
(2, Jeff, MALE, 1970-07-15, 7100.00),
(4, Chris, MALE, 1993-12-16, 1800.00),
(6, Li, MALE, 2001-05-09, 2400.00)]}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Grouping Data
Map<Person.Gender, Long> countByGender = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getGender,
Collectors.counting()));
System.out.println(countByGender);
{MALE=4, FEMALE=2}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Grouping Data
Map<Person.Gender, String> namesByGender = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getGender,
Collectors.mapping(Person::getName,
Collectors.joining(", "))));
System.out.println(namesByGender);
// Result :
{MALE=Ken, Jeff, Chris, Li, FEMALE=Donna, Laynie}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Grouping Data
Map<Person.Gender, Map<Month, String>> personsByGenderAndDobMonth =
Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getGender,
Collectors.groupingBy(p -> p.getDob().getMonth(),
Collectors.mapping(Person::getName,
Collectors.joining(", ")))));
System.out.println(personsByGenderAndDobMonth);
// Result
{FEMALE={DECEMBER=Laynie, JULY=Donna},
MALE={DECEMBER=Chris, JULY=Jeff, MAY=Ken, Li}}
Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Grouping Data
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(new Integer[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 });
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> evenOddMap = integerList
.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(i -> i % 2 == 0 ? 0 : 1));
// Will print 2, 4, 6, 8
System.out.println(evenOddMap.get(0));
// Will print 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
System.out.println(evenOddMap.get(1));Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Partitioning Data
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate,
Collector<? super T,A,D> downstream)Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Partitioning Data
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> partionedByMaleGender = Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(Person::isMale));
System.out.println(partionedByMaleGender);
{false=[(3, Donna, FEMALE, 1962-07-29, 8700.00),
(5, Laynie, FEMALE, 2012-12-13, 0.00)],
true=[(1, Ken, MALE, 1970-05-04, 6000.00),
(2, Jeff, MALE, 1970-07-15, 7100.00),
(4, Chris, MALE, 1993-12-16, 1800.00),
(6, Li, MALE, 2001-05-09, 2400.00)]}Java 8 STREAMS
Collectors on Streams
Partitioning Data
Map<Boolean,String> partionedByMaleGender =
Person.persons()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(Person::isMale,
Collectors.mapping(Person::getName, Collectors.joining(", "))));
System.out.println(partionedByMaleGender);
{false=Donna, Laynie, true=Ken, Jeff, Chris, Li}Java 8 STREAMS
Finding and Matching in Streams
boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)Java 8 STREAMS
Finding and Matching in Streams
// Check if all persons are males
boolean allMales = Person.stream().allMatch(Person::isMale);
System.out.println("All males: " + allMales);
// Result :
All males: falseJava 8 STREAMS
Finding and Matching in Streams
// Check if any person was born in 1970
boolean anyoneBornIn1970 = Persons.stream()
.anyMatch(p -> p.getDob().getYear() == 1970);
System.out.println("Anyone born in 1970: " + anyoneBornIn1970);
// Result :
Anyone born in 1970: trueJava 8 STREAMS
Finding and Matching in Streams
// Check if any person was born in 1955
boolean anyoneBornIn1955 = Persons.stream()
.anyMatch(p -> p.getDob().getYear() == 1955);
System.out.println("Anyone born in 1955: " + anyoneBornIn1955);
// Result
Anyone born in 1955: falseJava 8 STREAMS
Refactoring Legacy Code
public Set<String> findLongTracks(List<Album> albums) {
Set<String> trackNames = new HashSet<>();
for(Album album : albums) {
for (Track track : album.getTrackList()) {
if (track.getLength() > 60) {
String name = track.getName();
trackNames.add(name);
}
}
}
return trackNames;
}Java 8 STREAMS
Refactoring Legacy Code
public Set<String> findLongTracks(List<Album> albums) {
Set<String> trackNames = new HashSet<>();
albums.stream()
.forEach(album -> {
album.getTracks()
.forEach(track -> {
if (track.getLength() > 60) {
String name = track.getName();
trackNames.add(name);
}
});
});
return trackNames;
}Java 8 STREAMS
Refactoring Legacy Code
public Set<String> findLongTracks(List<Album> albums) {
Set<String> trackNames = new HashSet<>();
albums.stream()
.forEach(album -> {
album.getTracks()
.filter(track -> track.getLength() > 60)
.map(track -> track.getName())
.forEach(name -> trackNames.add(name));
});
return trackNames;
}Java 8 STREAMS
Refactoring Legacy Code
public Set<String> findLongTracks(List<Album> albums) {
Set<String> trackNames = new HashSet<>();
albums.stream()
.flatMap(album -> album.getTracks())
.filter(track -> track.getLength() > 60)
.map(track -> track.getName())
.forEach(name -> trackNames.add(name));
return trackNames;
}
Java 8 STREAMS
Refactoring Legacy Code
public Set<String> findLongTracks(List<Album> albums) {
return albums.stream()
.flatMap(album -> album.getTracks())
.filter(track -> track.getLength() > 60)
.map(track -> track.getName())
.collect(toSet());
}
Java 8 STREAMS
QA
Java 8 STREAMS
THANKS
Ümit ÜNAL

https://github.com/umitunal/java8-for-nerd/
Java 8 Streams
By umitunal
Java 8 Streams
Java 8 Streams
- 1,684
