React on the Blockchain
The missing Getting Started Guide.
Web / Mobile / VR / AR / IoT / AI / Blockchain
Software architect, author, entrepreneur

Lead Architect
creating a robust, performant, and feature-rich online conferencing experience

Blockchain
A blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data (generally represented as a Merkle tree). By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of its data. This is because once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks. (c) Wikipedia
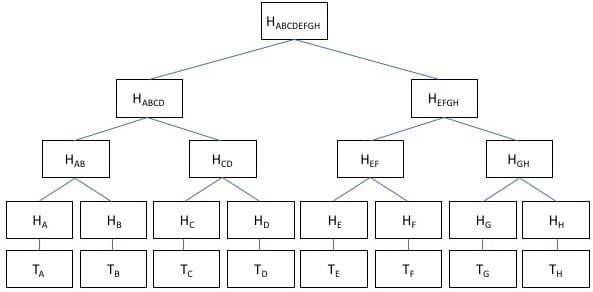
- Merkle trees
- Cryptography
- Transactions
- Blocks


Network
address (wallet)
You connect to a single Node
node
node
node
node
node
node
Database
Stores information
- Made up of transactions (any change is basically an immutable "record")
- Transactions are grouped into bundles called blocks
- All blocks grouped together is public ledger (Current state of the blockchain in the history)
Computer
Some blockchains support ways to run programs
- Every Node in the blockchain is a computer
- Node can run computations
Etherium
General purpose blockchain that allows you to run your own programs
To use Etherium you need an "account"
- public key
- private key
node
node
node
node
node
node
EVM Client
Local blockchain copy
account
submit transaction
Miner node
Miner node
Miner node
node
node
node
node
node
node
All nodes need to talk to each other and reach consensus
Transaction validation
Consensus Mechanism
Transaction validation
All nodes need to talk to each other and reach consensus
How mining works
Submit transaction (paying gas)
Transaction is submitted
Mining nodes try to "guess" the crypto puzzles
Transaction is complete
Nodes receive a reward for the Proof of Work
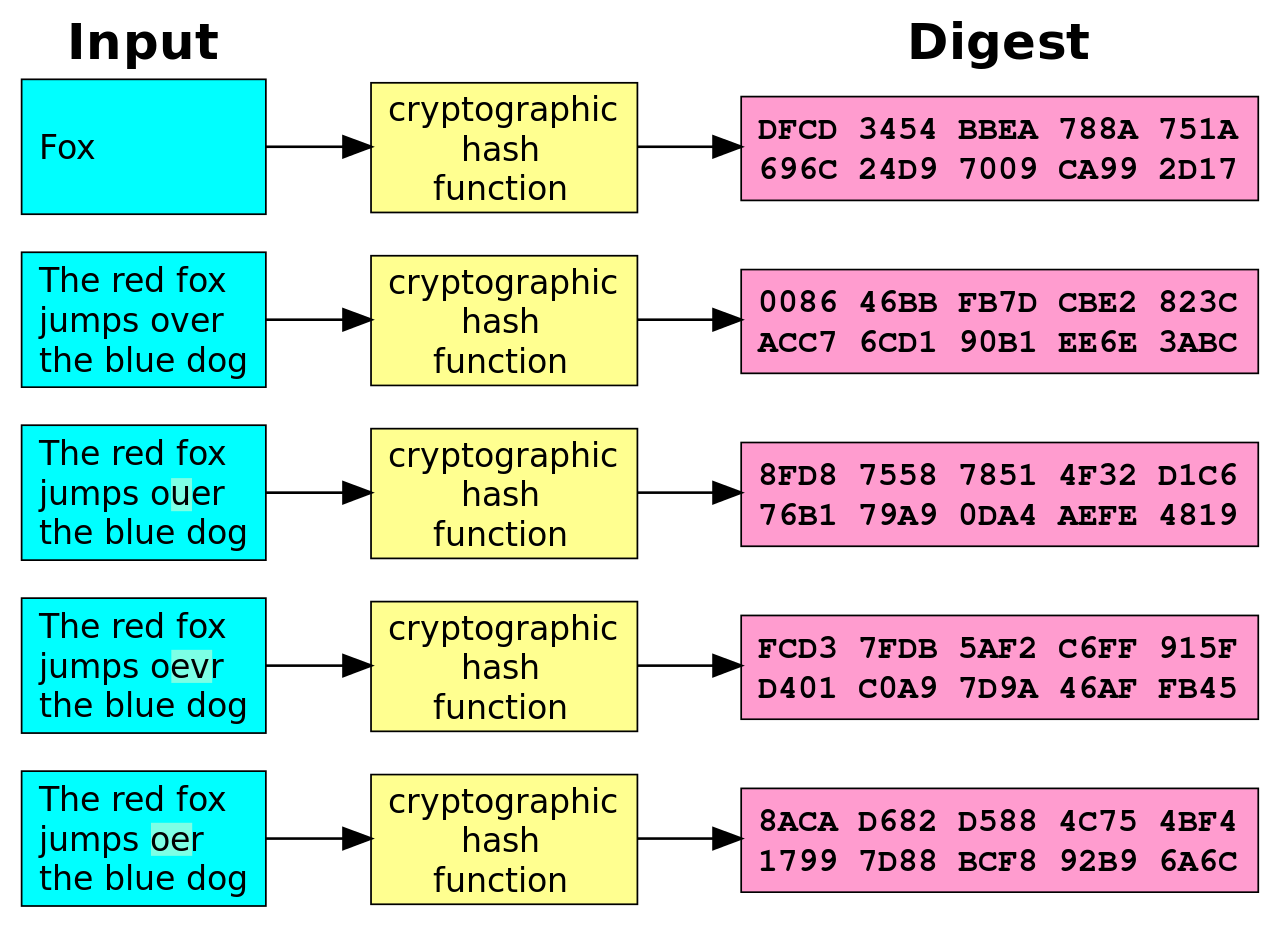
Cryptography
Hashes
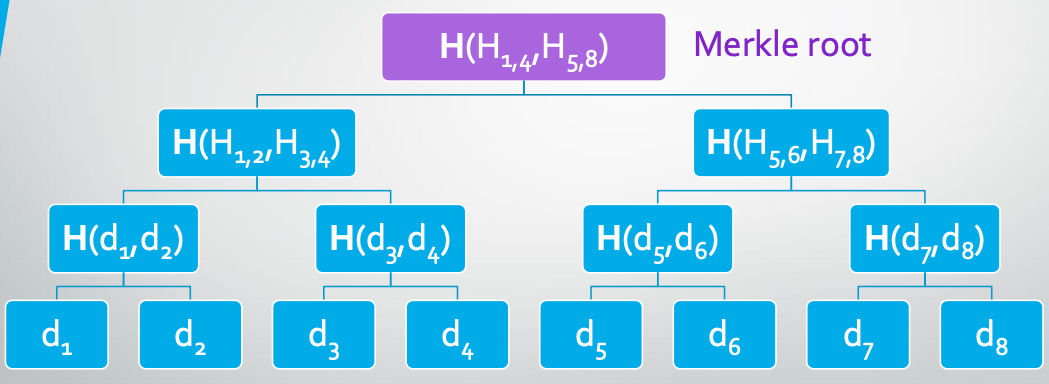
Merkle trees

Block hashes
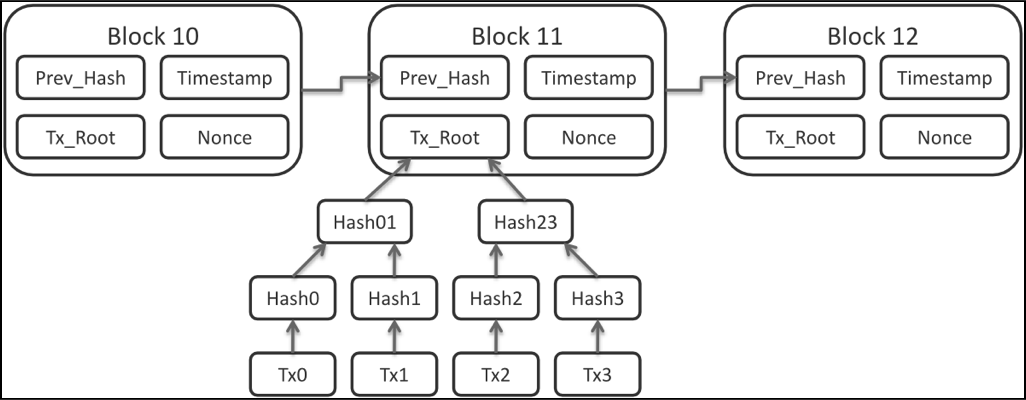
Each block is a list of transactions and it contains a header that contains the hash of entire block before it.
How does it work
transaction is requested
Block is created
Nodes validate the transaction
Transaction is complete
Block is added to blockchain
Nodes receive a reward for the Proof of Work
Gas
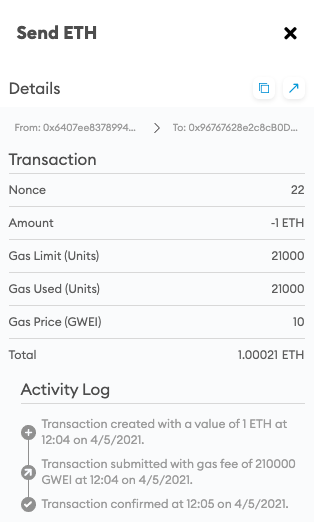
Gas fee is a fee sent to miner. Anytime the new transaction is created gas fee has to be paid
Less gas paid, the longer transaction will take, more gas paid, faster the transaction will work.
Dapps
Decentralized application
browser
Frontend
Blockchain
Backend
web3
web3

Smart contracts
Blockchain programs that are accessible to everyone on the network
node
node
node
node
node
node
MySmartContract
MySmartContract
MySmartContract
MySmartContract
MySmartContract
MySmartContract
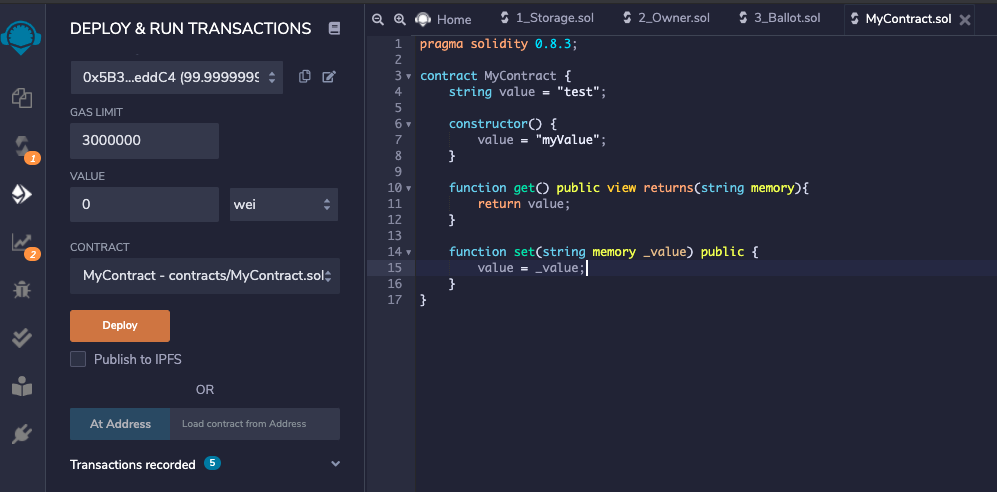
Solidity
Tokens
You either create your own blockchain or you use ERC-20 spec
Tokens can be created with smart contracts on Etherium
Web3
Web3 interface is used to connect to single etherium node
Web3 talks to Etherium client using JSON RPC. Web3.js give a JavaScript way to interact with the blockchain.
const Web3 = require(‘web3’);
const rpcUrl = `https://mainnet.infura.io/)….`;
const web3 = new Web3(rpcUrl);
web3.eth.getBlockNumber().then(console.log);We can validate that block is valid by using https://etherscan.io/
Connect to Etherium mainnet
Setting up dev environment
- NodeJS
- Python
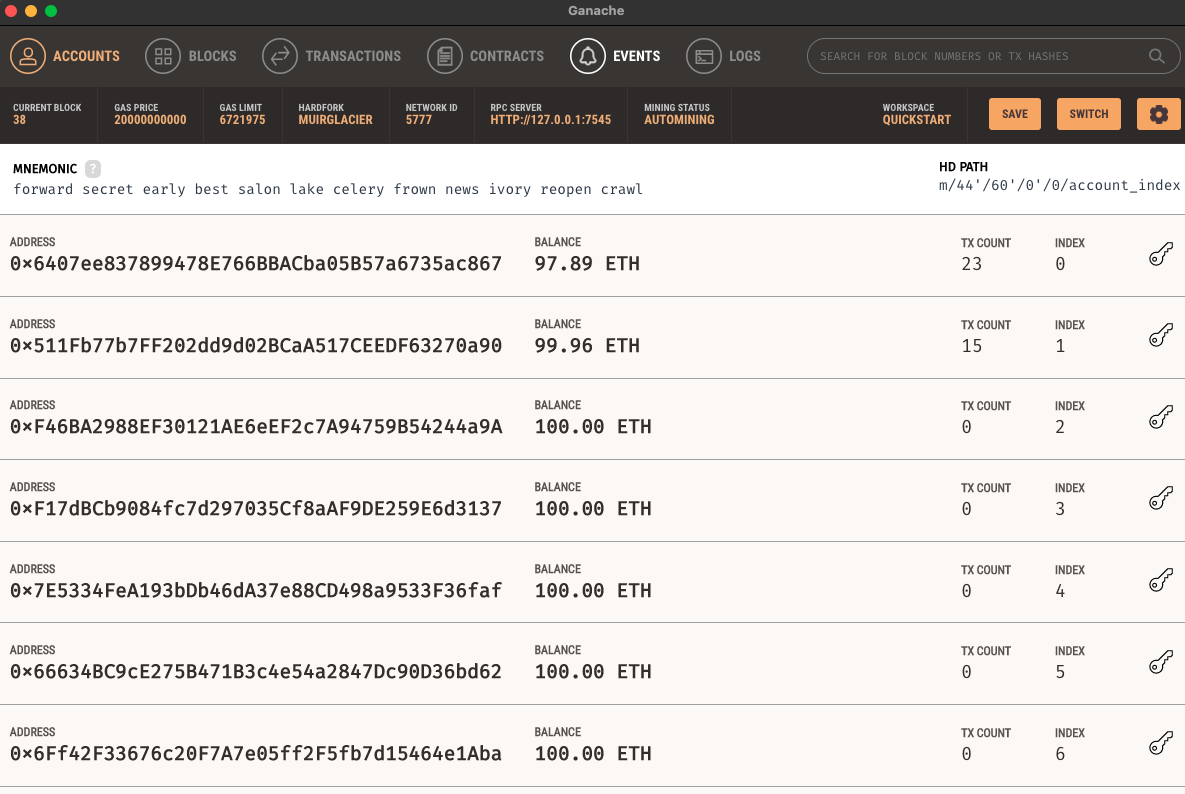
- personal blockchain for testing

Set up Truffle Framework
- Framework for smart contract development with solidity
npm install truffle -gSet up MetaMask
Let's start with a React Dapp
npx create-react-app demoappblockchain --template typescriptCreate truffle project
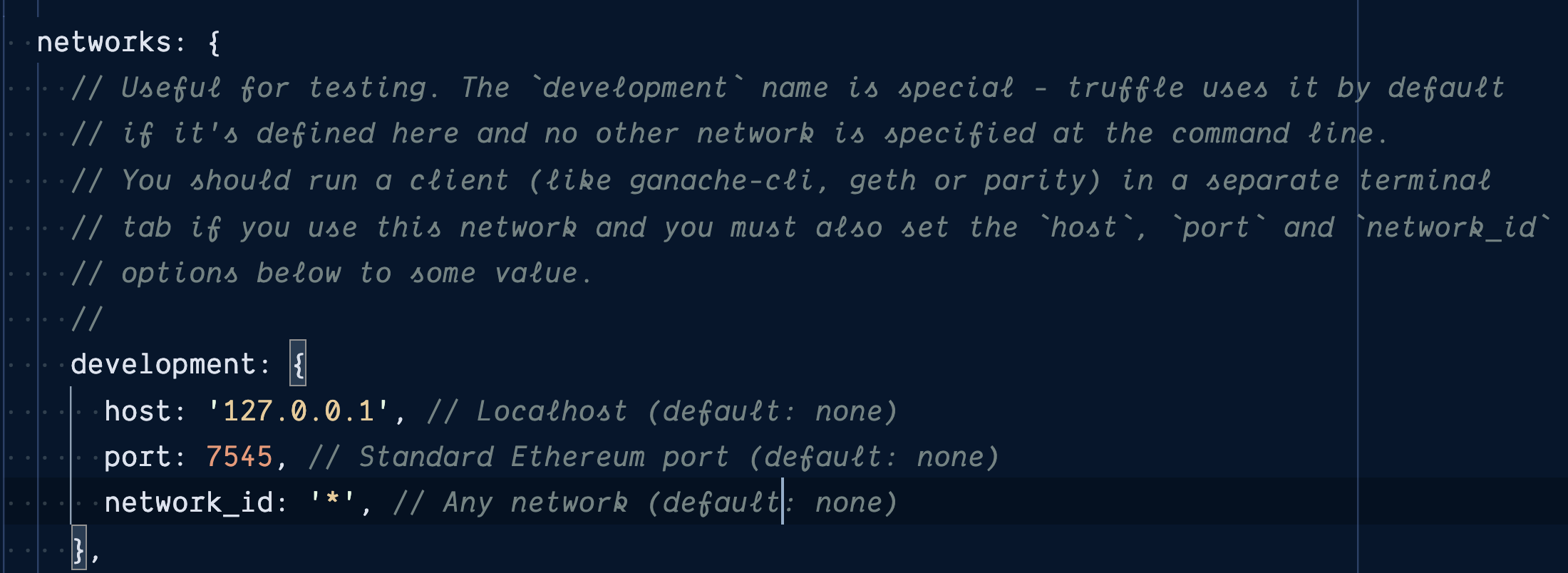
truffle initAdd to truffle-config.js
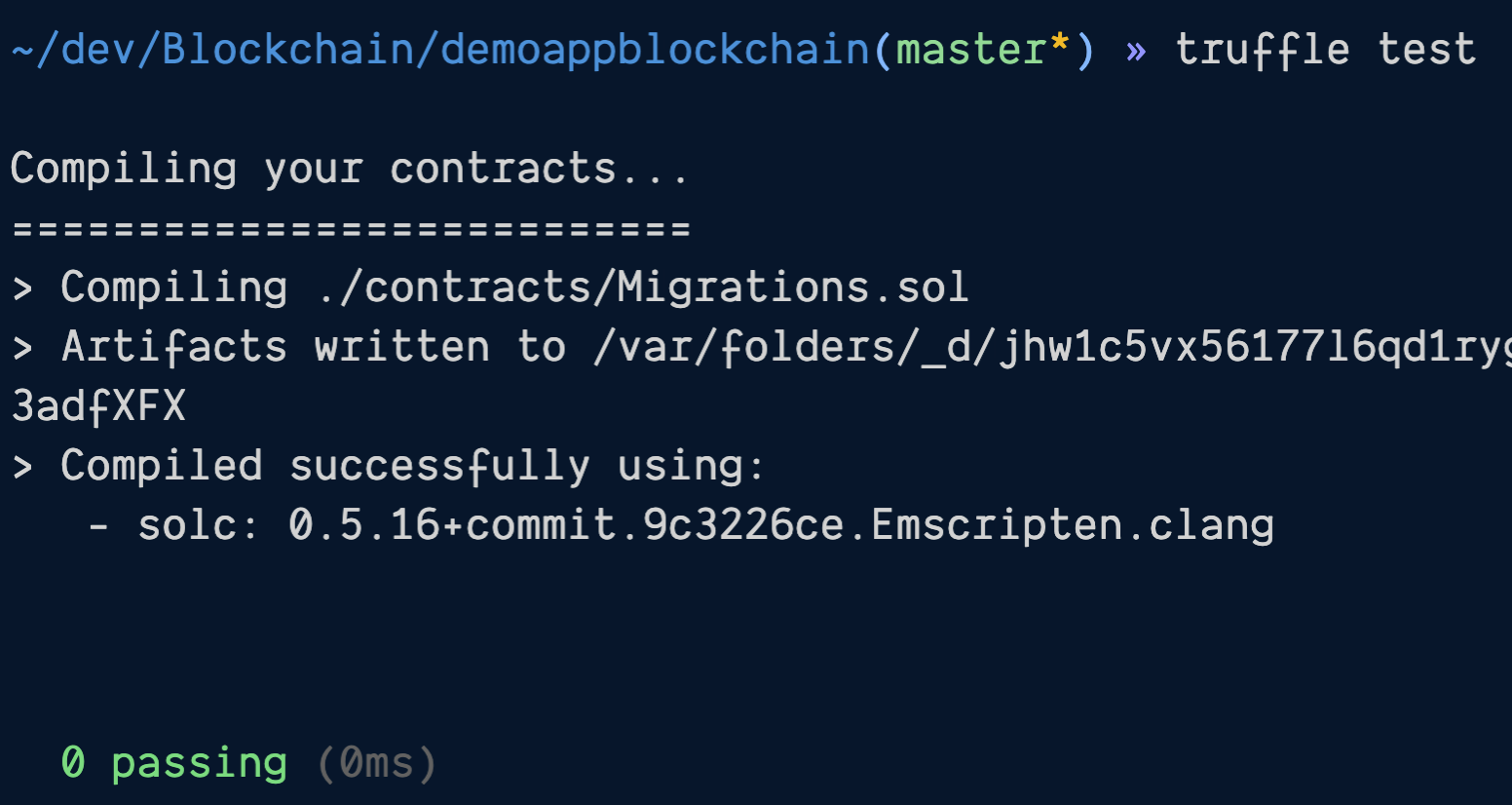
Test that it's working
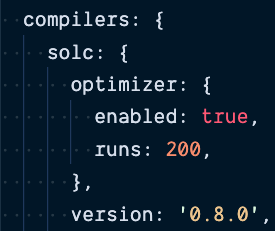
Change compiler version
truffle-config.js
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Migrations {
address public owner = msg.sender;
uint public last_completed_migration;
modifier restricted() {
require(
msg.sender == owner,
"This function is restricted to the contract's owner"
);
_;
}
function setCompleted(uint completed) public restricted {
last_completed_migration = completed;
}
}
Move generated files
Will put contracts and abis under src so we can read them from React app
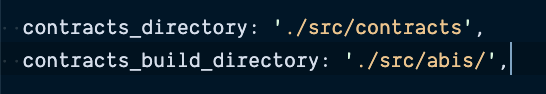
truffle-config.js
truffle compile- solidity-coverage → Linter
- openzeppelin-solidity → Math
- truffle → building smart contracts
- web3 → interface to blockchain
Install bunch of dependencies
yarn add chai chai-as-promised chai-bignumber openzeppelin-solidity solidity-coverage truffle truffle-flattener truffle-hdwallet-provider truffle-hdwallet-provider-privkey web3
Type your contracts
yarn add typescript ts-node typechain @typechain/truffle-v5 @typechain/web3-v1
yarn add @types/node @types/mocha @types/chai @types/chai-as-promised --save-dev register ts-node for truffle
require('ts-node').register({
files: true,
project: './tsconfig.truffle.json',
})truffle-config.js
{
"extends": "./tsconfig.json",
"compilerOptions": {
"noEmit": false,
"module": "CommonJS",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"strict": true
},
"include": ["./migrations-ts/*.ts", "./types/**/*.ts"]
}
tsconfig.truffle.json
rename migrations folder to migrations-ts and change migrations to .ts
Include all *.ts files in tsconfig
"include": ["**/*.ts"]Add helpful scripts for generating types and migrations
"test:contracts": "npm run compile && truffle test",
"compile": "truffle compile && npm run generate-types",
"generate-types": "npx typechain --target=truffle-v5 'src/abis/*.json' && npx typechain --target=web3-v1 'src/abis/*.json'",
"postinstall": "npx truffle compile && npm run generate-types",
"migrate": "tsc -p ./tsconfig.truffle.json --outDir ./migrations && truffle migrate"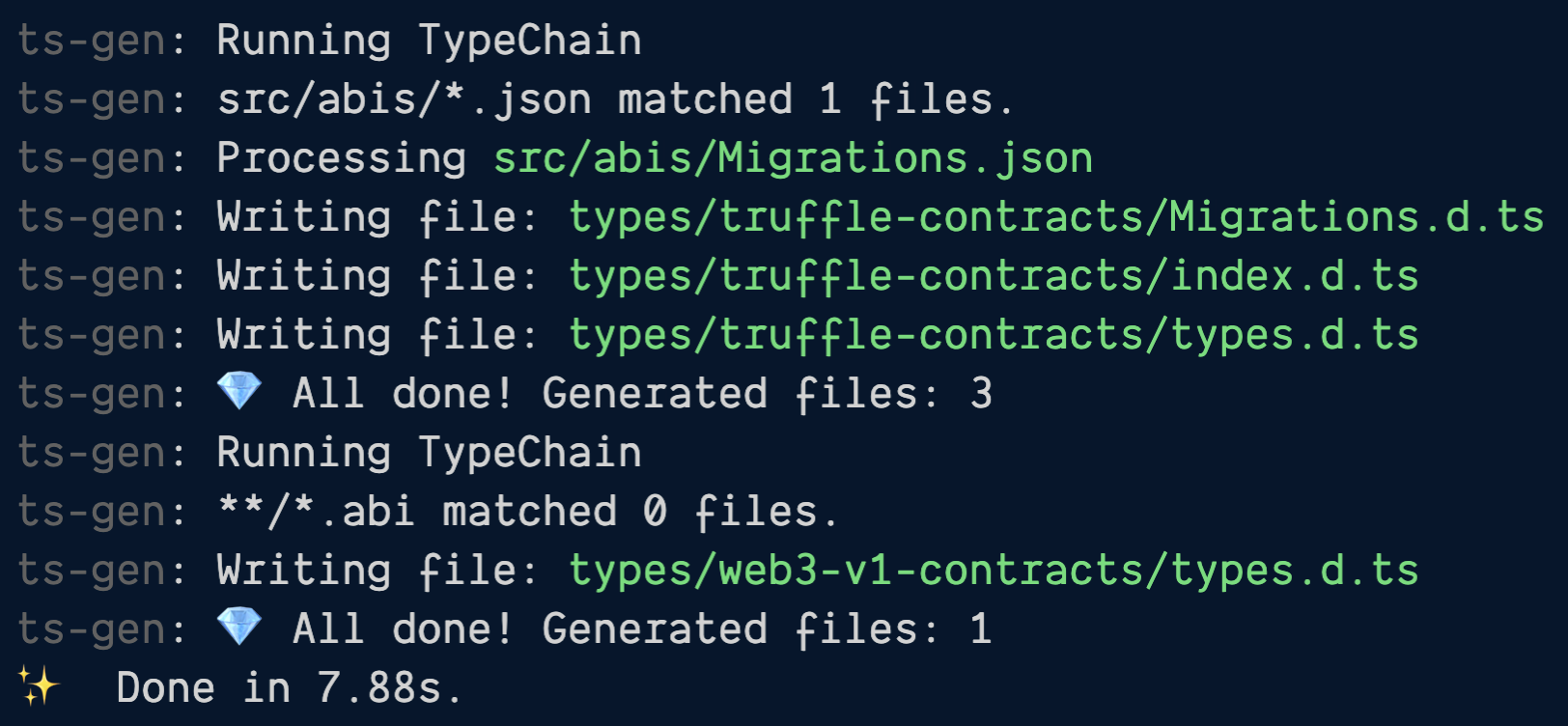
Start coding smart contracts
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "openzeppelin-solidity/contracts/utils/math/SafeMath.sol";
contract Token {
using SafeMath for uint;
string public name = "VNL Token";
string public symbol = "VNL";
uint256 public decimals = 18; //wei
uint256 public totalSupply;
//Events
//indexed in solidity means we can subscribed to events only if we are there (either from or to)
event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint256 value);
event Approval(address indexed owner, address indexed spender, uint256 value);
//Track balances
mapping(address => uint256) public balanceOf;
// nested mapping. address of person who approves the tokens and multiple places where person approves allowance and how much to spend
mapping(address => mapping(address => uint256)) public allowance;
constructor() public {
totalSupply = 1000000 * (10 ** decimals);
balanceOf[msg.sender] = totalSupply;
}
// Send tokens
function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) public returns(bool success) {
// Stops execution if error
require(balanceOf[msg.sender] >= _value);
_transfer(msg.sender, _to, _value);
return true;
}
function _transfer(address _from, address _to, uint256 _value) internal {
require(_to != address(0));
balanceOf[_from] = balanceOf[_from].sub(_value);
balanceOf[_to] = balanceOf[_to].add(_value);
emit Transfer(_from, _to, _value);
}
function approve(address _spender, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success) {
require(_spender != address(0));
allowance[msg.sender][_spender] = _value;
emit Approval(msg.sender, _spender, _value);
return true;
}
function transferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success) {
allowance[_from][msg.sender] = allowance[_from][msg.sender].sub(_value);
_transfer(_from, _to, _value);
return true;
}
}
Testing
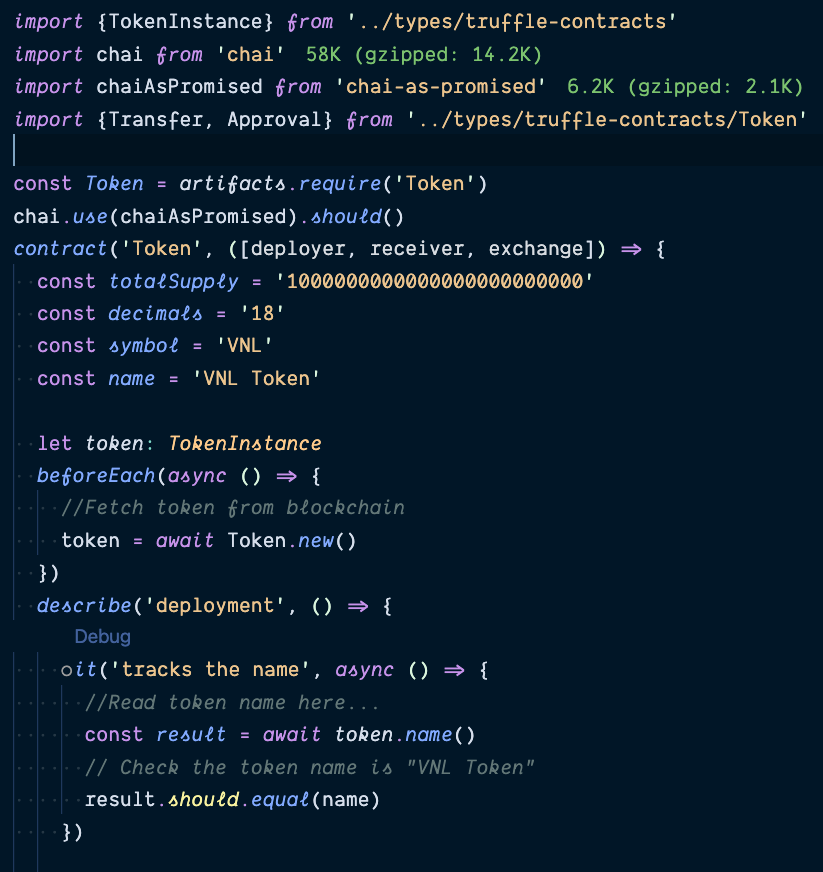
importing smart contracts
corresponds to testing accounts on ganache
Deploying
import { TokenContract } from "../types/truffle-contracts"
const Token = artifacts.require('Token')
module.exports = async function (deployer: { deploy: (arg0: TokenContract) => any }) {
await deployer.deploy(Token)
}
// because of https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40900791/cannot-redeclare-block-scoped-variable-in-unrelated-files
export {}
yarn migratetsc -p ./tsconfig.truffle.json --outDir ./migrations && truffle migrateThat's what it does
on the frontend
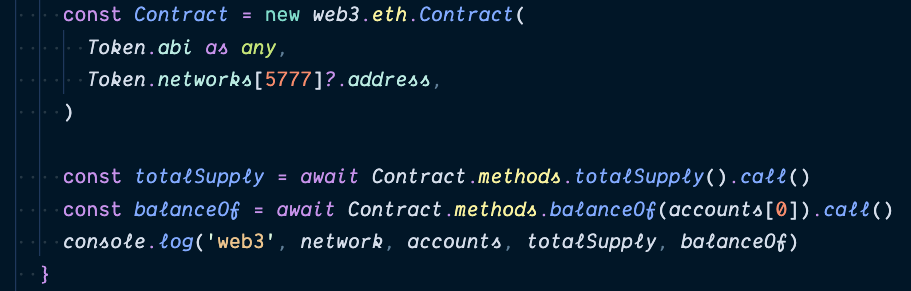
Web3
Metamask injects web3 provider. We will use it


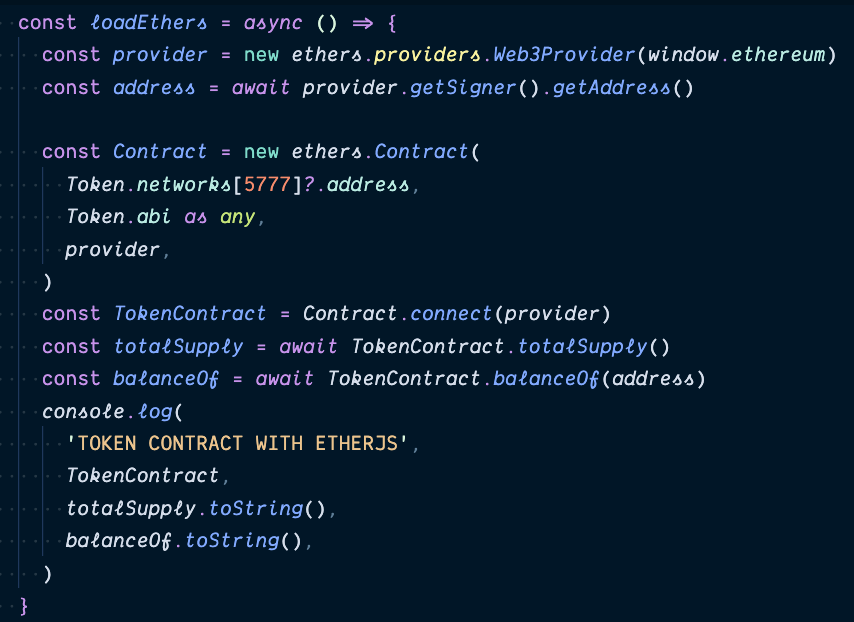
etherjs
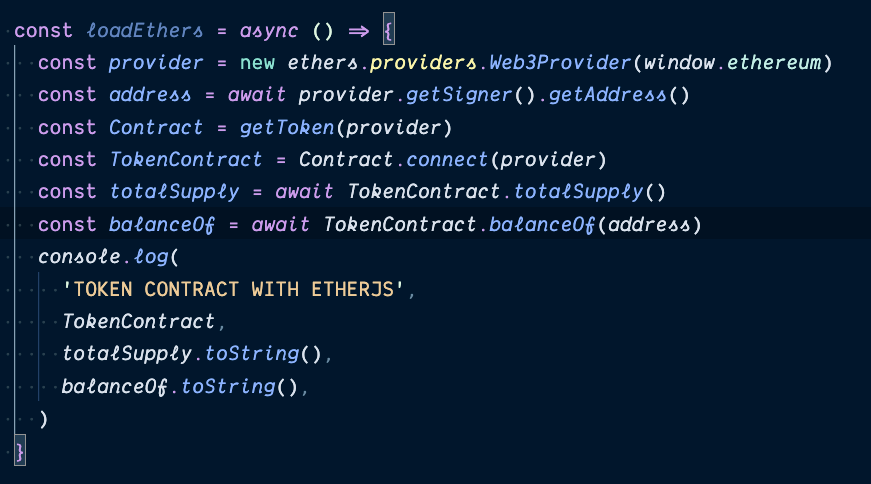
Working with contracts
Web3

Web3Modal
Enables to use different web3 providers
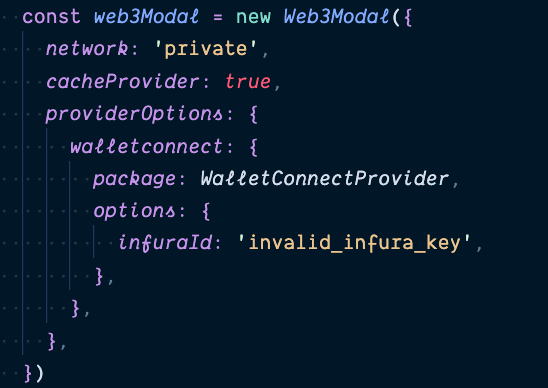



useWeb3Modal hook
function useWeb3Modal(config = {}) {
const [provider, setProvider] = useState<Web3Provider>()
const [singedInAddress, setSignedInAddress] = useState('')
const web3Modal = new Web3Modal({
network: 'private',
cacheProvider: true,
providerOptions: {
walletconnect: {
package: WalletConnectProvider,
options: {
infuraId: 'invalid_infura_key',
},
},
},
})
const loadWeb3Modal = useCallback(async () => {
const newProvider = await web3Modal.connect()
setProvider(new Web3Provider(newProvider))
setSignedInAddress(newProvider.selectedAddress)
}, [web3Modal])
const logout = useCallback(
async function () {
setSignedInAddress('')
await web3Modal.clearCachedProvider()
window.location.reload()
},
[web3Modal],
)
return {loadWeb3Modal, logout, provider, singedInAddress}
}
Interacting with tokens
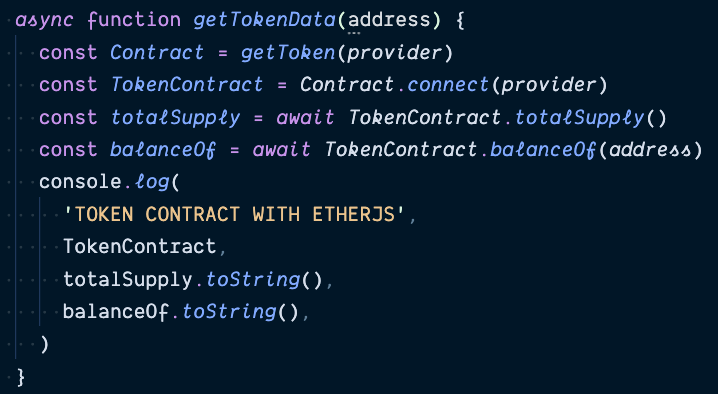
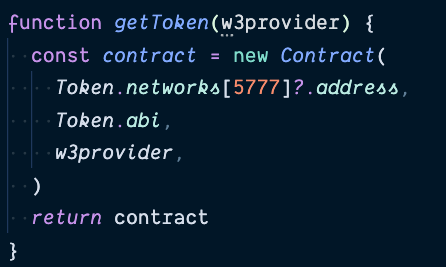
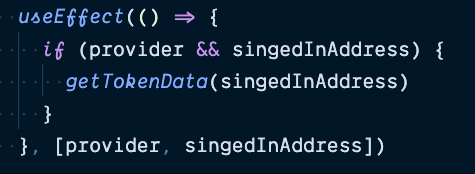
Multiple connectors
What's next
GraphQL for Blockchain



React on the Blockchain - the Missing Getting Started Guide.
By Vladimir Novick
React on the Blockchain - the Missing Getting Started Guide.
- 2,351

