- Understand where databases fit into common technology design patterns
- Understanding of basic database architecture
- Ability to write basic SQL queries
Goals
Definitions
Databases are a centralized place to store and retrieve data.
SQL database: A set of tables with defined relationships and data types.
SQL (Structured Query Language): A language for interacting with databases. Most commonly used to retrieve data.
Schema: The structure of a database. The schema defines the tables, the fields in each table, and the relationships between fields and tables.
SQL client: A tool used to connect and access a database. Can be GUI or CLI.
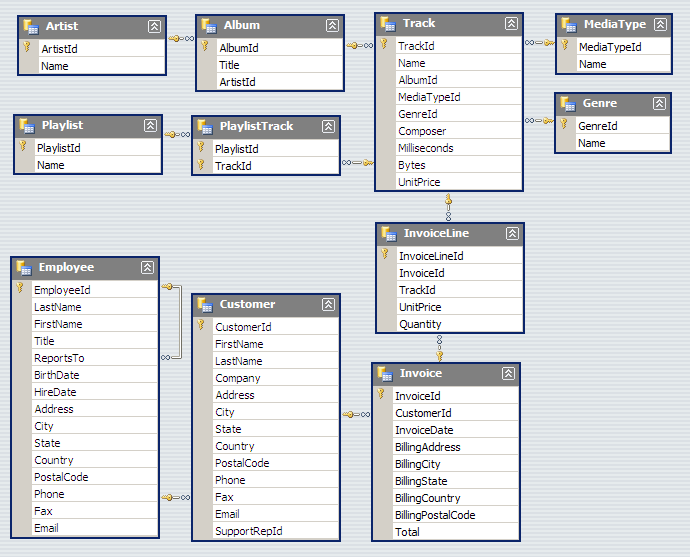
Example schema
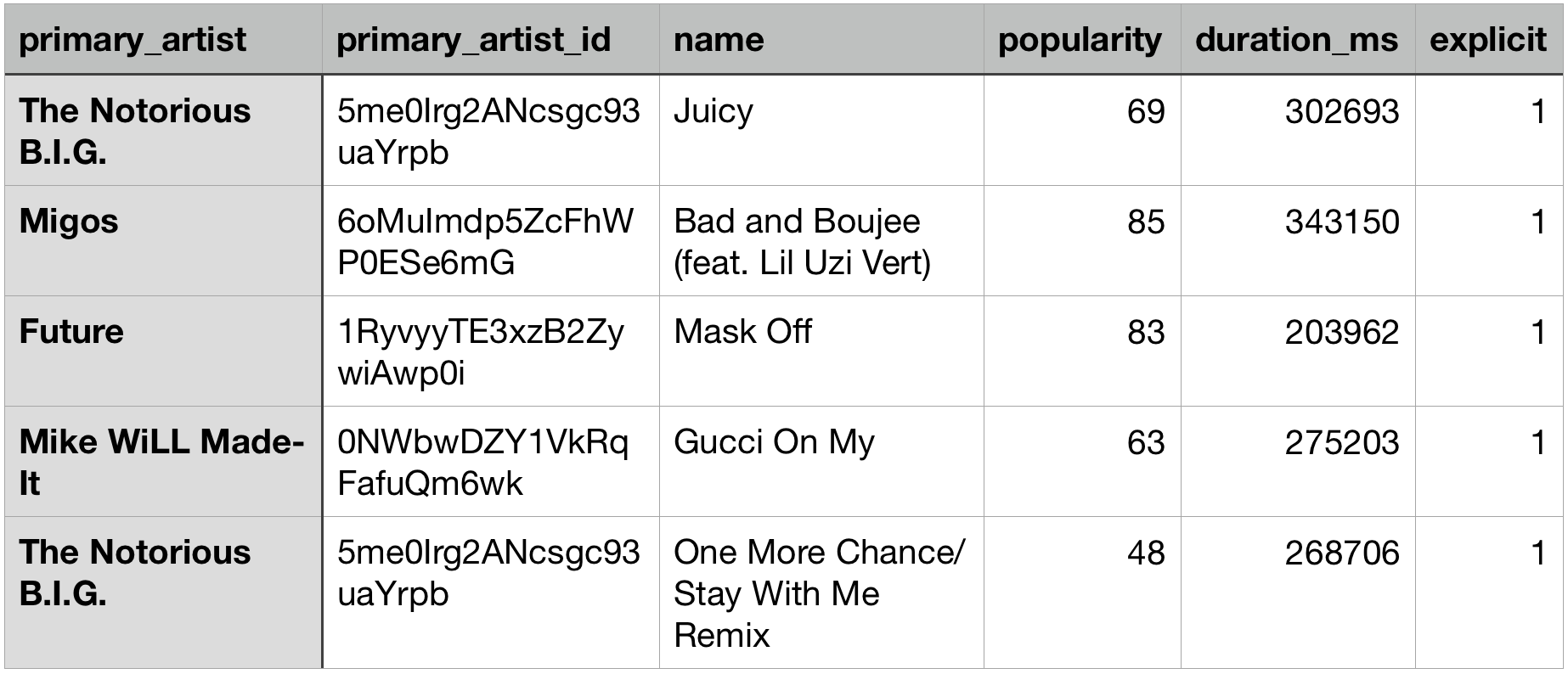
Example table
Example query
SELECT name, popularity, followers
FROM artists
ORDER BY followers DESC
LIMIT 5;| name | popularity | followers |
|---|---|---|
| Drake | 96 | 8775792 |
| Eminem | 90 | 7445304 |
| The Weeknd | 95 | 5107305 |
| Lil Wayne | 88 | 3546066 |
| J. Cole | 87 | 2515149 |
Design
Common Flavors



Client - Server


App with SQL Client
Clients
Web API
- Phone app - Desktop app - Web client
- CLI
SQL Server
Internet
Server
Clients
- App - Database
Web API
- Phone app - Desktop app - Web client
- CLI
Embedded

Raspberry Pi
- Code - Sensor - Database
Embedded

Let's connect!
bash> sqlite3 chinook.db
sqlite> .headers on
sqlite> .mode column
sqlite> .tablesOur Schema

Writing Queries
| SELECT | Columns / values to retrieve |
| FROM | What table to retrieve from |
| WHERE | Boolean filters |
| GROUP BY | Values to aggregate values on |
| ORDER BY | Sort your results |
| LIMIT | Limit the number of rows to return |
Bare minimum query
SELECT *
FROM table_name;Select, From
SELECT *
FROM tracks;Limit
SELECT *
FROM tracks
LIMIT 5;Select
SELECT name, composer
FROM tracks
limit 5;Where
SELECT name
FROM tracks
WHERE composer = "Miles Davis";Count, Group by
SELECT COUNT(name), composer
FROM tracks
GROUP BY composer;As, Order by
SELECT
COUNT(name) as count,
composer
FROM tracks
GROUP BY composer
ORDER BY count DESC
LIMIT 10;Multiple Aggregations
SELECT
COUNT(name) as count,
AVG(Milliseconds),
composer
FROM tracks
GROUP BY composer
ORDER BY count DESC
LIMIT 10;Joins
Joins let us combine data in multiple tables.
Syntax for a join
SELECT
tracks.Name AS track_name,
genres.Name AS genre_name
FROM tracks
LEFT JOIN genres ON genres.GenreId = tracks.GenreId;Left Join (enrich)

- All rows in the left table
- Columns from right table are added
Inner Join (filtering)

- Only that match are preserved
- All other rows are dropped from both tables
SELECT
tracks.Name AS track_name,
genres.Name AS genre_name
FROM tracks
LEFT JOIN genres ON genres.GenreId = tracks.GenreId;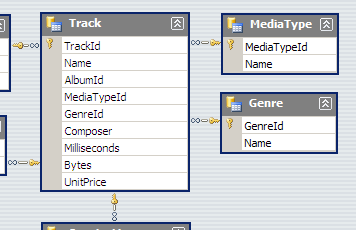
SELECT
AVG(Milliseconds) as avg_millis,
genres.Name AS genre_name
FROM tracks
LEFT JOIN genres ON genres.GenreId = tracks.GenreId
GROUP BY genre_name
ORDER BY avg_millis DESC
LIMIT 10;What genres have the longest tracks?
Loading New Data
Load a CSV file
// sqlite> .import {file name} {table name}
sqlite> .import rap_caviar.csv rap_caviarWhat should my first query be?
End
sql_flyby
By vndrewlee
sql_flyby
NYU ITP Flyby SQL slides
- 552