聊聊 IOC
2020/9/11
1、What and why ?
2、IOC在不同领域的应用场景
3、IOC实现的核心技术
4、浅谈Midway IOC 实现的原理
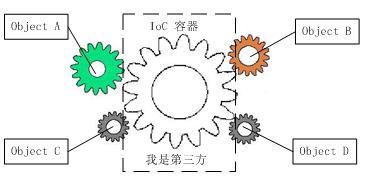
是面向对象编程中的一种设计原则,可以用来减低计算机代码之间的耦合度。其中最常见的方式叫做依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),还有一种方式叫"依赖查找"(Dependency Lookup)。通过控制反转,对象在被创建的时候,由一个调控系统内所有对象的外界实体,将其所依赖的对象的引用传递(注入)给它。
控制反转 (Inversion of Control,缩写为IoC)
What
— 维基百科
import {A} from './A';
import {B} from './B';
class C {
constructor() {
this.a = new A();
this.b = new B();
}
}无IOC
import {IA} from './A';
import {IB} from './B';
class C {
@inject()
a: IA
@inject()
b: IB
}IOC
依赖注入 Dependency Injection,简称DI
1,基于接口
2,基于set方法。
3,基于构造函数。
4,基于XML
5,基于注解
依赖基础容器
实现方式:
Why
碎片、难维护
简洁、中心化、易维护
aop/decorator/middleware/ioc :
异曲同工,业务和功能(可复用)的解耦,专注业务实现
1996 Michael Mattson https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Michael_Mattsson/publication/2238535_Object-Oriented_Frameworks/links/54d0a8ed0cf298d65667af54.pdf
2004 Martin Fowler 《Inversion of Control Containers and the Dependency Injection pattern[2]。》https://martinfowler.com/articles/injection.html
2006 Is IOC and Dependency Injection the Same Thing? https://www.dr-chuck.com/csev-blog/2006/01/is-ioc-and-dependency-injection-the-same-thing/
wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inversion_of_control
深入了解
IOC在不同开发领域的应用场景
Spring 39.2k
Core / IOC Container
AOP
Dao
ORM
JEE
Web
Server
XML的方式实现依赖注入
class SqlMapAccountDao {
// ....
}
class SqlMapItemDao {
// ...
}
class PetStoreServiceImpl {
// ...
}
1. 定义类及相互引用的对象声明
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!-- services -->
<bean id="petStore"
class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.services.PetStoreServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
<property name="itemDao" ref="itemDao"/>
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions for services go here -->
<bean id="accountDao"
class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.ibatis.SqlMapAccountDao">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="itemDao" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.ibatis.SqlMapItemDao">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
</beans>2. XML定义类之间的相互引用关系
// create and configure beans
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"config.xml"});
// retrieve configured instance
PetStoreServiceImpl service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreServiceImpl.class);
// use configured instance
List userList service.getUsernameList();3. 容器初始化加载xml然后直接获取实例
butterknife 25.4k
class ExampleActivity extends Activity {
@BindView(R.id.user) EditText username;
@BindView(R.id.pass) EditText password;
@BindString(R.string.login_error) String loginErrorMessage;
@OnClick(R.id.submit) void submit() {
// TODO call server...
}
@Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.simple_activity);
ButterKnife.bind(this);
// TODO Use fields...
}
}Client
过时了
Front

Angular 65.7k

Next.js 53k

InversifyJS 6.5k

Midway.js 3k
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HEROES } from './mock-heroes';
@Injectable({providedIn: 'root'})
export class HeroService {
getHeroes() { return HEROES; }
}1.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Hero } from './hero';
import { HeroService } from './hero.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-hero-list',
template: `
<div *ngFor="let hero of heroes">
{{hero.id}} - {{hero.name}}
</div>
`
})
export class HeroListComponent {
heroes: Hero[];
constructor(heroService: HeroService) {
this.heroes = heroService.getHeroes();
}
}2.
Angular
IOC实现的核心技术
XML实现
1、动态加载类 Class.forName / require
2、反射
装饰器实现
1、装饰器收集元信息
2、静态语言-反射 / 动态语言 - 反射或者直接通过元信息实例化
class Apple {
// ....
}
const instance = new Apple(); // 正射
const instance = Reflect.construct(Apple, []); // 反射JavaScript 反射示例
TypeScript 装饰器示例
const requiredMetadataKey = Symbol("required");
function required(target: Object, propertyKey: string | symbol, parameterIndex: number) {
// 元信息收集
// 1. 通过requiredMetadataKey获取函数参数的存储队列
// 2. 如果存在则将参数的元数据进行存储
// 3. 如果不存在则创建当前函数唯一的元信息存储队列
let existingRequiredParameters: number[] = Reflect.getOwnMetadata(requiredMetadataKey, target, propertyKey) || [];
existingRequiredParameters.push(parameterIndex);
Reflect.defineMetadata(requiredMetadataKey, existingRequiredParameters, target, propertyKey);
}
function validate(target: any, propertyName: string, descriptor: TypedPropertyDescriptor < Function > ) {
let method = descriptor.value;
// 元信息遍历
// 1. 为该方法新增拦截逻辑,重写descriptor的value即可
// 2. 当调用该方法时(运行时触发),遍历此前的元信息,挨个取值并验证是否符合验证条件
descriptor.value = function () {
let requiredParameters: number[] = Reflect.getOwnMetadata(requiredMetadataKey, target, propertyName);
if (requiredParameters) {
for (let parameterIndex of requiredParameters) {
if (parameterIndex >= arguments.length || arguments[parameterIndex] === undefined) {
throw new Error("Missing required argument.");
}
}
}
// 执行方法本身
return method.apply(this, arguments);
}
}
class Greeter {
greeting: string;
constructor(message: string) {
this.greeting = message;
}
@validate
greet(@required name: string) {
return "Hello " + name + ", " + this.greeting;
}
}
let gg = new Greeter('...')
console.log(gg.greet('xx'))debounce decorator
export function debounce(delay: number): Function {
return (
target: Object,
propertyKey: string,
propertyDesciptor: PropertyDescriptor
) => {
const method = propertyDesciptor.value;
let timer = null;
propertyDesciptor.value = (...args) => {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
}
timer = setTimeout(() => method(...args), delay);
};
return propertyDesciptor;
};
}
class A {
@debounce(1000)
say(message: any) {
console.log(message);
}
}
let a = new A()
a.say('hello')vue-property-decorator
Text
import { Vue, Component, Watch, Emit } from 'vue-property-decorator'
@Component
export default class YourComponent extends Vue {
count = 0
@Watch('child')
onChildChanged(val: string, oldVal: string) {}
@Emit()
addToCount(n: number) {
this.count += n
}
}export default {
data() {
return {
count: 0,
}
},
watch: {
child: [
{
handler: 'onChildChanged',
immediate: false,
deep: false,
},
],
},
methods: {
onChildChanged(val, oldVal) {},
addToCount(n) {
this.count += n
this.$emit('add-to-count', n)
}
},
}inject装饰器
Text
function inject(identifier?: ObjectIdentifier) {
return function (target: any, targetKey: string, index?: number): void {
if (typeof index === 'number') {
if (!identifier) {
const args = getParamNames(target);
if (target.length === args.length && index < target.length) {
identifier = args[index];
}
}
const metadata = new Metadata(INJECT_TAG, identifier);
tagParameter(target, targetKey, index, metadata);
} else {
if (!identifier) {
identifier = targetKey;
}
const metadata = new Metadata(INJECT_TAG, identifier);
tagProperty(target, targetKey, metadata);
}
};
}
// https://github.com/midwayjs/injection/blob/master/src/annotation/inject.tsMidway IOC 应用和实现原理
简单介绍
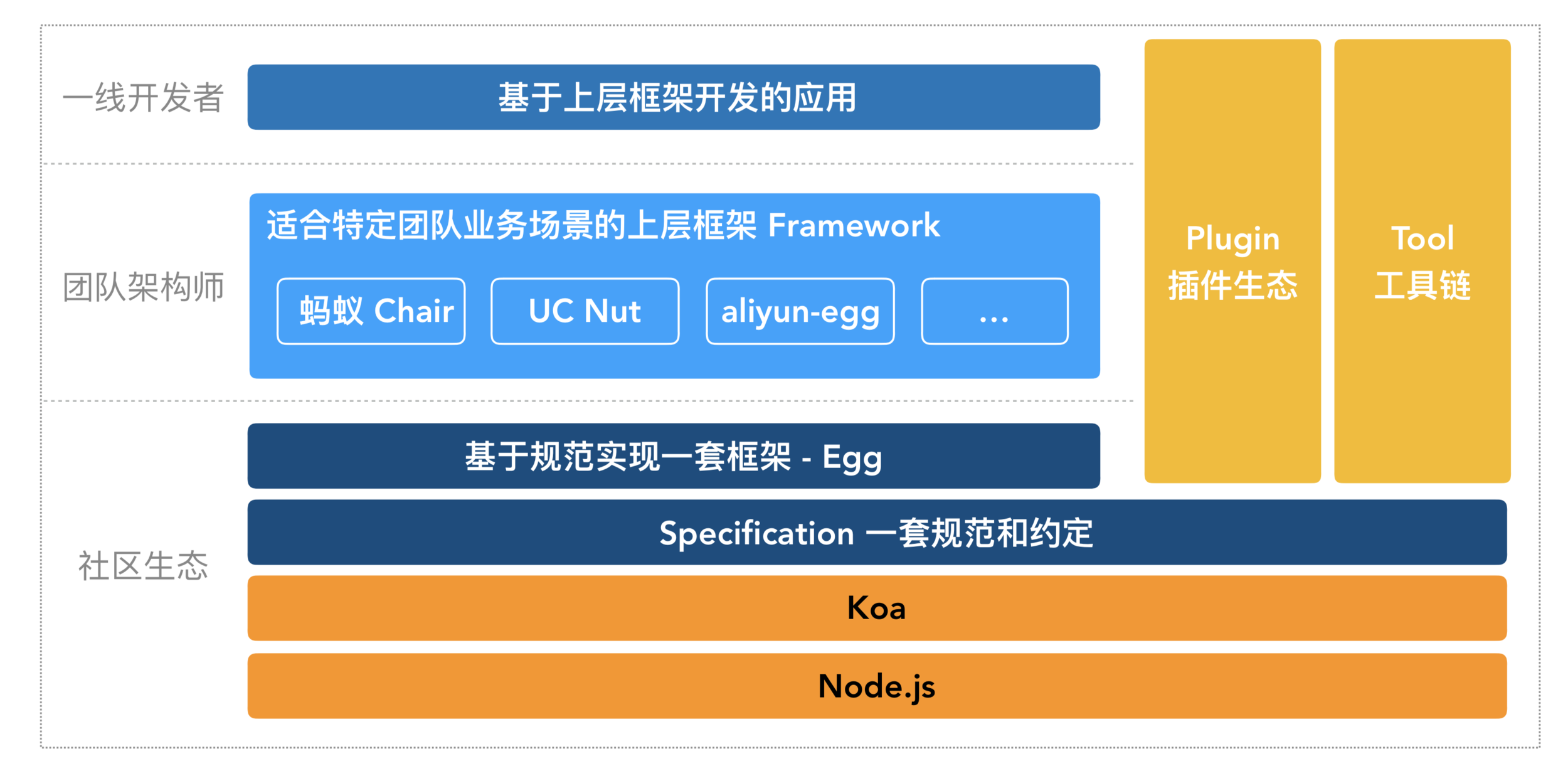
midway
Midway 使用示例
import { provide } from 'midway';
import { IUserService, IUserOptions, IUserResult } from '../../interface';
@provide('userService')
export class UserService implements IUserService {
async getUser(options: IUserOptions): Promise<IUserResult> {
return new Promise<IUserResult>((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({
id: options.id,
username: 'mockedName',
phone: '12345678901',
email: 'xxx.xxx@xxx.com',
});
}, 10);
});
}
}import { controller, get, inject, provide } from 'midway';
import { IUserService, IUserResult } from '../../interface';
@provide()
@controller('/user')
export class UserController {
@inject('userService')
service: IUserService;
@get('/:id')
async getUser(ctx): Promise<void> {
const id: number = ctx.params.id;
const user: IUserResult = await this.service.getUser({id});
ctx.body = {success: true, message: 'OK', data: user};
}
}
ioc container : injection
// 使用 IoC
import {Container} from 'injection';
import {A} from './A';
import {B} from './B';
const container = new Container();
container.bind(A);
container.bind(B);
class C {
consturctor() {
this.a = container.get('A');
this.b = container.get('B');
}
}Injection 使用示例
不友好 ?
load(opts: {
loadDir: string | string[];pattern?: string | string[];ignore?: string | string[];
}) {
const loadDirs = [].concat(opts.loadDir || []);
// TODO set 去重
for (const dir of loadDirs) {
const fileResults = run(['**/**.ts', '**/**.tsx', '**/**.js'].concat(opts.pattern || []), {
cwd: dir,
ignore: [
'**/**.d.ts',
'**/logs/**',
'**/run/**',
'**/public/**',
'**/view/**',
'**/views/**'
].concat(opts.ignore || []),
});
for (const file of fileResults) {
debug(`binding file => ${file}`);
const exports = require(file);
this.bindClass(exports);
}
}
}
自动注册的核心实现
source: https://github.com/midwayjs/midway/blob/master/packages/midway-core/src/container.ts
injection的核心实现
1,provide、inject
2,bind
3,get
// A.js
...
@provide()
export class A {
@inject
b: IB
}
// B.js
...
@provide()
export class B {
@inject
a: IA
}
// main.js
import {Container} from 'injection';
import {A} from './A';
import {B} from './B';
const container = new Container();
container.bind(A);
container.bind(B);
class C {
consturctor() {
this.a = container.get('A');
this.b = container.get('B');
}
}Definition
Factory Creator
Instance
bind
get
container
steps:
1,init: 读、写metadata
2,bind: 构建每个注入类的定义Definition[内部抽象]
3,get: 通过内部Definition来构建最终实例
project
read
metadata
TypeScript
@provide/@inject
store
relect-matadata
function provide(identifier?: ObjectIdentifier) {
return function (target: any) {
if (Reflect.hasOwnMetadata(TAGGED_CLS, target)) {
throw new Error(DUPLICATED_INJECTABLE_DECORATOR);
}
if (!identifier) {
identifier = camelCase(target.name);
}
Reflect.defineMetadata(TAGGED_CLS, {
id: identifier,
originName: target.name,
} as TagClsMetadata, target);
// init property here
initOrGetObjectDefProps(target);
return target;
};
}
function inject(identifier?: ObjectIdentifier) {
return function (target: any, targetKey: string, index?: number): void {
if (typeof index === 'number') {
if (!identifier) {
const args = getParamNames(target);
if (target.length === args.length && index < target.length) {
identifier = args[index];
}
}
const metadata = new Metadata(INJECT_TAG, identifier);
tagParameter(target, targetKey, index, metadata);
} else {
if (!identifier) {
identifier = targetKey;
}
const metadata = new Metadata(INJECT_TAG, identifier);
tagProperty(target, targetKey, metadata);
}
};
}1,provide、inject
save metadata
2,bind
bind<T>(identifier: ObjectIdentifier, target: T, options?: ObjectDefinitionOptions): void {
let definition;
// definition.autowire = true;
if (is.class(identifier) || is.function(identifier)) {
options = target;
target = <any> identifier;
identifier = this.getIdentifier(target);
options = null;
}
if (is.class(target)) {
definition = new ObjectDefinition();
} else {
definition = new FunctionDefinition(this);
}
definition.path = target;
definition.id = identifier;
debug(`=> bind and build definition, id = [${definition.id}]`);
// inject constructArgs
const constructorMetaData = Reflect.getMetadata(TAGGED, target);
if (constructorMetaData) {
debug(` register inject constructor length = ${target[ 'length' ]}`);
const maxLength = Math.max.apply(null, Object.keys(constructorMetaData));
for (let i = 0; i < maxLength + 1; i++) {
const propertyMeta = constructorMetaData[ i ];
if (propertyMeta) {
const refManagedIns = new ManagedReference();
refManagedIns.name = propertyMeta[ 0 ].value;
definition.constructorArgs.push(refManagedIns);
} else {
// inject empty value
const valueManagedIns = new ManagedValue();
valueManagedIns.value = undefined;
definition.constructorArgs.push(valueManagedIns);
}
}
}
// inject properties
const metaDatas = recursiveGetMetadata(TAGGED_PROP, target);
for (const metaData of metaDatas) {
debug(` register inject properties = [${Object.keys(metaData)}]`);
for (const metaKey in metaData) {
for (const propertyMeta of metaData[ metaKey ]) {
const refManaged = new ManagedReference();
refManaged.name = propertyMeta.value;
definition.properties.set(metaKey, refManaged);
}
}
}
this.convertOptionsToDefinition(options, definition);
// 对象自定义的annotations可以覆盖默认的属性
this.registerCustomBinding(definition, target);
this.registerDefinition(identifier, definition);
debug(` bind and build definition complete, id = [${definition.id}]`);
}3,get
...
get<T>(identifier: ObjectIdentifier, args?: any): T {
...
return this.getManagedResolverFactory().create(definition, args);
}
....
doConstruct(Clzz: any, args?: any): any {
...
inst = Reflect.construct(Clzz, args);
return inst;
}Reflect new
Thanks
聊聊 IOC
By wang dong
聊聊 IOC
- 230
