wojciech-dabrowski
wojciech-dabrowski
wojc.dabrowski@gmail.com

Serverless Microservice
there and back again


Once upon a time...
public class CustomerHasTakenLoanEventHandler : IEventHandler<CustomerHasTakenLoanEvent>
{
...
public void Handle(CustomerHasTakenLoanEvent @event)
{
...
var mailBody = $"Hi, {@event.CustomerFirstName}\n\n" +
$"You have taken a loan for {@event.LoanAmount} {@event.LoanCurrency}.";
SendMail(@event.CustomerMailAddress, mailBody);
}
private void SendMail(string toMailAddress, string mailBody)
{
using (var emailMessage = new MailMessage())
{
emailMessage.To.Add(toMailAddress);
emailMessage.From = mailConfig.FromMailAddress;
emailMessage.Subject = MailSubject;
emailMessage.Body = mailBody;
emailMessage.IsBodyHtml = true;
emailMessage.BodyEncoding = Encoding.Unicode;
using (var smtpClient = new SmtpClient(smtpConfig.SmtpServerHost))
{
smtpClient.Port = smtpConfig.SmtpPort;
smtpClient.UseDefaultCredentials = false;
smtpClient.Credentials = new NetworkCredential(smtpConfig.SmtpUserName, smtpConfig.SmtpUserPassword);
smtpClient.Send(emailMessage);
}
}
}
}public class LoanHasBeenPaidOffEventHandler : IEventHandler<LoanHasBeenPaidOffEvent>
{
...
public void Handle(LoanHasBeenPaidOffEvent @event)
{
...
var mailBody = $"Hi, {@event.CustomerFirstName}\n\n" +
$"Your loan for {@event.LoanAmount} {@event.LoanCurrency} has been paid off.";
SendMail(@event.CustomerMailAddress, mailBody);
}
private void SendMail(string toMailAddress, string mailBody)
{
using (var emailMessage = new MailMessage())
{
emailMessage.To.Add(toMailAddress);
emailMessage.From = mailConfig.FromMailAddress;
emailMessage.Subject = MailSubject;
emailMessage.Body = mailBody;
emailMessage.IsBodyHtml = true;
emailMessage.BodyEncoding = Encoding.Unicode;
using (var smtpClient = new SmtpClient(smtpConfig.SmtpServerHost))
{
smtpClient.Port = smtpConfig.SmtpPort;
smtpClient.UseDefaultCredentials = false;
smtpClient.Credentials = new NetworkCredential(smtpConfig.SmtpUserName, smtpConfig.SmtpUserPassword);
smtpClient.Send(emailMessage);
}
}
}
}Approach #1
Repetition mania

Cons
Cons
- Increases codebase which has to be maintained.
Cons
- Increases codebase which has to be maintained.
- Lack of testability.
PROS
PROS

https://giant.gfycat.com/TautWarmheartedBetafish.webm
Approach #2
Single responsibility principle application
public class SmtpClientEmailSender : IEmailSender
{
...
public void SendMail(SendEmailModel model)
{
using (var emailMessage = new MailMessage())
{
emailMessage.To.Add(model.ToMailAddress);
emailMessage.From = mailConfig.FromMailAddress;
emailMessage.Subject = model.MailSubject;
emailMessage.Body = model.MailBody;
emailMessage.IsBodyHtml = true;
emailMessage.BodyEncoding = Encoding.Unicode;
using (var smtpClient = new SmtpClient(smtpConfig.SmtpServerHost))
{
smtpClient.Port = smtpConfig.SmtpPort;
smtpClient.UseDefaultCredentials = false;
smtpClient.Credentials = new NetworkCredential(smtpConfig.SmtpUserName, smtpConfig.SmtpUserPassword);
smtpClient.Send(emailMessage);
}
}
}
}public class CustomerHasTakenLoanEventHandler : IEventHandler<CustomerHasTakenLoanEvent>
{
...
private readonly IEmailSender _emailSender;
public CustomerHasTakenLoanEventHandler(IEmailSender emailSender)
{
_emailSender = emailSender;
}
public void Handle(CustomerHasTakenLoanEvent @event)
{
...
var mailBody = $"Hi, {@event.CustomerFirstName}\n\n" +
$"You have taken a loan for {@event.LoanAmount} {@event.LoanCurrency}.";
var sendEmailModel = new SendEmailModel(@event.CustomerMailAddress, MailSubject, mailBody);
_emailSender.SendMail(sendEmailModel);
}
}public class LoanHasBeenPaidOffEventHandler : IEventHandler<LoanHasBeenPaidOffEvent>
{
...
private readonly IEmailSender _emailSender;
public LoanHasBeenPaidOffEventHandler(IEmailSender emailSender)
{
_emailSender = emailSender;
}
public void Handle(LoanHasBeenPaidOffEvent @event)
{
...
var mailBody = $"Hi, {@event.CustomerFirstName}\n\n" +
$"Your loan for {@event.LoanAmount} {@event.LoanCurrency} has been paid off.";
var sendEmailModel = new SendEmailModel(@event.CustomerMailAddress, MailSubject, mailBody);
_emailSender.SendMail(sendEmailModel);
}
}
PROS
PROS
- Reuse in current module/context.
PROS
- Reuse in current module/context.
- Testability.
PROS
- Reuse in current module/context.
- Testability.
- Better maintenance.
What if...
Cons
- No possibility to use this functionality outside current module/context.
Approach #3
Common closure principle application



PROS
PROS
- Reuse in current logical container
(for example solution in .NET).
What if...
Cons
- No possibility to use this functionality outside current logical container. For example new project/product.
Approach #4
Portable library













What if...
Cons
- No possibility to use this package in other technology.
Cons
- No possibility to use this package in other technology.
- Scalability?
Cons
- No possibility to use this package in other technology.
- Scalability?
- Availability?
Approach #5
One service to serve them all



API Gateway


API Gateway

Lambda


API Gateway

Lambda

SQS


API Gateway

Lambda

SQS

CloudWatch


API Gateway

Lambda

SQS

CloudWatch

SES


API Gateway

Lambda

SQS

CloudWatch

SES

S3


API Gateway

Lambda

SQS

CloudWatch

SES

S3


public class SmtpClientEmailSender : IEmailSender
{
...
public void SendMail(SendEmailModel model)
{
using (var emailMessage = new MailMessage())
{
emailMessage.To.Add(model.ToMailAddress);
emailMessage.From = mailConfig.FromMailAddress;
emailMessage.Subject = model.MailSubject;
emailMessage.Body = model.MailBody;
emailMessage.IsBodyHtml = true;
emailMessage.BodyEncoding = Encoding.Unicode;
using (var smtpClient = new SmtpClient(smtpConfig.SmtpServerHost))
{
smtpClient.Port = smtpConfig.SmtpPort;
smtpClient.UseDefaultCredentials = false;
smtpClient.Credentials = new NetworkCredential(smtpConfig.SmtpUserName, smtpConfig.SmtpUserPassword);
smtpClient.Send(emailMessage);
}
}
}
}using (var smtpClient = new SmtpClient(smtpConfig.SmtpServerHost))
{
...
smtpClient.Send(emailMessage);
}



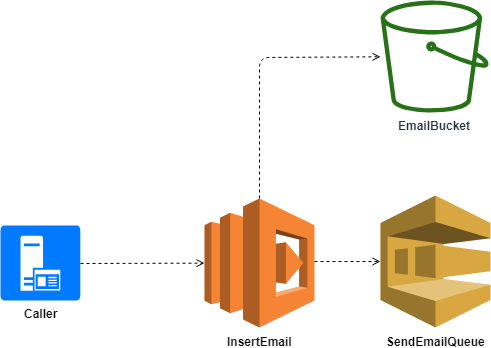
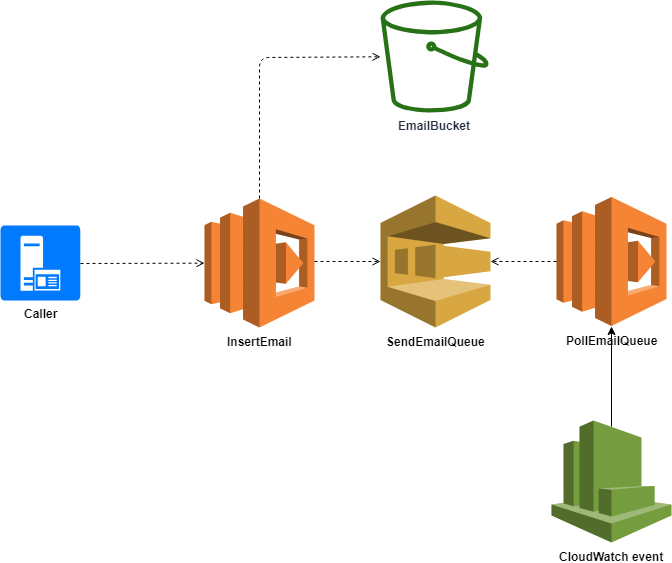
public async Task<string> InsertEmailAsync(InsertEmailModel emailModel, ILambdaContext context)
{
var emailStorageId = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
await UploadEmailToS3(emailStorageId, emailModel);
await sqsClient.SendMessageAsync(
EnvironmentVariables.MailQueue,
JsonConvert.SerializeObject(emailStorageId)
);
return emailStorageId;
}private async Task UploadEmailToS3(string emailStorageId, InsertEmailModel emailModel)
{
using (var stream = new MemoryStream(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(emailModel))))
{
var s3PutRequest = new PutObjectRequest
{
BucketName = EnvironmentVariables.MailSendingBucket,
Key = emailStorageId,
InputStream = stream
};
await s3Client.PutObjectAsync(s3PutRequest);
}
}
private async Task PollQueueAsync(ILambdaContext context)
{
var request = new ReceiveMessageRequest
{
QueueUrl = EnvironmentVariables.MailQueue,
MaxNumberOfMessages = EnvironmentVariables.MailNumberPerBatch
};
var sqsResult = await sqsClient.ReceiveMessageAsync(request);
var sendEmailTasks = sqsResult.Messages
.Select(async sqsMessage => await InvokeLambdaAndDeleteMessage(sqsMessage));
await Task.WhenAll(sendEmailTasks);
}private async Task InvokeLambdaAndDeleteMessage(Message sqsMessage)
{
var request = new InvokeRequest
{
FunctionName = EnvironmentVariables.SendEmailLambdaName,
Payload = sqsMessage.Body
};
var invokeResponse = await lambdaClient.InvokeAsync(request);
if (WasCorrectlySent(invokeResponse))
{
await DeleteMessage(sqsMessage, invokeResponse);
}
}private async Task DeleteMessage(Message sqsMessage)
{
var deleteMessageRequest = new DeleteMessageRequest
{
QueueUrl = EnvironmentVariables.MailQueue,
ReceiptHandle = sqsMessage.ReceiptHandle
};
await sqsClient.DeleteMessageAsync(deleteMessageRequest);
}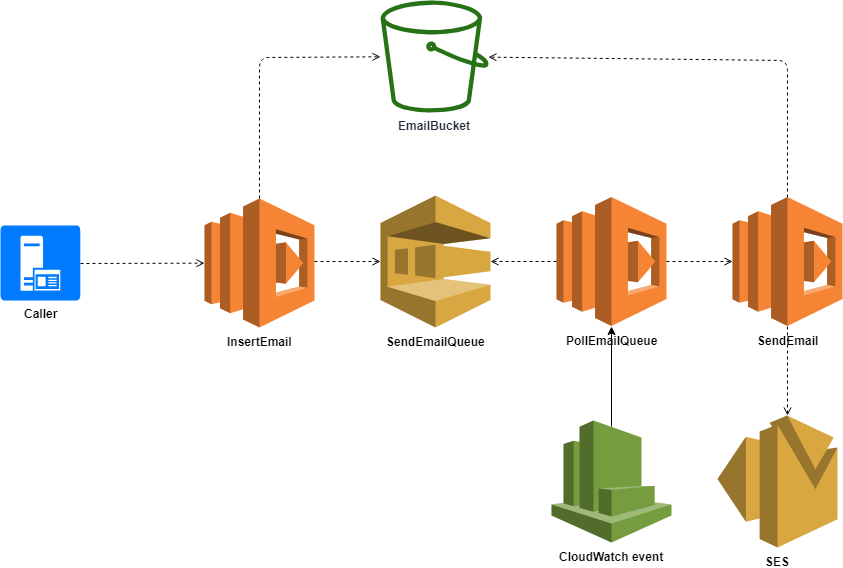
public async Task<bool> SendEmailAsync(string emailTaskId, ILambdaContext context)
{
var insertEmailModel = await GetEmailObjectFromS3(emailTaskId);
var sendEmailRequest = CreateRawEmailModel(insertEmailModel);
var result = await sesClient.SendRawEmailAsync(sendEmailRequest);
return result.HttpStatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK;
}private async Task<InsertEmailModel> GetEmailObjectFromS3(string emailTaskId)
{
var s3Object = await s3Client.GetObjectAsync(EnvironmentVariables.MailSendingBucket, emailTaskId);
using (var reader = new StreamReader(s3Object.ResponseStream))
{
var s3Contents = reader.ReadToEnd();
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<InsertEmailModel>(s3Contents);
}
}How to use it?
public async Task<string> InsertEmailAsync(InsertEmailModel insertEmailModelModel)
{
var lambdaRequest = new InvokeRequest
{
FunctionName = insertEmailLambdaName,
Payload = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(insertEmailModelModel)
};
var invokeResult = await lambdaClient.Value.InvokeAsync(lambdaRequest);
CheckLambdaResult(invokeResult);
return invokeResult.Payload.Deserialize<string>();
}public class LoanHasBeenPaidOffEventHandler : IEventHandler<LoanHasBeenPaidOffEvent>
{
...
private readonly IEmailClient _emailClient;
public LoanHasBeenPaidOffEventHandler(IEmailClient emailClient)
{
_emailClient = emailClient;
}
public void Handle(LoanHasBeenPaidOffEvent @event)
{
...
var insertMailModel = new InsertEmailModel
{
To = @event.CustomerMailAddress,
Subject = MailSubject,
Body = mailBody
};
_emailClient.InsertEmail(insertMailModel);
}
}
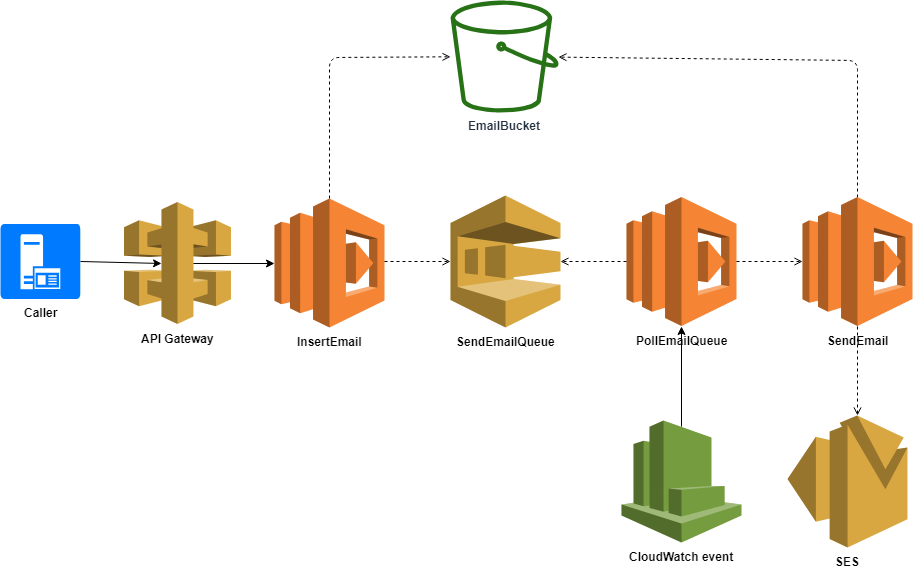
def insertEmail(insertEmailModel):
return requests.post(insertEmailUrl, data = insertEmailModel)
def insertEmail(insertEmailModel):
return requests.post(insertEmailUrl, data = insertEmailModel)
export class EmailService {
...
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}
insertEmail(insertEmailModel: InsertEmailModel): Observable<string> {
return this.http.post<string>(this.insertEmailUrl, insertEmailModel);
}
}

Challenges
Challenges
Increased system complexity
Challenges
Increased system complexity
Maintenance, service ownership in team or organization
Challenges
Increased system complexity
Maintenance, service ownership in team or organization
Versioning
Challenges
Increased system complexity
Maintenance, service ownership in team or organization
Versioning
Testing
Challenges
Increased system complexity
Maintenance, service ownership in team or organization
Versioning
Testing
Deploying
Challenges
Deploying


HOW TO
HOW TO
Deploy new version of the code (e.g. Lambda)
HOW TO
Deploy new version of the code (e.g. Lambda)
Update infrastructure
HOW TO
Deploy new version of the code (e.g. Lambda)
Update infrastructure
Create new environment from scratch


AWS
CloudFormation
https://www.dccomics.com/characters/superman
"Resources":{
"MailSendingBucket":{
"Type":"AWS::S3::Bucket"
},
"InsertEmail":{
"Type":"AWS::Serverless::Function",
"Properties":{
"Handler":"ServerlessMicroservice::ServerlessMicroservice.Lambdas.InsertEmailLambda::InsertEmailAsync",
"Environment":{
"Variables":{
"MailQueueUrl":{ "Ref":"MailQueue" },
"MailSendingBucket":{ "Ref":"MailSendingBucket" }
}
}
}
},
"SendEmail":{
"Type":"AWS::Serverless::Function",
"Properties":{
"Handler":"ServerlessMicroservice::ServerlessMicroservice.Lambdas.SendEmailLambda::SendEmailAsync",
"Environment":{
"Variables":{
"MailQueueUrl":{ "Ref":"MailQueue" },
"MailSendingBucket":{ "Ref":"MailSendingBucket" }
}
}
}
}
}Resources:
MailSendingBucket:
Type: "AWS::S3::Bucket"
InsertEmail:
Type: "AWS::Serverless::Function"
Properties:
Handler: "ServerlessMicroservice::ServerlessMicroservice.Lambdas.InsertEmailLambda::InsertEmailAsync"
Environment:
Variables:
MailQueueUrl:
Ref: MailQueue
MailSendingBucket:
Ref: MailSendingBucket
SendEmail:
Type: "AWS::Serverless::Function"
Properties:
Handler: "ServerlessMicroservice::ServerlessMicroservice.Lambdas.SendEmailLambda::SendEmailAsync"
Environment:
Variables:
MailQueueUrl:
Ref: MailQueue
MailSendingBucket:
Ref: MailSendingBucketaws cloudformation deploy --template-file serverless-mail.yaml --stack-name serverless-mail --region eu-west-1

https://giphy.com/gifs/machine-goldberg-rube-SFq1DyiaqOxK8

AWS CodePipeline
ArtifactStore:
Type: S3
Stages:
- Name: Source
Actions:
- Name: CodePackage
ActionTypeId:
Category: Source
Owner: AWS
Provider: S3
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: CodePackage
PollForSourceChanges: true
- Name: CodeConfiguration
ActionTypeId:
Category: Source
Owner: AWS
Provider: S3
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: CodeConfiguration
PollForSourceChanges: trueStages:
...
- Name: CreateChangeSet
Actions:
- Name: CreateChangeSet
InputArtifacts:
- Name: CodePackage
- Name: CodeConfiguration
ActionTypeId:
Category: Deploy
Owner: AWS
Provider: CloudFormation
Configuration:
ActionMode: CHANGE_SET_REPLACE
- Name: DeployChangeSet
Actions:
- Name: DeployChangeSet
ActionTypeId:
Category: Deploy
Owner: AWS
Provider: CloudFormation
Configuration:
ActionMode: CHANGE_SET_EXECUTE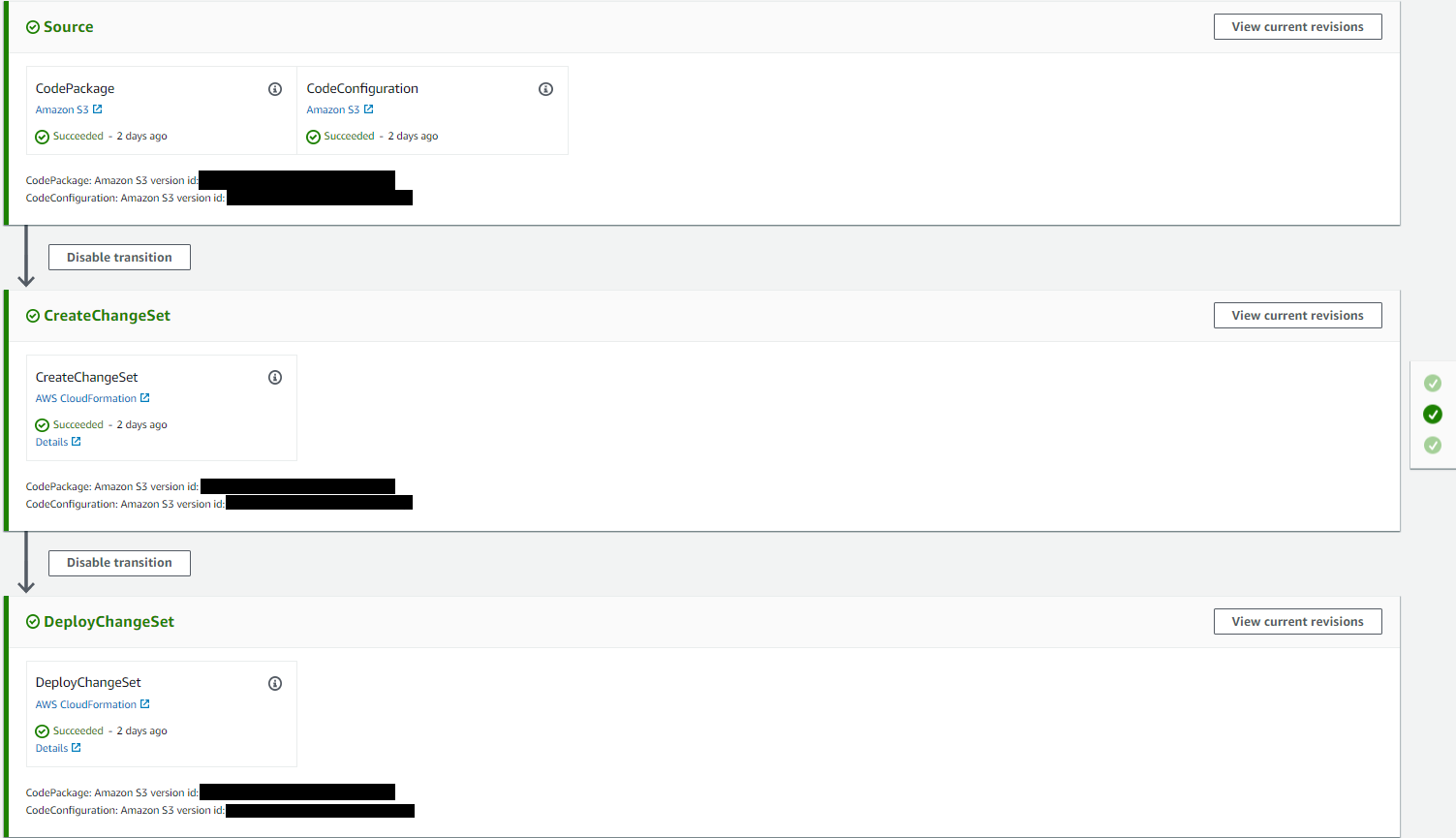
Full ci/cd pIPELINE
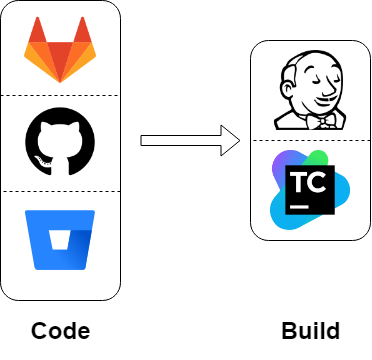
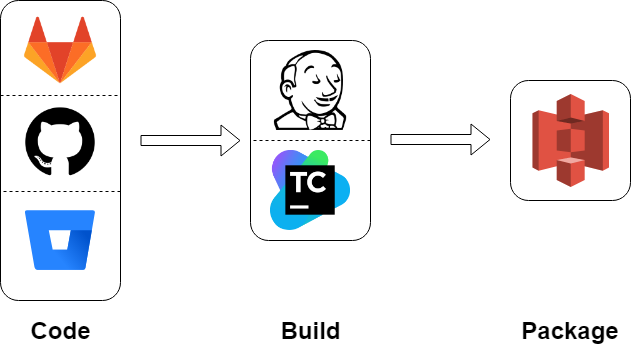
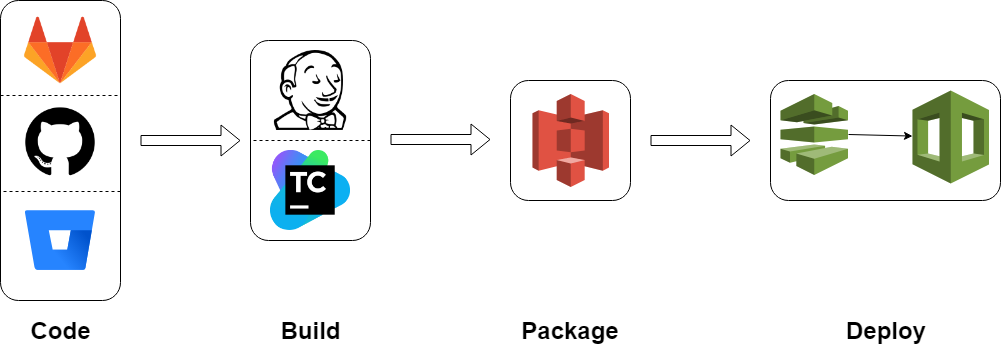
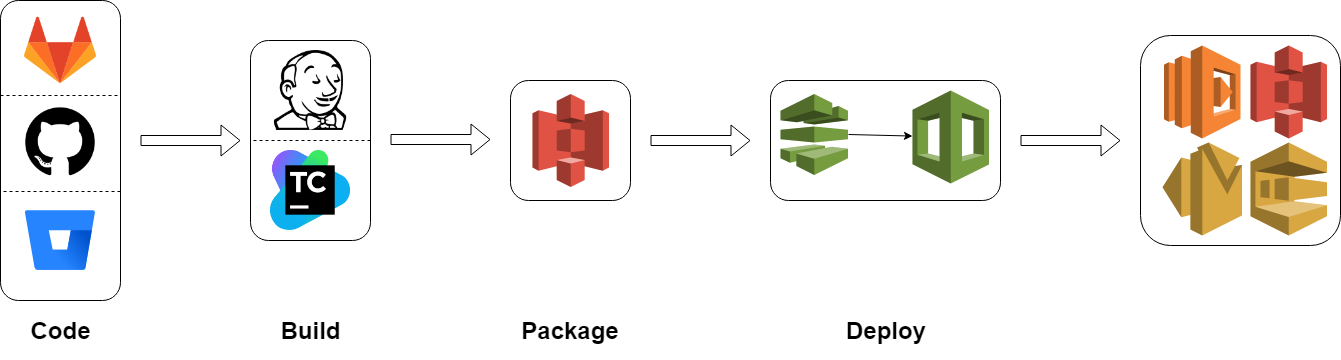
Deploy new version of the code (e.g. Lambda)

Deploy new version of the code (e.g. Lambda)
Update infrastructure


Deploy new version of the code (e.g. Lambda)
Update infrastructure
Create new environment from scratch



FINAL THOUGHTS
FINAL THOUGHTS
Trivial example
FINAL THOUGHTS
Trivial example
FINAL THOUGHTS
Match the solution with requirements
Trivial example
wojciech-dabrowski
wojciech-dabrowski

wojc.dabrowski@gmail.com





Northmill
facebook.com/northmill.se
northmill.com




SpreadIT
facebook.com/SpreadITpl
spreadit.pl





Gruba IT
facebook.com/grubait
gruba.it


Q&A
Serverless microservice - there and back again (Just DevOps)
By Wojciech Dąbrowski
Serverless microservice - there and back again (Just DevOps)
- 113



