Big Data
Outline
- The problem
- Hadoop
- Ecosystem
- What we have @IMA
- Hive
- HQL
- MapReduce
- Why bother?
The Problem
Facebook: 20+ TB compressed/day
CERN: 40 TB / day (15 PB / day)
NYSE: 1 TB / day
R1: 4 TB / day
And growth is accelerating
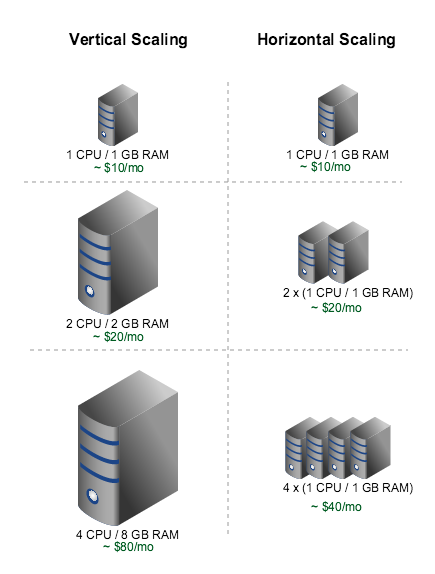
Horizontal scalability = $$$
Hadoop
Hadoop is an ecosystem
Distributed File System
Fault tolerant
Handles replication
Parallel computation
Scalable
(for all your graphic needs, contact amitteau@rhythmone.com)

Horizontal storage







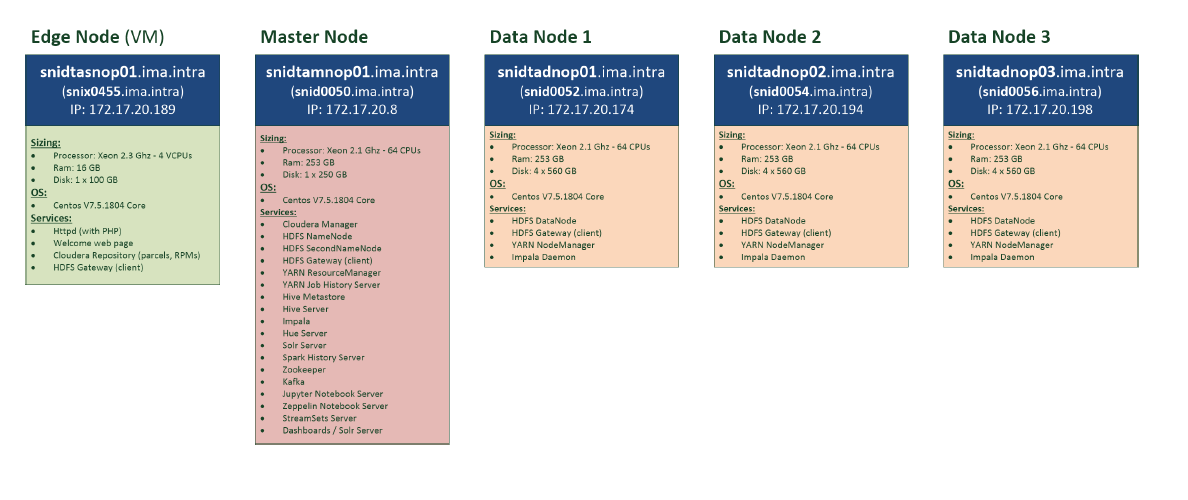
Our cluster

Partitioning
Split the data in regards of one variable (eg. date) and allocate to various nodes (computers)
With a date partitioning, the Master will allocate:
- Node 1 would store data from 06/01/2013, 06/03/2013 and 06/04/2013
- Node 2 would store data from 06/02/2013 and 06/05/2013
N1
N2
DO NOT QUERY DATA WITHOUT A CONDITION ON PARTITIONS
(we will come back to that later... But don't do it, really)
Hive
Hive SQL: HQL
This is like SQL but different
Hive is not a language, it's only a wrapper for MapReduce
+++ ETL (Extract Transform Load)
--- Update, Insert
MapReduce:
Parallel computing
A simple programming model that apply to many large scale computing problem
Typical problem solved by MapReduce
- Read a lot of data
- Map: Extract something you care about each record
- Shuffle and sort (tiny part, not really important)
- Reduce: Aggregate, summarize, filter or transform
- Write the results
Outline stays the same, map and reduce change to fit the problem
Count words with MapReduce


Map
Reduce
MapReduce + SQL = HQL
Real life example:
SELECT
-- Reduce
pixel,
COUNT(uuid) AS nb_people
FROM radiumone_json.pixel_firings
WHERE
-- Map
dt BETWEEN 20180101 AND 20180115
AND pixel IN (45022, 45023)
GROUP BY pixel -- Reduce- Increase the volume of partitions you are looking for (here dt partitions) = Increase Map
- Increase number of computation in SELECT (count, sum, cast,...) or in GROUP BY (having, order,...) = Increase Reduce
Why bother?
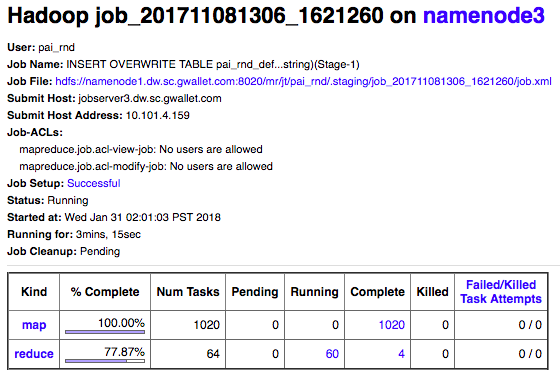
Because when you launch a Hive SQL query, this is the only thing you will see to track it:
Copy of BigData
By Yann Carbonne
Copy of BigData
- 624



