REST API
client-server model
- Client-server model is one of the most successful and used architectural design
- Speaking of architectural design, we need talk about:
- Components
- Connectors
- Constraints
-
Qualities
components
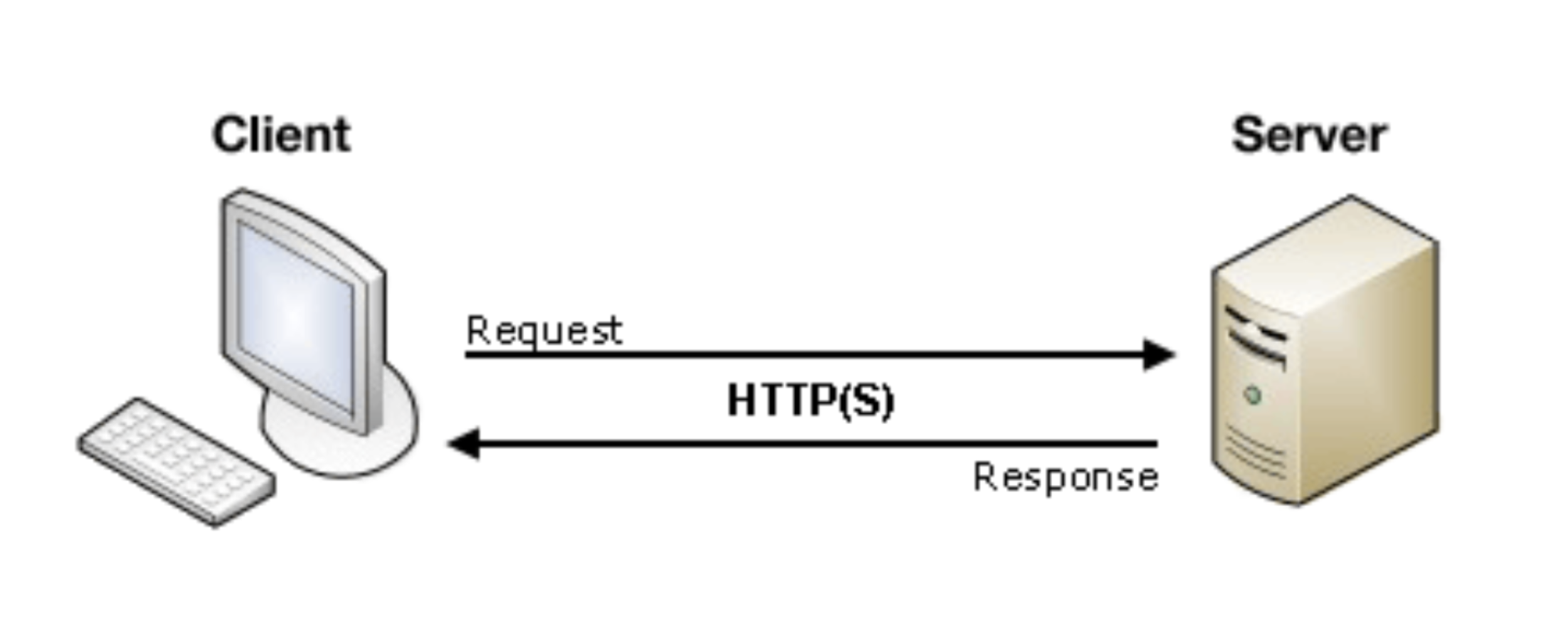
CONNECTORS
- Network protocols
- Examples:
- HTTP/HTTPS
- TCP
constraints
-
Many clients contact one server
-
Server does not know identity of client
-
Clients do not talk to clients
qualities yielded
-
Centralization: computation focused on the server
-
Evaluability and maintainability: change one server, impact many clients
-
Efficiency impacts: bandwidth limitations
-
Reliability impacts: server is single point of failure
- Stands for Representational State Transfer
- The World Wide Web is mostly based on REST architecture
Components
- Web services containing resources
- Resource providers
Connectors
- Primarily application level network protocols, HTTP and HTTPS
Constraints
- Client-server
- Stateless
- Cacheable
- Uniform Interface
- Layered system
- Code on demand (optional)
constraint: Uniform interface
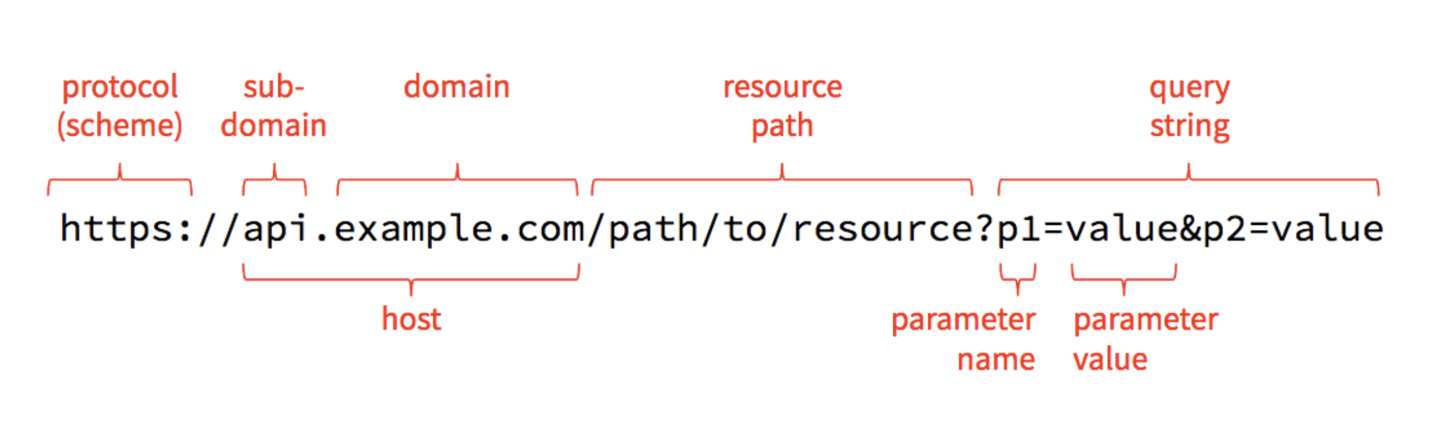
HTTP Verbs: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTION
qualities yielded
- Scalability
- Efficiency
- Decoupling
- Stands for Asynchronous JavaScript And XML
- It allows us to dynamically fetch data and display it on page without refreshing the page
- It not a programming language; it is a technique
xmlhttpRequest
- An object for exchanging data between client and server behind the scenes
- All browsers provide this object
- Demo: https://www.w3schools.com/js/tryit.asp?filename=tryjs_ajax_first
- XMLHttpRequest is complicated, so let's create a abstract wrapper that encapsulates its complexity
API fun time
Coding Ninjas Bootcamp - Class 6: REST API
By Zico Deng
Coding Ninjas Bootcamp - Class 6: REST API
Introduction to REST API
- 172



