User Experience Design:
A crash course
Andrew Baker
Senior Experience Developer - Karsh Hagan
04.08.2015
What does An experience developer do?
digital strategy and creative concepting
user experience design
interaction/visual design
front-end development
Workshop Outline
1) Introduction
What is User Experience
Science!
Business Goals
User Research
Workshop Outline (continued)
2) Users and Research
Personas
Usability
Testing
Information Architecture
Workshop Outline (continued)
3) UX Design
User Journeys
Wireframes
Interaction Design
Why UX?
Everything has a user experience. Our job is to make that experience meaningful, efficient,and beautiful
Design is a plan for arranging elements in such a way as best to accomplish a particular purpose
— Charles Eames
Whats the point?
Design smarter things
Make people's lives easier
What can benefit from UX?
- web/native applications
- products
- systems of interaction
- marketing websites
- products

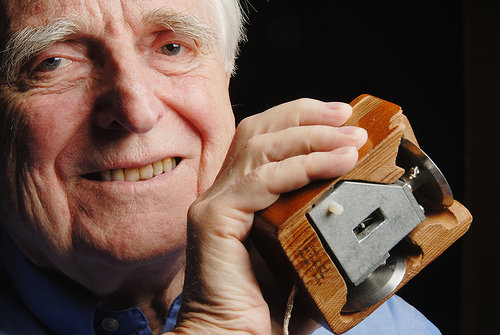
the original mouse, created by Douglas Engelbart in 1964
Life before the Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Command line everything!

Experimentation
THE GRAFACON : a hand-operated, gyro-style pointing device

Experimentation
The Knee-operated pointing device
One of many original pointing devices tested by Englebart and his team

The Mouse
An essential innovation in the advancement of graphical user interfaces
UX Fundamentals are rooted in science
Research to understand our users
Ideas to solve user needs while keeping in mind the objectives of the business
Build and Measure our solutions
business goals
information
user needs
scientific theories
are a matter of
constructing models through experimentation
Business Goals
KPI's (Key Performance Indicators) are established by:
1) Interviewing key stakeholders
2) User Research (usability testing, surveys, structured interviews, card sorting, etc
3) Analytics
Stakeholder interviews - best practice
1) No guessing
2) Stay away from talking solutions
3) Get out all of the issues
4) Develop evidence and impact
Stakeholder interview Example Q's
What defines the success of this project?
Who is your primary target and what is their objective?
What are the strengths/weaknesses of your competitors projects?
How do you know 'X' is a problem?

Interview question types
Open Questions — “How would you describe the app?”
Leading Questions — “What features are missing from the app?”
Closed/Direct Questions — “Which feature would you rather have, feature A or feature B ?”
tailored questions
tailoring questions to your specific stakeholder shows preparedness and thoughtful planning
“What are the most important types of information on yourwebsite.com?”
“As the VP of Marketing, how do you use yourwebsite.com to accomplish your team’s goals?”
User Research
'People’s behavior makes sense if you think about it in terms of their goals, needs, and motives'
- Thomas Mann
User Needs
What is your visitor's motivation?
Personas! (expanded on later)
Examples
"As a user, I need to be able to access my account"
"I need to be able to quickly purchase the items I have selected"
"I need to access an archive of posts related to this category"
How to understand user needs
1) User interviews
2) Observation
3) Focus groups
4) Surveys
5) Card Sort Exercise

card sorts are an easy way to gather user research and begin building IA
Users and Research
The first step in your UX Design Process
USER Personas
"Personas are archetypes built to identify our real users profile, needs, wants and expectations in order to design best possible experience for them"
User Centered Design
The ultimate goal of defining User Personas is to set up your product/interface design to be user oriented and meet the user goals
Personas are ‘fictional’ characters created based on real data and research around a problem domain, or a focus target

Goal-driven Persona Design
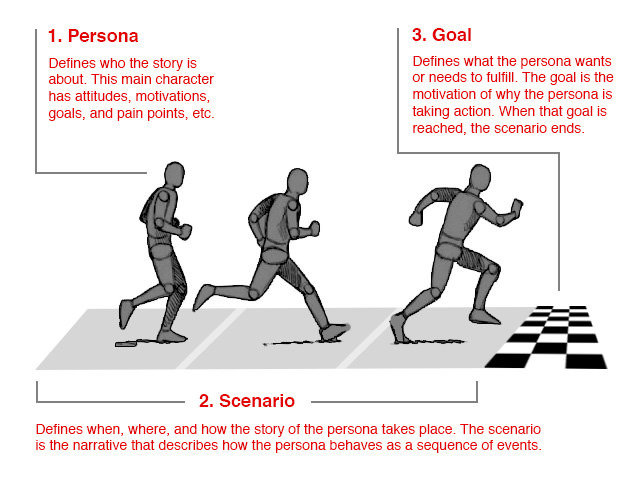
1) Persona: Who is the story about? What are his/her attitudes, motivations, objectives, pain-points, etc
2) Scenario: When, where, and how does this story take place? A narrative that describes how a persona would interact with website/product in a particular context to achieve their end goal(s)
3) Goal: What is the want or need that our persona is trying to fulfill by using our website/product? What are the tasks that will drive his/her success?
Goal-driven design
How to create Personas
- Interview and/or observe an adequate number of people.
- Find patterns in the responses and actions, and use those to group similar people together.
- Create archetypical models of those groups, based on the patterns found.
- Share those models with other team members and stakeholders, confirming that they are aligned with your stakeholders vision of your key users
Persona numbers
minimize number of personas (4-6) so the design is focused and can guarantee better success
establish primary persona and then define percentages for each persona
example
Jill - primary focus: fitness (50%)
Marci - focus: weight loss (30%)
Mark - focus: sports performance (10%)
Harold - focus: HR director (5%)
Dawn and Peter - focus: Donors (5%)
Personas answer 3
primary questions
what are the user's:
- needs
- wants
- limitations
Example Persona

Usability
Usability refers to the quality of a user's experience when interacting with products or systems, including websites, software, devices, or applications
"effectiveness, efficiency and the overall satisfaction of
the user"
Key Principles of Usability
- Intuitive design: a nearly effortless understanding of the architecture and navigation of the site
76% OF USERS AGREE THAT THE MOST CRUCIAL FACTOR IN ANY WEBSITE IS “MAKING IT EASY FOR ME TO FIND WHAT I WANT.”
- Ease of learning: a person has never seen the user interface. how long before he/she can accomplish basic tasks?
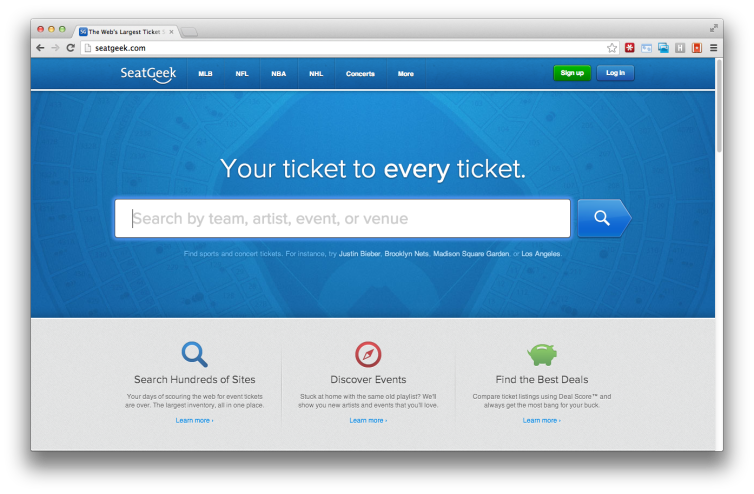
SeatGeek's exaggeratedly large search box tells users this site’s primary function is finding one thing: tickets
- Efficiency of use: How fast an experienced user can accomplish tasks
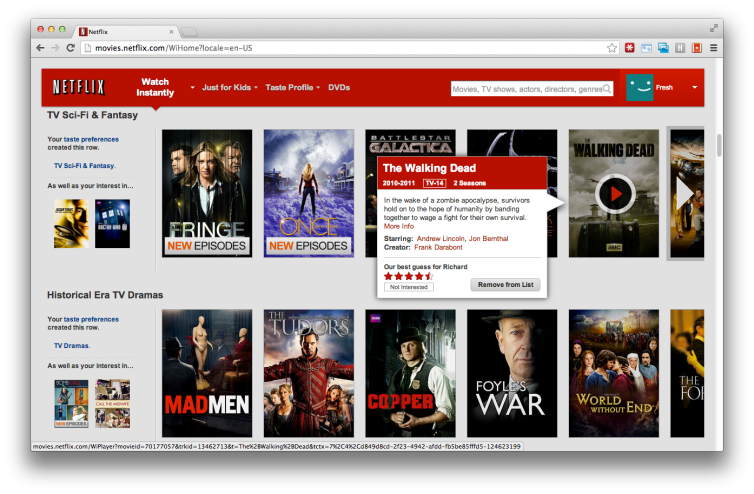
For Netflix, the most important function is streaming video. The site uses a gallery of teaser posters which serve as play buttons to directly access the streaming content
- Memorability: after visiting the site, if a user can remember enough to use it effectively in future visits

- Error frequency and severity: how often users make errors while using the system, how serious the errors are, and how users recover from the errors
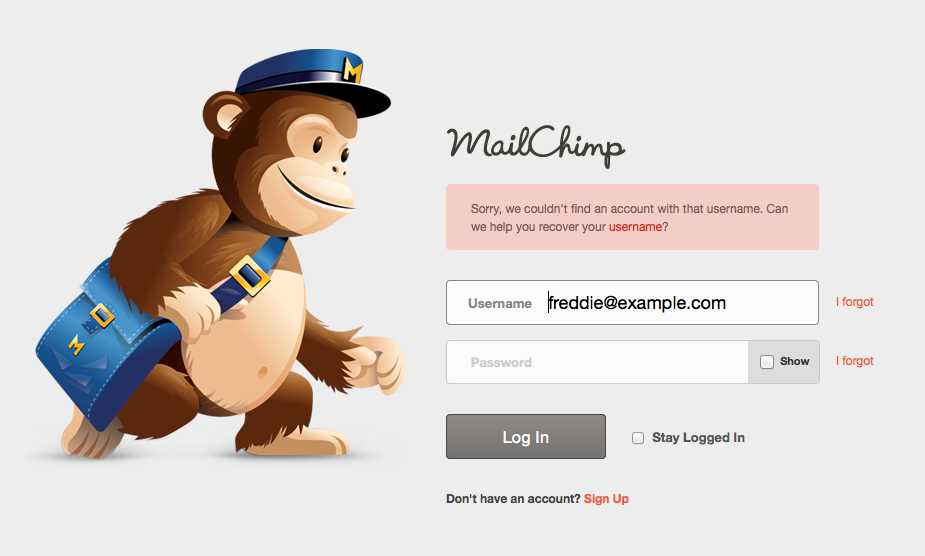
Mailchimp's login screen split the username and password errors so the form would tell users exactly where their credentials are incorrect
- Subjective satisfaction: If the user likes using the system

Ultra-satisfied web user
User Testing
USABILITY TESTING INFORMS THE DESIGNER AND THE DESIGN
Testing During Requirements Gathering phase
Talking to users about what features and functionality resonate most will help inform decisions on how to prioritize requirements.
Options for user requirements testing :
- Phone interviews
- Web surveys
Testing During The Design Phase
interactive wireframes are a design tool that are instantly-testable artifacts and require a minimal amount of setup before they are ready to be put in front of real users
Process :
- create tasks
- walk your tester through each task, observe their interactions, noting frustrations and successes.
- Ask them about their reactions and how they felt overall about the experience.
Information Architecture
creating structures to facilitate effective communication
The all important site map
A visual representation of your website's content and organization. Typically designed in a standard 'tree' heirarchical format
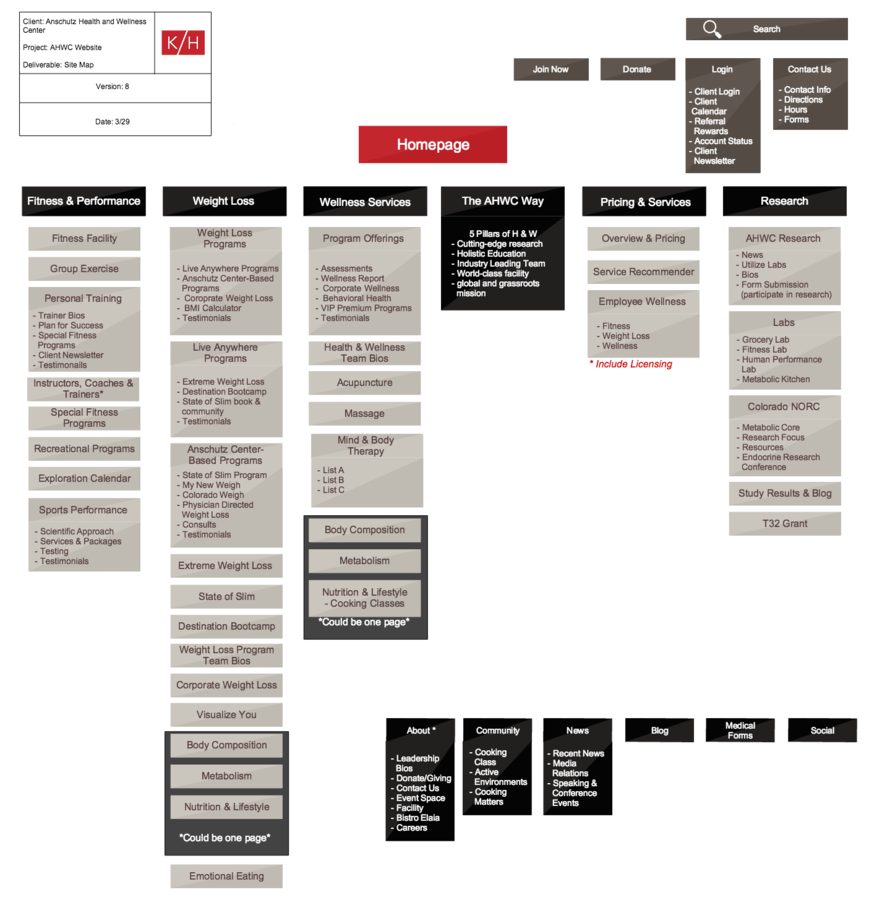
UX Design
Put this theory into practice!
Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works
— Steve Jobs
User Journey
User Journey/ Story
Illustrate the potential pathways that your user will follow leading up to and through your website/app/product
Google search
Website home
Promotion landing page
Newsletter
signup
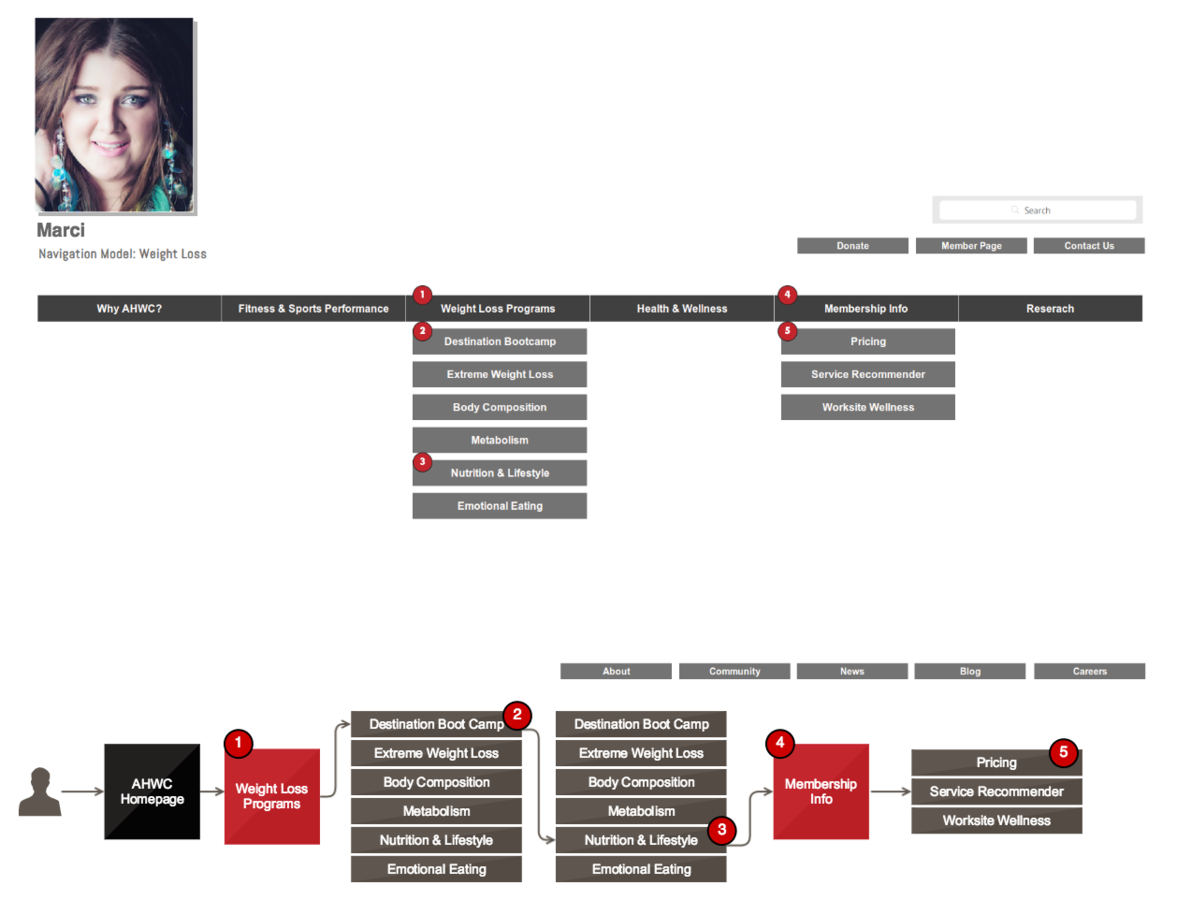
NaviGation Model
Based on the your user personas. Illustrate the specific navigation elements your user will use in order to land at their final destination
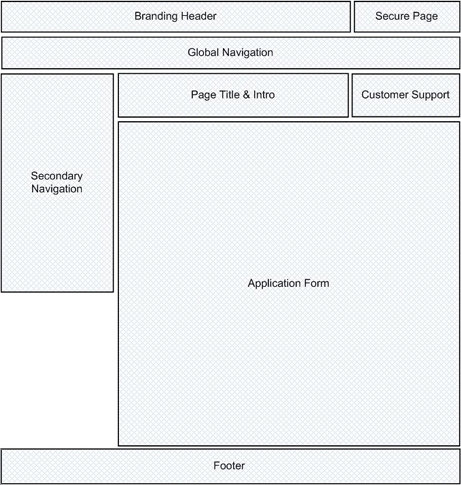
Wireframing
An iterative design method that helps build out the skeletal architecture of a website or software application
Wireframes are flat and static. The represent a single 'view' or page of a website interface.
Thus, they are more like stills from a movie or animation, and less like a photo.
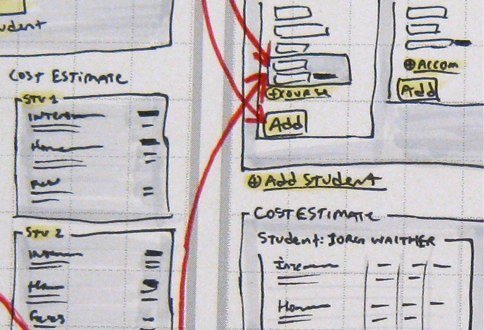
Where to start
Sketch (pen/pencil and paper)
Whiteboard
Key insights: It DOES NOT need to be pretty. The idea is to quickly get something that can be reviewed by teams, stakeholders, etc.
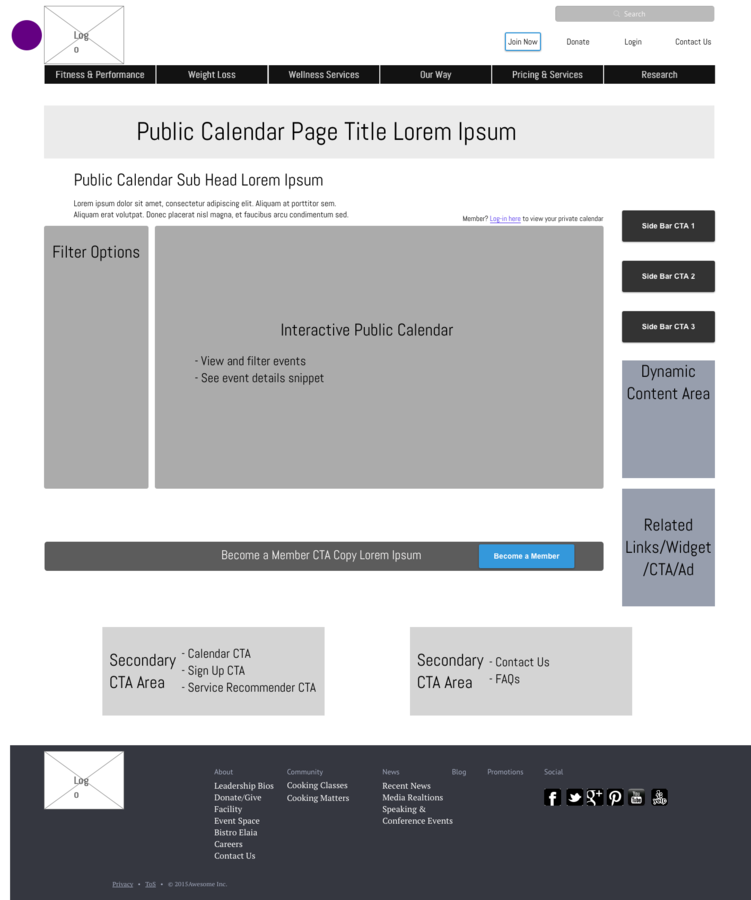
Next Step
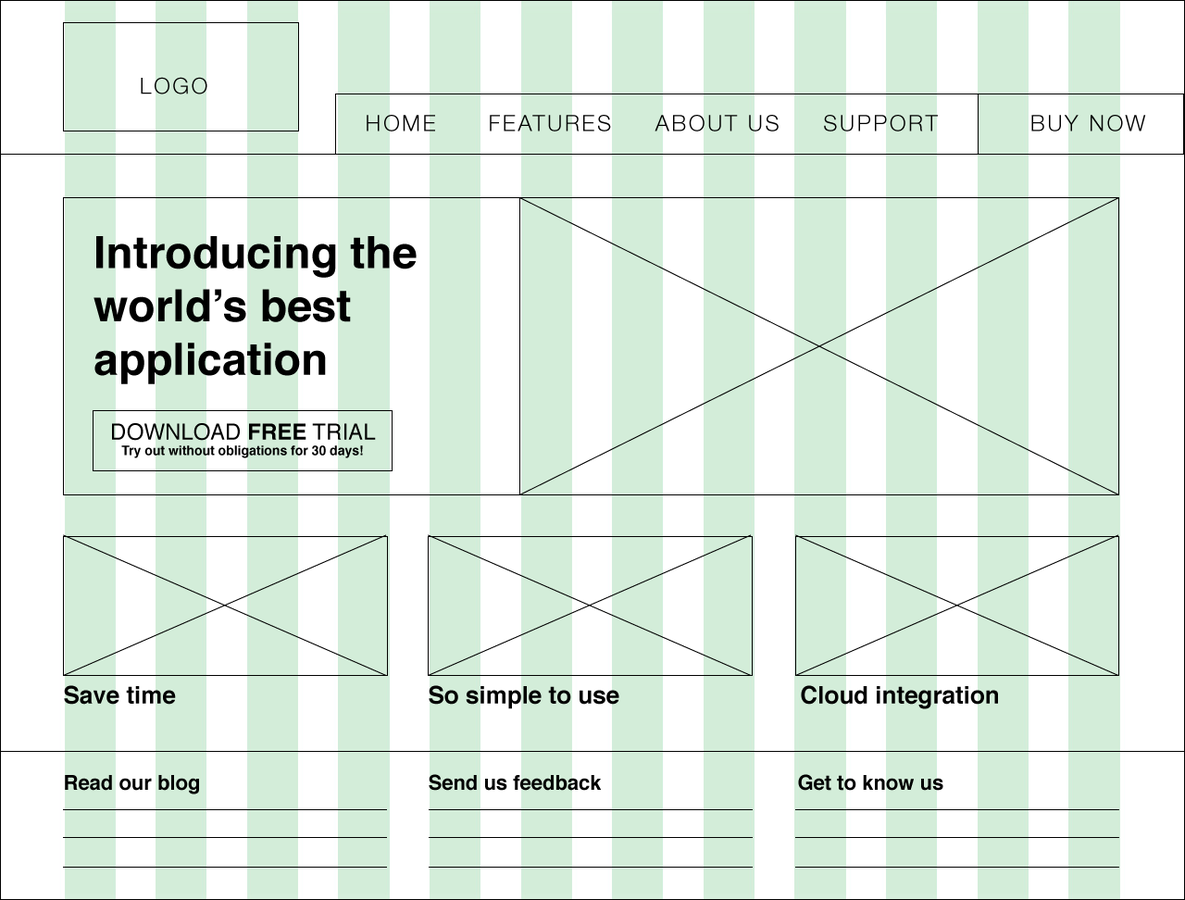
Low fidelity wireframes
Tools: Adobe Illustrator, UXPin, Balsamiq, Axure, Gliffy
Creating lo-fi wireframes
Set up a grid or ruler system
Create wireframe grids for each 'breakpoint' you determine in your requirements

Content arrangement with boxes
Simple boxes will help you outline which content should flow through the layout of your page
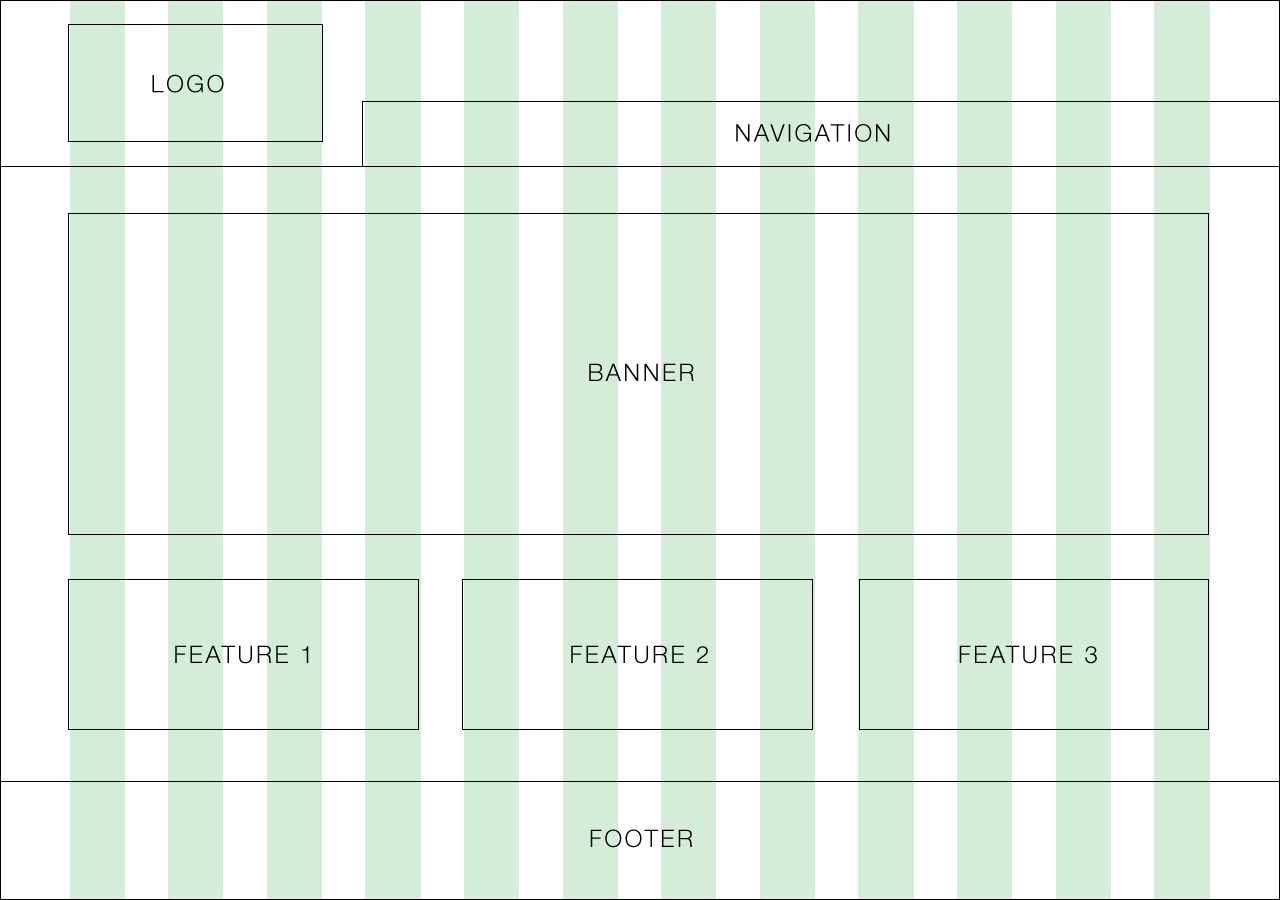
Determine heirarchy with typography and buttons
Experiment with weight and size, not fonts or font-styles
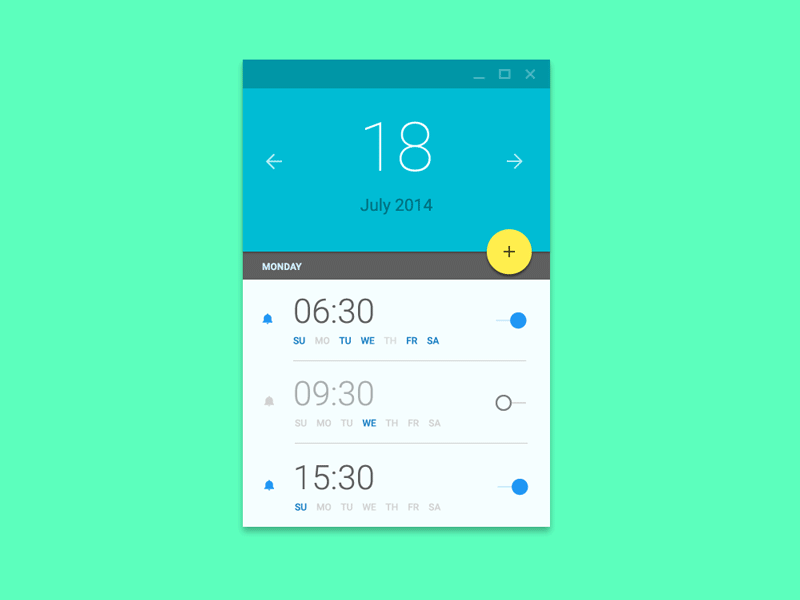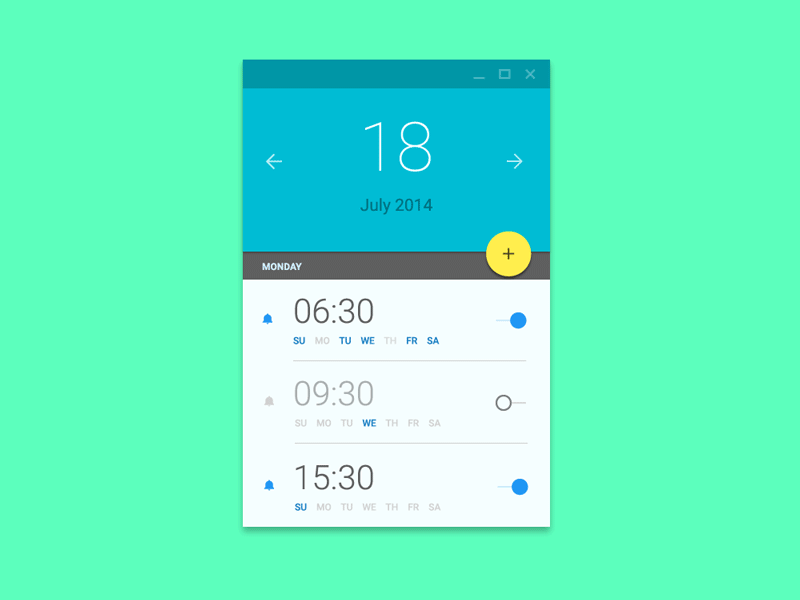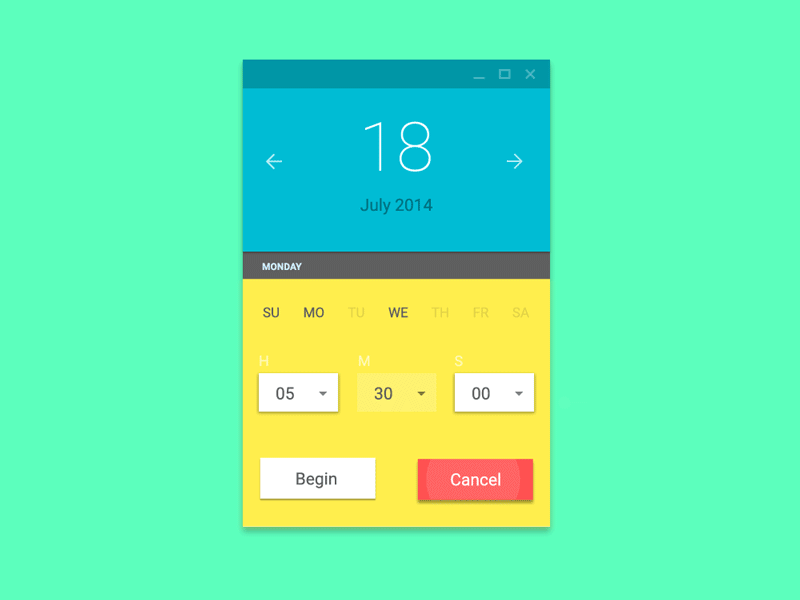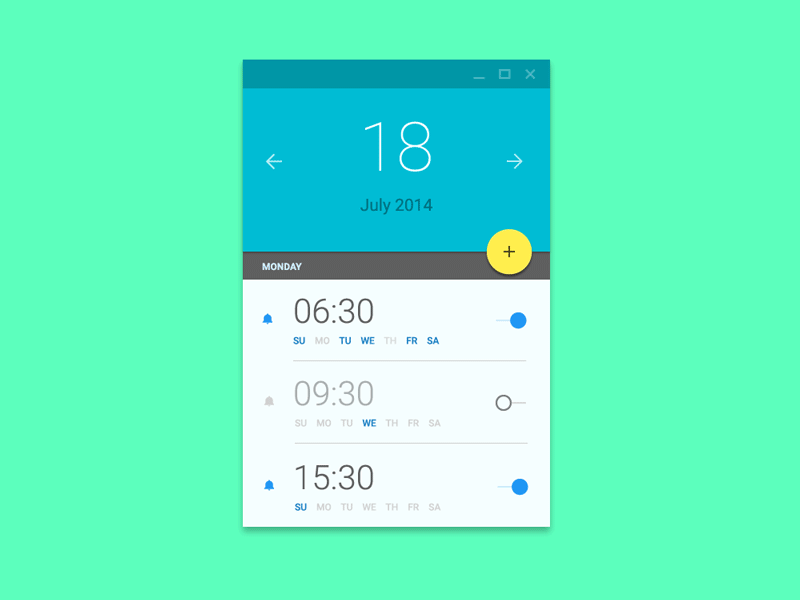
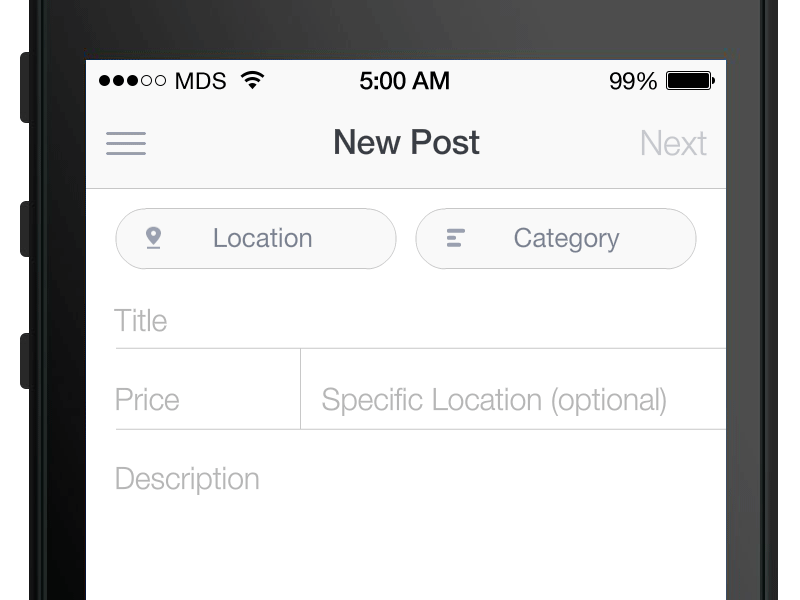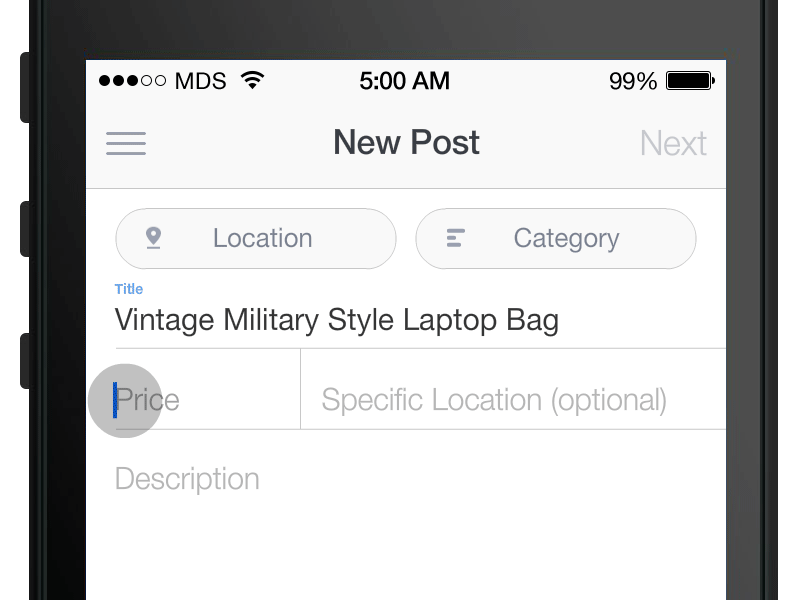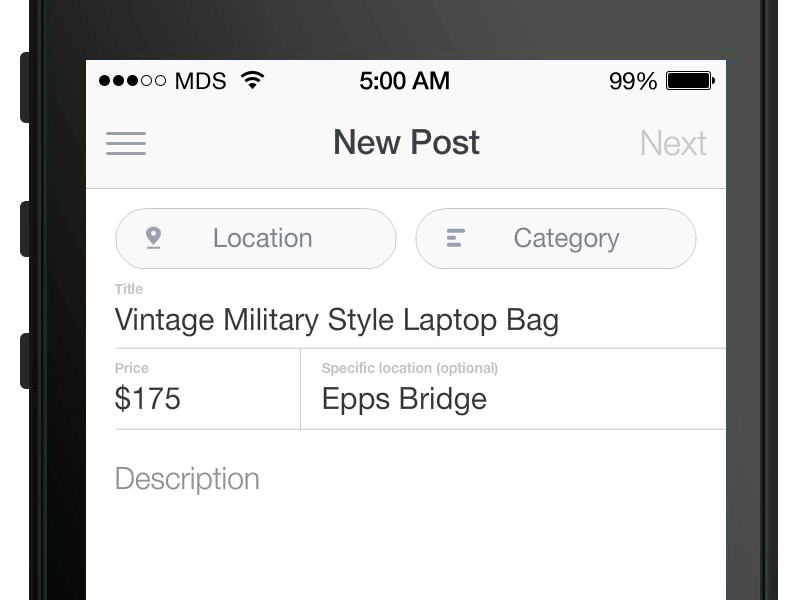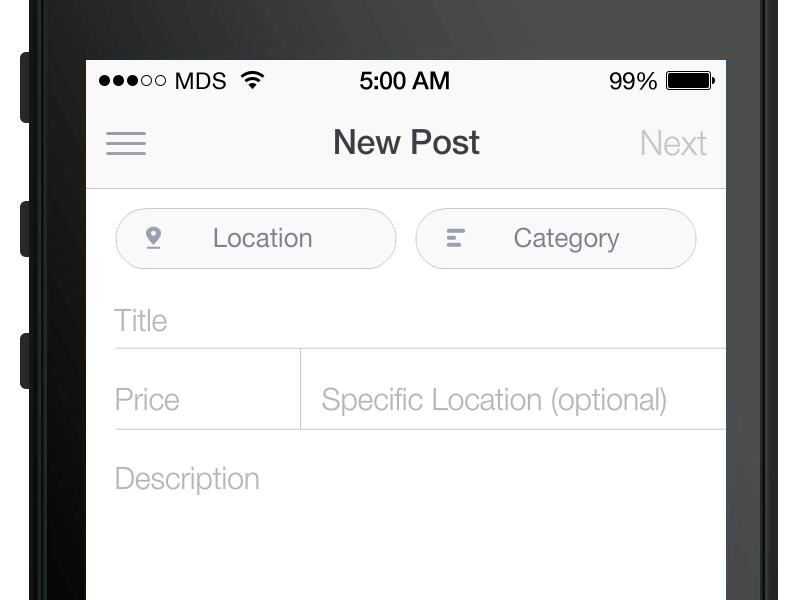
Interaction Design
Defines How Users Can Interact with an Interface
Questions to consider
- What can a user do with their mouse, finger, or stylus to directly interact with the interface?
- Can they push buttons, drag and drop content, pinch to zoom?
- What about the appearance (color, shape, size, etc) gives the user a clue about how it may function?
- What information do you provide to let a user know what will happen before they perform an action?
- What feedback does a user get once an action is performed?
- Are the interface elements a reasonable size to interact with?
dribbble.com is a great resource for finding interaction design inspiration
How have i put css animation to use?
karshhagan.com
How have i put css animation to use?
Brussels and Muscles via Be Colorado
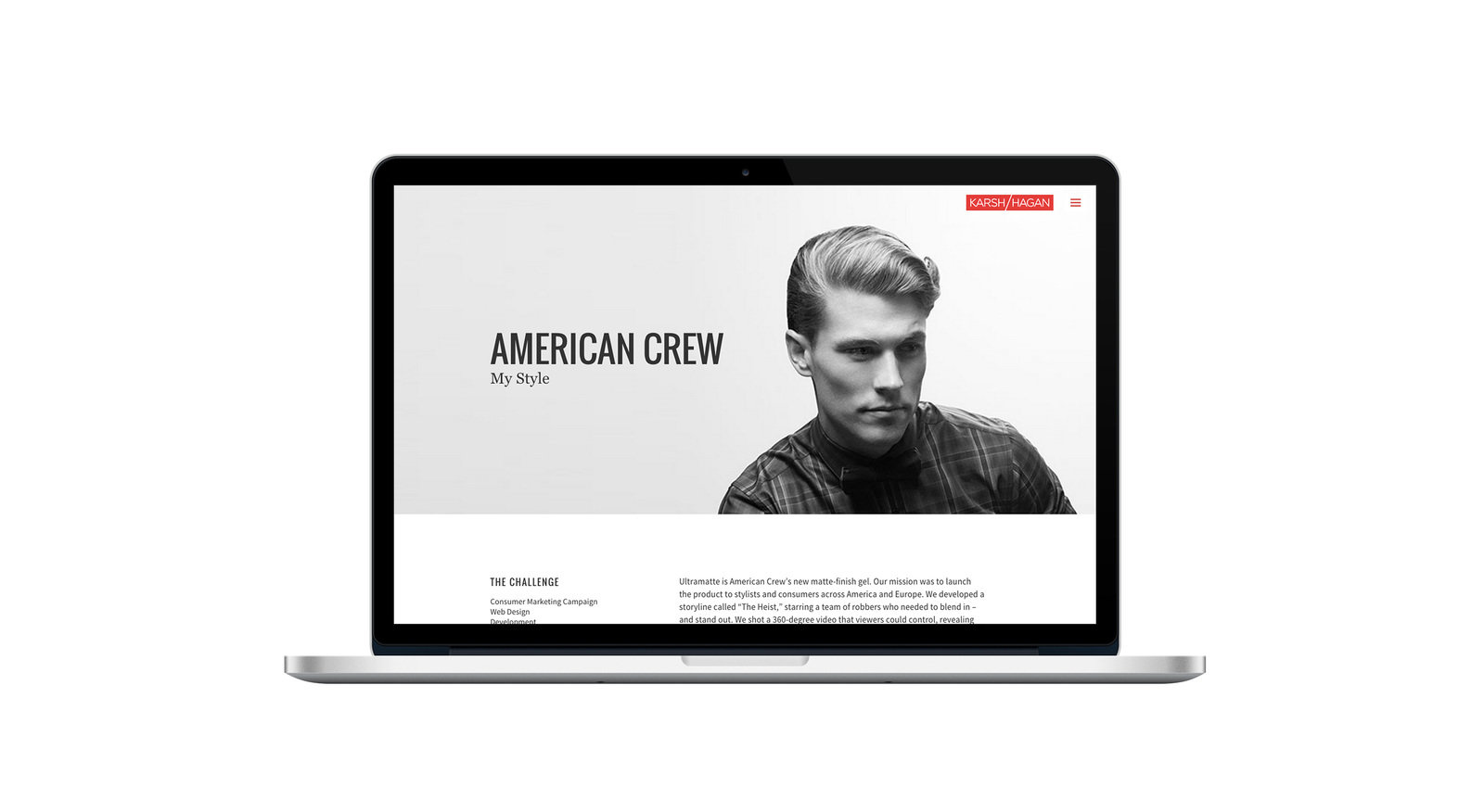
How have i put css animation to use?
Mystyle by American Crew
USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN: A CRASH COURSE
By Andrew Baker
USER EXPERIENCE DESIGN: A CRASH COURSE
- 1,062