DNA goes 3-dimensional: chromatin structure
Aleksandra Galitsyna
Invited lecture for SMTB 2020

Classical view on DNA
- DNA is a linear molecule of biopolymer that contains genetic information.

First proof that DNA is lineraly ordered
- Early Benzer experiments on E. coli and T4 bacteriophage:
Benzer, 1950-1960
https://slideplayer.com/slide/1400263/
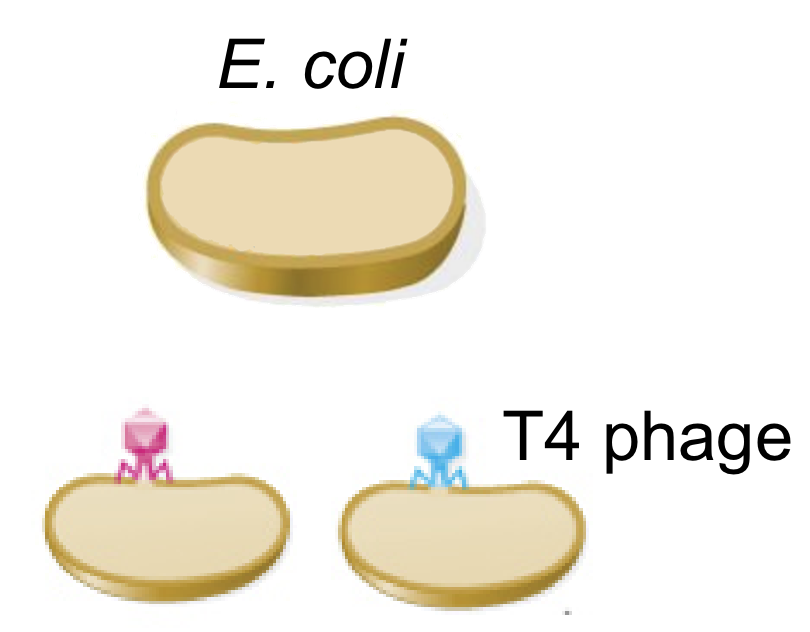

Bacterial loan on the agar plate,
plaques are formed at the locations infected by the virus
First proof that DNA is lineraly ordered
- Co-transfection by two mutants:
Benzer, 1950-1960
https://slideplayer.com/slide/1400263/
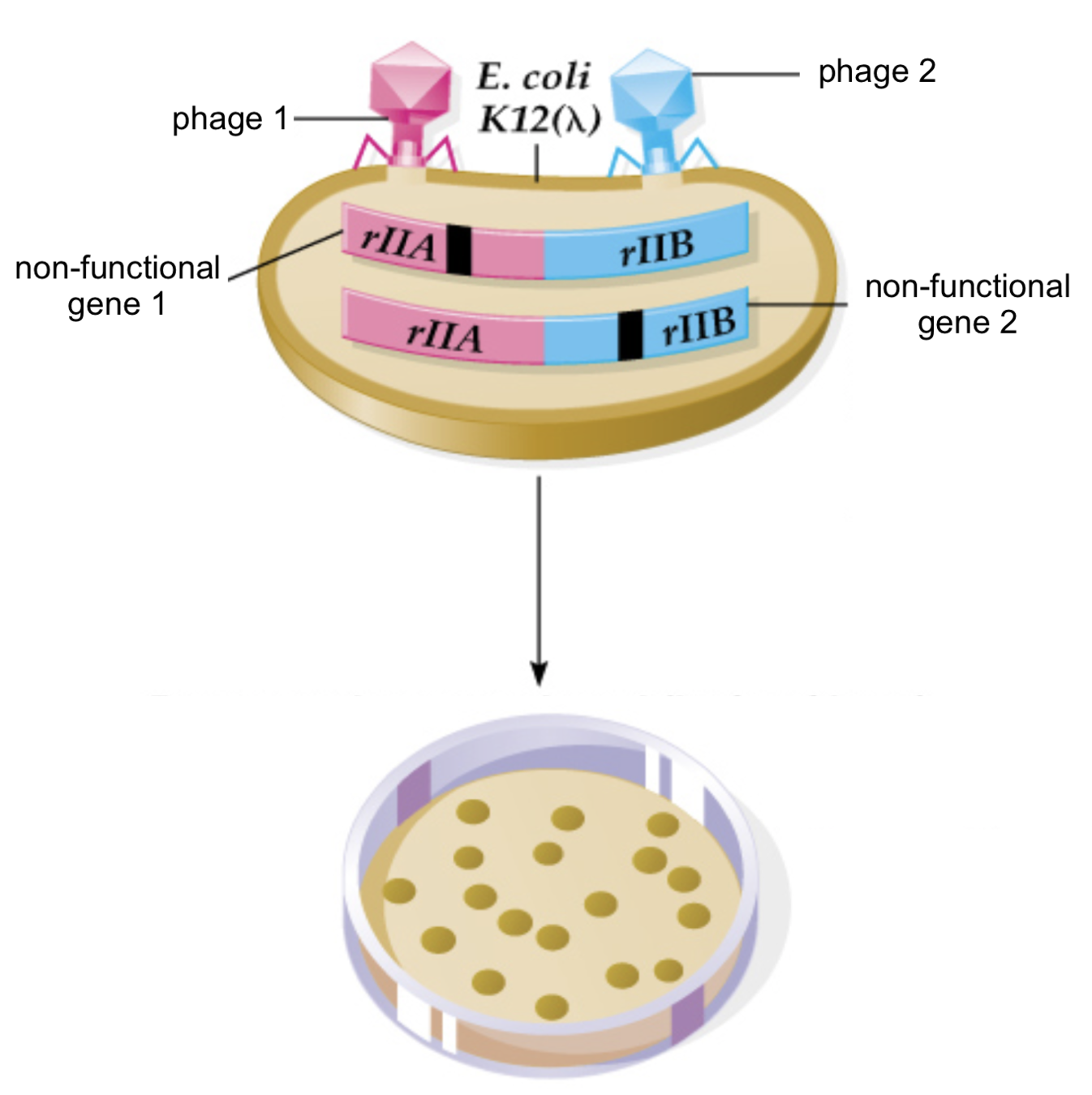
Plaques are formed
(infection takes place, wild type)
Plaques are not formed
(no infection)
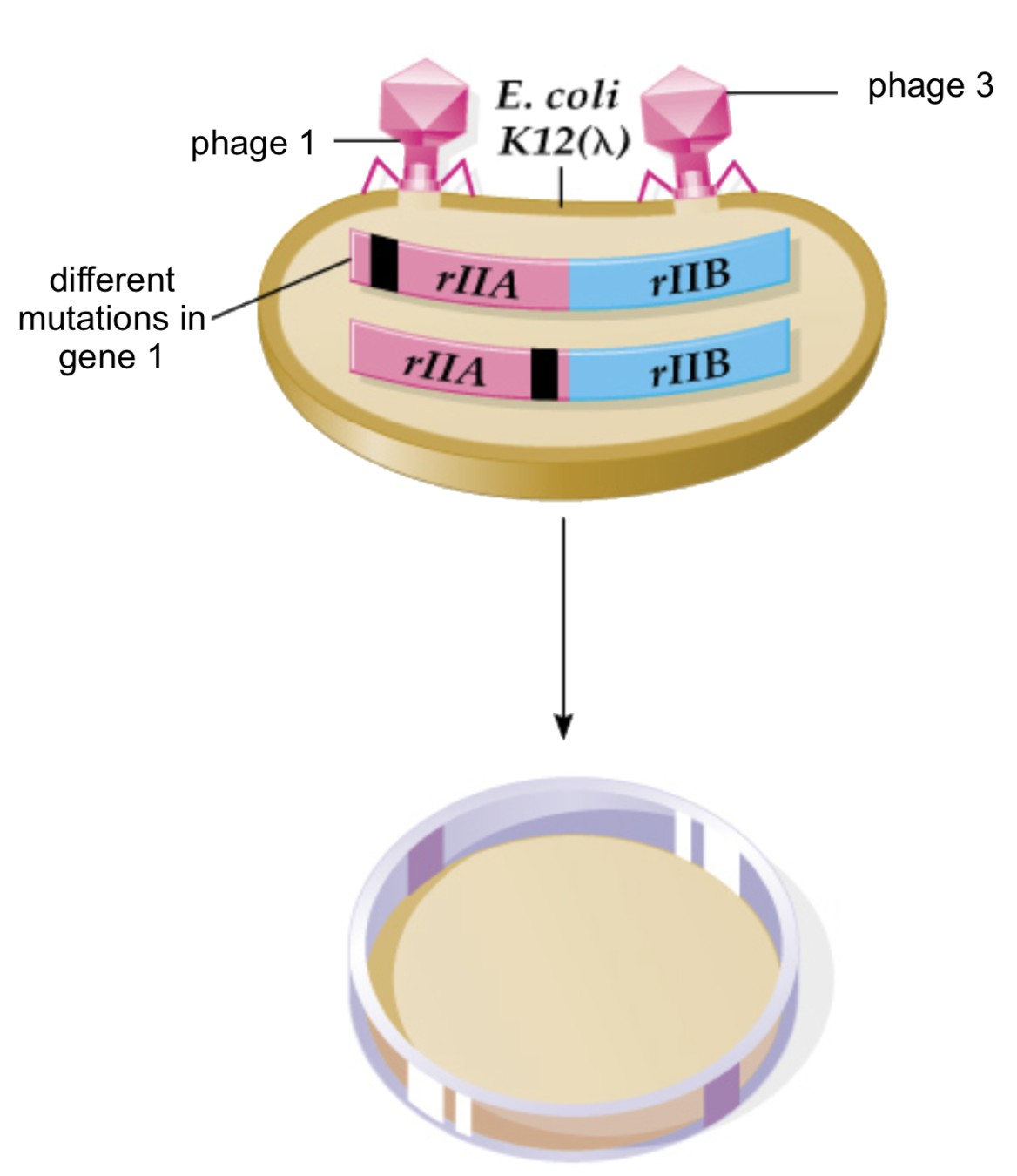
First proof that DNA is lineraly ordered
- Genetic map of bacteriophage
Benzer 1961
О - no infection, |- wild type
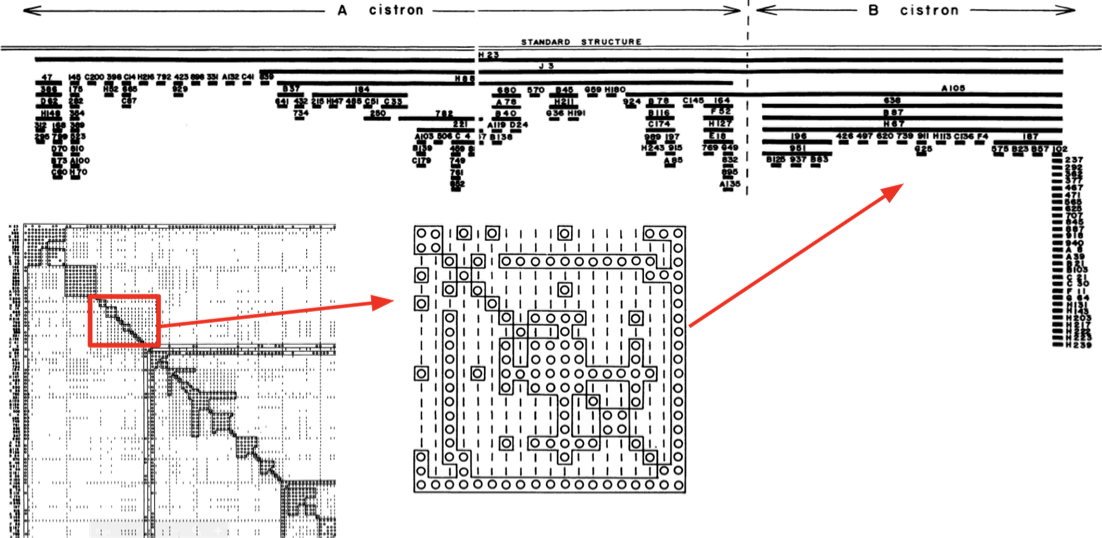
Mutations of phage,
ordered by similarity of patterns
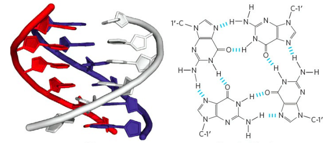
DNA as double helix
- Watson, Crick and Franklin: X-ray crystallography (1953)

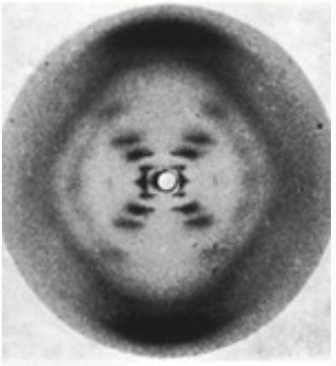
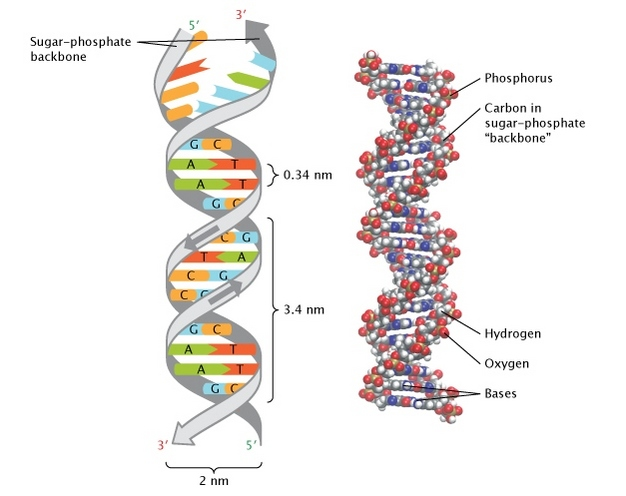
Pray Nature Education 2008

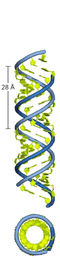

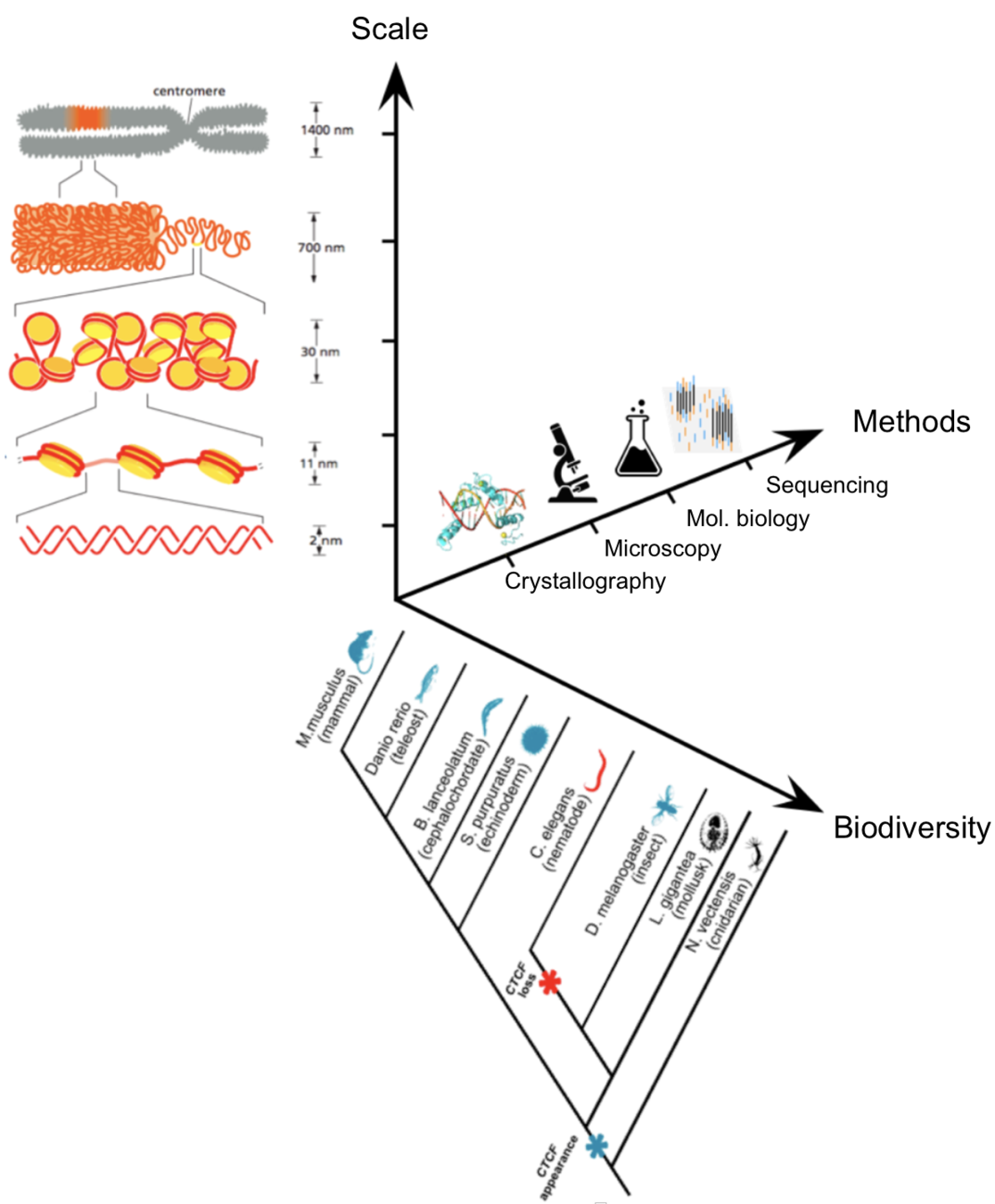
Levels of chromatin organisation
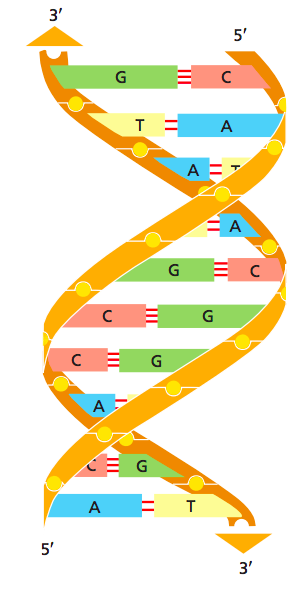
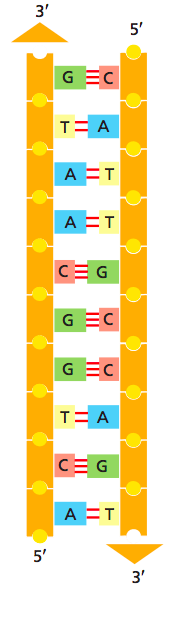
Sequence
Secondary structure
A-helix
B-helix
Z-helix
G-quadruplex
DNA hairpin
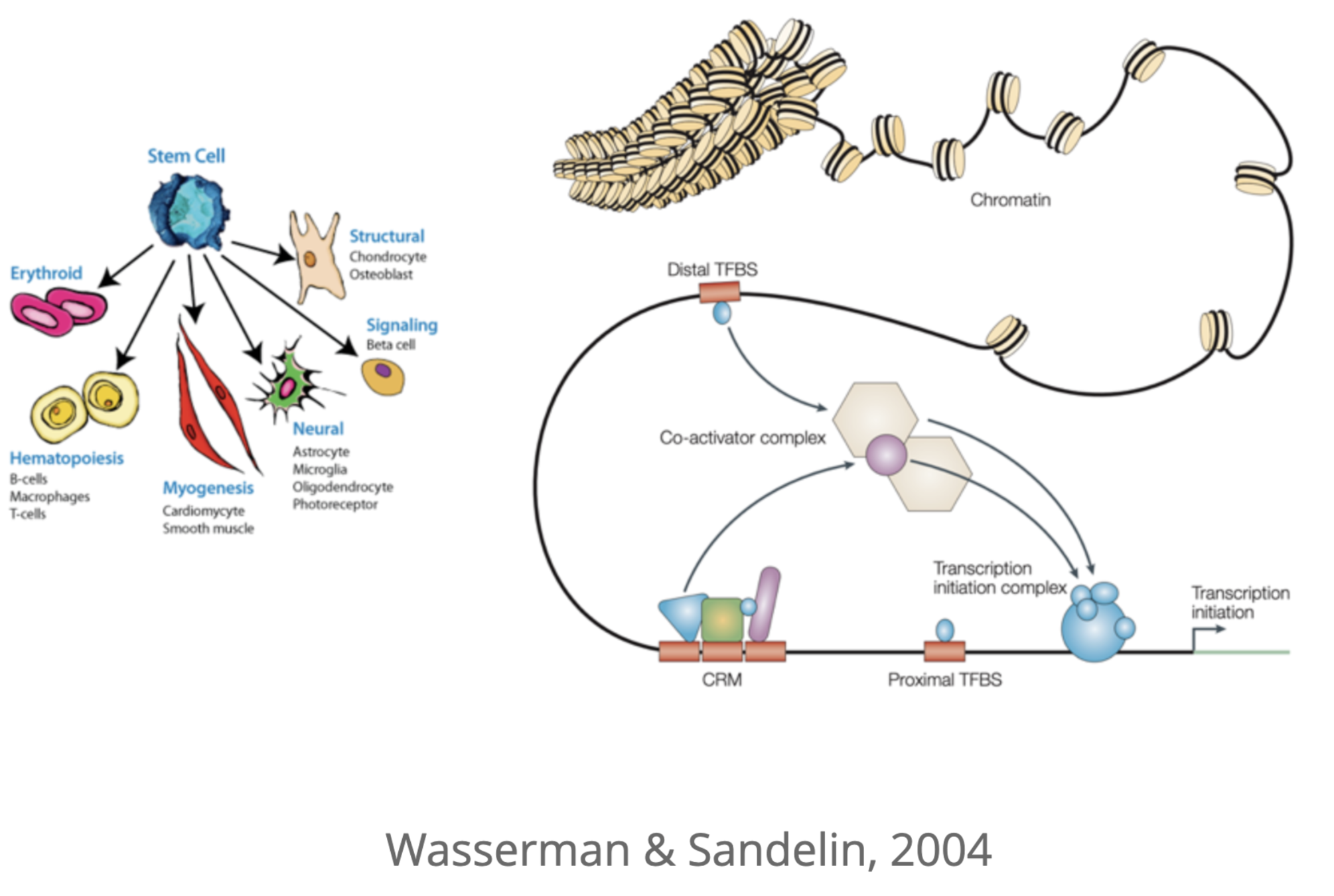
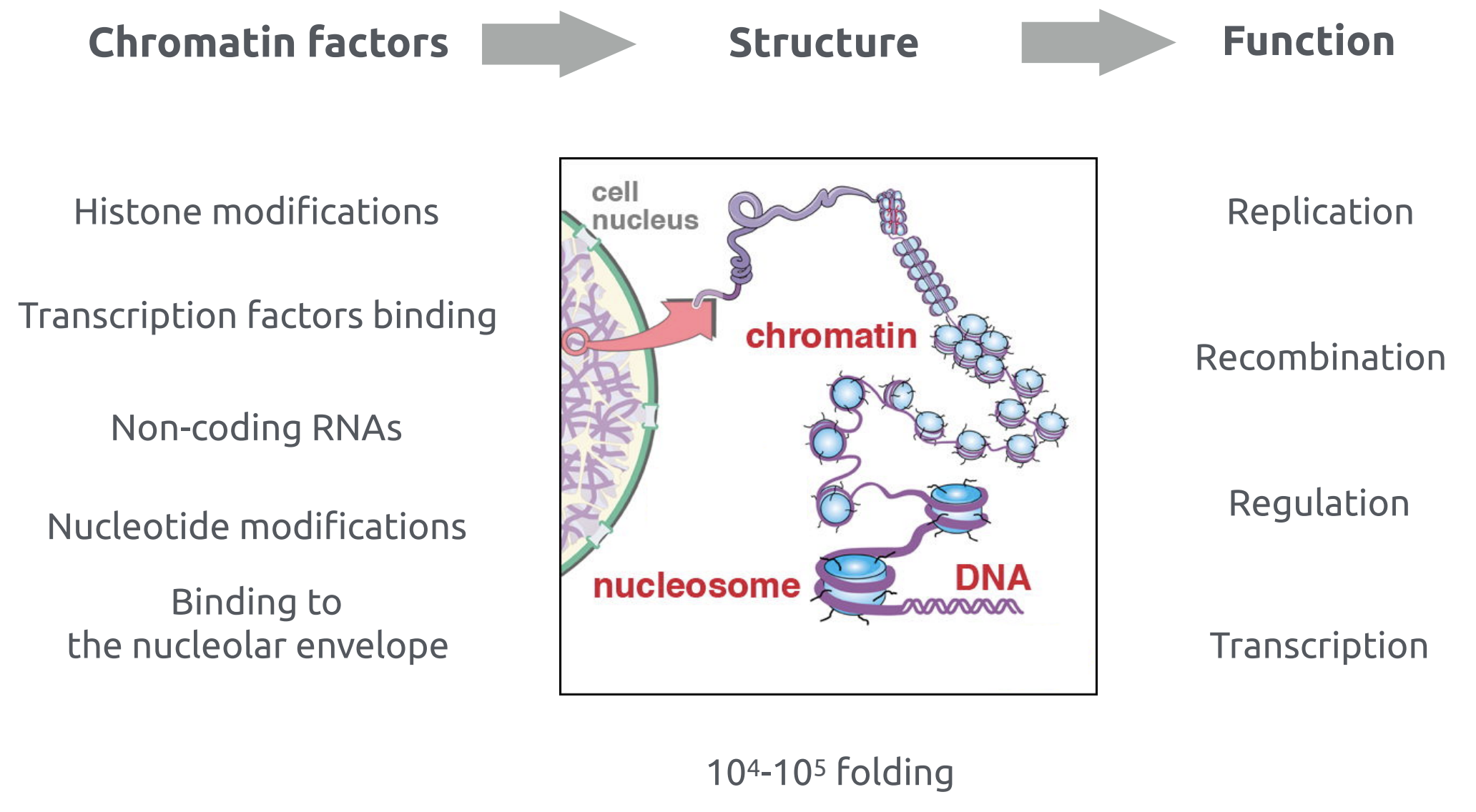
Chromatin is DNA-protein complex
DNA forms more complex structures upon the binding of proteins. For example, the binding of histones:
Alberts 2015 "Molecular Biology of the Cell" 6th edition
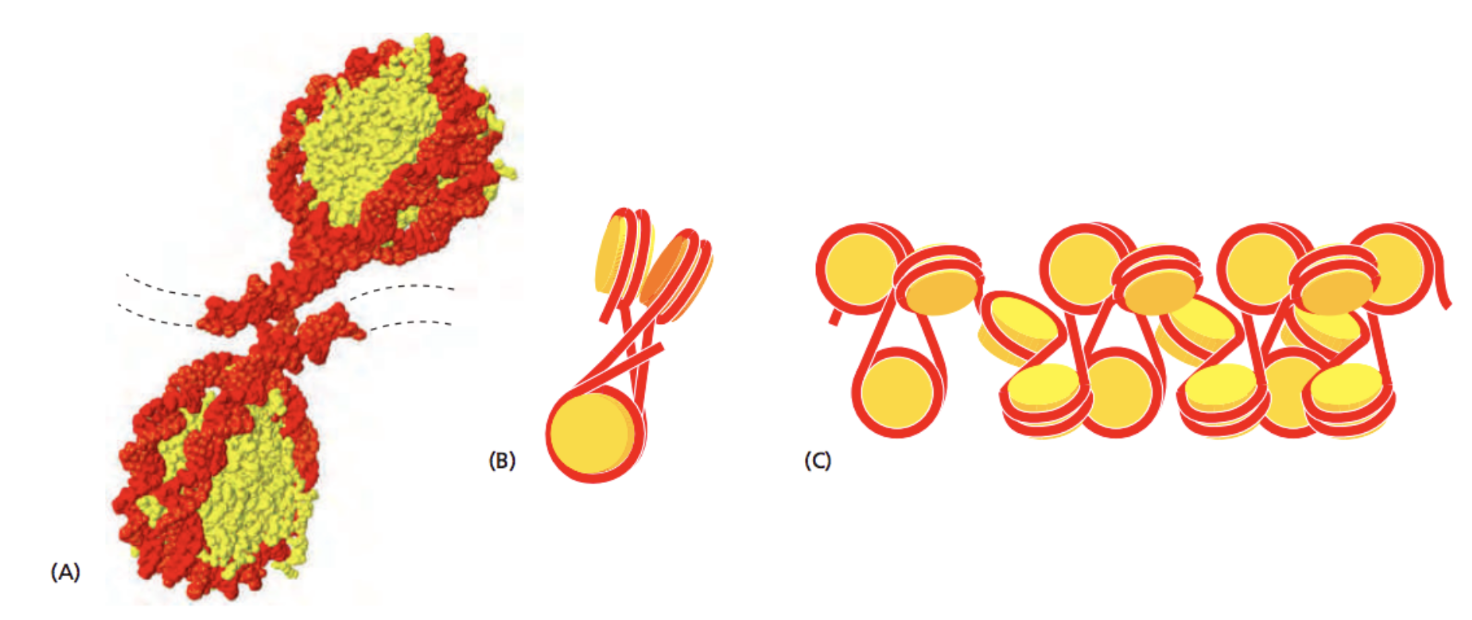
Chromatin is DNA-protein complex
Binding of transcription factors:
Robinson, 2016
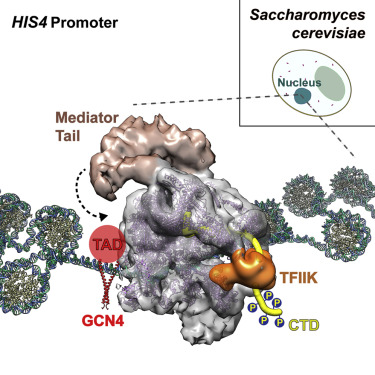
Enhancers are regulators of gene expression
The promoter-enhancer protein complex is required for the activation of gene expression:
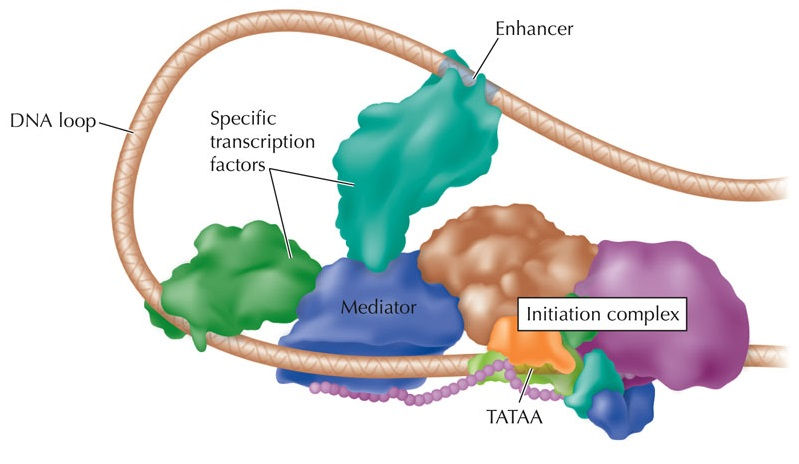
Promoter
How promoters and enhancers interact?
Enhancer can be located thousands of nucleotides away from its target promoter (gene start).
Hypothetical mechanisms of interactions:
Dean 2006
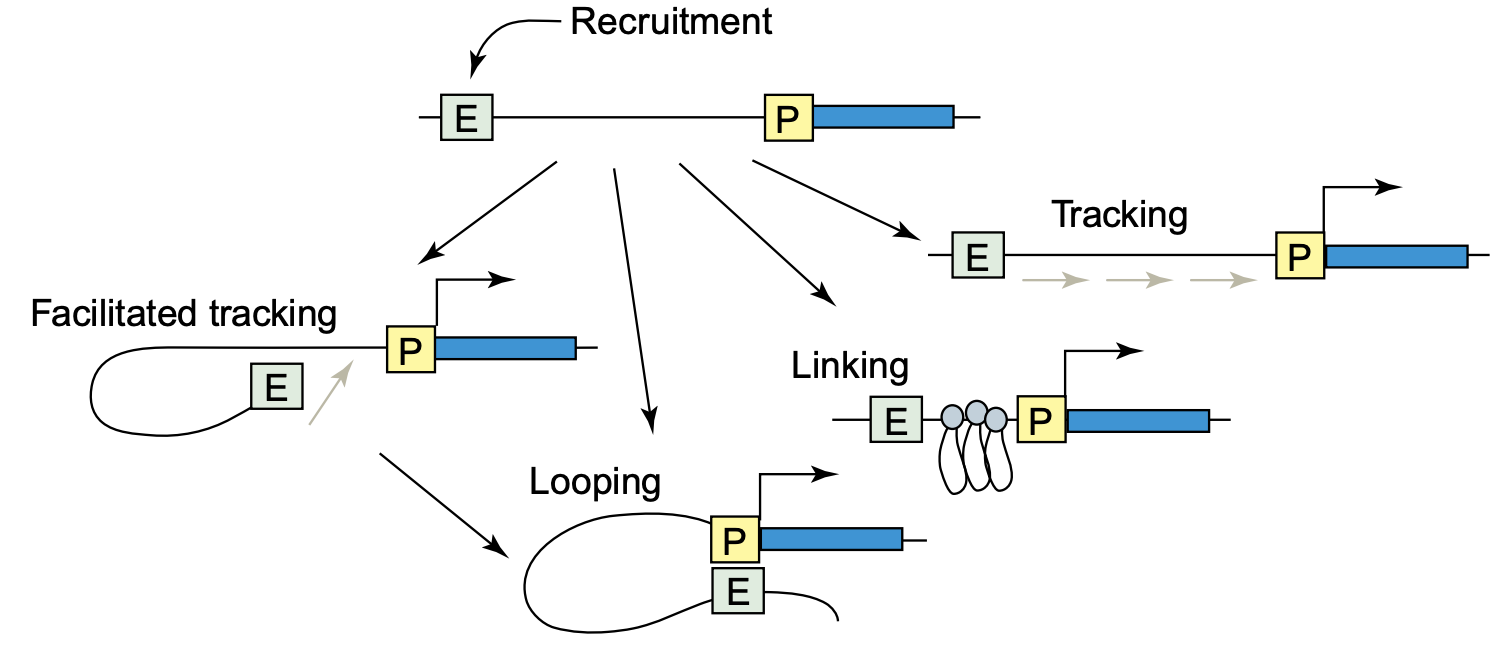
Regulatory networks of enhancers
Single gene might be regulated by multiple enhancers, and one enhancer might regulate several genes:
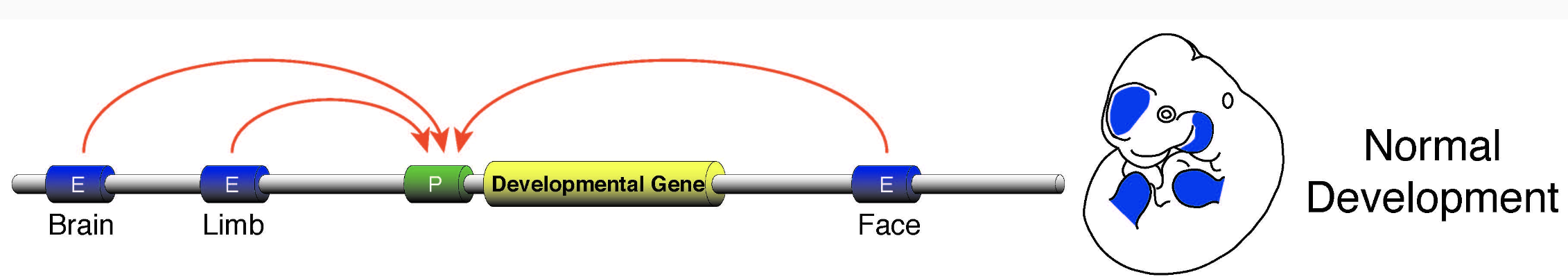
Regulatory networks of enhancers
Long-range regulation helps to generate different phenotypes of cells in multi-cellular organism:
Approaches to study long-range interactions and chromatin structure
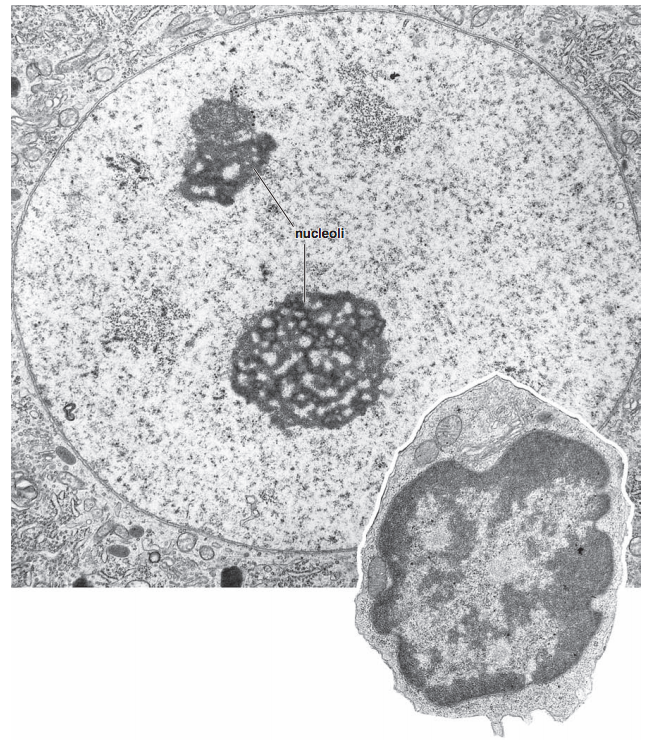
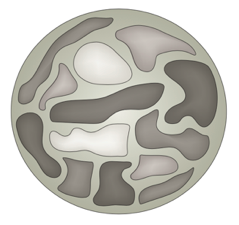
Microscopy of the nucleus
Ros 2006 "Histology Atlas with Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology"
Two approaches:
microscopy and molecular biology




FISH-microscopy
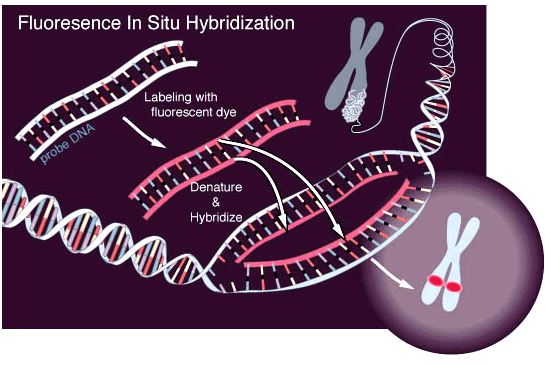
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
FISH-microscopy
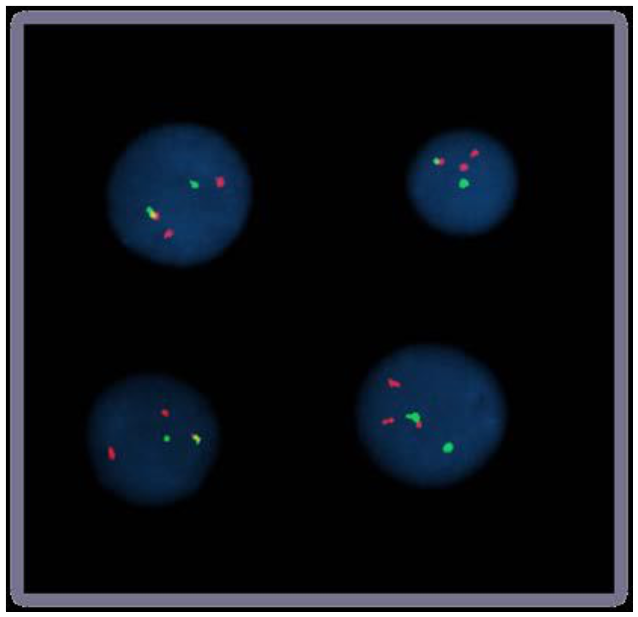
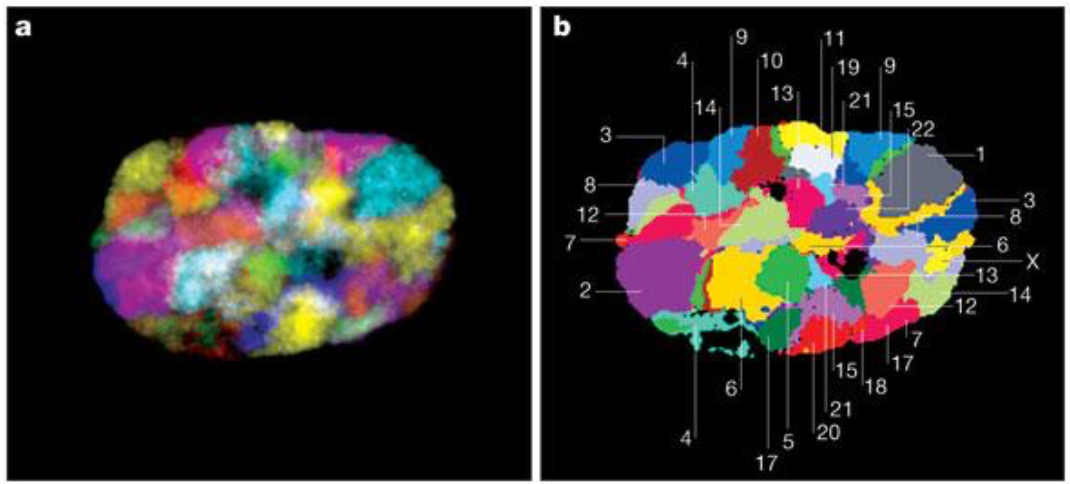
Bolzer et al., PLoS Biol. 2005
Speicher & Carter 2005 Nature
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
Chromosomes Conformation Capture (3C)
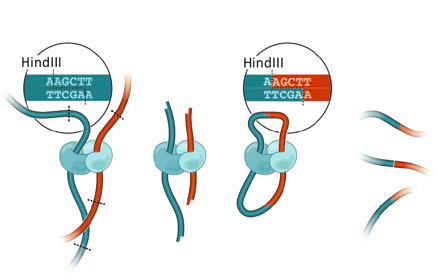
Formaldehyde crosslinking
DNA restriction
Ligation
DNA purification
DNA-DNA interactions library
3C: Dekker et al. 2002 Science
Hi-C: Chromosomes Conformation Capture + sequencing
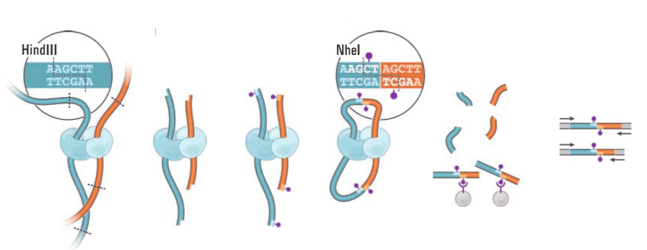
Formaldehyde crosslinking
DNA restriction
Ligation
DNA purifiction
Sequencing
Mapping
Lieberman-Aiden et al. 2009 Science
DNA-DNA interactions map
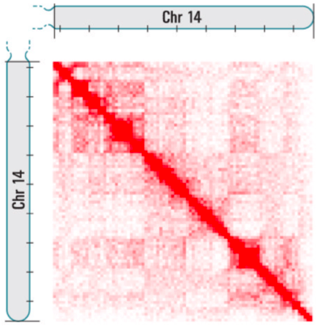
Lieberman-Aiden et al. 2009 Science
Color is the frequency of interactions
DNA-DNA interactions map

Lieberman-Aiden et al. 2009 Science
Color is the frequency of interactions
The map of pairwise interactions of SMTB-2020 students
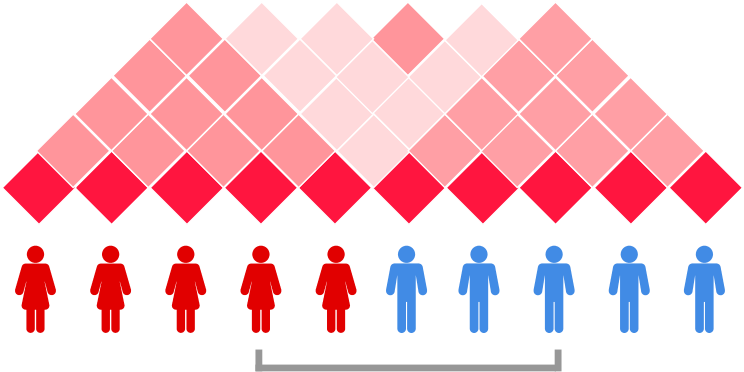
Met at summer school, study molecular biology together
Color: number of messages in Telegram
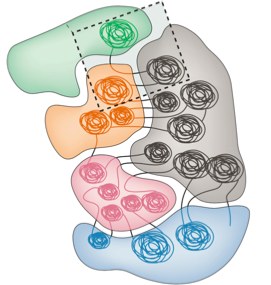
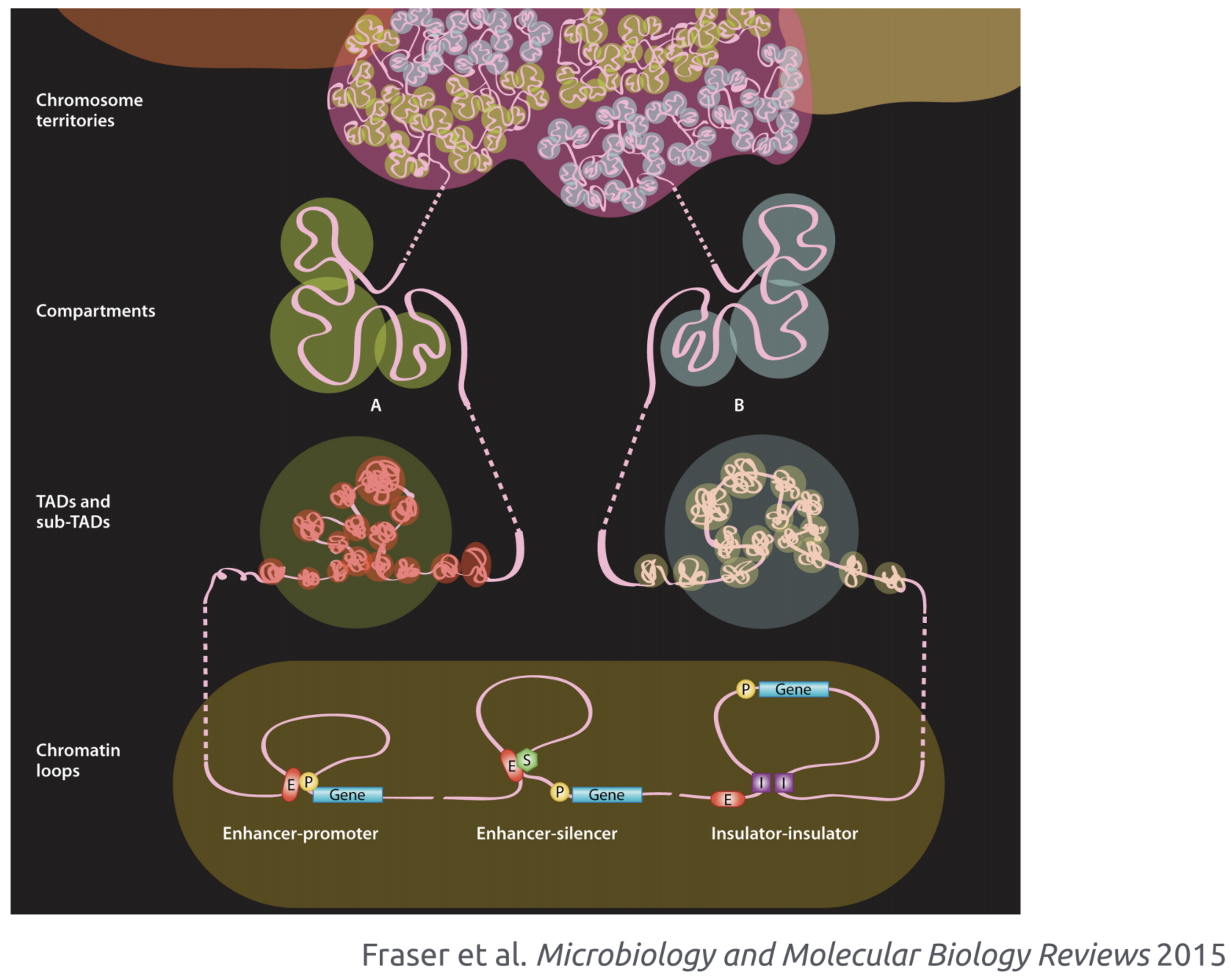
Chromosome territories
Bonev et al. 2016 Nature Reviews
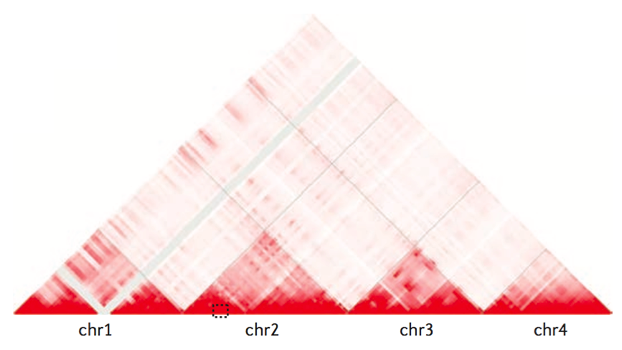

Topologically associating domains (TADs)
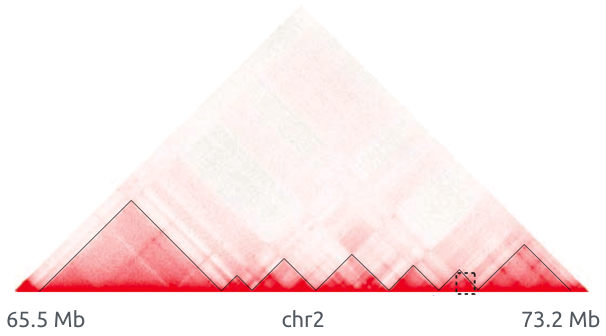
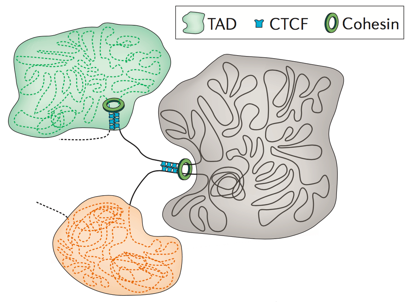
Bonev et al. 2016 Nature Reviews
Compartments
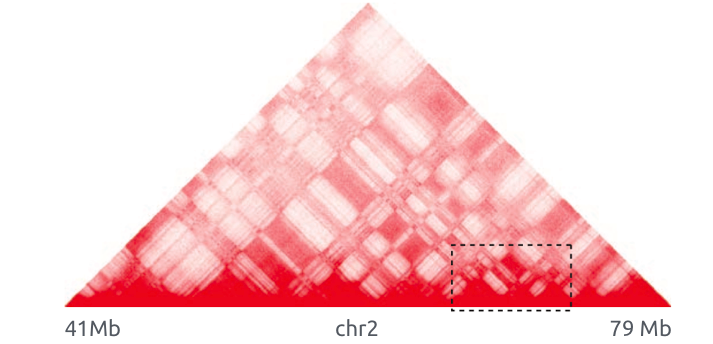
Bonev et al. 2016 Nature Reviews
Loops
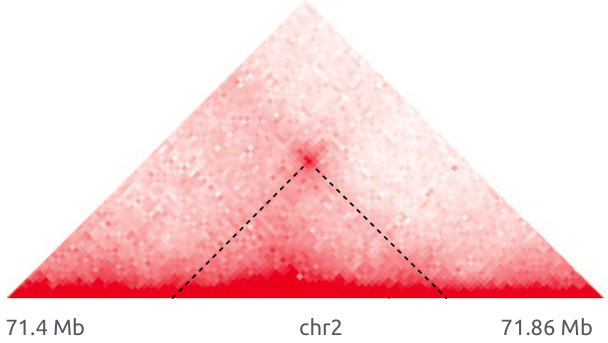
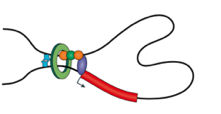
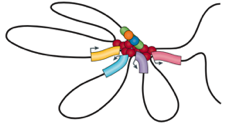
Architectural loops
Promoter-enhancer loops
Polycomb-loops
Bonev et al. 2016 Nature Reviews
Levels of chromatin organization
Loop extrusion is the major hypothesis of chromatin folding
MirnyLab Youtube channel
Simplified visualization of key components: DNA, extruder (cohesin) and barrier element (CTCF)
Loop extrusion model
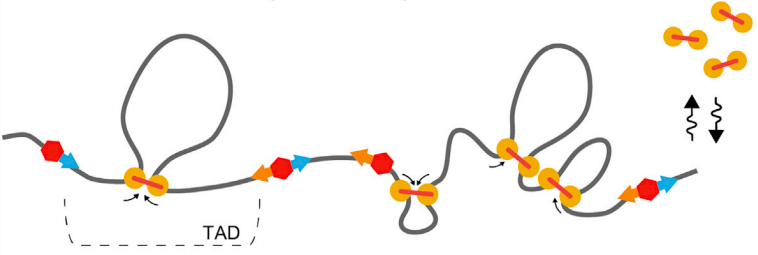
Fudenberg et al. 2016 Cell Reports

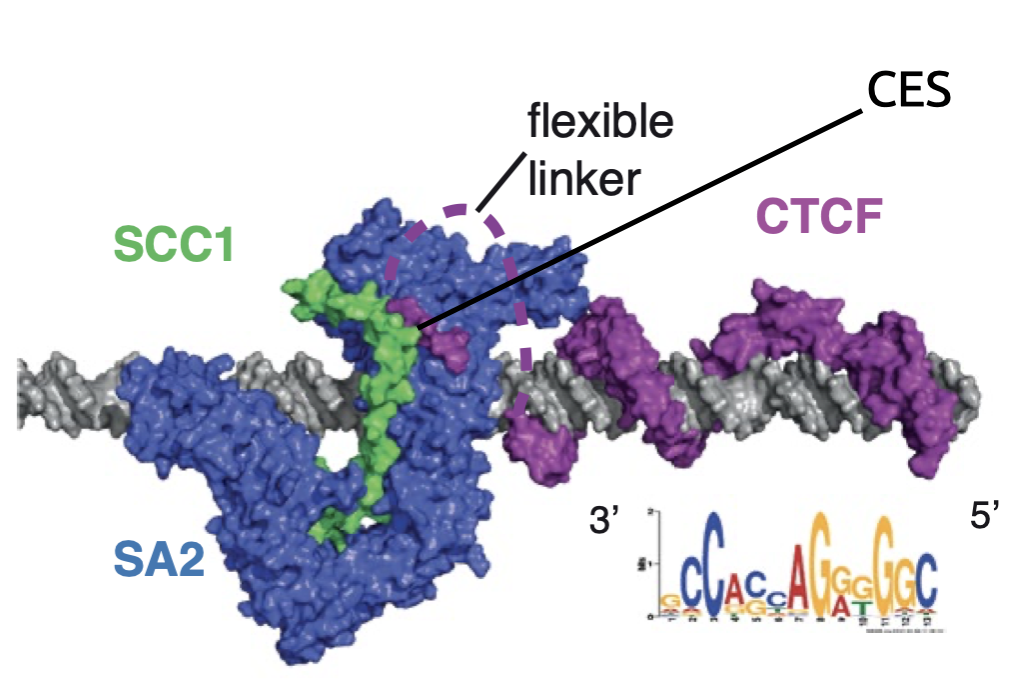
cohesin is extruding factor
CTCF is a barrier element
Architectural protein CTCF
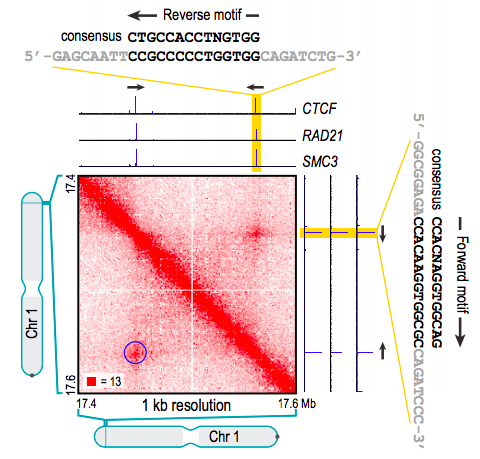
Rao et al. 2014 Cell
Ganji et al. 2018 Science
Ganji et al. 2018 Science
Direct proof of extrusion mechanism
Model of active chromatin folding
Mirny Lab Youtube channel
Chromatin is actively folded structure that is formed by extruding factors
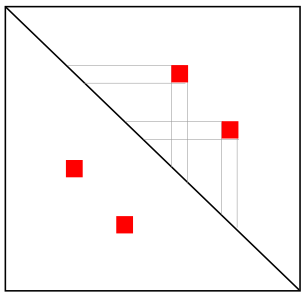
Quiz: Reconstruction of 3D from Hi-C map

Loop

Quiz: Reconstruction of 3D from Hi-C map
Multiple loops
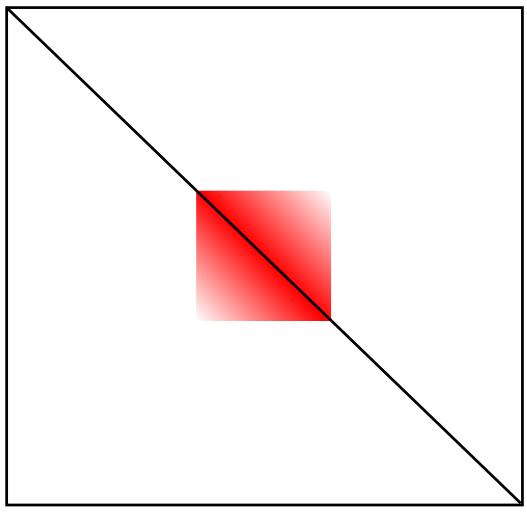

Quiz: Reconstruction of 3D from Hi-C map
TAD
More exotic structure...
hairpin

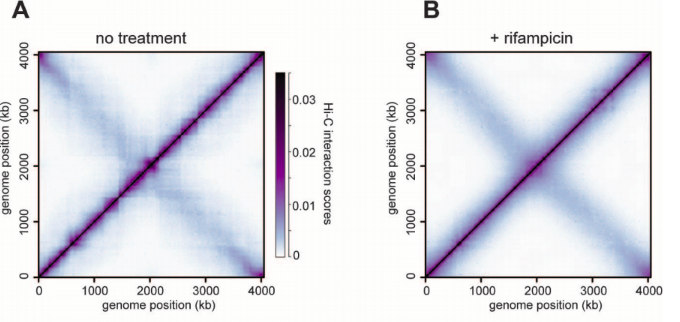
In vivo hairpins
Caulobacter crescentus
(bacteria)

In vivo hairpins
Caulobacter crescentus
Pseudoknot
Rare case
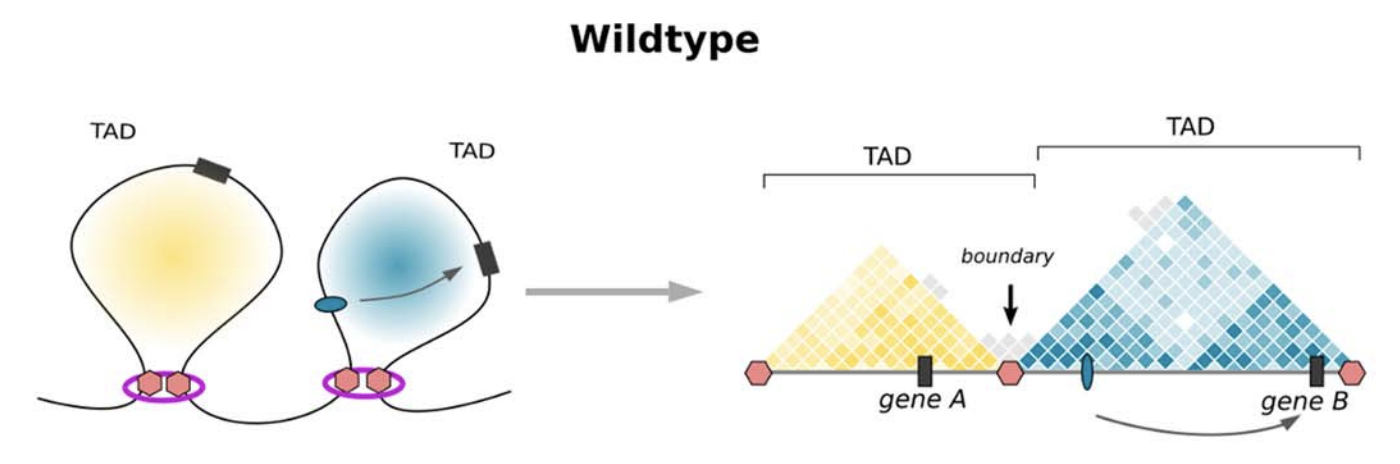
Clinical examples
Anania and Lupiáñez, 2020; Lupiáñez et al. 2015
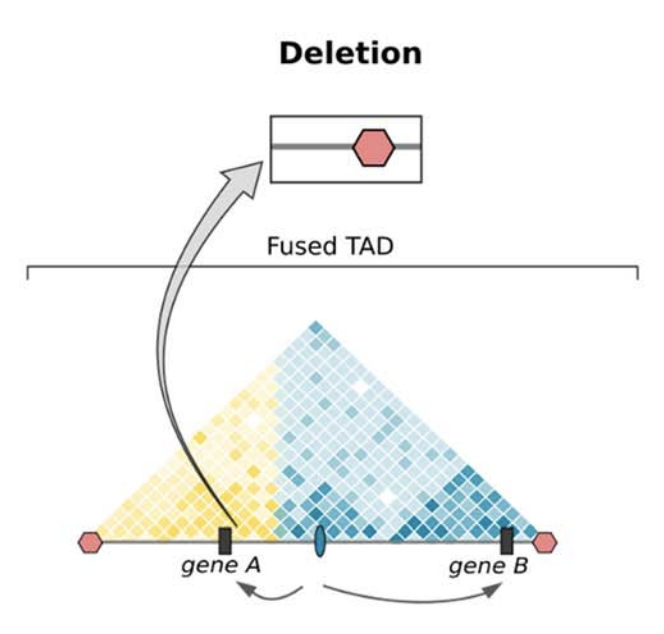
Clinical examples
Anania and Lupiáñez, 2020; Lupiáñez et al. 2015

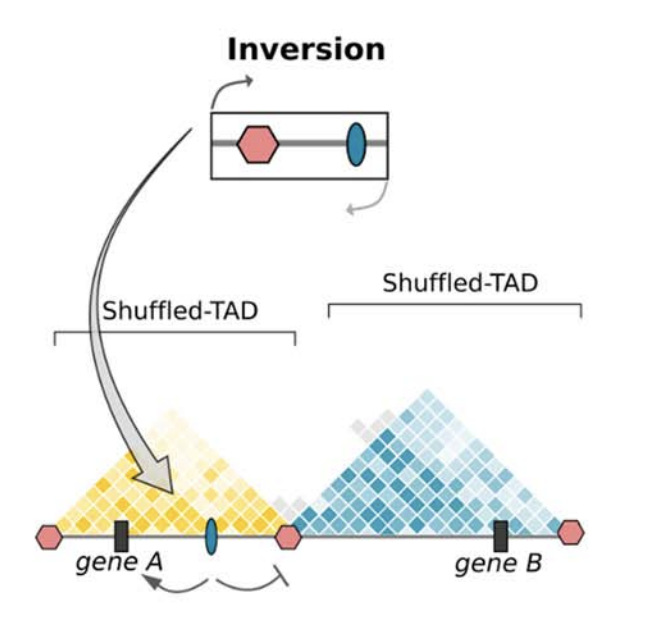
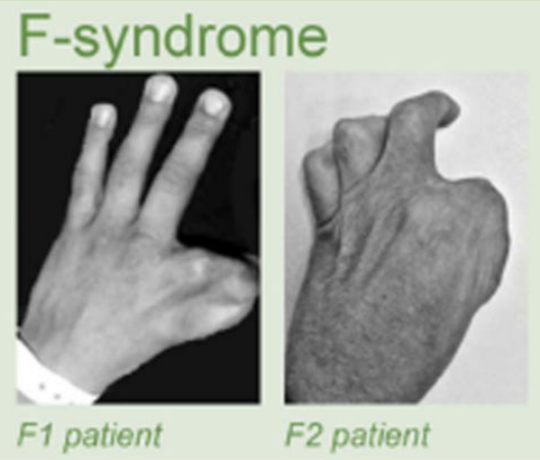
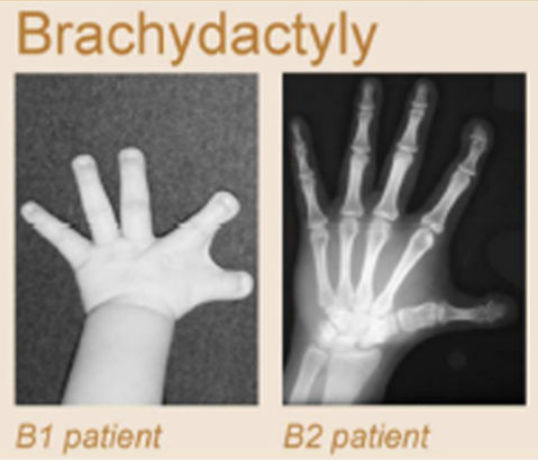
Clinical examples
Anania and Lupiáñez, 2020; Lupiáñez et al. 2015

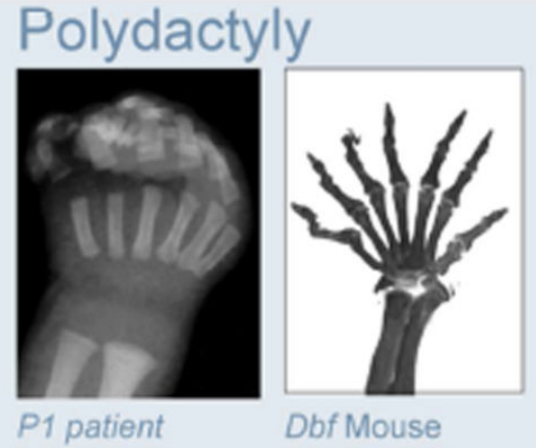
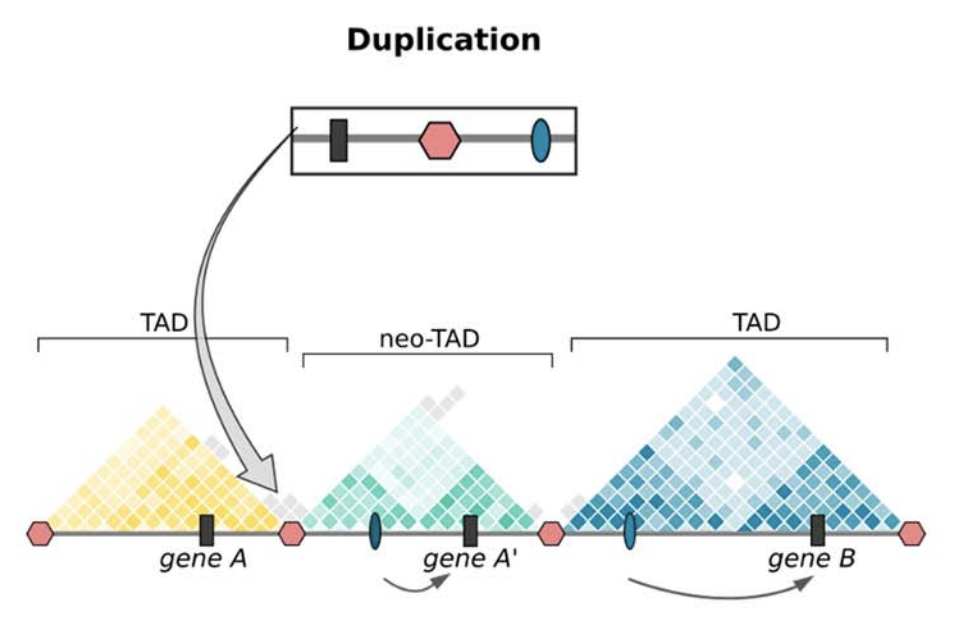
Take-home message
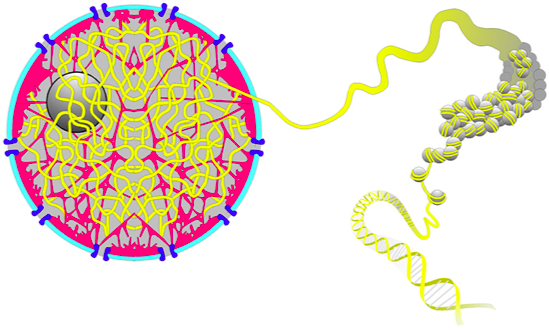
Human: 2 meters of DNA inside of 10 um nucleus
100-stores building in a grain of rice

Chromatin structure for SMTB 2020
By agalicina
Chromatin structure for SMTB 2020
DNA goes 3-dimensional: chromatin structure. Classical genetics has taught us to consider genome a linear DNA with genes encoded in its sequential fragments. Yet it completely disregards that 2 meters of DNA are packed into a tiny nucleus, less than 10 micrometers in diameter! Is there a chance that it happens randomly, without complex molecular machinery operating this process? Recent studies suggest that the nucleus behaves more like a busy city of micrometer size, where several types of drivers actively compact DNA and rule the genes expression.
- 183







