Creating web widgets with
Module Federation
and Angular Elements
https://slides.com/agesteira/ng-india-web-widgets

Agenda
-
Microfrontends -
Modules -
Module Federation -
The User Story -
Demo
Andrés Gesteira
Twitter: @GeorgeKaplan_G
Born in Madrid.
Tech Lead Front End
Longer than 6 years playing with Angular.
Likes cinema, books, and food.

Microfrontends
Microfrontends architecture
-
Breaks up a FE app into smaller parts, called microfrontends.
-
Each MFE should be separately built and deployed.
-
Each MFE takes care of a different UI.
-
Each MFE can be handled by a different squad.
-
A MFE can be either:
-
An application.
-
A component.
-
There is not only 1 way
iframes are evil


Web Components (I)
-
They allow us to create reusable custom elements.
-
They contain an encapsulated DOM called Shadow DOM.
-
They build their markup with:
-
<template> & <slot>
-
-
They need to be registered in the DOM by using:
-
customElements.define('tag', HtmlElement)
-
wrapperElement.appendChild()
-
Web Components (II)


Web Components (III)


The Includes approach
-
A system creates the self-contained HTML fragments.
-
Depending on who assembles the fragments:
-
It can be Server-Side Includes (SSI)...
-
... or Client-Side Includes (CSI).
-
-
Module Federation uses this approach.
Modules
<script>
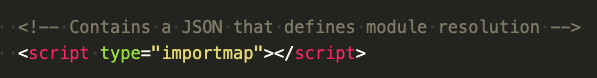
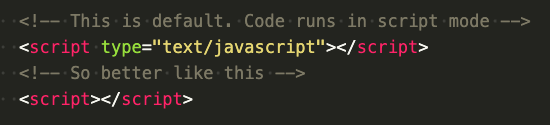

What do you mean "module mode"?
-
In JavaScript we have different execution contexts...
-
...we call them scopes.
-
If the code runs in script mode it uses the global scope.
-
But there are also 3 types of local scope
- Function scope.
- Block scope.
- Module scope.
So what is a module?
-
It is a mechanism to split JavaScript programs.
-
It it typically implemented in a separate file (js/mjs).
-
It must contain import and/or export declaration/s.
- ES modules can run in module mode.
- Non ES modules (e.g. CommonJS) cannot...
- Unless they are compiled to ES modules with a building tool...
- ...like Webpack.
Module Federation
It's a mental model...
...not an architecture.
-
Because it can produce multiple architectures.
-
The code is federated across different servers.
-
Each part of the federation is a module.
-
The host module wraps the other ones....
-
...which are called remote modules.
-
Any module can communicate with any module.
-
So circular dependencies are allowed.
Federation
Shell / Host
Remote 1
Remote 1
import()
Remote 2
import()
Remote 3
import()
remoteEntry.js
remoteEntry.js
-
It is not a module.
-
It is a manifest...
-
...that enables the dynamic sharing.
-
It includes fine-grained information about:
-
Modules.
-
Libraries.
-
Considerations
-
PROS:
-
No code duplication (better than Webpack's default).
-
Shared libraries.
-
Version control.
-
-
CONS:
-
Cross-framework not guaranteed.
-
In Angular, it creates several root scopes.
-
The User Story
My manager told me to.

Requirements
-
You need to do it with Angular.
-
You need to deploy self-contained HTML fragments.
-
BUT You don't have the routing app. And you will never have it.
You need to find a solution.

Module Federation Web Components
Web Component
Shell
Remote
Web Component
Shell
Remote
Any Web App
Demo
Creating web widgets with Module Federation and Angular Elements
By Andres Gesteira
Creating web widgets with Module Federation and Angular Elements
- 620



