Analysis of User Behavior
Ahcène Boubekki
Leuphana, Lüneburg
UiT, Tromsø
in Educational Science

The mBook Project
The mBook Project
Objectives
Evaluate the use of an electronic textbook for history in middle school
Bring new methods to Educational Science
The mBook Project
The mBook
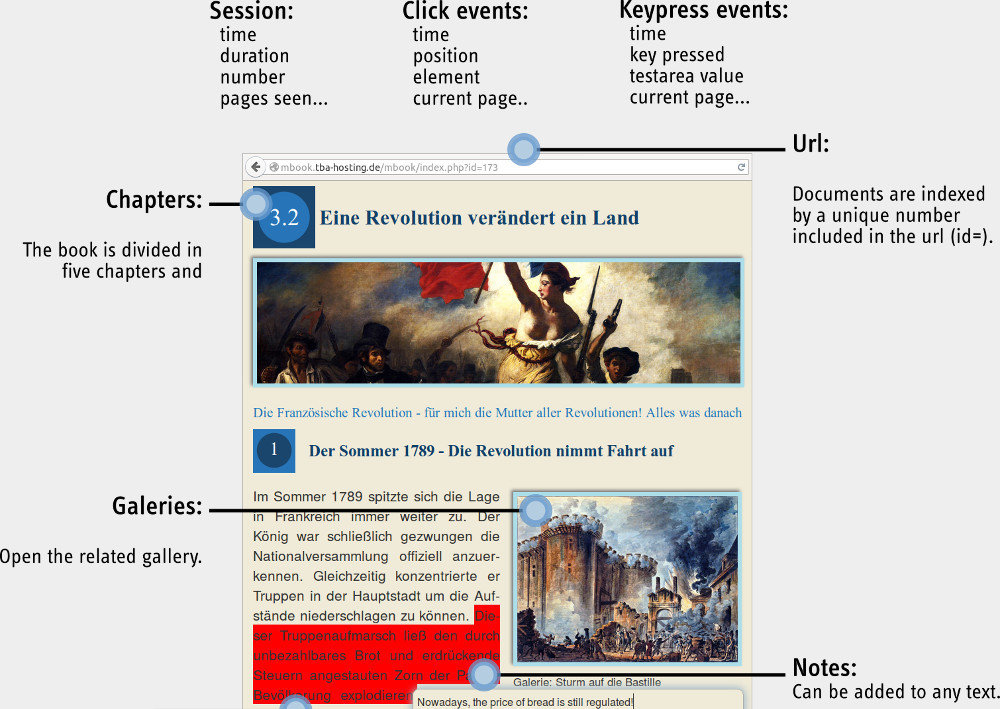
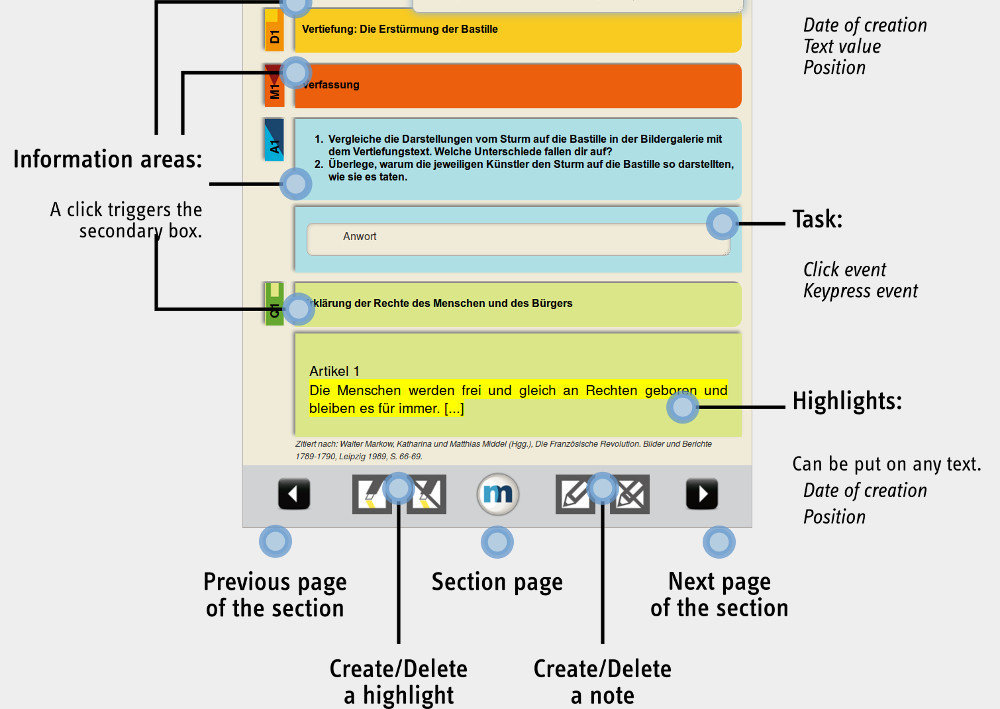
The mBook Project
Some statistics

From January 31st to July 11th 2017
2,197 sessions
400 users
195 pupils (537 sessions)
The mBook Project
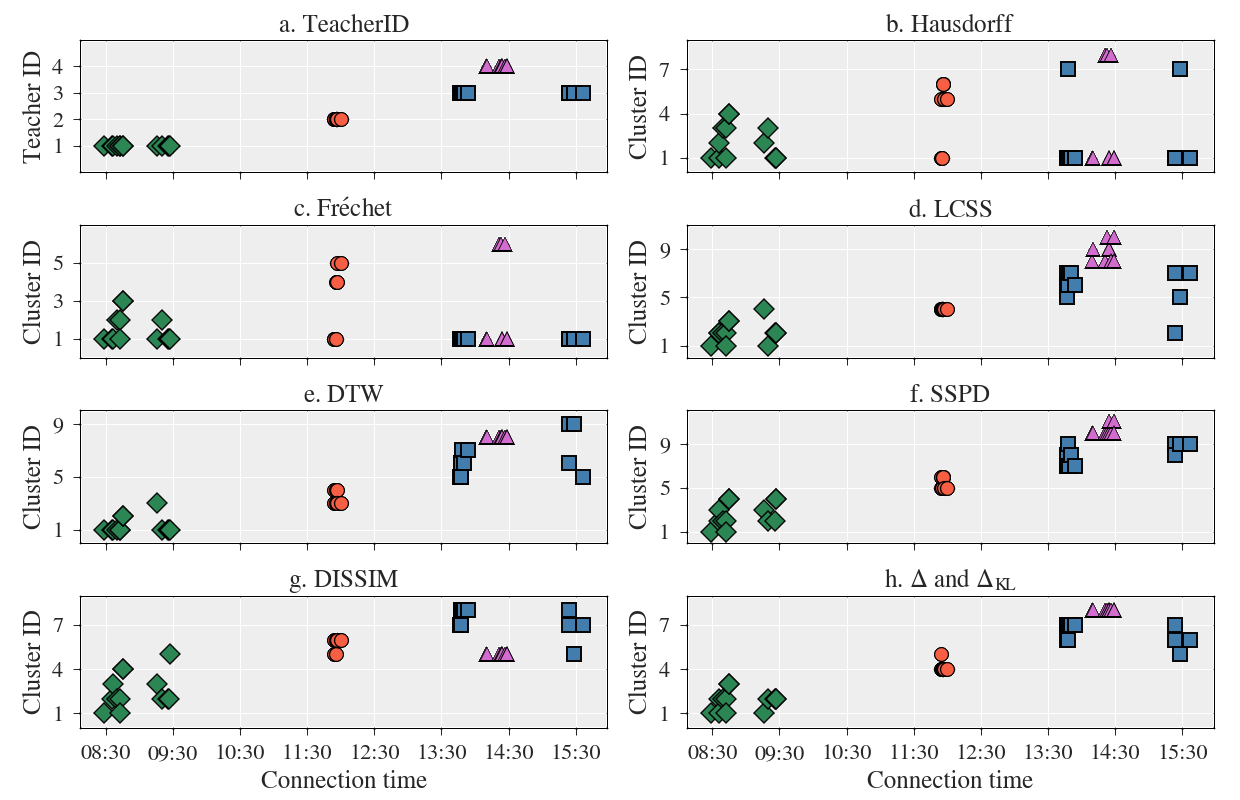
Classical Approaches
Bi-variate factor analysis

Markov Chains
Contributions
Summary
Archetypal Analysis
Content Analysis
Markov Chains
Periodic Behaviors
Bayesian Markov Chains
Scrolling Behaviors
Trajectories
Online Behaviors
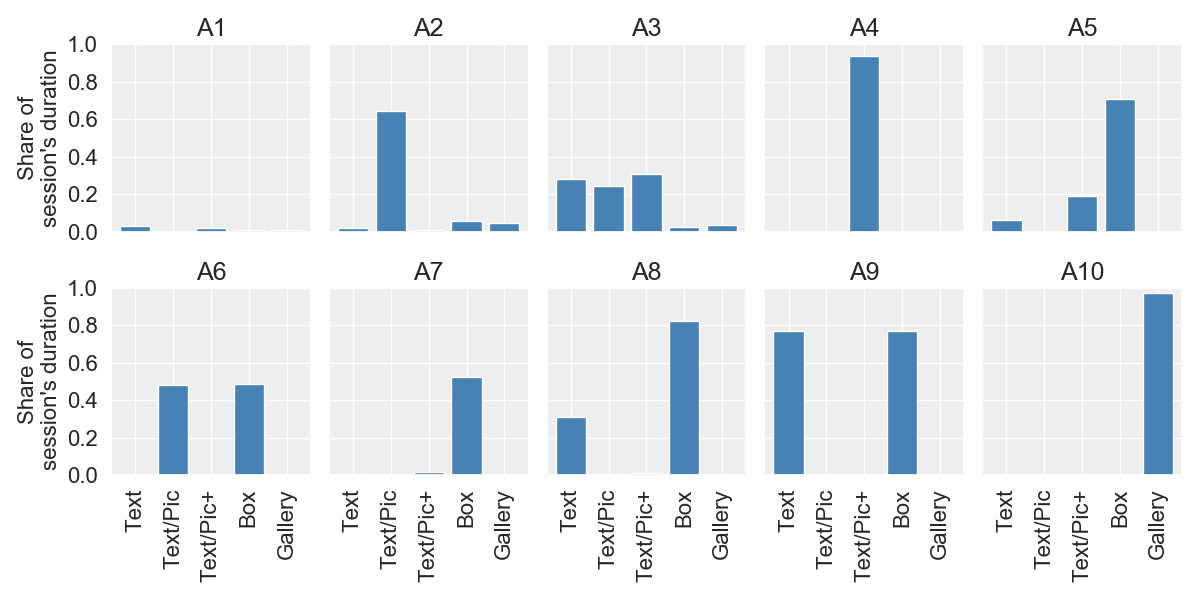
Archetypal Analysis and Content Analysis
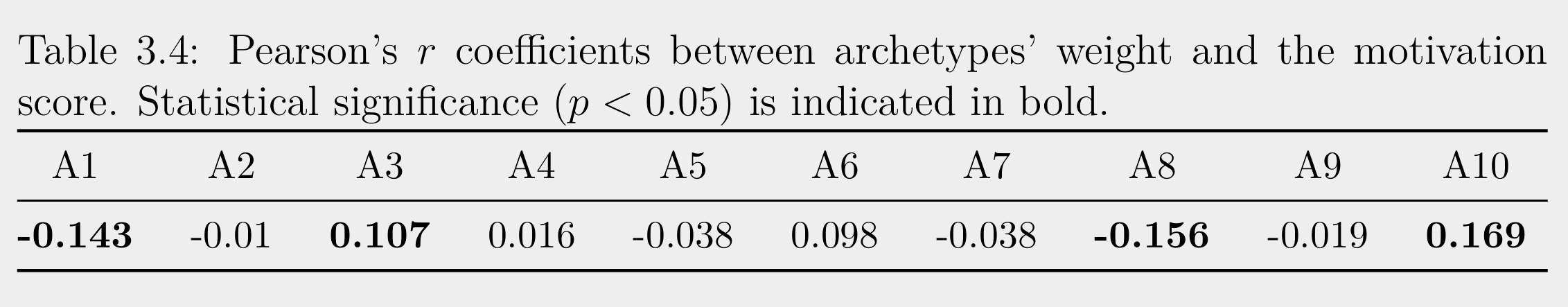
Is there a correlation between the visibility time of
highly informative content and motivation?

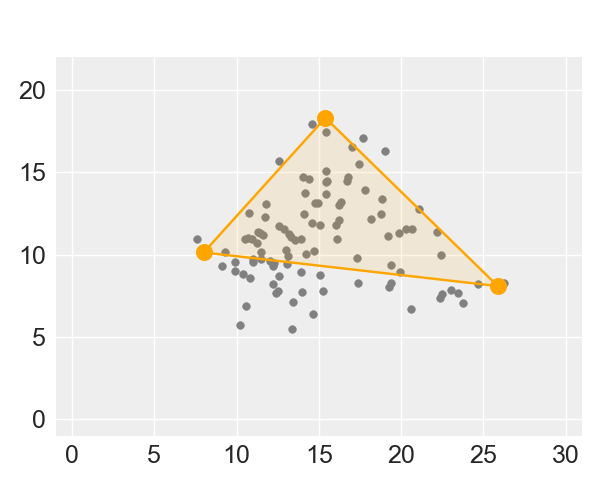
Archetypal Analysis
Strange
Explained by the sequences
Objective
To enclose the data within a convex k-polyhedron while minimizing the reconstruction loss.


Simple factor analysis
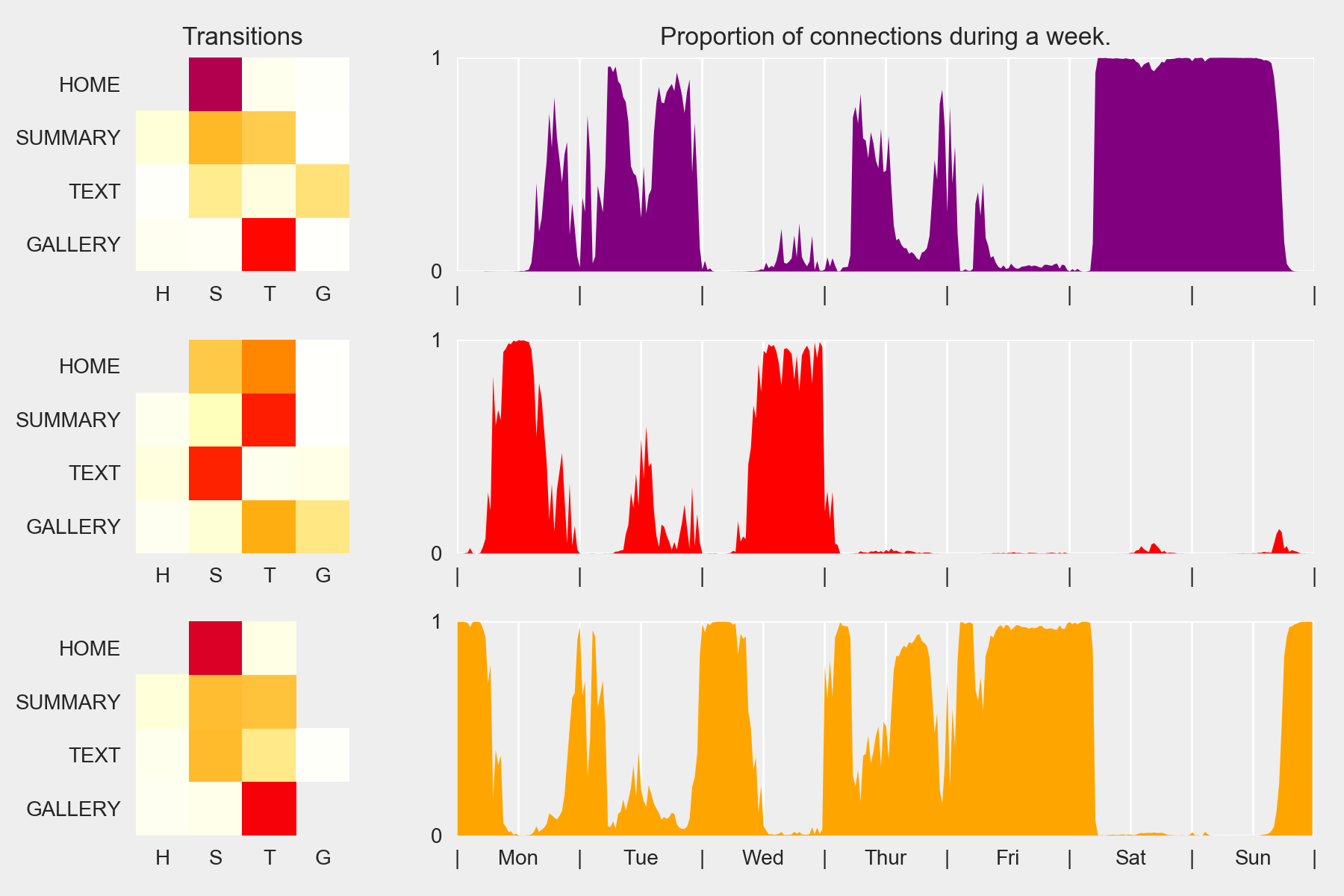
Markov Chains and Periodic Behaviors
Do the pupils use the mBook the same way over the week?
k-means
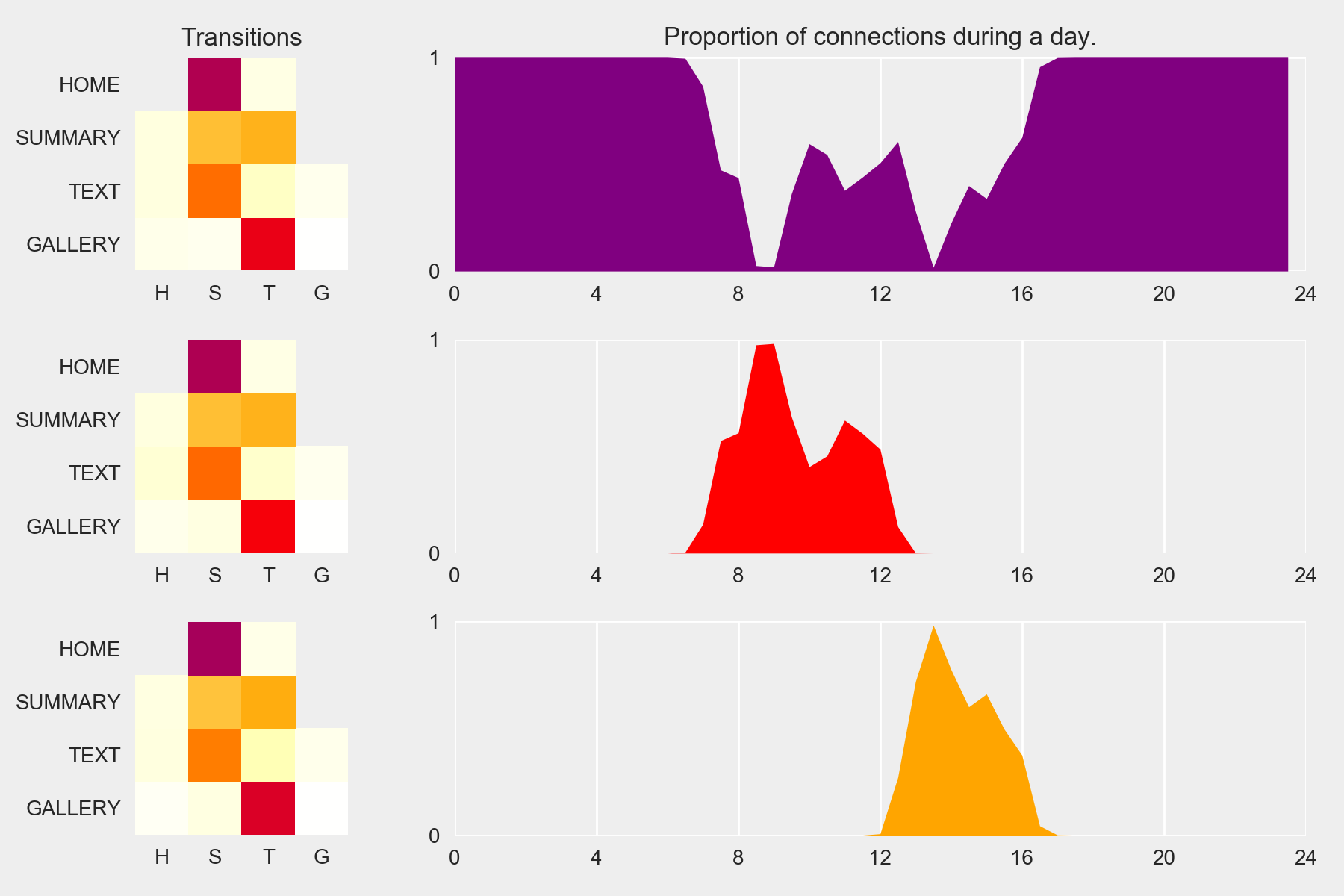
Nested Mixture of Markov Chains
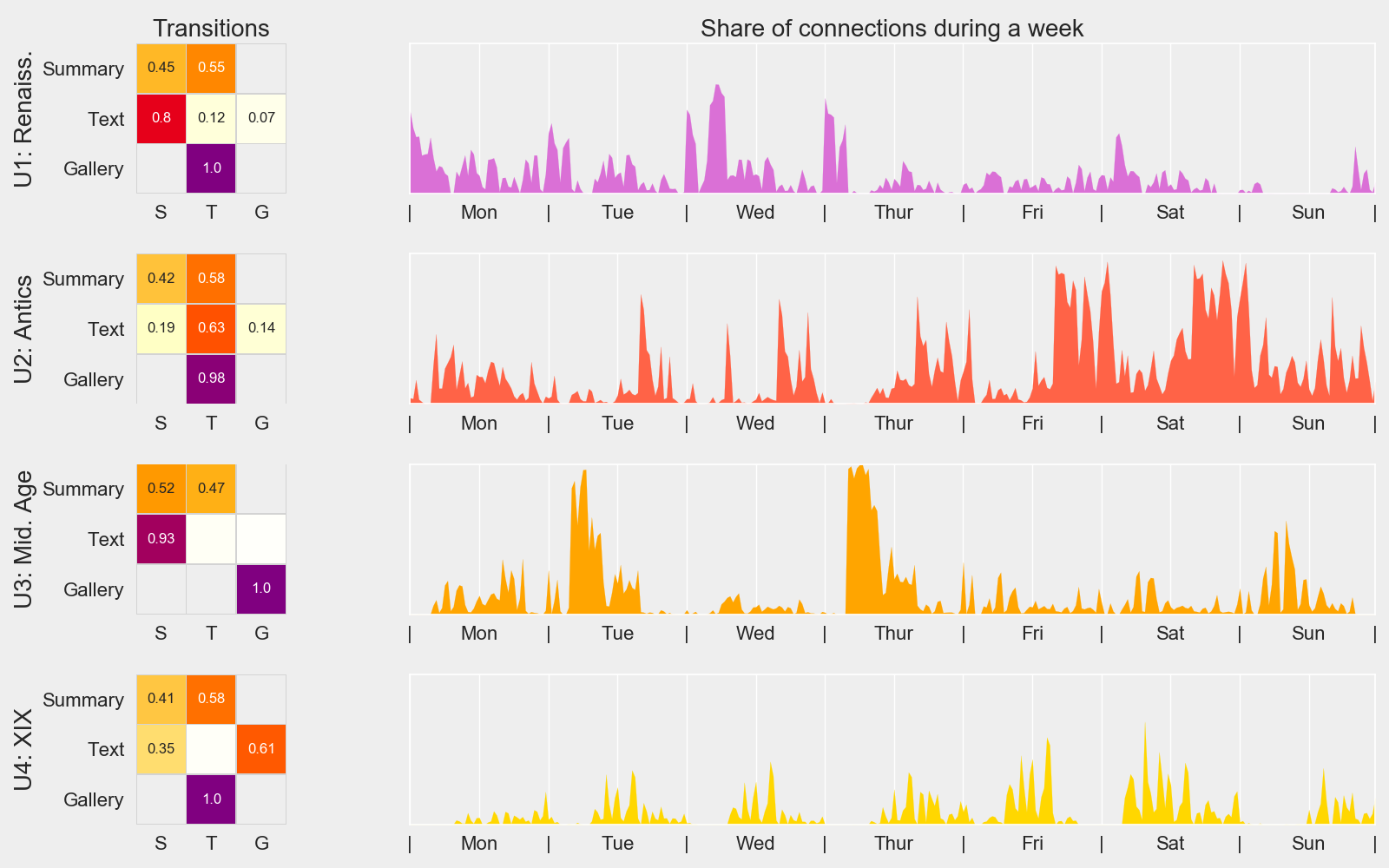
Influence of
the class or teacher

Time follows a GMM with fixed μ and Σ:
48 daily compo ⇔ 30min
42 weekly compo ⇔ 4h
Truly periodic
Page view conditioned
on the chapter
User model averages
the session model
Bayesian Markov Chains and Scrolling Behaviors
One weakness of MMC is the model selection.
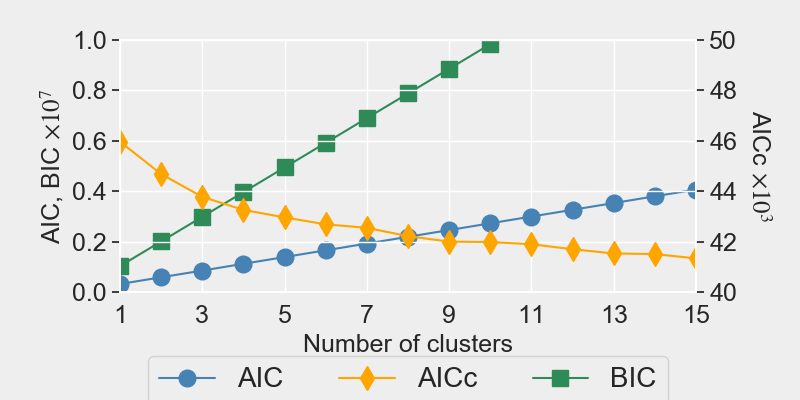
Dirichlet Processes govern
the number of mixtures and of events.
Infinite Mixture of Markov Chains (iMMC)
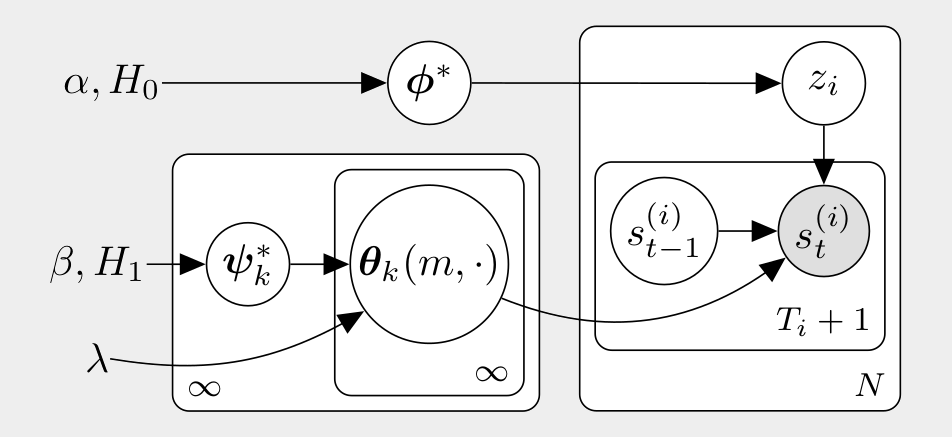
In Practice
Degree k-weak approximations instead of DPs
⇕
Bayesian with
⇓
blocked-Gibbs sampler
Scrolling Behaviors
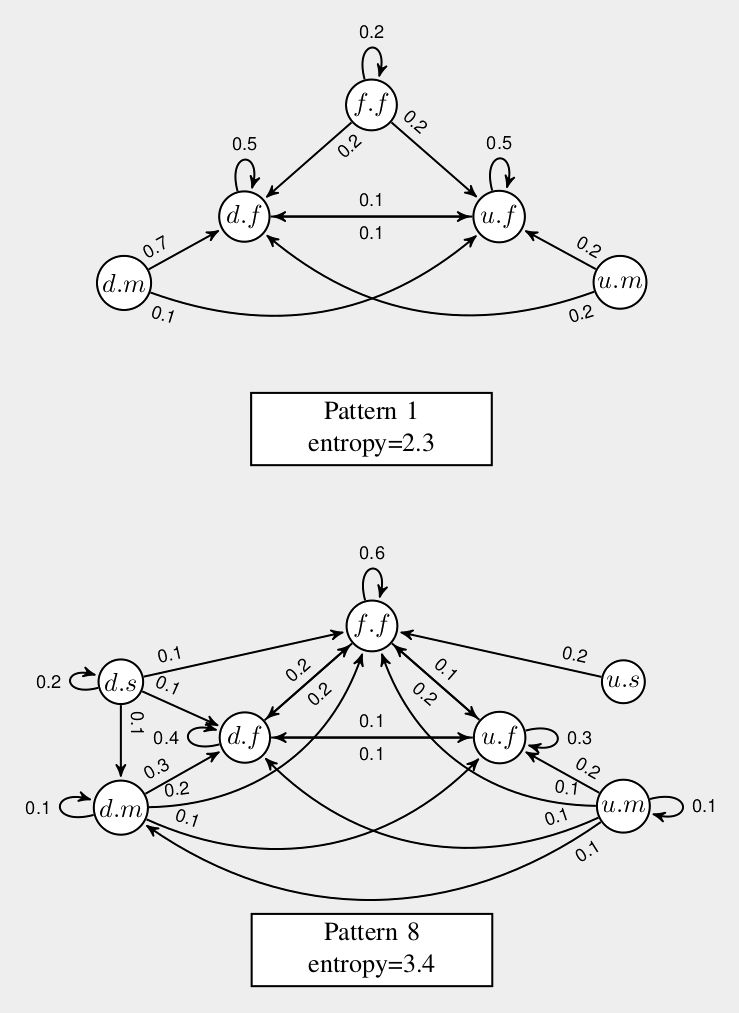
Simple
Pattern
Complex
Pattern
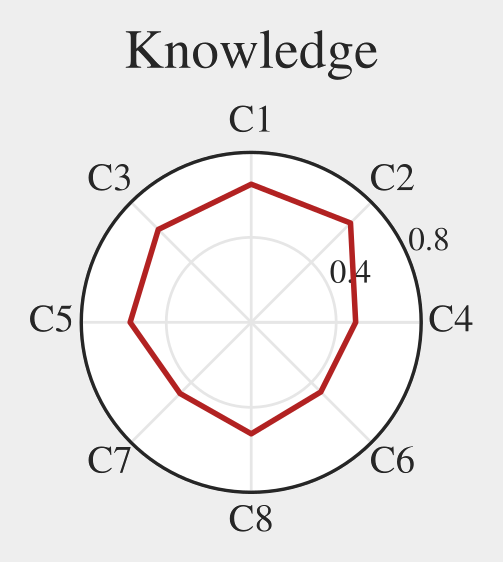
Pupils with higher Knowledge score
have simpler scrolling pattern
Simple
Pattern
Complex
Pattern
Trajectories and Online Behaviors





Is it relevant to study sessions as
spatio-temporal trajectories?
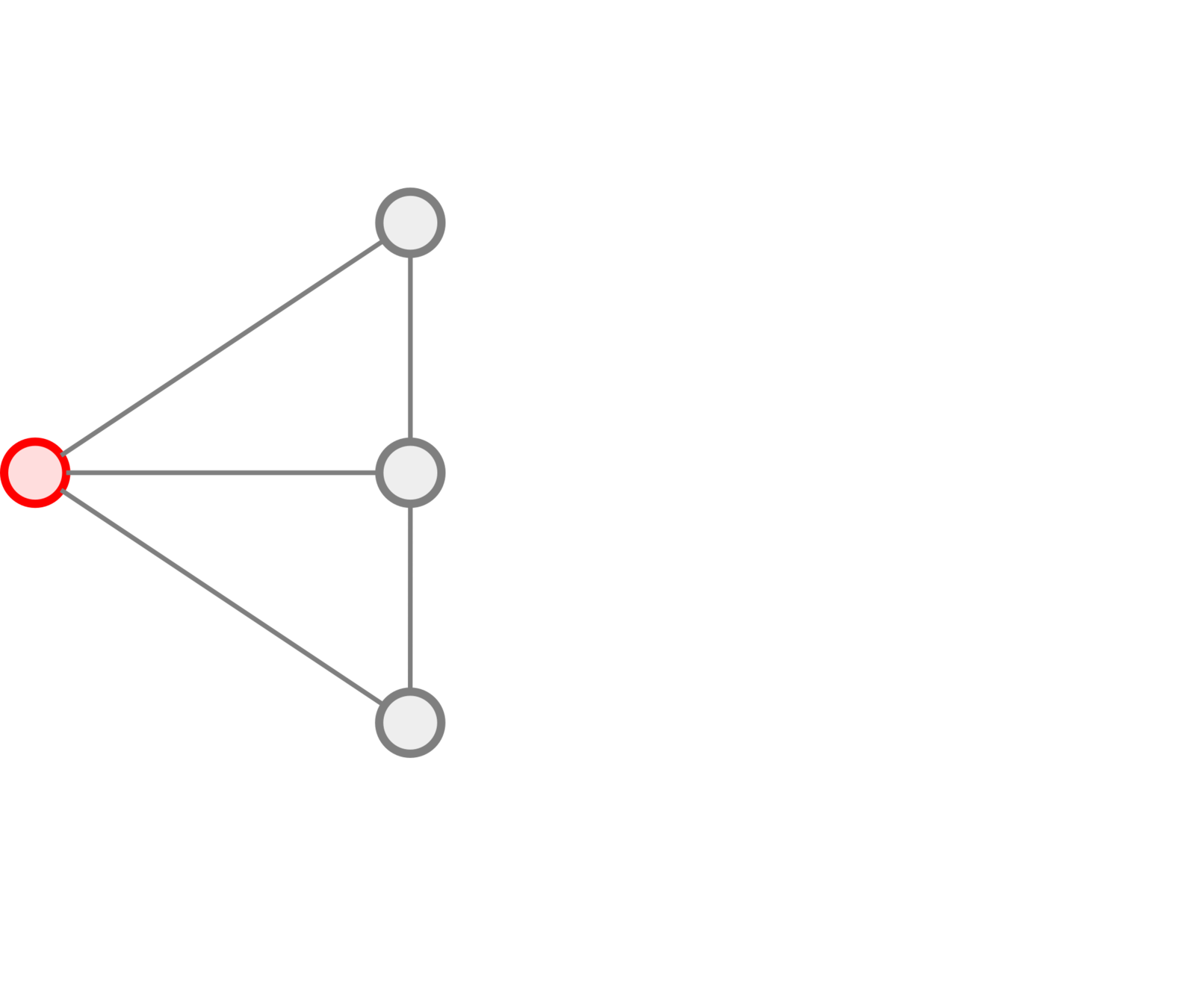
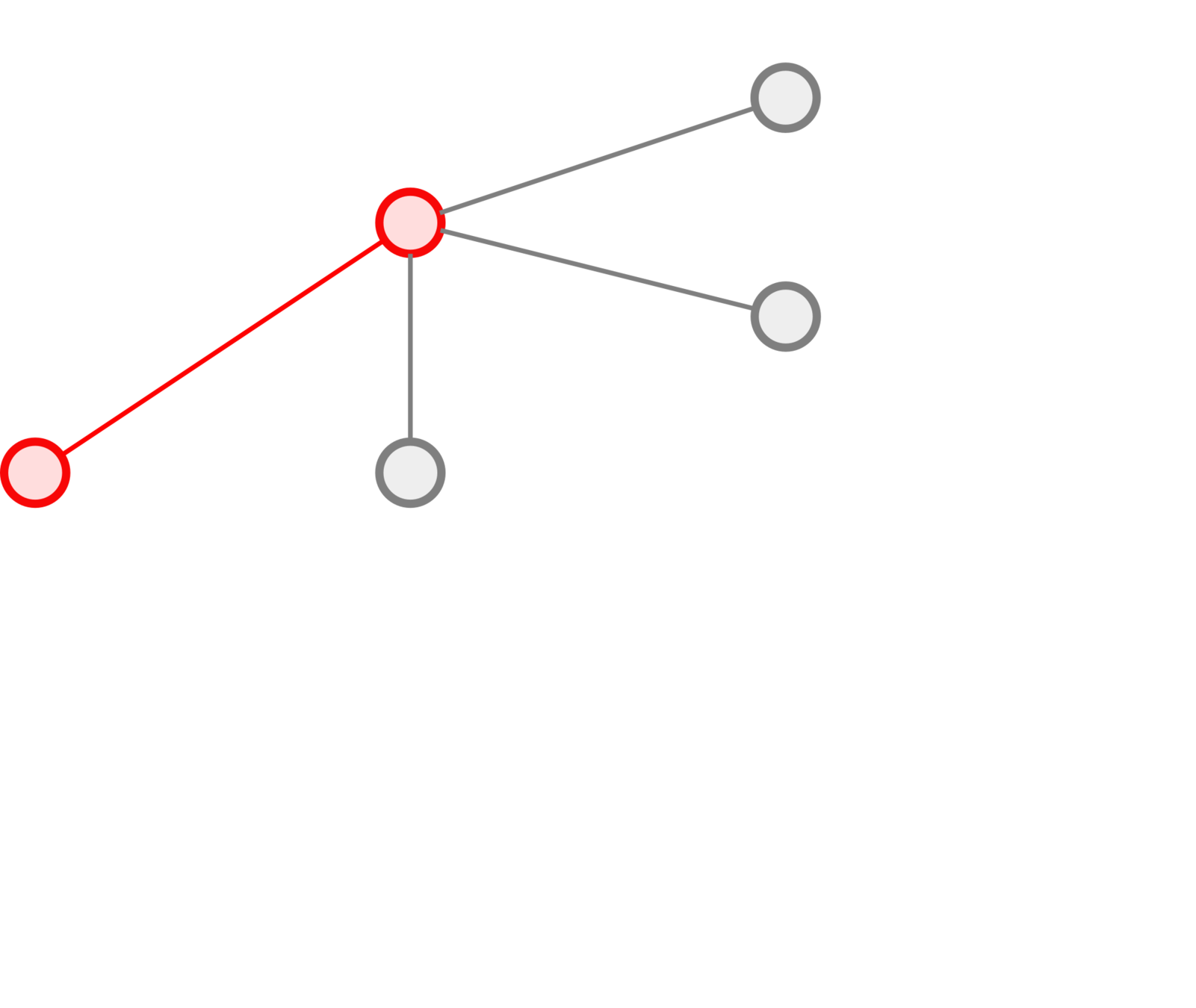
Sequence of pages
↓
Path in the page graph
+
Timestamps
+
Metric on the page graph
↓
Spatio-temporal
trajectory
Construction
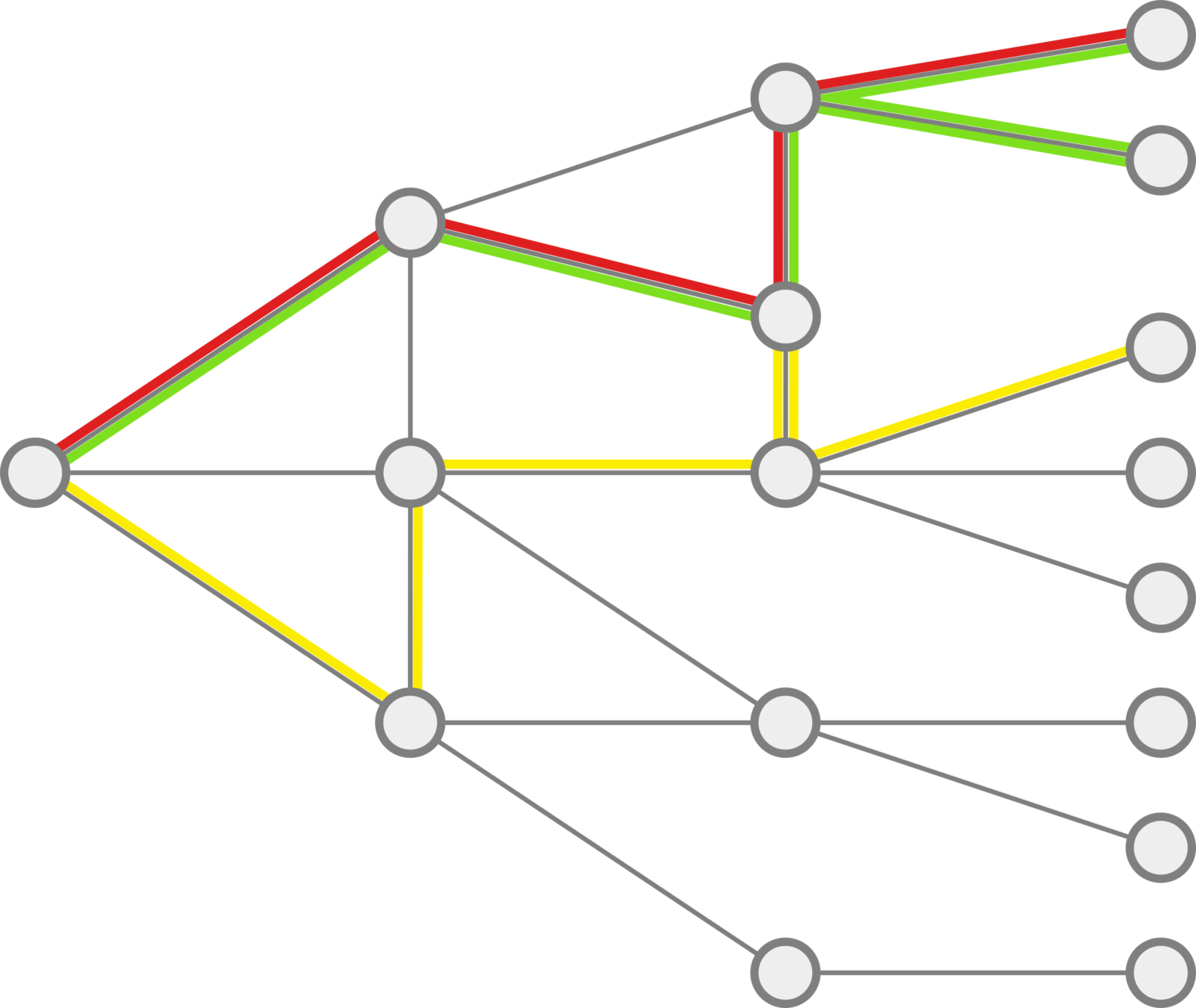
Trajectories and Online Behaviors
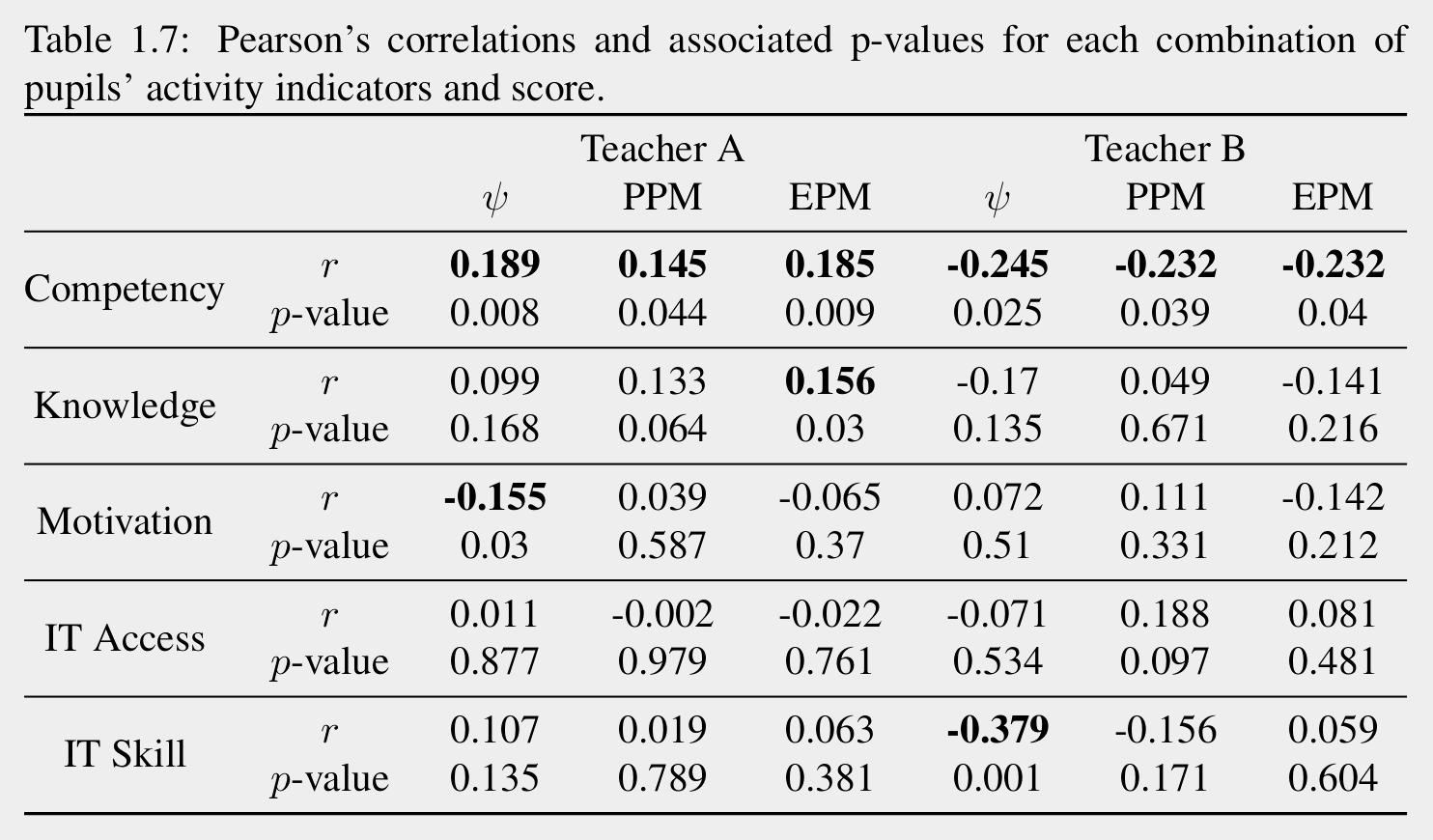
Extracting Class Groups
DP-means clusterings for K=20
Positive Correlation ↔ High ≈ More freedom
Negative Correlation ↔ Low ≈ Less freedom
Statistically significant
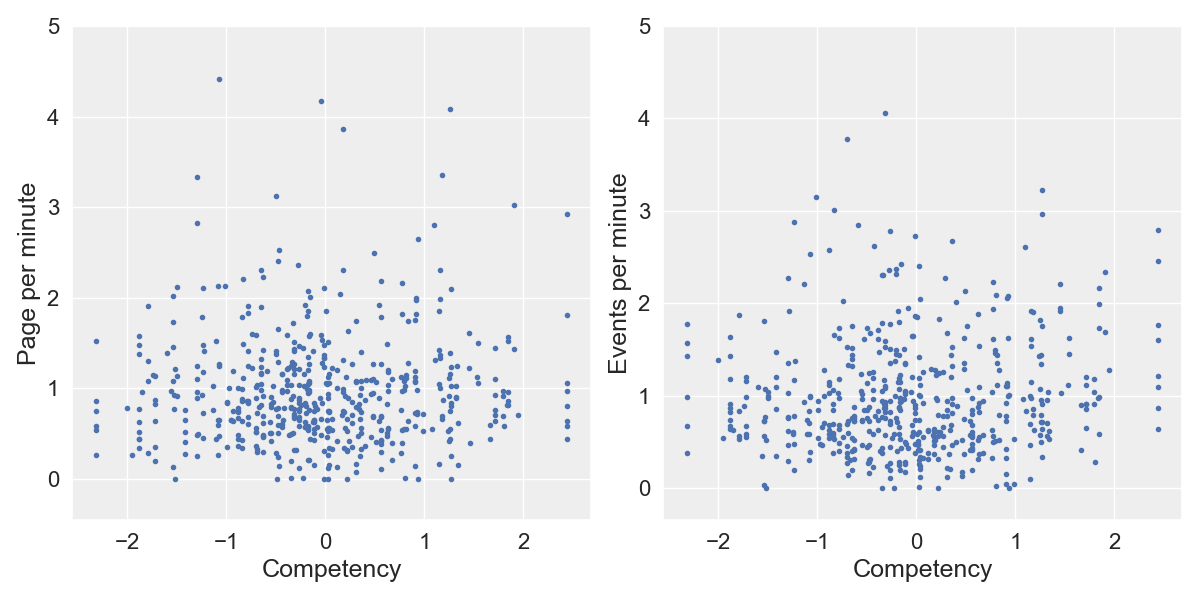
Activity Indicator
average distance between one pupil
and her classmates
number of page per minute
number of event per minute

Conclusion
Conclusion
- AA is an alternative to usual factor analysis;
- MC are robust enough to handle fine-grained data;
- Sessions can be represented and processed as
spatio-temporal trajectories;
- Pupils' performance and motivation can be predicted from the data;
- Teachers are moderators in these correlations;
Analysis of User Behavior
Ahcène Boubekki
Leuphana, Lüneburg
UiT, Tromsø
Ed. Science
By ahcene
Ed. Science
- 162



