Machine learning
Aleksander Levental
20% Checklist
- What I learned:
- Verbiage and definitions
- Survey of ML tools and platforms
- Basic/introductory toolset (algorithms, data formatting tricks, resources to practice)
- What I hope you learn:
- Verbiage and definitions
- Tangible picture of what machine learning looks like
Summray
- What is Machine Learning?
- Algorithm types
- Theoretical example
- Real example
- Math sidetrack
Machine learning
(noun) Field of study that improves the ability of computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. - Arthur Samuel, 1959

"A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E." - Tom Mitchel, 1998
Colloquial
- Quality or quantity that needs to be predicted or decided
- Listing price of home for sale
- Email is spam or not
- Tumor is malignant
- People that will like each other ;-)
- Find or build a dataset
- Write an algorithm
- Algorithm: set of steps to be followed
- Check the predictive accuracy of your algorithm
- Predictive accuracy should get better with more data
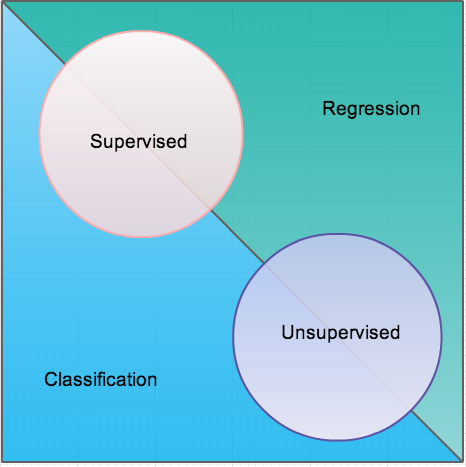
Algorithm Types
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Regression
- Classification
Supervised learning
Input dataset has* the 'correct' answers.
- Real estate sales data predicting prices
- Heights and weights of babies based on parent dimensions
- Television show ratings based on twitter activity
Unsupervised learning
No correct answers in the training or input data set. Goal is to find out if there is any internal structure to the data.
- Google News recommending similar articles
- Netflix recommending movies
- NSA looking for terrorists in phone metadata
Regression
Result is a number from a continuum/spectrum

Classification
Result is membership of a group. Spam or no spam, male or female.

Algorithm types
What this actually looks likE
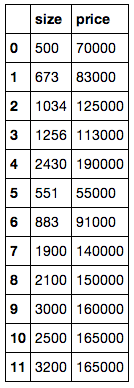
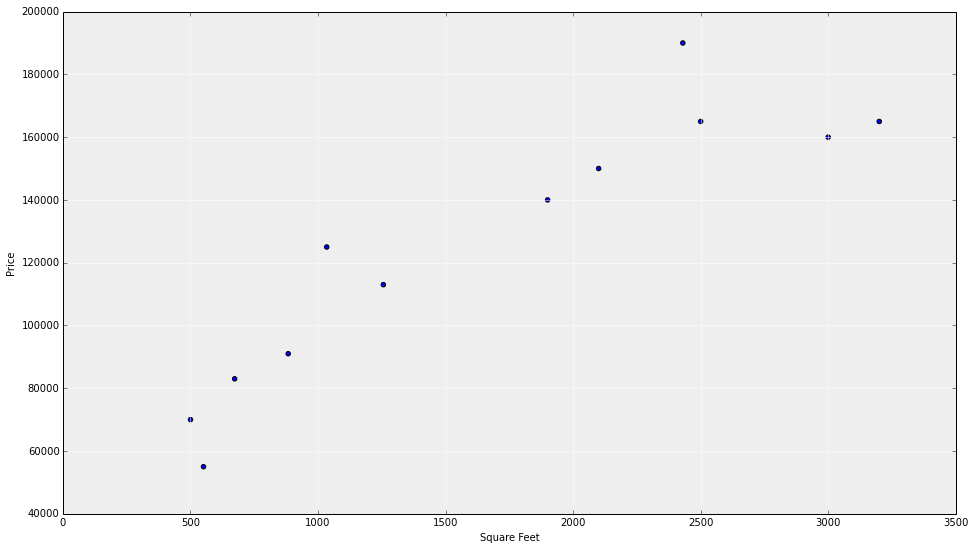
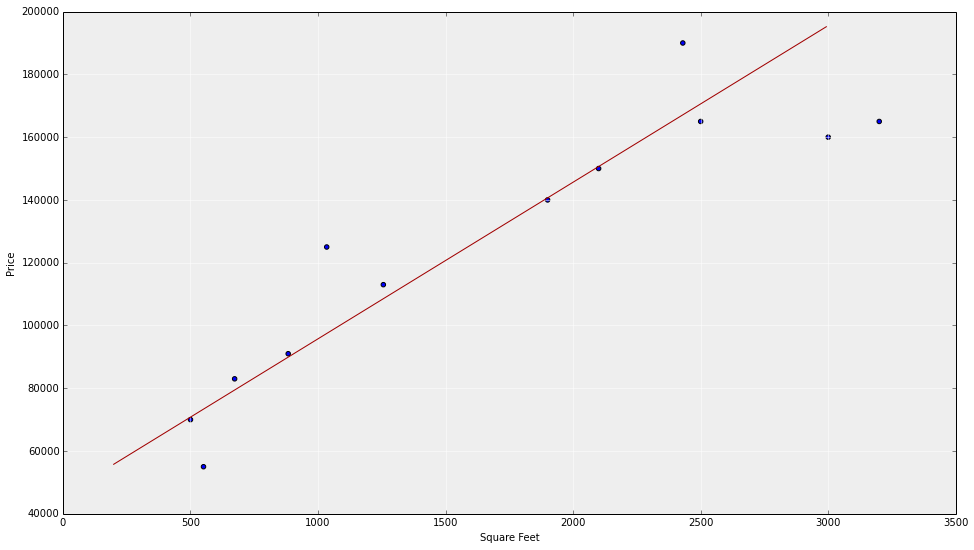
homes sales vs square footage
Model!
Simplest model is a straight line
-
x = size (in square feet)
- Theta = vector of parameters
- h = hypothesis (prediction)
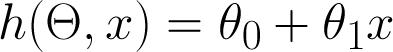
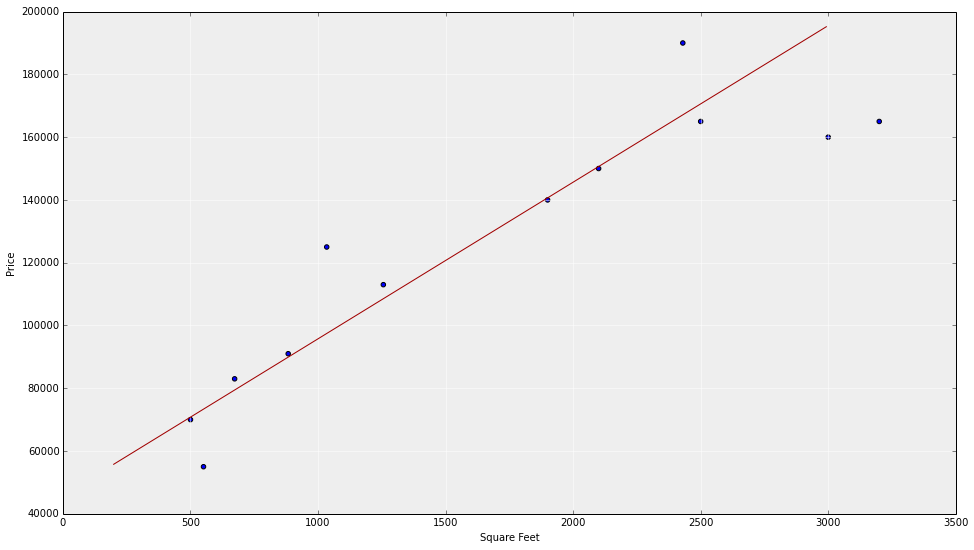
Model --> Algorithm
Cost function, and Gradient Descent
Cost function or Loss function
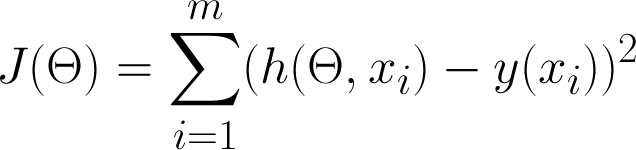
J is only a function of Theta (parameters).
J represents the 'error' between your model, and the training data.
Object is to find Theta that minimizes J (error of model)
Gradient descent
Cost function visualized

Gradient descent
Repeat for all j, over and over
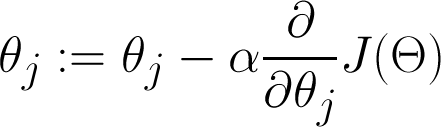

Conclusion
Improvements
- Line is nearly the simplest possible model, and is not required by 'linear' regression. Linear doesn't mean line. Model could be improved.
-
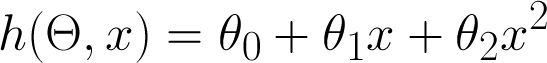
- More input features
- Number of bedrooms, bathrooms
- Age
- Property size
- Larger data set
More interesting example
kaggle.com Digit Recognizer competition
Classify handwritten digits using MNIST dataset of 70k + images
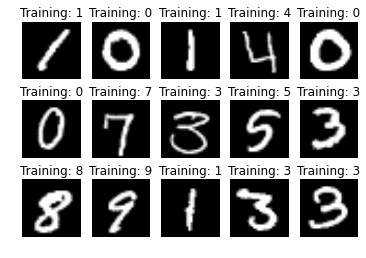
kaggle competition
Training set 42000 images
Test set 28000 images
Graded on accuracy of the prediction
kNearestNeighbor Algorithm
Dataset
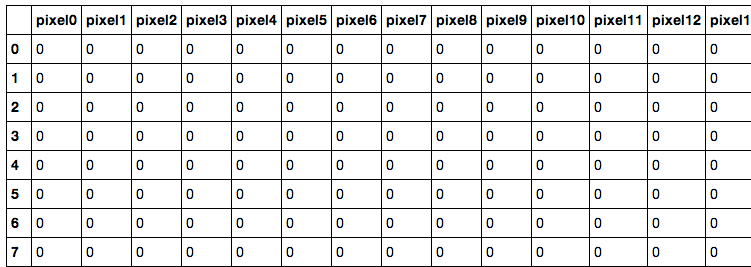
28x28 pixel images = 784 pixels, value of 0-255 for brightness
784 pixels -> 784 dimension feature space
k-Nearestneighbor
- Load your entire training set into memory (not actually necessary, just imagine.
- Get your query input, or test point.
- Map it with your training set.
- Take the 'distance' between your query input and all other points, choose the k nearest neighbors, and then 'poll' the neighbors and ask them what they are. Majority rules
k-nearestneighbor
k-nearestneighbor
Digit Recognizer problem has 784 dimension space.
How do you define 784 dimensional distance?
How do you define 3 dimensional distance?
What is distance?
Are you Feathr?
Metric
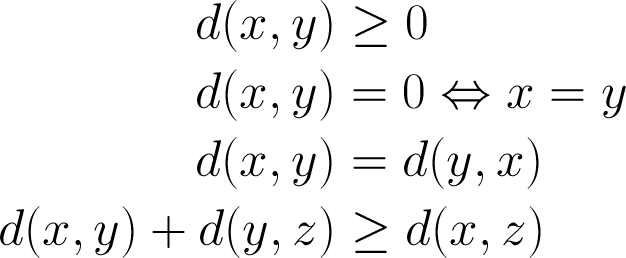
Discrete Metric:
d(x, y) := 1, x != y
minkowski metric
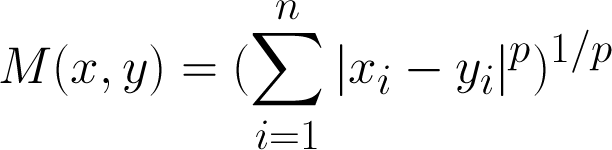
Euclidean distance is just a special case of the Minkowski metric for p = 2
p = 1 corresponds to the Manhattan Metric or Taxi Cab metric
Unit circle in different minkowski spaces

Holmes metric(*)
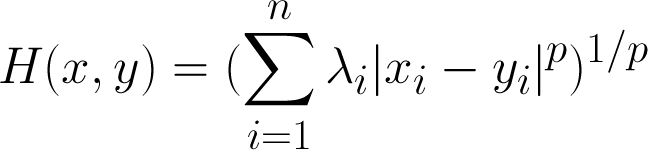
Lambda is an n-dimensional vector, that weights how 'important' a particular dimension is for the distance.
*Fails the triangle inequality, therefore not a real metric
Digit recognition for now

Machine learning
By Aleksander Levental
Machine learning
- 1,332

