Layer 2 and 3 Addressing
Dr. Alexios Louridas
Index

How a NIC is identified?
- A MAC address (short for medium access control address) is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC).
- It serves as a hardware address for devices within a network segment.
- Commonly used in IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
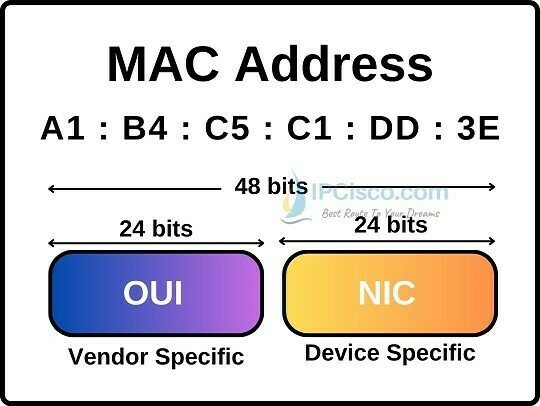
These addresses are hardcoded into the hardware by the manufacturer and serve as a permanent identifier for the device within a network segment.
Are MAC addresses UNIQUE?

-
Device Identification:
- Each network interface controller (NIC) has a unique MAC address.
- It acts like a digital fingerprint for devices, allowing them to be identified within a network segment.
- When data packets travel across a network, routers and switches use MAC addresses to direct them to the correct destination.
-
Address Resolution:
- In local networks, devices communicate using MAC addresses.
- When a device wants to send data to another device, it first resolves the recipient’s IP address to its corresponding MAC address using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
- ARP maintains a mapping between IP addresses and MAC addresses.
-
Access Control:
- Wi-Fi routers and switches use MAC addresses for access control.
- By filtering based on MAC addresses, network administrators can allow or deny specific devices from connecting to the network.
- This is useful for securing Wi-Fi networks and preventing unauthorized access
Reasons of MAC Address

-
Privacy and Security:
- Changing your MAC address can enhance privacy. By using a different address, you make it harder for others to track your device.
- Some public Wi-Fi networks may restrict access based on MAC addresses. Changing it allows you to bypass such restrictions.
-
Network Troubleshooting:
- If you encounter network issues, altering the MAC address can help diagnose problems.
- It allows you to simulate a different device on the network, which can reveal whether the issue is specific to your hardware.
-
Avoiding IP Conflicts:
- In some cases, multiple devices on the same network segment might accidentally have the same IP address.
- Changing the MAC address ensures that your device gets a unique IP address from the DHCP server.
-
Testing and Development:
- Developers and network administrators often need to test network configurations.
- Changing the MAC address allows them to simulate different devices without physically swapping hardware.
-
Spoofing and Anonymity:
- MAC address spoofing is used for anonymity or to bypass network restrictions
Reasons to change MAC Address

-
DHCP and IP Assignment:
- DHCP servers assign IP addresses dynamically to devices when they join a network.
- They use the device’s MAC address to ensure consistent IP assignments.
- This simplifies network management and prevents IP conflicts.
-
Virtualization and Cloning:
- In virtual environments, virtual machines (VMs) often share the same physical NIC.
- Each VM has a unique MAC address, allowing them to function independently.
- Cloning VMs involves changing their MAC addresses to avoid conflicts.
More Reasons to change MAC Address


Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- ARP connects an ever-changing Internet Protocol (IP) address to a fixed physical machine address, also known as a media access control (MAC) address, within a local-area network (LAN).
ARP operates between the data link layer (MAC address) and the network layer (IP address).


How does ARP work
- When a new computer joins a LAN, it receives a unique IP address.
- When data packets arrive at a gateway, the gateway asks ARP to find the matching MAC address for a given IP address.
- ARP maintains an ARP cache with IP-to-MAC address mappings.
- If the translation already exists, no new request is made. Otherwise, ARP performs the translation.
- ARP caches are dynamic and limited in size, ensuring privacy and security.


- Purpose: Static entries are manually configured and kept in the cache table on a permanent basis.
-
Use Case:
- Ideal for devices that need to communicate with other devices regularly within the same network.
- These entries remain unchanged unless explicitly modified by an administrator.
-
Reliability:
- Static entries serve as a reliable record of specific IP-MAC address mappings.
- They persistently link an IP address to a MAC address.
-
Management:
- Requires manual intervention to create and maintain.
- Useful for critical devices like servers or network infrastructure components.
STatic
ARP CACHING
- Purpose: Dynamic entries are automatically added by the network device (such as a router or switch) and have a limited lifespan in the cache.
-
Creation Process:
- When a device wants to communicate with an IP address, it performs an ARP request.
- The request broadcasts to the local LAN, asking, “Who has IP address X, and what is your Ethernet MAC address?”
- The responding device provides its MAC address, and the entry is added to the dynamic ARP cache.
-
Lifespan:
- Dynamic entries remain in the cache as long as they are actively used.
- If an entry remains unused for a certain period (the ARP cache timeout), it is removed.
-
Benefits:
- Dynamic entries adapt to network changes and are more flexible.
- They minimize management overhead compared to static entries.
Dynamic
MAC - ARP
By Alexios Louridas
MAC - ARP
- 117



