VLANs and DHCP
Dr. Alexios Louridas
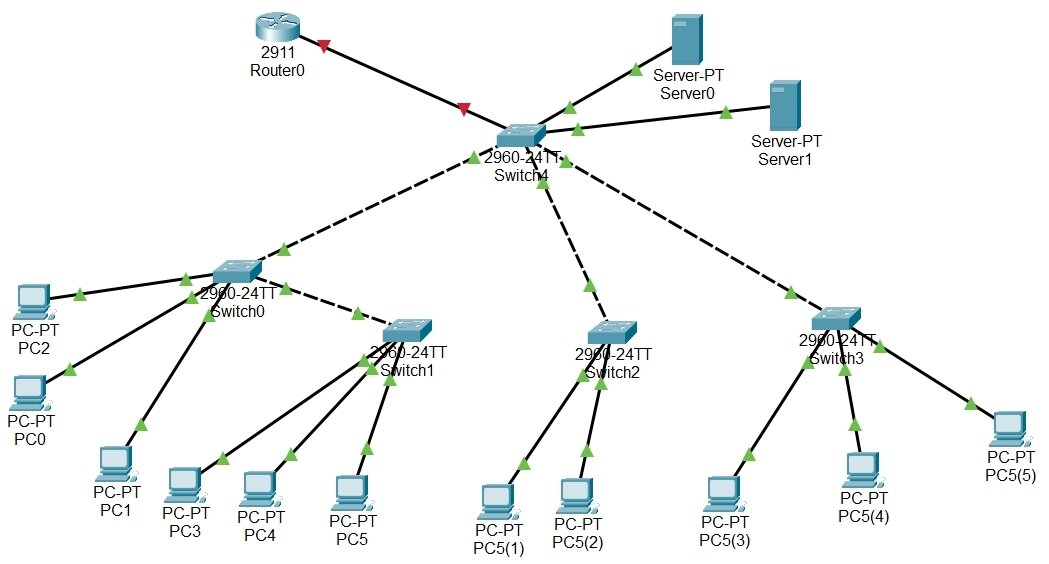
Virtual LANs
- One user moves office, but would need to connect to a different switch?
- single broadcast domain:
- all layer-2 broadcast traffic must cross entire LAN
- security/privacy, efficiency issues
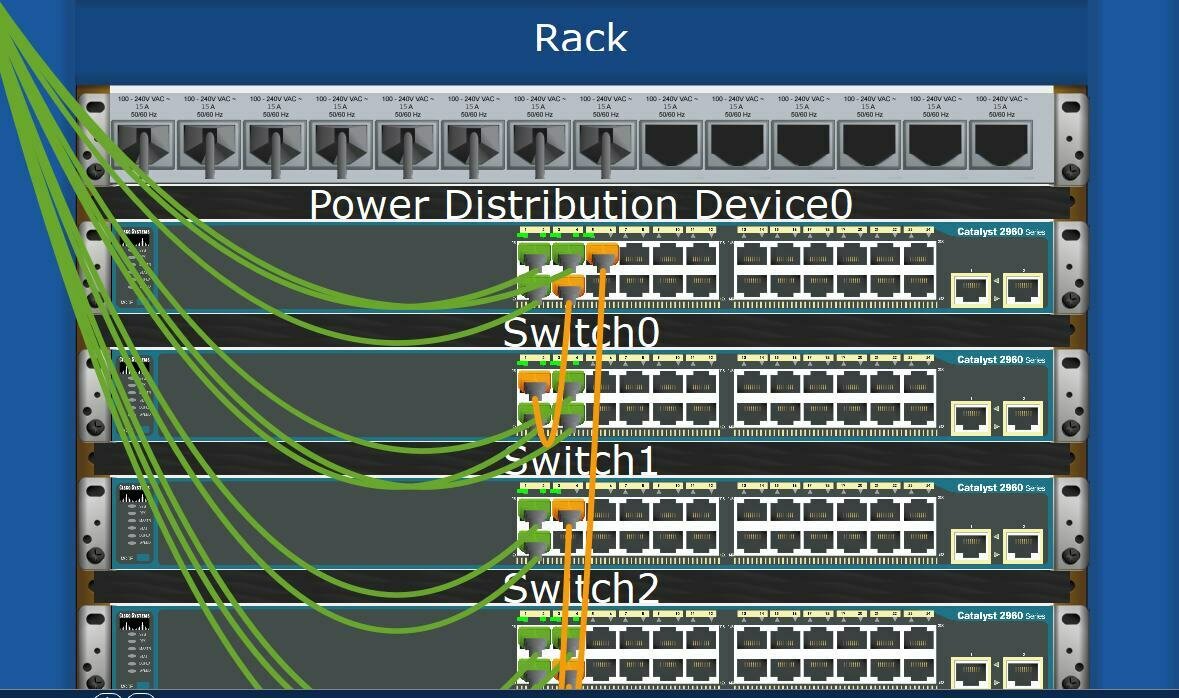
Port-based vlan
switch ports grouped (by switch management software) so
single physical switch ……
-
traffic isolation: frames to/from ports 1-n can only reach ports 1-n can also define VLAN based on MAC addresses of endpoints, rather than switch port.
-
dynamic membership: ports can be dynamically assigned among VLANs
-
forwarding between VLANS: done via
routing (just as with separate switches)
• in practice vendors sell combined switches plus routers
VLAN Advantages

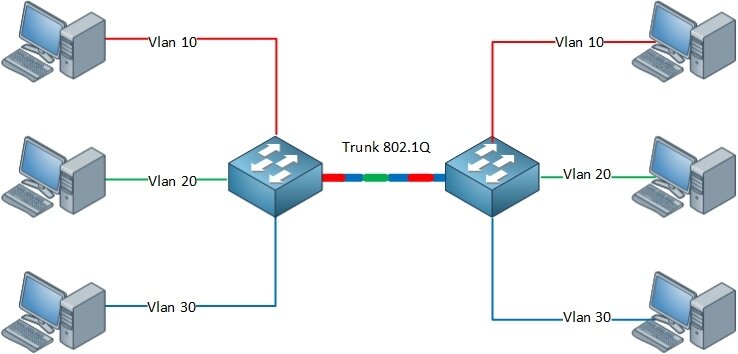
-
trunk port: carries frames between VLANS defined over multiple physical
switches-
frames forwarded within VLAN between switches can’t be vanilla 802.1 frames
(must carry VLAN ID info) -
802.1q protocol adds/removed additional header fields for frames forwarded
between trunk ports
-
Trunking

How to get an IP Address
- Hard Coded
- Configuration Files
- Auto Allocate
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)

-
To dynamically obtain IP address from network server
-
Leasing
-
IP address is not assigned forever
-
-
Can Reuse address pool
-
Supports mobile users
DHCP




How does DHCP work
DORA Phases:
- Discover: A host broadcasts a request for an IP address on its network using a DHCP DISCOVER packet.
- Offer: Once a DISCOVER packet is received by a DHCP server the server will allocate a free IP address and send it to the host using a DHCP OFFER packet.
- Request: Once an OFFER packet is received by a host it will send a DHCP REQUEST packet back to the DHCP server.
- Acknowledge: The server as a final act will send a DHCP ACKNOWLEDGE packet to the host.

DHCP not only IP
- Subnet Mask
- Network vs Host
- Default Gateway
- DNS server (Name and IP address)
- IP address for first hop router
〞
Does DHCP use TCP or UDP?
-
Local Network uses a SINGLE IP Address
-
How many and the ranges of IP addresses are irrelavant to ISP
-
Can alter local IP addresses without notifying the world
-
ISP can be changed without changing local addresses
-
Local devices are protected as they cannot be seen from the outside world
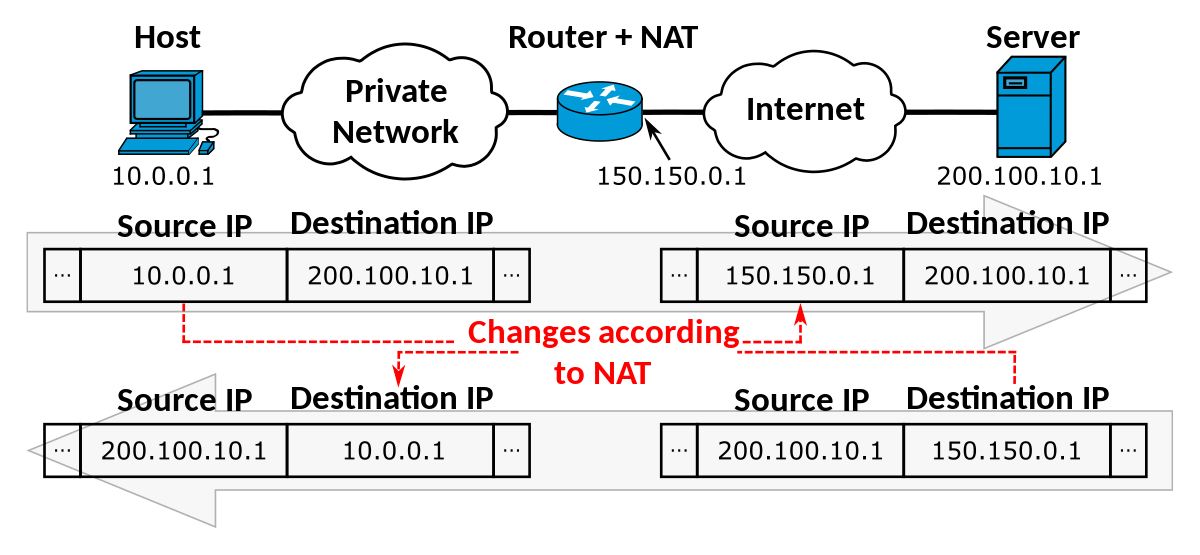
Network Address Translation

-
outgoing datagrams: replace(source IP address, port #) of every outgoing datagram to (NAT IP address, new port #) . . . remote clients/servers will respond using (NAT IP address, new port #) as destination address
-
remember (in NAT translation table) every (source IP address, port #) to (NAT IP address, new port #) translation pair
-
incoming datagrams: replace(NAT IP address, new port #) in dest fields of every incoming datagram with corresponding (source IP address, port #) stored in NAT table
NAT ROUTER

〞
NAT Controversy - Find out why NAT been a topic of debate?
1
Privacy and Security Concerns:
- IP address hiding
- Security Implications
2
Breaking End to End connectivity
3
Scarcity of IPv4 Addresses
Perpetuates the use of IPv4
5
Impact on Peer-to-Peer Applications
4
Complexity and Maintenance
6
Use of Large Scale NATS (LSN) or sometimes called CarrierGrade NAT (CGN)
Minimal
By Alexios Louridas
Minimal
- 128


