Interpreting network structure
Context
- We are given a network which performs some task
- We want to understand how the network’s structure relates to that task
(e.g. trained from Moritz or Mihai, or experimentally measured from Hamutal or Mina)
Local motifs
Global structure
- Laplacian
- Hodge Laplacian
- triangles, stars, chains, …
- simplices,
cells
- graph
- simplicial complex,
cell complex
Functional decomposition



See also (Hoppe, Grande, 2025, Don’t be afraid of Cell Complexes)

Bridging structure & function with a shift operator

Discrete Fourier transform
Decompose into modes

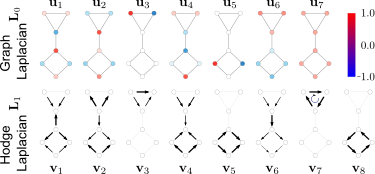

Graph Laplacian
Hodge Laplacian

This is a global description of the graph
Modes
Low dim representation of functions on the graph
Possible direction: Can we go more local w/ subpops?
Linear, random connectivity within each subpopulation

Transfer function in terms of functional Fourier modes
What we might explore
- Generalize to a (Hodge) Laplacian shift operator?
- Does the basis also work with sharp activity spikes?
Daniel Moreno Soto
New tool: Model comparison under uncertainty

Consistent criterion even when no model is correct
Strength of criterion depends on dataset size
More samples
One model is correct
No model is correct
Selection criterion (lower ⇒ better model)
BIC
Bayes factor
MDL
AIC
elpd
EMD
(ours)
May be useful for testing model hypotheses
(René, Longtin, 2025; Selecting fitted models under epistemic uncertainty)
ASSIGN Kickoff 17 Oct 2025
By alexrene
ASSIGN Kickoff 17 Oct 2025
- 31



