
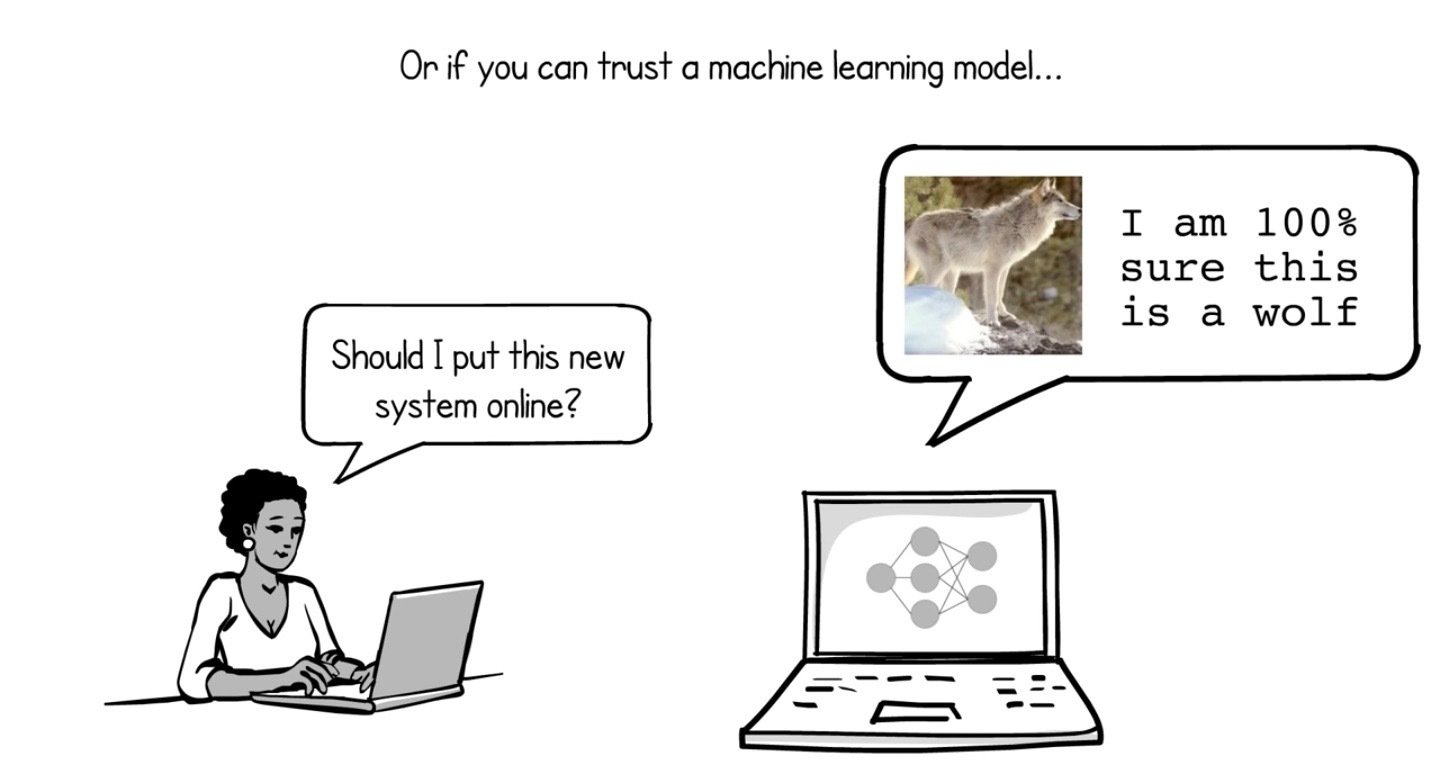
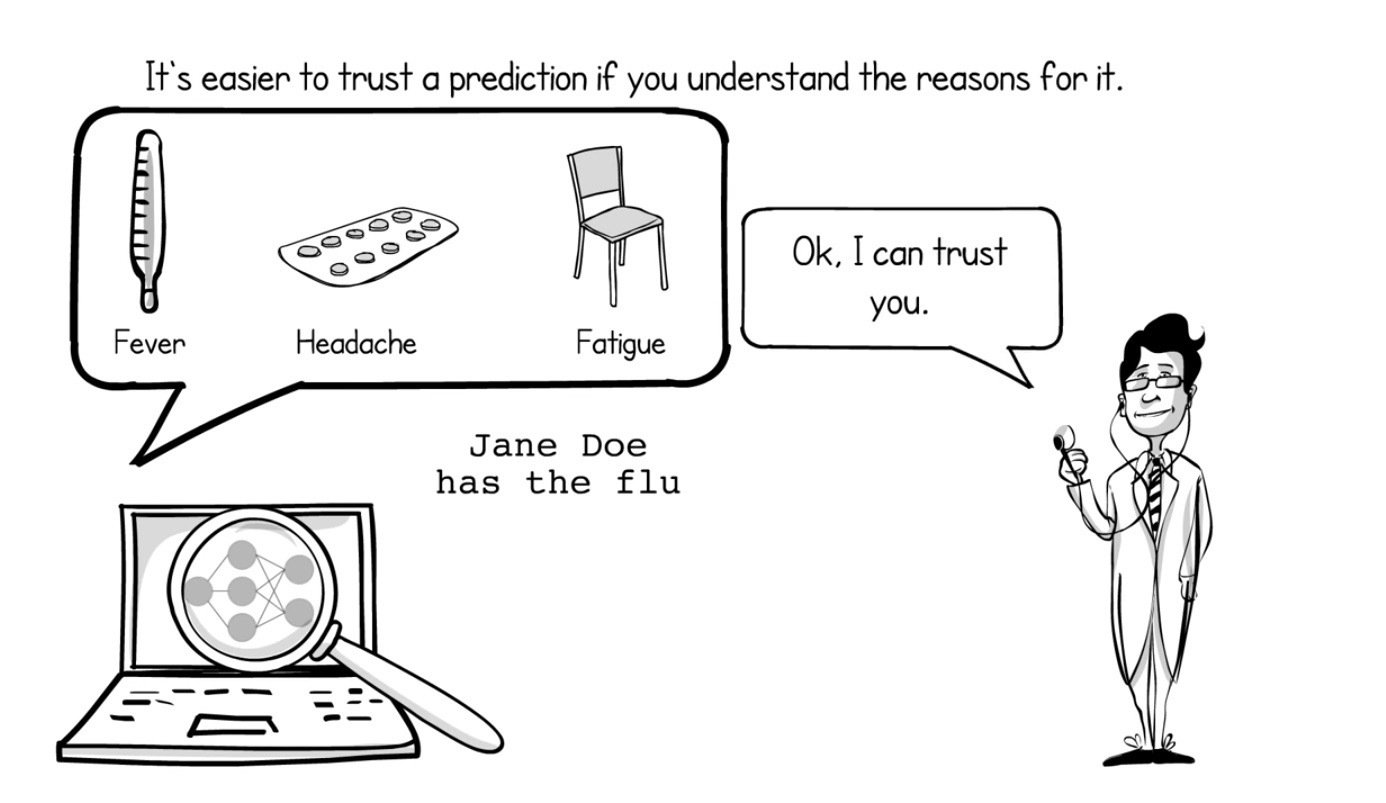
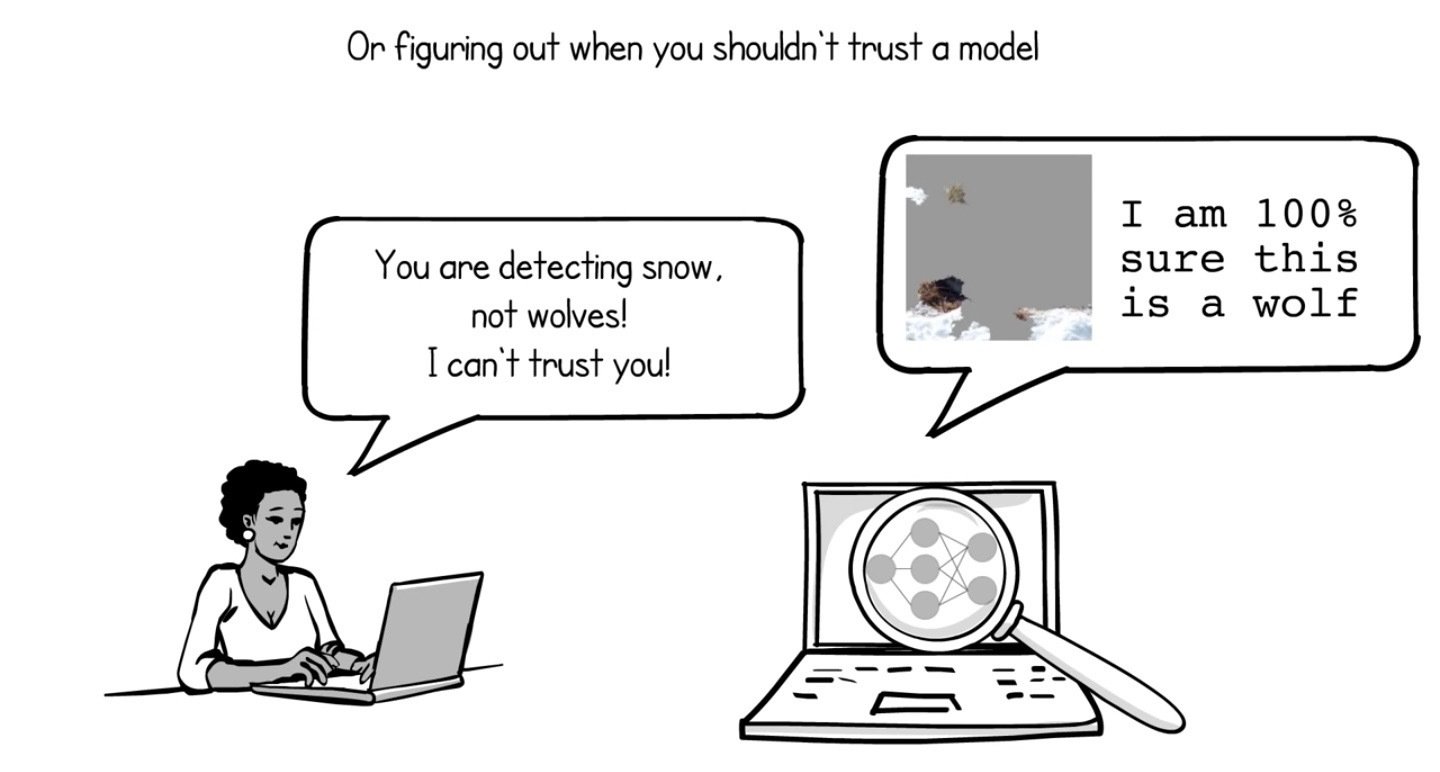
Why Should I Trust You?
Image credit: Interpretable ML Book
Introduction

Image credit: LIME paper video
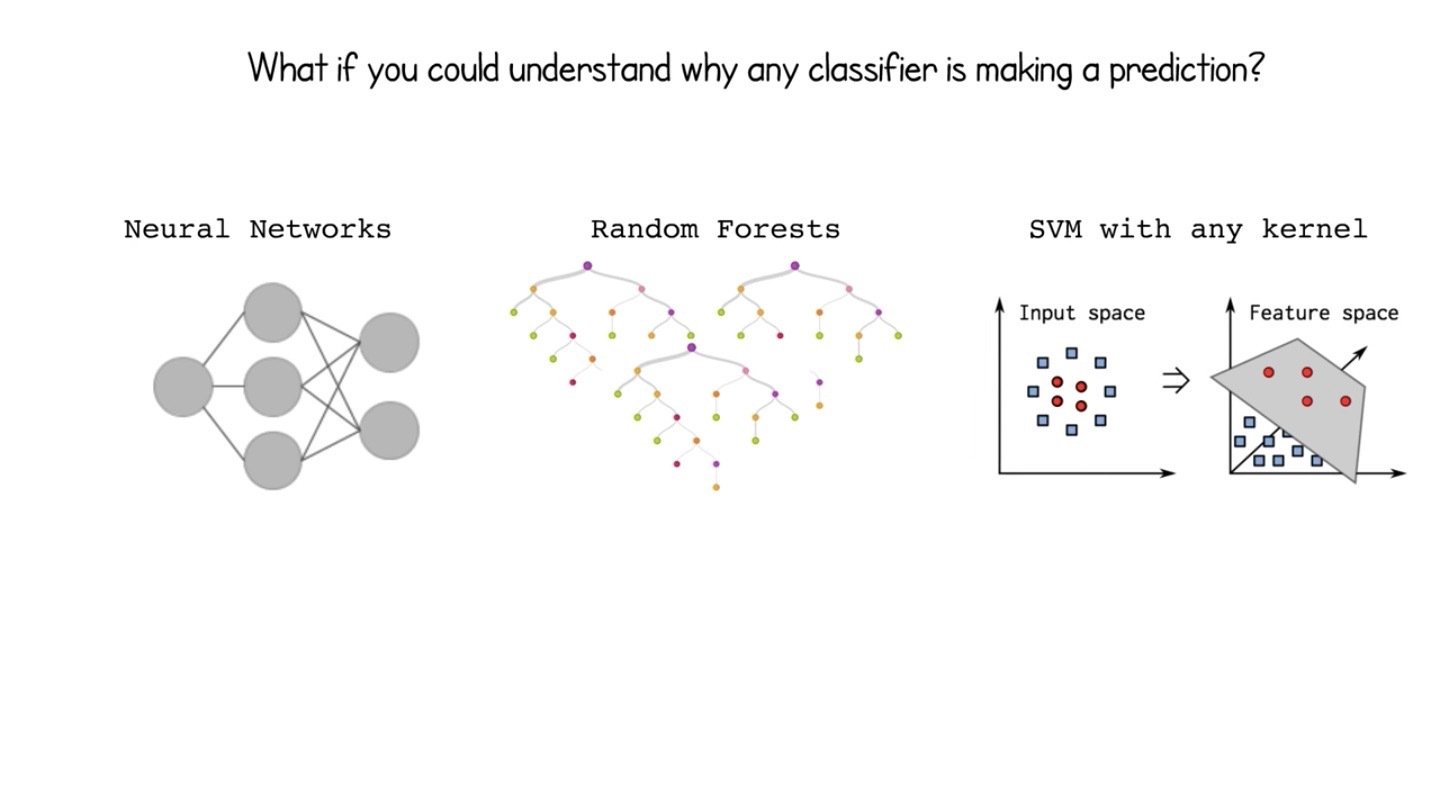
Areas of Interpretability
-
Algorithm Transparency
-
Scope of interpretation
- Local Interpretation
- Global Interpretation
-
Model restriction
- Blackbox models
- Restricted models
Related Work
Local
Intereptable
Model-Agnostic
Explanations
How does LIME work?
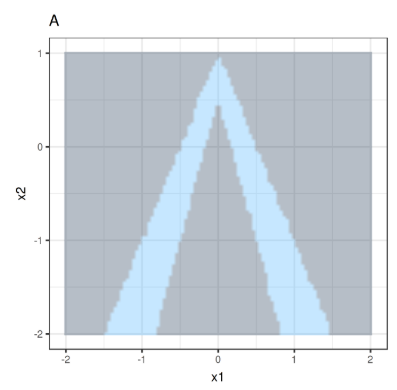
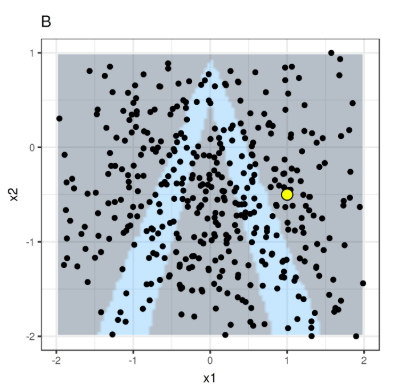
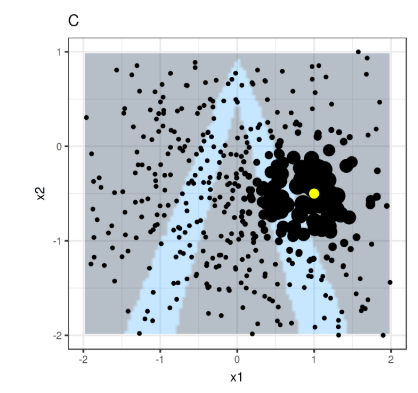
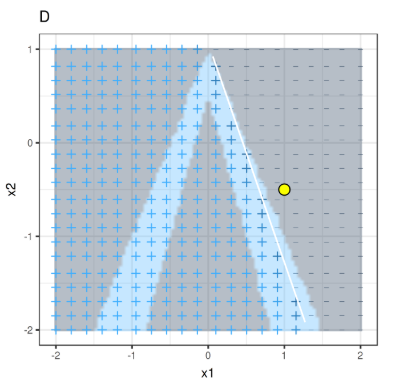
Objective Function Formulazition
\text{explanation(x)} = \text{argmin}_{g \in \mathcal{G}} L(f, g, \pi_x) + \Omega(g)
\Omega(g) \to \text{Complexity of model } g
\mathcal{G} \to \text{set of all possible models}
\pi_x \to \text{a neighbourhood of } x
L \to \text{ Loss function for approximation}
Some LIME Samples
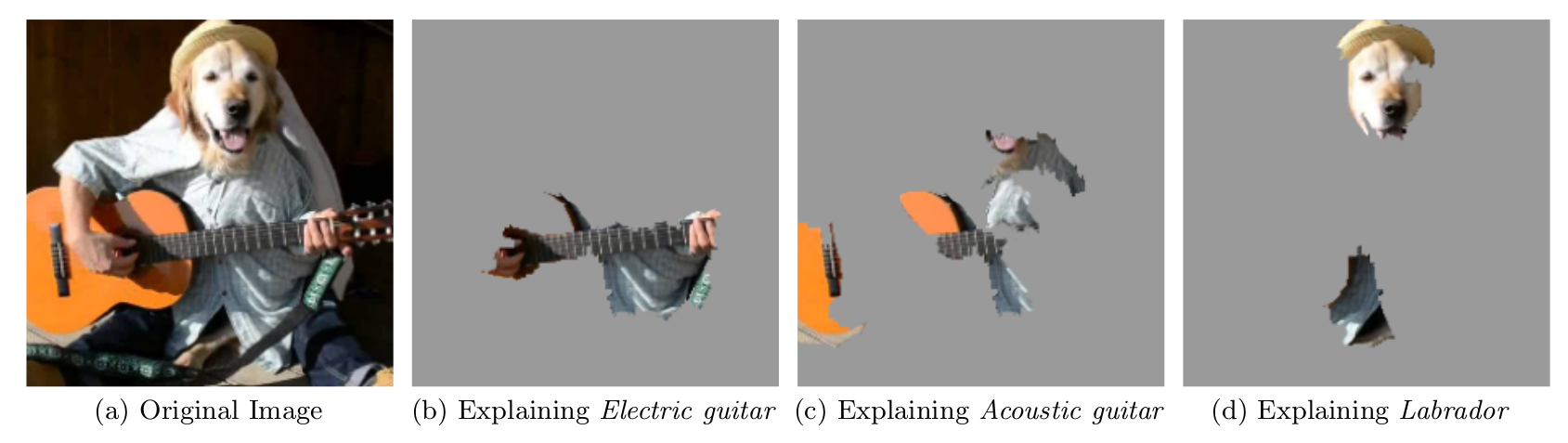
Proposed Method
Interpretability Via Model Extraction
x \in \mathcal{X}
f
y \in \mathcal{Y}
x \in \mathcal{X}
T
T(x) \approx y
Algorithm Properties
Global
Blackbox
T as a Decision Tree
But Decision Tree Overfits!
Solution: Use Active Learning
The more samples used
The more generalized the tree
Model Extraction Algorithm
1. Input Distribution
\text{General Gaussian Mixture Model}
+
X_{train} \text{ dataset used for training } f
EM
\mathcal{P} \text{ distribution}
2. Exact Decision Tree
\text{Define } T^* \text{ such that } \\
\forall x; T^*(x) = f(x)
Gain(f,C_N) = \\ 1 - \sum_{y \sim \mathcal{Y}}{Pr_{x \sim P}[f(x) = y \, | \, C_N]}
3. Estimated DT
\text{Approximate } Gain(f, C_N) \text{ using n } i.i.d \text{ samples}
\text{Simplify } C_N = (s_1 \le x_1 \le t_1) \cdots (s_d \le x_d \le t_d)
pdf_{\mathcal{P} \, | \, C_N}(x) \varpropto \sum_{j=1}^{k}{\phi_j
\prod_{i=1}^{d}{\mathcal{P}_{\mathcal{N}(\mu_{ji}, \sigma_{ji})|(s_i \le x \le t_i)}(x_i)}}
3. Estimated DT Cont.
\text{Using } pdf_{\mathcal{P} \, | \, C_N}(x) \\ \text{ we can calculate probability
of each component of } \mathcal{P}
x \sim \mathcal{P} \, | \, C_N \\ (j \sim Categorical(\tilde{\phi})) \wedge (x \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu_{ji}, \sigma_{ji}) \, | \, (s_i \le x_i \le t_i))
4. Theoretical Gaurentee
Pr_{x \sim \mathcal{P}}{[T(x) \ne T^*(x)]} \le \epsilon \text{ has probability at least } 1-\delta
\text{As } n \to \infty \text{, } T \to T^* \text{. In other words, for all } \epsilon , \delta:
Sample Visualizations
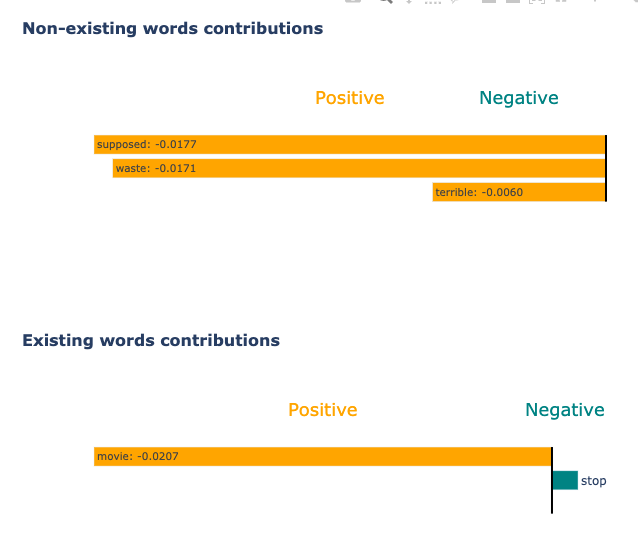
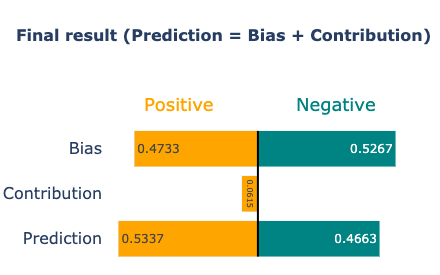
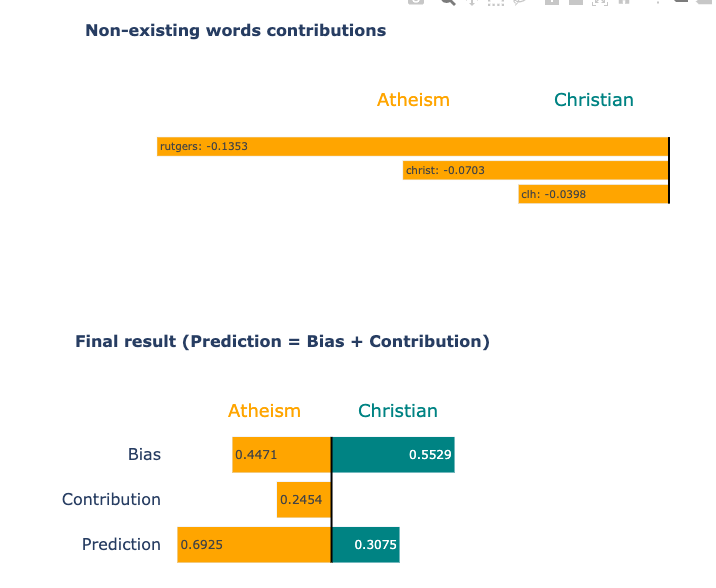
Conclusion
Comparision with CART
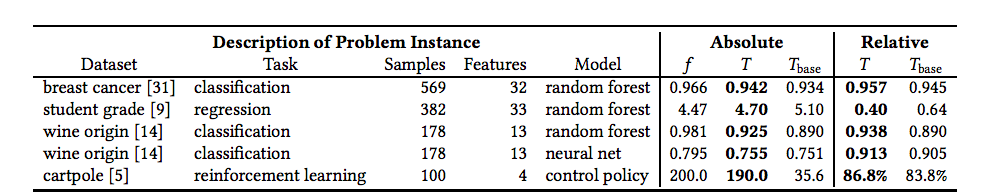
Implementation
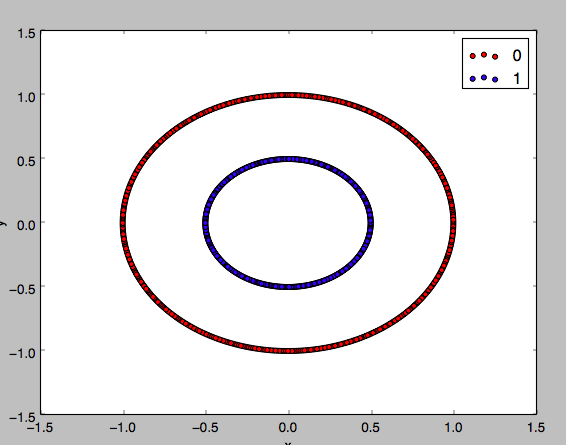
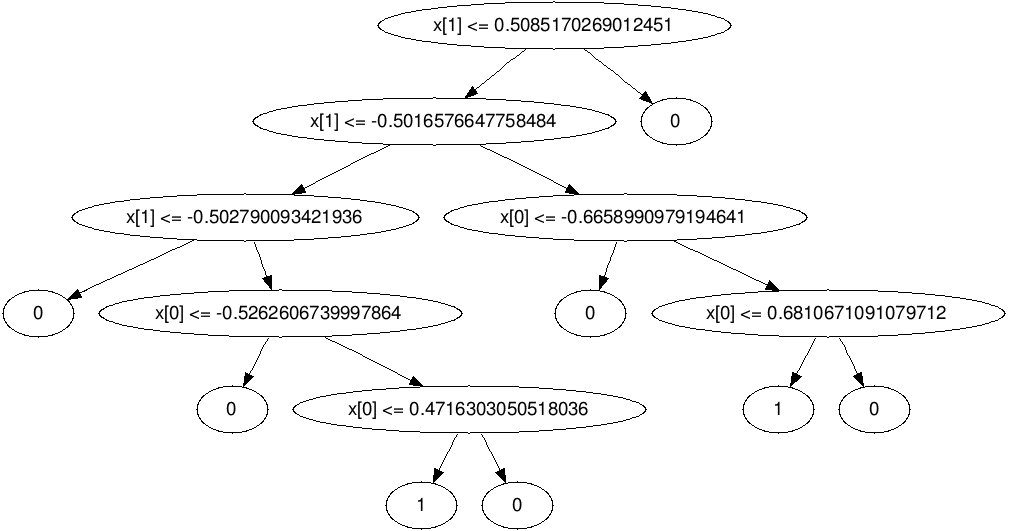
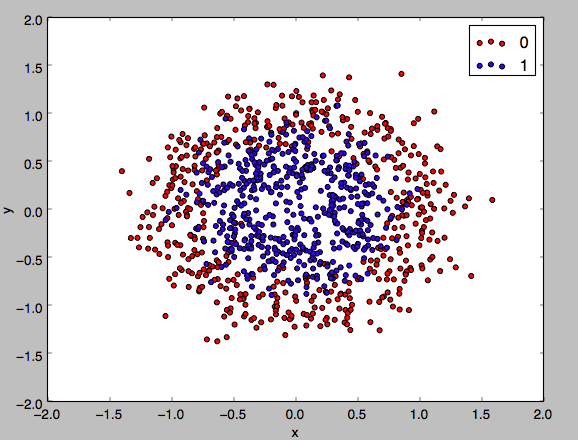
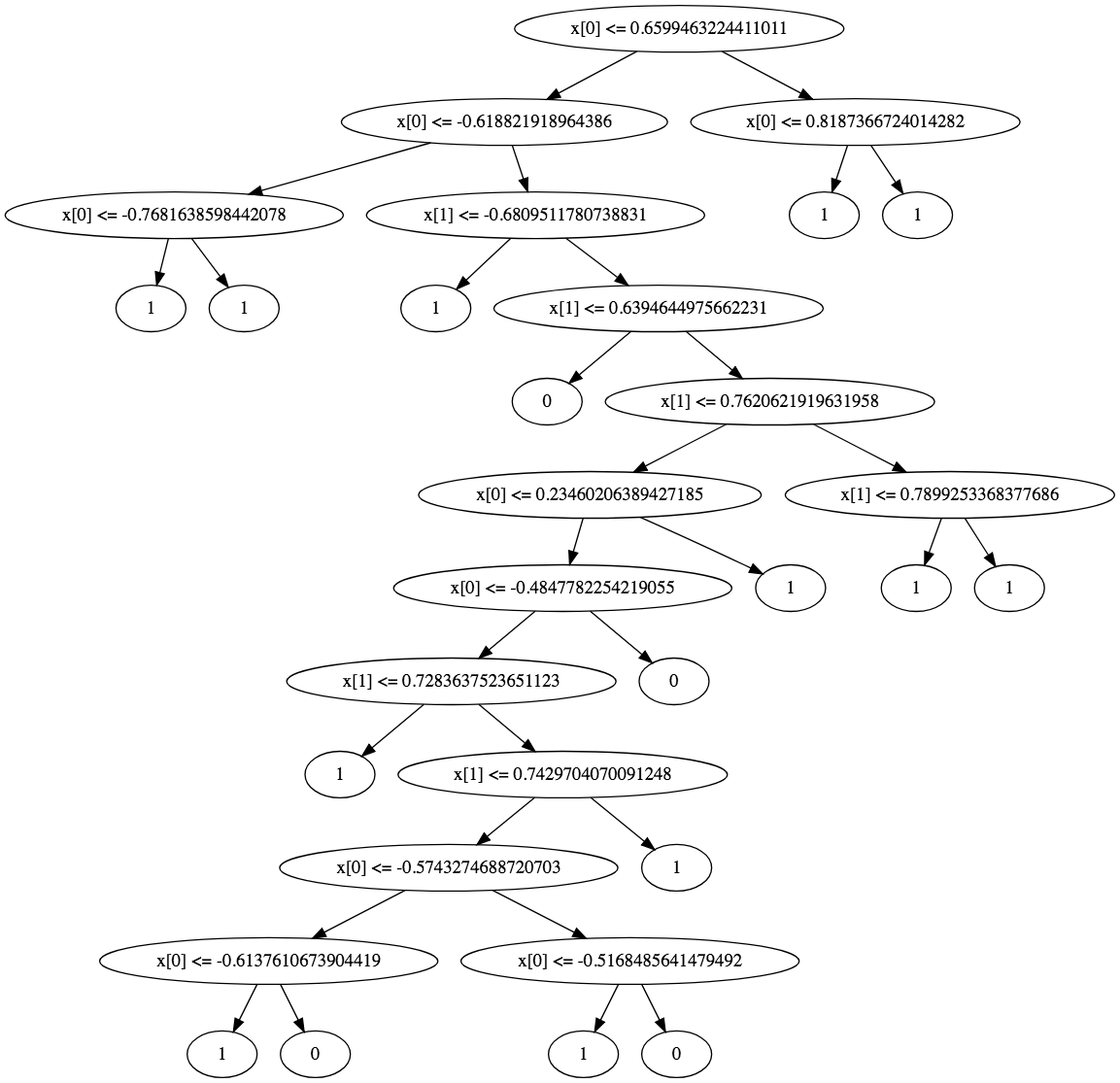
Reference
- Bastani, O., Kim, C., Bastani, H. Interpreting Blackbox Models via Model Extraction. 2017
- Breiman, L., Friedman, J., Stone, C. J., and Olshen, R. A. Classification and regression trees. CRC press, 1984.
- Ribeiro, M.T. Singh, S. Guestrin C. "Why Should I Trust You?": Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier, 2016
Thanks!
Here's the potato

Presentation: Why Should I Trust You?
By Amin Mohamadi
Presentation: Why Should I Trust You?
- 327




