DOM
What is the DOM?
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents. It represents the page so that programs can change the document structure, style, and content. The DOM represents the document as nodes and objects. That way, programming languages can connect to the page.
createElement
const newDiv = document.createElement("div");
// and give it some content
const newContent = document.createTextNode("Hi there and greetings!");
// add the text node to the newly created div
newDiv.appendChild(newContent);
// returns a Boolean value indicating whether the given Node has child nodes or not
console.log(newDiv.hasChildNodes());
// add the newly created element and its content into the DOM
const currentDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
document.body.insertBefore(newDiv, currentDiv);
// replaces a child node within the given (parent) node
document.body.replaceChild(newDiv, currentDiv);
// removes a child node from the DOM and returns the removed node
document.body.removeChild(newDiv);Traversing
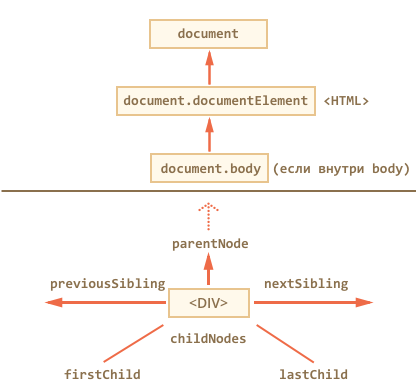
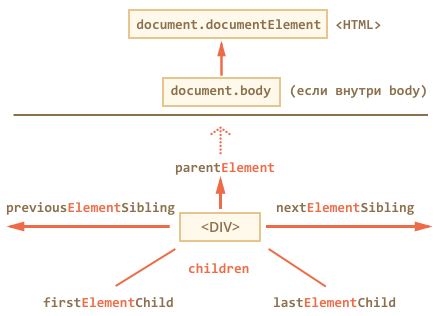
Searching
Attributes
classList
const div = document.createElement('div');
div.className = 'foo';
// our starting state: <div class="foo"></div>
console.log(div.outerHTML);
// use the classList API to remove and add classes
div.classList.remove("foo");
div.classList.add("anotherclass");
// <div class="anotherclass"></div>
console.log(div.outerHTML);
// if visible is set remove it, otherwise add it
div.classList.toggle("visible");
// add/remove visible, depending on test conditional, i less than 10
div.classList.toggle("visible", i < 10 );
console.log(div.classList.contains("foo"));
// add or remove multiple classes
div.classList.add("foo", "bar", "baz");
div.classList.remove("foo", "bar", "baz");
// add or remove multiple classes using spread syntax
const cls = ["foo", "bar"];
div.classList.add(...cls);
div.classList.remove(...cls);
// replace class "foo" with class "bar"
div.classList.replace("foo", "bar");data-*
The data-* global attributes form a class of attributes called custom data attributes, that allow proprietary information to be exchanged between the HTML and its DOM representation by scripts.
<img class="spaceship cruiserX3" src="shipX3.png"
data-ship-id="324" data-weapons="laserI laserII" data-shields="72%"
data-x="414354" data-y="85160" data-z="31940">
</img>const img = document.getElementsByTagName('img');
console.log(img.dataset.x); // "414354"Contents
const newDiv = document.createElement("div");
newDiv.innerHTML = "<p>Hi there and greetings!</p>";
console.log(newDiv.innerHTML); // "<p>Hi there and greetings!<p>"
console.log(newDiv.textContent); // "Hi there and greetings!"
console.log(newDiv.outerHTML); // <div><p>Hi there and greetings!<p></div>
Styles
const newDiv = document.createElement("div");
newDiv.style.color = "#ffffff";
newDiv.style.backgroundColor = "#000000";
newDiv.style.margin = "5px";
// or
newDiv.style.cssText = `
color: #ffffff;
background-color: #000000;
margin: 5px;
`;
const computedStyle = getComputedStyle(newDiv);
newDiv.style.marginTop = "calc(computedStyle.marginTop + 5px)";Links
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Document_Object_Model/Introduction
- https://learn.javascript.ru/traversing-dom
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Element/classList
- https://learn.javascript.ru/attributes-and-custom-properties
- https://learn.javascript.ru/basic-dom-node-properties
- https://learn.javascript.ru/styles-and-classes
DOM
By Andrew Bogomolov
DOM
- 86



