Security and Data Integrity
- show understanding of the need to keep data safe from accidental damage, including corruption and human errors
- show understanding of the need to keep data safe from malicious actions, including unauthorised viewing, deleting, copying and corruption

Objectives
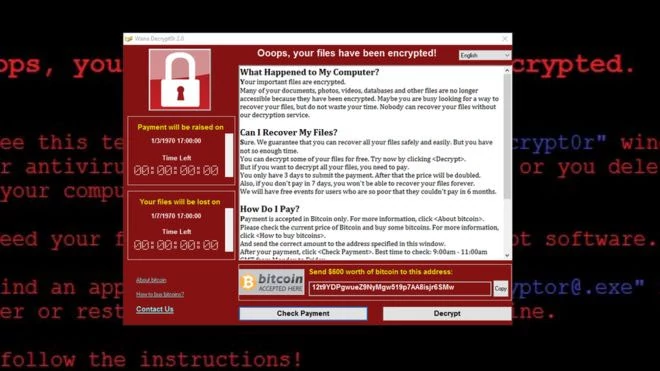
In 2017, a ransomware called WannaCry appeared
How will a computer lost data?
In notebook, write down situations that might cause the computer to loss of data or resulted in data corruption.
Backups
- Make one or more copies of data
- Stored in separate storage medium, (preferably) in separate locations
- When main data is lost, corrupted, the backup copy is Restored to the main system
[classwork] Scenarios on backup
| Scenario | Which storage media | What is backed up | When is it backed up | Where is it stored |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Student storing school works | ||||
| A small shop that records its accounts | ||||
| A university that stores student data and work | ||||
| An online shop that sells thousands of items a day | ||||
| A hospital that stores patient records | ||||
| A family who store their films and music that they have downloaded |
Security Threats
- Malware
- Computer Viruses
- Spyware and key-logger
- Phishing
- Pharming
- DoS and DDoS
- Wardriving
Protection from attacks
- Physical Security
- Authentication
- Login/Password
- Biometric
- Firewall & Proxy Server
- Encryption
- Safety protocol (SSL and TLS)
Topic overview (2019)
| Week | Mon | Tue | Thu |
|---|---|---|---|
| 28/10 | | Array | Backup and data integrity |
| 4/11 | Phishing Pharming |
Encryption Encryption exercise |
Virus Spyware/keylogger |
| 11/11 | DDoS, Firewall and proxy |
Pre-release material tasks | Hacking, Wardriving Quiz |
| 18/11 | Security Protocol | Pre-release material tasks | Biometric Authentication, Password |
| 25/11 | Freeware, shareware Quiz |
Pre-release material tasks | Chapter Revision |
Hacking
Gaining illegal access to a computer system
through Hacking password, deploying malicious software etc.
Why?
- Steal personal data
- Identity theft (password)
- Corrupt / destroy data in the owner's system
Prevention
- Firewall
- Strong passwords
- Anti-malware program
Hacking
- Hacking is not always illegal
- e.g. assume you zip a folder and forgot the password, you can "hack" the password and gain access to it, which is legal to do so.
- Ethical hacker / White Hat hacker to break in to a system and report security issue to the owner
Cracking
- Edits a program source code to exploit the system
- Illegal and non-ethical
- e.g. Serial cracker to by-pass the copyright protection of a computer software (i.e. pirate software)
Wardriving
Locating and using wireless internet connections illegally
Why?
- Steal Internet Bandwidth / Time
- Hack into the wireless network and steal information
Prevention
- Enable Encrypted wireless connection (WEP or better WPA)
- Strong passwords in WiFi Network
- Firewall
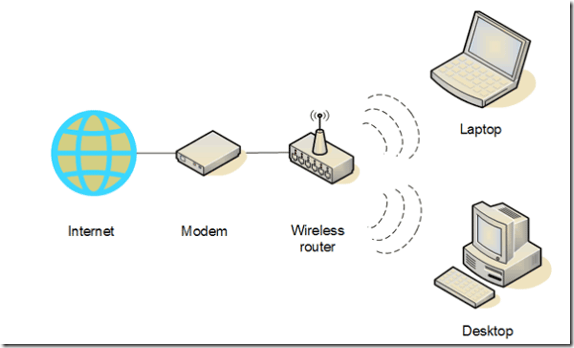
Home wireless network diagram
Authentication
- Verify the data is from trusted source
- Techniques
- Username and password
- Biometrics
- Digital Certificates
Digital Certificate
- Websites or emails can attach a digital certificate, to prove that the sender is legitimate
- Digital certificates are usually issued by third-party websites, or government
Passwords / codes
- Username and password combination
- Chip and PIN for debit cards (usually in payment)
- Chip means IC or smart card
- In contrast to Magnetic Stripe cards, it is more secure
Better authentication method
Recall those online services / website you've been using, what other methods they apply to make the authentication more secure than just username and passwords?
Discuss in pairs.

Strong passwords
- Passwords that is difficult to guess by the hackers
- Principle for strong passwords:
- (list after watching video)
Phishing
The creator sends out a legitimate-looking email which aims to redirect the victim to a fake website
Why?
- Steal personal data
Prevention
- Firewall
- Spam Filter
- Be careful on clicking links in email
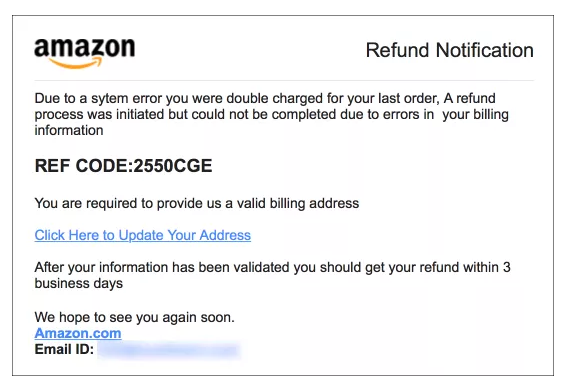
Phishing Email
- Phishing email usually target user login credentials
- Unusual behavior, bank / companies usually won't ask you to sign in or give personal data by email
- Sometimes have lots of typo / grammar mistake (why?)
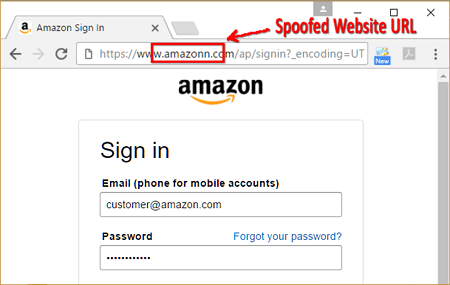
Phishing website, address is wrong (but hard to notice)
Pharming
Malware is installed on user computer, which will redirect user to a fake website
Why?
- Steal personal data
Prevention
- Anti-Malware application
- Digital Certificate
Technique used in Pharming
- DNS (Domain Name Service) Spoofing
- Malware modify the DNS setting or tamper the DNS data
- Public WiFi
Phishing
- Malware are not involved
- A legitimate looking email is sent out (which is the bait of fishing) and user will visit the fake website
- Usually the address of the fake website is very similar to the legit one
- e.g. facelook.com
Pharming
- Malicious code is installed in victim's computer, can be spyware or virus etc.
- When user try to visit the legitimate website, the code makes the computer go to the fake one
- Very difficult to detect since the address will be correct and the website looks exactly the same as real
Viruses
Malware that can replicate itself
What may happen?
- Corrupt/delete data
- Cause computer became unresponsive, slow, or crash
Prevention
- Anti-virus software
- Don't install/use software from unknown sources
- Be careful on email attachments, verify before opening
Spyware
Gathers information and send back the data to the person who sent the spyware
Why?
- Steal personal data, e.g.
- Identity theft (password)
- Credit card number
Prevention
- Anti-spyware software
- Firewall
- Advanced authentication:
- Two-step verification
- Biometric
Spyware
- Malware that aims to collect personal data without the user's consent
- Data will be collected and send back to who sent this spyware
-
Keylogger is an example that will monitor key press on keyboard
- Still username, password and maybe credit card information
- Some can record the network traffic, browsing records
- Another examples are those webcam spy, microphone spy etc.
Secured Protocol
Protocol to ensure secure data communication, e.g.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and it's predecessor, Transport Layer Security (TLS)

SSL/TLS involves
- Obtain and verify server certificate
- Obtain and verify client certificate (optional, depending on application)
- Establishing Encryption Keys
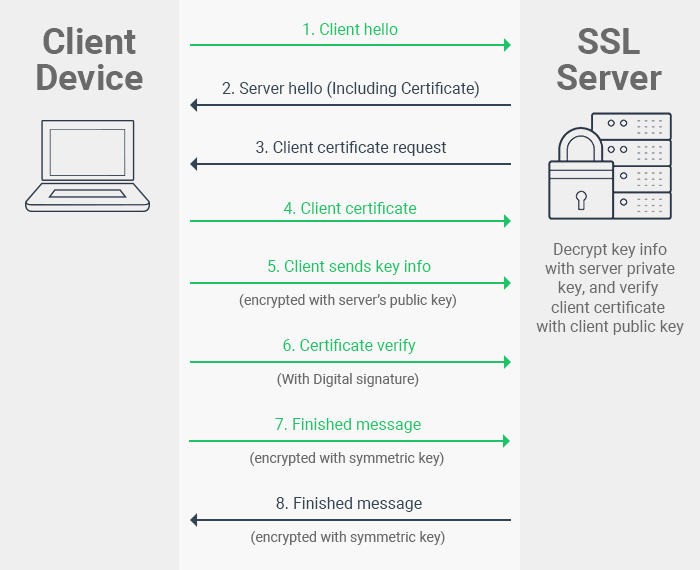
More about SSL/TLS
- All data transmitted is encrypted after establishing connections
- It involves both Authentication and Encryption
- TLS is more recent and secure which replaced SSL
- Encryption or security protocol does impact the performance of the data transmission (but we still need it)
Encryption
Encodes a message to something that only intended reader can understand
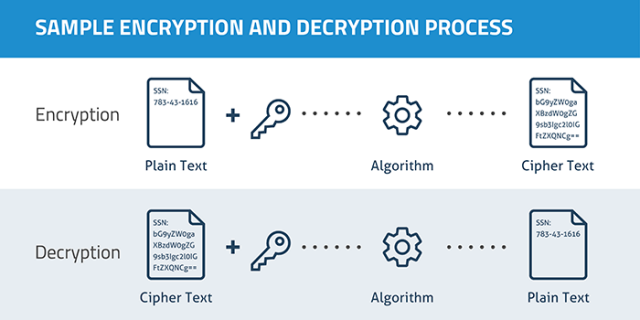
Terms
- Plaintext - The original message
- Encryption Algorithm - The "Method" used to encrypt
- Encryption/Decryption Key - The additional information provided to algorithm for encrypt and decrypt
- Ciphertext - Encoded Message (usually meaningless)
Symmetric Key Encryption
- The encryption and decryption key is shared between sender and receiver
- Issues with symmetric key?
Asymmetric Key Encryption
- Encryption key and decryption key is different
- In Internet communication:
- Receiver generate a private key (and key it as secret)
- Receiver generate a public key using the private key
- Receiver shares public key to sender
- Sender encrypt with public key
- Receiver decrypts with private key
-
Types of software
- Proprietary software
- Paid
- Freeware / Shareware
- Opensource software
Proprietary software
- Sometimes referred as closed-source software
- Source code are closed - Not disclosed, and usually not allow to change or reverse-engineering (work from the compiled code to reveal the source code)
- End-users pay for the software for the right to use it. Under the limitation on the license agreement.
- Where can use it
- How many computers can install it
- No redistribution of the software
Freeware, shareware
- Freeware are proprietary software, only difference is user do not need to pay for the right to use
- Funding the developers:
- Some freeware provide a limited function and user will required to purchase for a full version
- Other methods?
Watch video about open source and note on the difference between open source and proprietary software
Open Source
- Sometimes called Free Software
- Source code is open for public access
- Allow modification and redistribute of the software (provided that the original authors are credited)
Properitary
- Includes paid, freeware or shareware
- Source code is not accessible
- No modification and usually no redistribution of the software
Open Source
Properitary




[F4CS] Security and data integrity
By Andy tsui
[F4CS] Security and data integrity
- 407



