Networking Fundamentals
(Kalyana+Soma).Sundaram
Kishan Gupta
Aneesh Dogra
What happens when you open www.google.com
AGENDA
- DNS, UDP (0.5 days)
- HTTP/(S) (0.5 days)
- TCP, IP Routing (0.5 days)
- Conclusion and Noc session(0.5 days)
DNS
- why DNS
IP vs Domain Name - StakeHolders
TLD owners- ccTLD,gTLD etc
Registrars- Godaddy, Orderbox
DNS Cache- ISP, local
Transport Layer Protocols
UDP
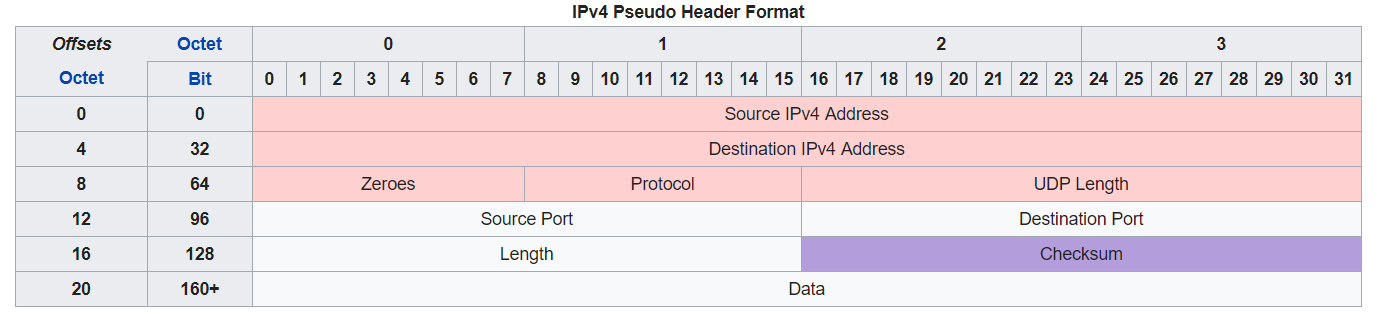
- TCP
- UDP
TCP
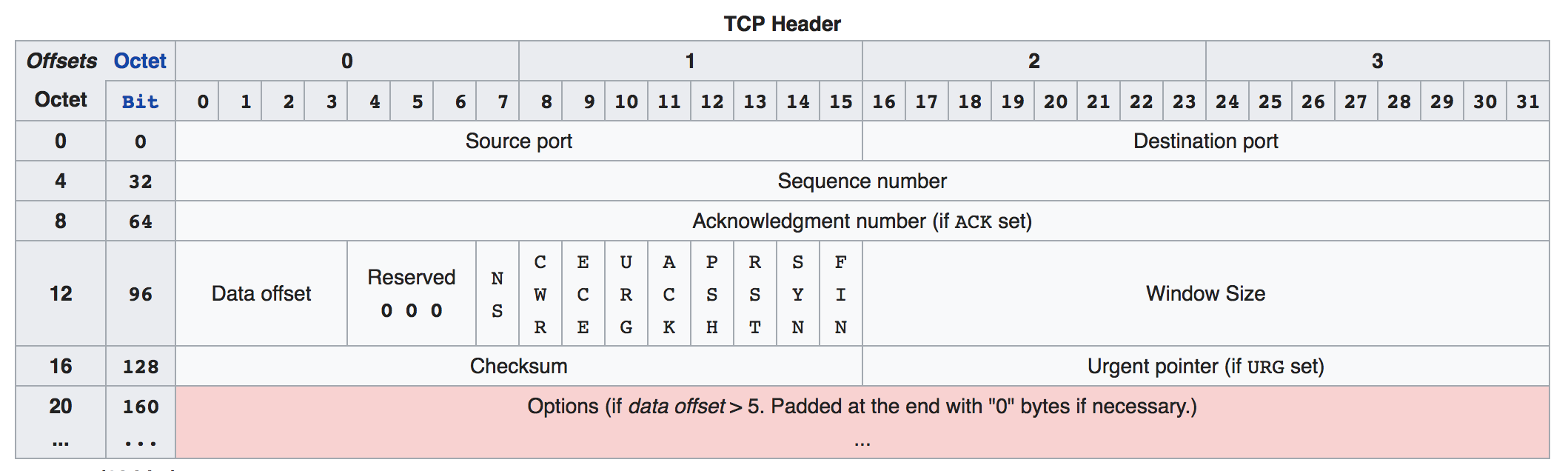
Flags
- NS (1 bit): ECN-nonce - concealment protection (CANT EXPLAIN)
- CWR (1 bit): Congestion Window Reduced (CWR) flag is set by the sending host to indicate that it received a TCP segment with the ECE flag set and had responded in congestion control mechanism (added to header by RFC 3168).
- ECE (1 bit): ECN-Echo has a dual role, depending on the value of the SYN flag.
- URG (1 bit): indicates that the Urgent pointer field is significant
Flags
- ACK (1 bit): indicates that the Acknowledgment field is significant. All packets after the initial SYN packet sent by the client should have this flag set.
- PSH (1 bit): Push function. Asks to push the buffered data to the receiving application.
- RST (1 bit): Reset the connection
- SYN (1 bit): Synchronize sequence numbers. Only the first packet sent from each end should have this flag set. Some other flags and fields change meaning based on this flag, and some are only valid when it is set, and others when it is clear.
- FIN (1 bit): Last packet from sender.
Options
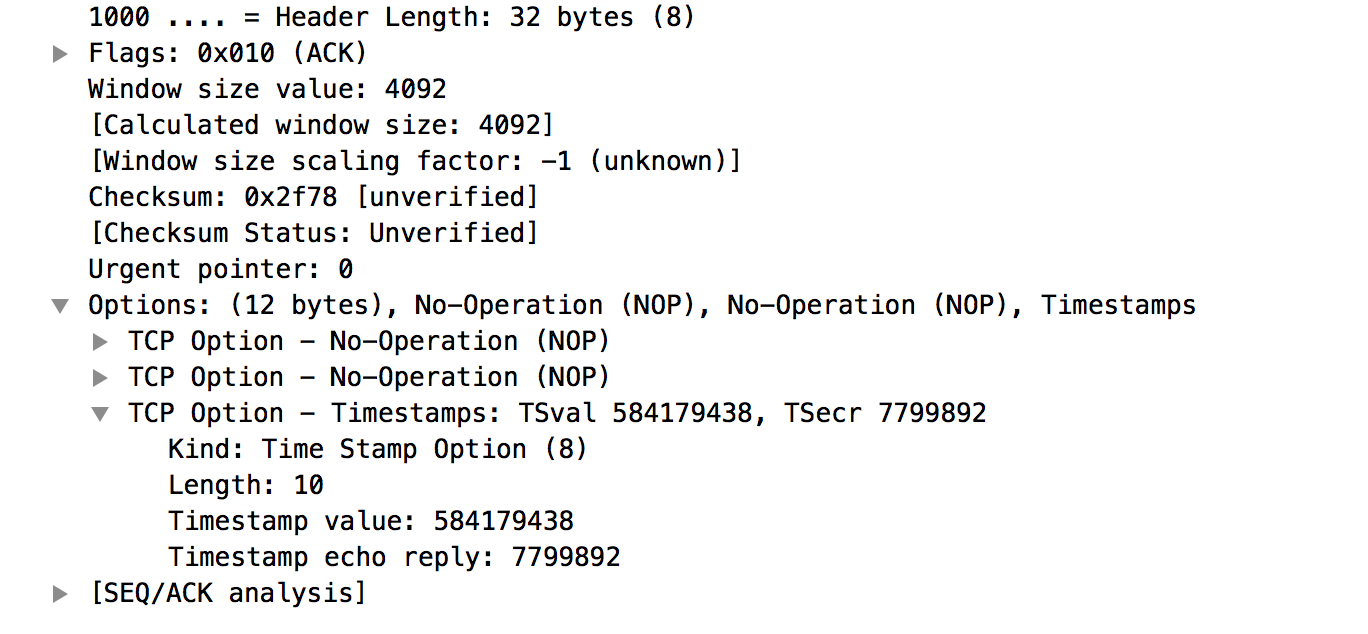
TCP
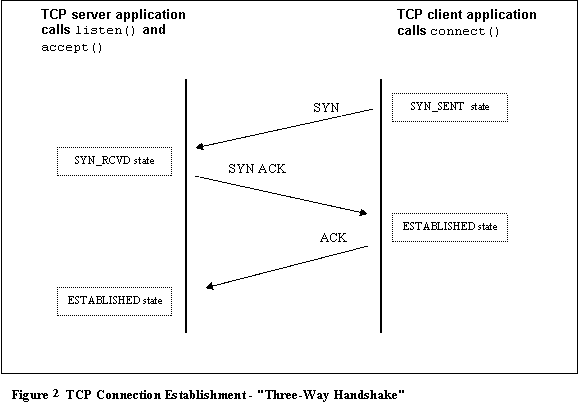
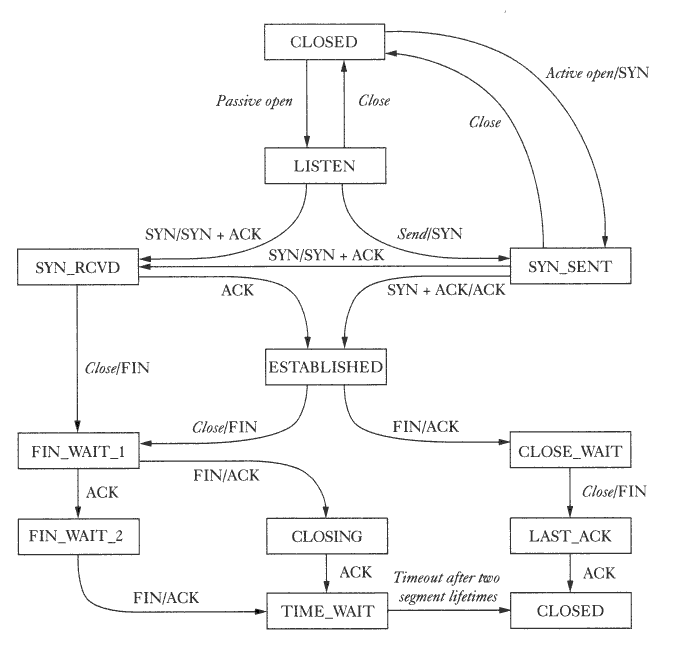
- 3 way handshake
- Acknowledgements and reliability
- tcpdump and check sequence numbers
- Push Reset Flags
sysctl values
- tcp_orphan_retries - (7) - how many times to retry before killing a connection (web server optimization)
- tcp_fin_timeout - (60sec) - time to hold socket in FIN-WAIT-2
- tcp_max_orphans, tcp_abort_on_overflow
- tcp_window_scaling
- tcp_syncookies (FALSE), tcp_max_syn_backlog (1024)
- tcp_rmem,tcp_wmem
- tcp_max_syn_backlog
-
tcp_recycle,tcp_fintimeout
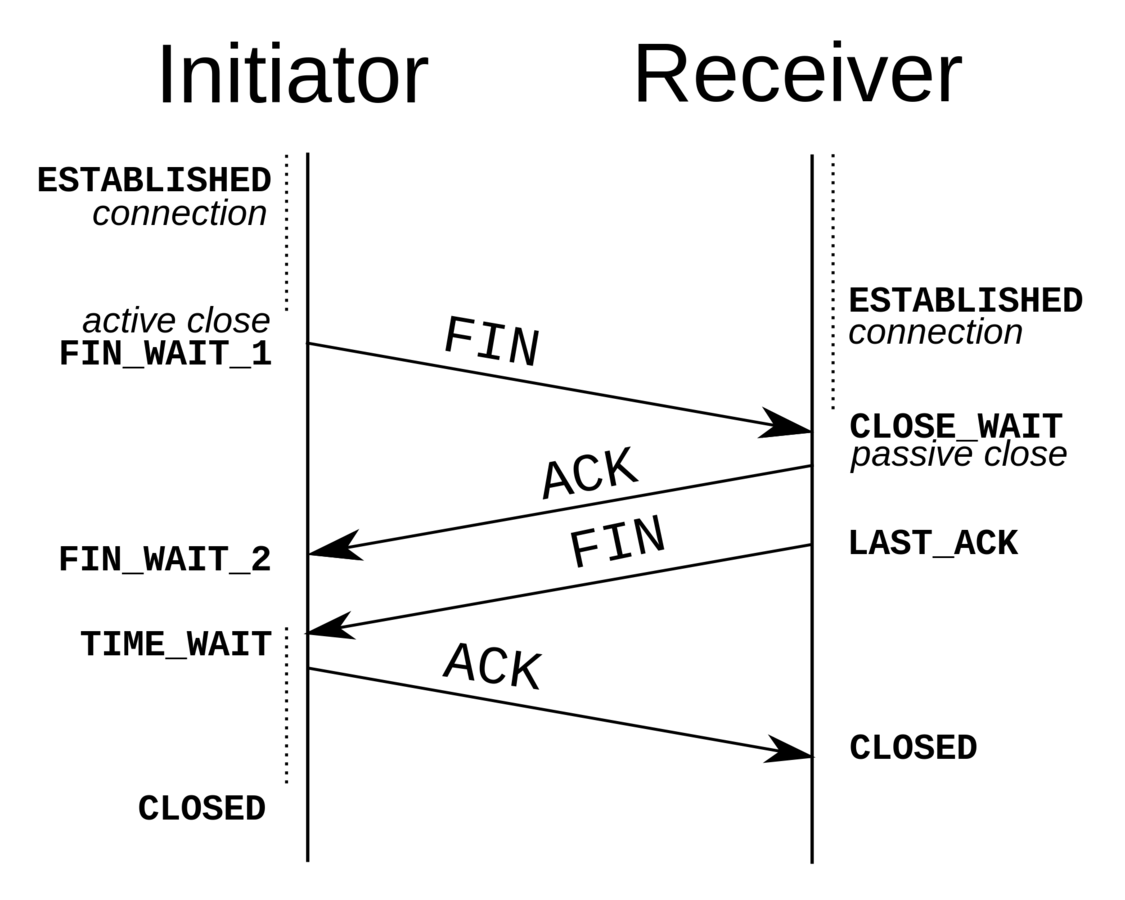
Connection Teardown
Out-of-path Vulnerability in TCP (CVE-2016-5696)
A global system variable

How to hack?
- 1) send spoofed packets to the connection under test (with a specific four-tuple)
- 2) create contention on the global challenge ACK rate limit, i.e., by creating a regular connection from the attacker to the server and intentionally triggering the maximum allowed challenge ACKs per second
- 3) count the actual number of challenge ACKs received on that connection.
If this number is less than the system limit, some challenge ACKs must have been sent over the connection under test, as responses to the spoofed packets.
SEQUENCE Number Inference
- 1) the attacker will now send 100 non-spoofed in-window RST packets to exhaust the challenge ACK count.
- Once again, based on how many challenge ACKs are received, the attacker can tell if the guessed sequence number in the spoofed RST, is in-window or out-of-window.

Ack Inference
- After an in-window sequence number of an active connection is identified, the attacker now will need to guess a valid ACK number
- In the first case where the spoofed ACK packet has an ACK number in challenge ACK window (but with an in-window sequence number), the server will reply with a challenge ACK

What if somebody spoofs Syn and send to me?
- Syn+Ack goes to spoofed ip
- Syn+Ack goes to correct ip
- Syn+Ack is dropped
- Hodor
TCP Attacks
- SYN/ACK flood
- SYN Cookies, somaxconn, tcp_syn_backlog
Network + Data Link Layer
- Routing table
route -n - CIDR subnet mask
mask XOR IP=net - Gateway 0.0.0.0 ARP
- Net 0.0.0.0
- rp_filter(way to prevent spoofed ip)
Network + Data Link Layer
Q From your system to Access point what part of the packet addresses the access point when you open google.com?
- Source IP Address
- Dest IP Address
- Dest Port
- Mac Address
NAT
- Port based nat
Activity - Setup Nat using iptables masquerade and ip_forwarding on one vm and change routing table on another vm to use the nat
http://www.revsys.com/writings/quicktips/nat.html - Tcp recycle
Can the NAT box see HTTPS Application Level Data?
- Yes
- No
Recap opening www.google.com
Advanced
- BGP
looking glass lg.he.net - Tunnels
- Anycast
- CDN
- Load Balancing
- Mitigation
Network Fundamentals
By Aneesh Dogra
Network Fundamentals
- 945



