Introduction to Python
Python is a widely used high-level programming language created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991.

Identifiers
A Python identifier is a name used to identify a variable, function, class, module or other objects.
An identifier starts with a letter (A - Z or a - z) or an underscore (_) followed by zero or more letters, underscores and digits (0 to 9).
var1 = 1
var2 = 10
Keywords
These are reserved words and you cannot use them as constant or variable or any other identifier names. All the Python keywords contain lowercase letters only.
Examples -
print, and , exec, for, if etc.
Hello World!
Lets use the print keyword to print "Hello World!"
print "Hello World!"
Declaring variables
Variables are nothing but reserved memory locations to store values. This means that when you create a variable you reserve some space in memory.
var1 = 1 var2 = 10
name = "John"
Standard Data Types
Python has five standard data types −
-
Numbers
-
String : identified using quotation marks
-
List : items separated by commas enclosed in brackets. Size can be changed.
-
Tuple : similar to list enclosed in parentheses. Size cannot be further updated.
-
Dictionary
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'}
Decision Making
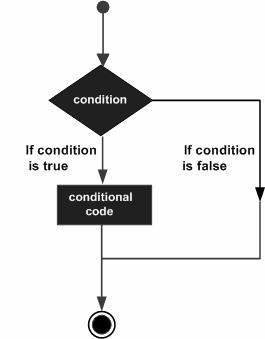
Odd or Even
Check if the number is odd or even
Loops
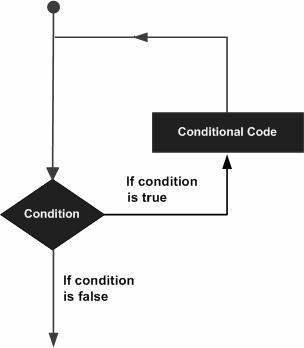
- While
- For
- Do while
Print number 1 - 100
Use loops to print numbers from 1 - 100
Fahrenheit to Celsius
Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius
C = (F- 32) / 1.8
Can you convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
Lists
In Python list can be written as a list of comma-separated values (items) between square brackets
list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000]; list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ]; print "list1[0]: ", list1[0] print "list2[1:5]: ", list2[1:5]
Tuples
A tuple is a sequence of immutable Python objects.
#!/usr/bin/python tup1 = ('physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000); tup2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ); print "tup1[0]: ", tup1[0] print "tup2[1:5]: ", tup2[1:5]
Dictionary
Each key is separated from its value by a colon (:), the items are separated by commas, and the whole thing is enclosed in curly braces.
#!/usr/bin/python dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'} print "dict['Name']: ", dict['Name'] print "dict['Age']: ", dict['Age']
Open a file
file = open('filename', 'r')
Largest number in a file
Find the largest number from a text file
Functions
A function is a block of organized, reusable code that is used to perform a single, related action.
def printme( str ):
"This prints a passed string into this function"
print str
return
def functionname( parameters ):
"function_docstring"
function_suite
return [expression]
Example -
Introduction to Python
By Aniketh Gireesh
Introduction to Python
- 1,150



