Modelling human/machine generated text detection
- Anna (she/her)
-
MA student
- BA on modeling probabilistic reduction
-
Involved in multiple projects across departments
- Speech to text for Kinyarwanda
- Modelling probabilistic speech reduction
- Morphological representations in embeddings
- Teaching assistant for CL courses
- FOSS enthusiast
- Outside of university: bouldering, gaming, crocheting
$whoami
SemEval
- The 18th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation
- NLP research challenges on issues in semantic analysis
-
SemEval 2024 categories:
- Semantic Relations
-
Discourse and Argumentation
-
LLM Capabilities
-
Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
- Focus on multilingual and multimodal approaches
SemEval taSk 8
- Classification tasks between human-written and machine-generated texts
-
Tracks:
- Subtask A: human vs. machine classification
- Subtask B: human vs. specific machine classification
- Subtask C: boundary detection in mixed texts
- Monolingual (English) or multilingual
Subtask A: Binary classification for monolingual human- and machine-generated texts¹
¹Co-authors: Vittorio Ciccarelli, Cornelia Genz, Nele Mastracchio, Hanxin Xia and Wiebke Petersen
M4 dataset
-
Multi-Generator, Multi-Domain, and Multi-Lingual Black-Box Machine-Generated Text Detection (Wang et al. 2023)
- Five machines
- Six domains
- Seven languages: Chinese, Russian, Urdu, Indonesian, Arabic, English
M4 dataset
Data splits:
| labels | train | dev | test |
|---|---|---|---|
| machine | 56,406 (53%) | 2,500 (50%) | 180,00 (53%) |
| human | 63,351 (47%) | 2,500 (50%) | 16,272 (47%) |
| total | 119,757 (75%) | 5,000 (3%) | 34,272 (22%) |
M4 dataset
| Wikipedia | Wikihow | ArXiv | PeerRead | Outfox | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| train | 25,530 (21%) | 27,499 (23%) | 27,500 (23%) | 27,497 (23%) | 11,731 (10%) | - |
| dev | 1,000 (20%) | 1,000 (20%) | 1,000 (20%) | 1,000 (20%) | 1,000 (20%) | - |
| test | - | - | - | - | - | 34,272 (100%) |
| total | 26,530 | 28,499 | 28.500 | 28,497 | 12,731 | 34,272 |
Domains:
M4 dataset
LLMs:
- Davinci-text-003/GPT 3.5 (OpenAI 2023)
- chatGPT (OpenAI 2023)
- GPT4 (OpenAI 2023)
- Cohere
- Dolly-v2 (Conover et al. 2023)
- BLOOMz 176B(Muenninghoff et al. 2022)
M4 dataset
LLM prompts:
- 2-8 different prompts for each LLM
- PeerRead example:
- "Please write a peer review for the paper + title" (Wang et al. 2023:A.3)
- "Write a peer review by first describing what problem or question this paper addresses, then strengths and weaknesses, for the paper + title, its main content is as follows: + abstract" (Wang et al. 2023:A.3)
M4 dataset
LLM splits in data:
| train | dev | test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| chatGPT | 14,339 (12%) | - | 3,000 (0.09%) |
| Davinci | 14,343 (12%) | - | 3,000 (0.09%) |
| Dolly-v2 | 14,046 (12%) | - | 3,000 (0.09%) |
| Cohere | 13,678 (11%) | - | 3,000 (0.09%) |
| GPT4 | - | - | 3,000 (0.09%) |
| BLOOMz | - | 2,500 (100%) | 3,000 (0.09%) |
M4 dataset
Machine-generated text sample:
{"text":"Building a Railroad Tie Retaining Wall can be a daunting task, but with the proper tools and techniques, it can be completed with ease. If you want to create a strong and durable retaining wall that is both functional and attractive, follow the steps below.\n\nBulldoze or Dig a Section of the Dirt from the Hill Out to Where You Want to Build a Railroad Tie Retaining Wall\n\nThe first step in building a Railroad Tie Retaining Wall is to determine where you want to build it. Once you have located the perfect spot, you will need to bulldoze or dig a section of the dirt from the hill out to this area. [...] But, by following these steps, you can create a strong, durable, and attractive Retaining Wall that will serve you for years to come.","label":1,"model":"chatGPT","source":"wikihow","id":7}M4 dataset
{"text":" It is possible to become a VFX artist without a college degree, but the path is often easier with one. VFX artists usually major in fine arts, computer graphics, or animation. Choose a college with a reputation for strength in these areas and a reputation for good job placement for graduates. The availability of internships is another factor to consider.Out of the jobs advertised for VFX artists, a majority at any given time specify a bachelor\u2019s degree as a minimum requirement for applicants. [...] To build your specialization, start choosing jobs with that emphasis and attend additional training seminars.For example, some VFX specialists focus on human character\u2019s faces, animal figures, or city backgrounds.\n\n","label":0,"model":"human","source":"wikihow","id":56408}Human-written text sample:
Submission idea
- Establish baseline using traditional ML classifers like logistic regression and random forrest
- RoBERTa + MLP classifiers as an ensemble model
- Correctional MLP classifiers for RoBERTa output
- Focus on label features, not domains
- Compute features of texts based on previous literature
- Feature selection by correlation with the labels
Architecture
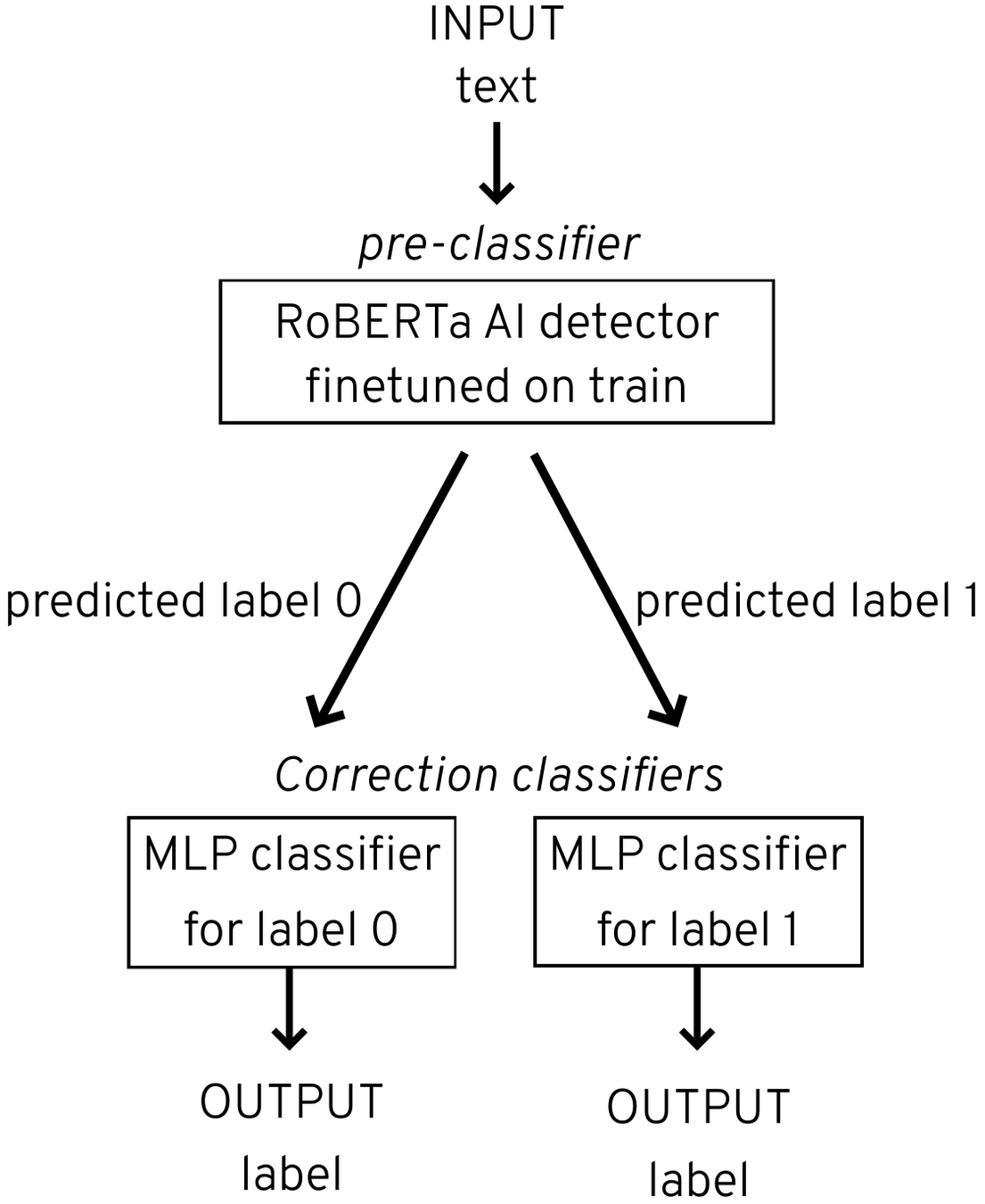
- RoBERTa AI detector (Soleiman et al. 2019)
- 1.5B-parameter GPT-2 model
- Fine-tuned with 10% of training data, no features
- 0.89 accuracy on dev
- Multi-layer perceptron classifier
- Hidden layer size = 100, ReLu activation
- Trained on train and dev dataset, with features
features
Count-based features:
- Mean sentence length
- Mean word length
- Ratio of punctuation to words
- Ratio of word types to tokens
- Ratio of vowels to words
- Number of hapax legomena
- Number of negation words
- Type-to-token ratio (TTR)
- Number of unique words
features
features
features
Frequency features:
- Mean log. frequency of content words
- Ratio of frequent words to content words
- Ratio of hapax legomena to content words
- Ratio of content words to top 10% of high frequency words/fantasy words in Wikipedia lists
FEATURES
Syntactic features:
- Ratio of words to
- Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, adpositions, conjunctions, numerals, pronouns, determiners
- Ratio of adjectives to nouns
- Ratio of verbs to nouns
- Maximum dependency distance in a syntactic tree (text)
- Maximum dependency distance in a syntactic tree (sentence)
- Number of passive constructions
FEATURES
Word difficulty features:
- Ratio of content words to
- A1-level words
- A2-level words
- B1-level words
- B2-level words
- C1-level words
- C2-level words
- Both on the basis of stemmed and lemmatized words
FEATURES
Stylistic features:
- Ratio of words with negative opinion (Liu et al. 2005)
- Readability by Flesch-ease reading score¹
Sentiment features:
- Scores for "neutral", "anger", "disgust", "fear", "joy", "sadness", "surprise" by DistilRoBERTa-base (Hartmann et al. 2022)
- Score for "positive" or "negative" by Huggingface sentiment analysis pipeline
- Score for "formal" and "informal" by a formality ranker (Babkov et al. 2023)
- Score for "toxic" and "non-toxic" by finetuned-RoBERTa model (s-nlp 2022)
FEATURES
RoBERTa-based features:
- Logits of RoBERTa for each text
- Last hidden states of RoBERTa for each text, reduced by
- Principal component analysis (PCA)
- Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP), distance measures: cosine and jaccard
computational cost
- Feature extraction:
- Ran locally with 24GB RAM, no GPU
- ~6hours for 'expensive' spacy-based features for all datasets
- ~4mins for all other features for all datasets
- RoBERTa fine-tuning:
- Ran on Google Colab with T4 GPU
- ~45 minutes
results
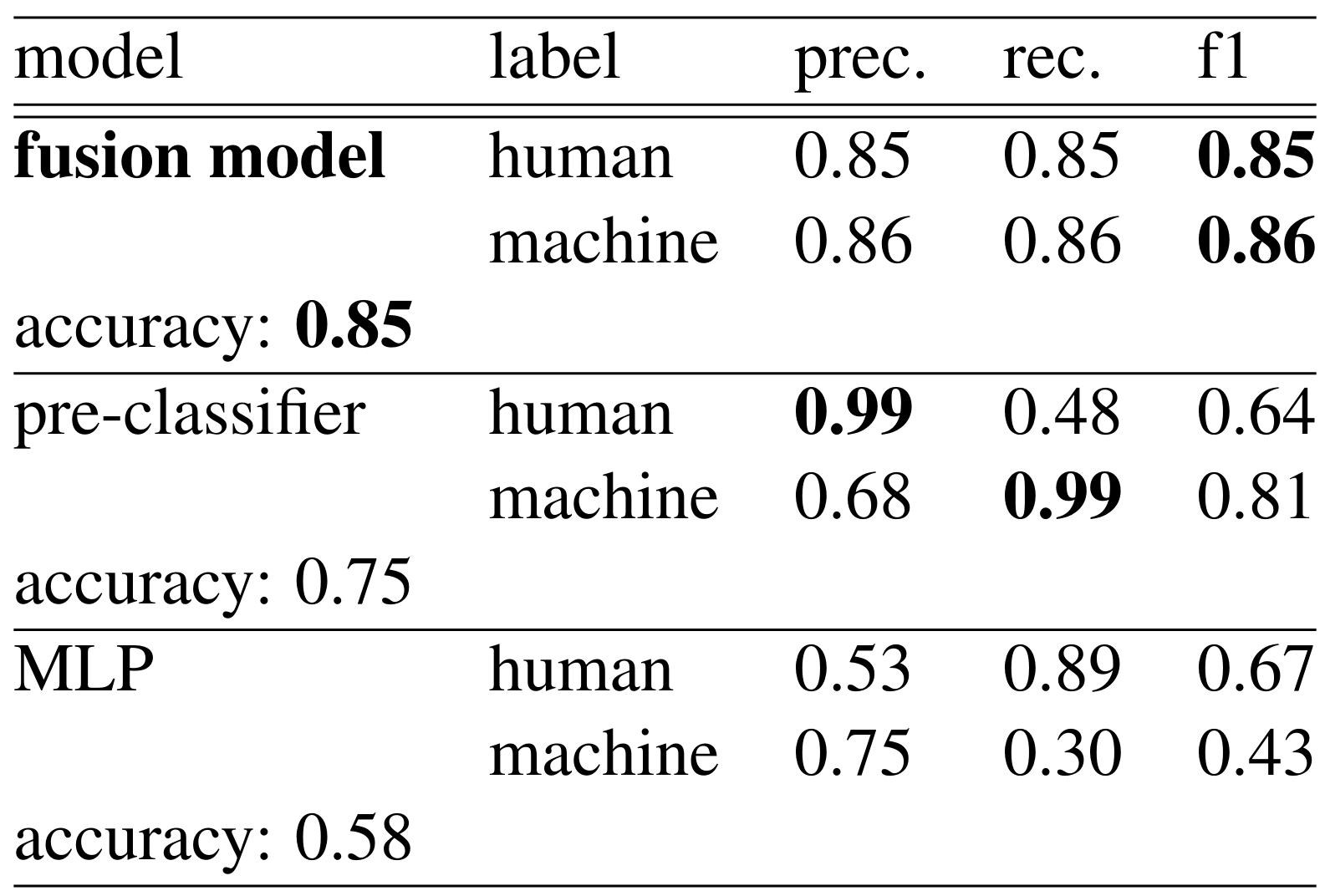
- Placement: 32nd of 141 with an accuracy of 0.85
- RoBERTa-base baseline accuracy: 0.74
Error Analysis
Classification errors by model:
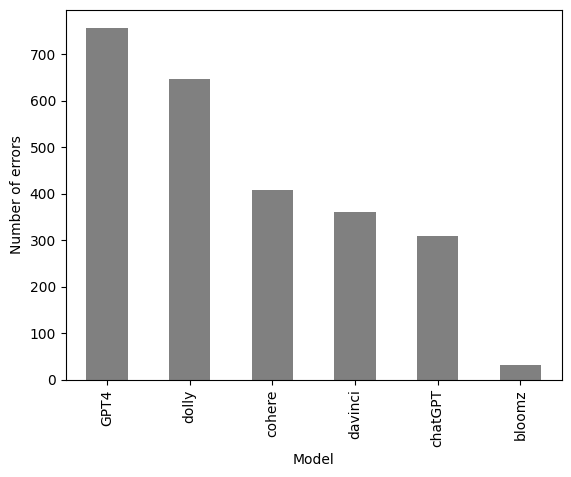
Error Analysis
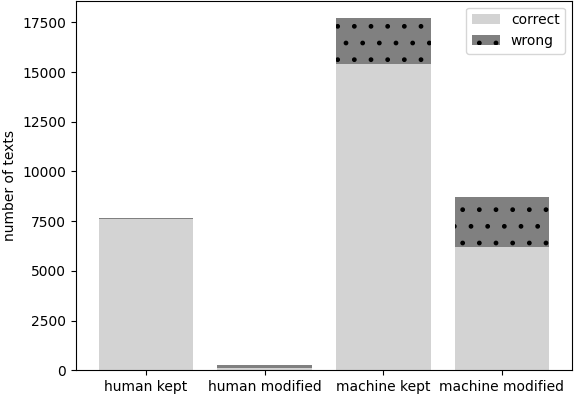
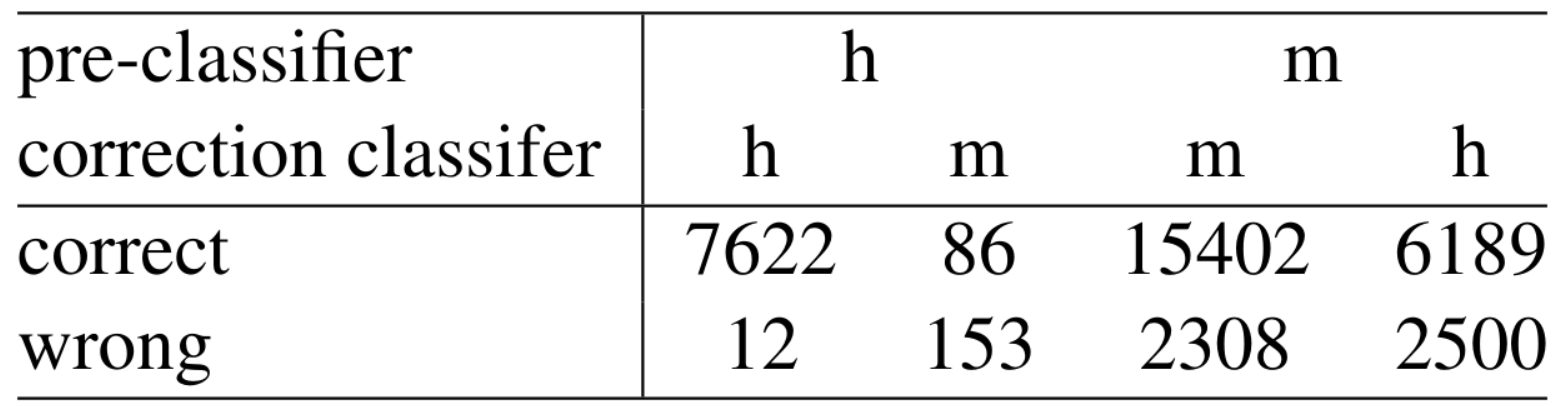
Correction errors:
Conclusion
- Feature-informed MLP classifier helped adjust machine label bias in RoBERTa model
-
MLP classifier was better at capturing human-like texts
- Human > machine correction 64% wrong
- Machine > human correction 28% wrong
Ensemble model worked semi-well
Conclusion
- Combat bias
- Fine-tune the RoBERTa AI detector with more data
- Analyze correction classifier for performance
- Particularly wrong human > machine corrections
-
Improve performance
- Analyze distribution of features for all LLMs
- Add more sophisticated features such as argument structure, contextual predictability
- Different correctional classifier?
Future directions for this architecture:
References
assets

results
RoBERTa-base OpenAI detector on test (acc. 0.64):

Fine-tuned RoBERTa classifier used in our submission on dev:

gettoknow
By ansost22
gettoknow
- 40



