What will we be talking today?
- Classical Computers: What they cannot do?
- What are QCs? Why are they disrupting our current views on computation?
- Quantum Supremacy and what it beholds
- Qubits and their properties
- Demo
Classical Computers: What they cannot do?
- Exponential Scaling
- Optimization problems
- Chemical Compound Representation/Simulation
- Security Encryptions

- All of these problems have exponential scaling in common
- This is a major hurdle with our classical computers and supercomputers too
Church-Turing Thesis
- Accepted rule: It states that if a problem can be solved by a Turing machine, it can also be solved by a computational device.
- Extension on the Thesis: It states that a Turing machine (like a classical computer) can always efficiently simulate any computational model, even to simulate an inherently quantum computation.

Quantum Supremacy and what it beholds
- Quantum computers could efficiently solve a computation that a classical computer can only solve inefficiently, is known as Quantum Supremacy
- Google Quantum Supremacy- What did they do?-News article with technical terms
- Later-after qubit-Theoretically, if you reach a certain number of efficient qubits, usually said to 56, you can thereby simulate problems that a Classical computers nowhere can
Google Quantum
- Superconducting Bits
- Electrical Circuits to generate qubits
- Sycamore The 54-qubit QC by Google
- Compared to IBM, they actively release blogs and had a chance to meet one of them
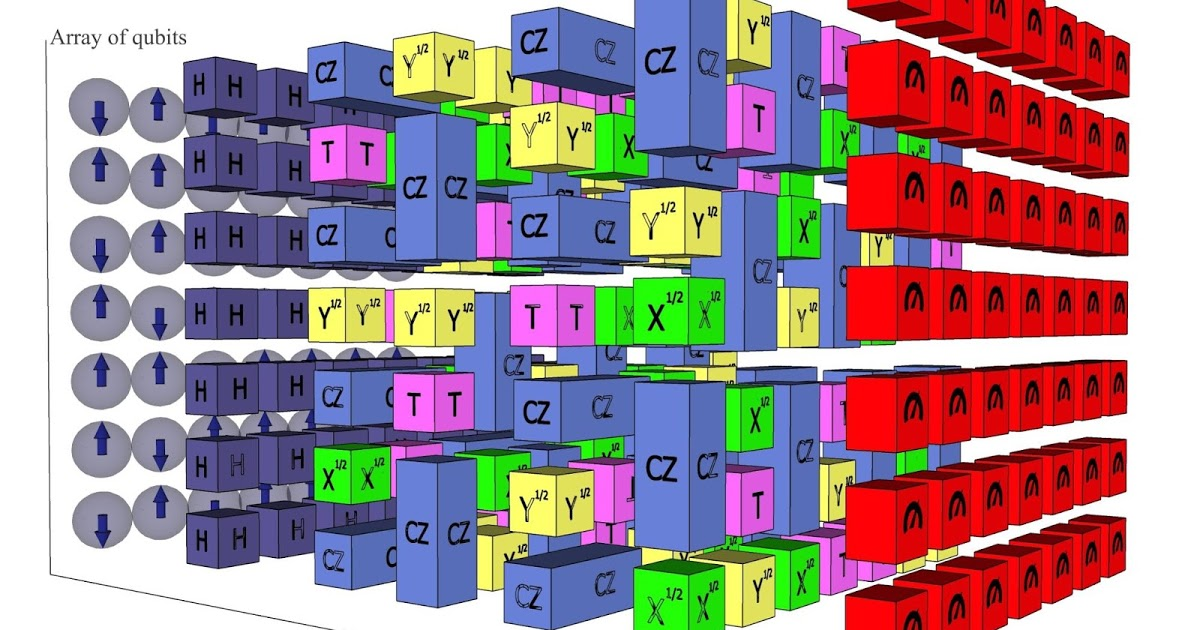
Qubits and their properties
- Qubits or quantum bits are the fundamental building block for quantum information processes.
- Whereas conventional computers store and process data as a series of '1's and '0's. Quantum Computers can use Qubits.
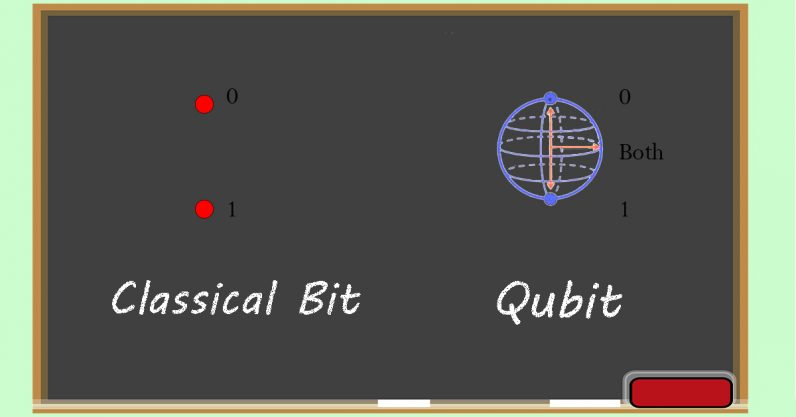
- Property of Superposition
- Property of Entaglement
- Quantum Supremacy slide
Property of Superposition
- At any given time, the qubit can be in a superposition of both 0 and 1
- Hence you are expanding your information space and this becomes more complex
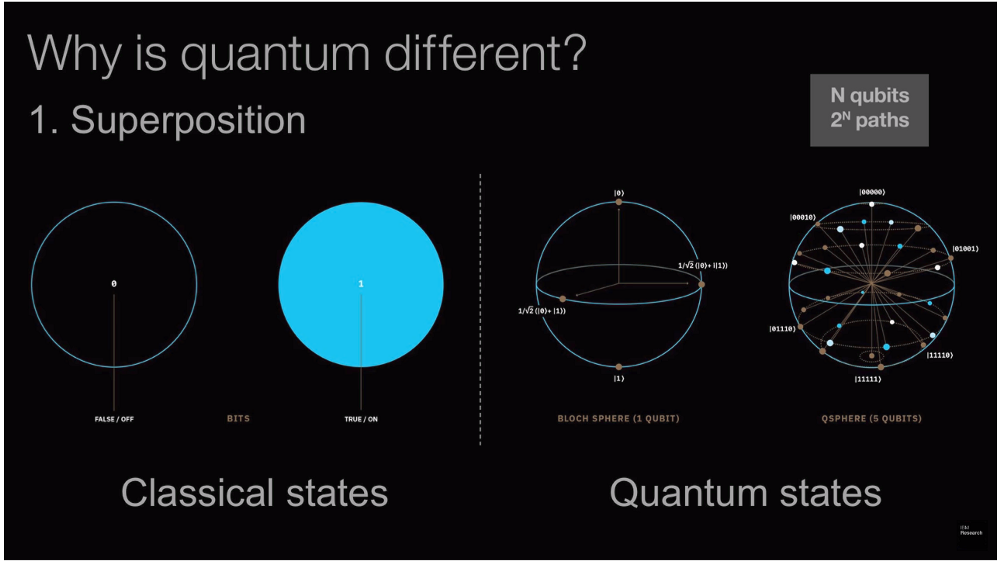
Property of Entaglement
- Quantum State of each particle cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance.
- So you can judge an adjacent's qubit's property by this qubit
Why do QCs have different rules to play by?
- Limitations of QCs: Suprise Quantum Computers aren't perfect.
- Quantum Error Correction
- Qubit DeCoherence


Demo
QC
By archana iyer
QC
- 814



