字元 & 字串
Arvin Liu @ Sprout
什麼是字元?
就是一個字嘛! (character)
怎麼用數字表達文字?
電腦只有0跟1啊!
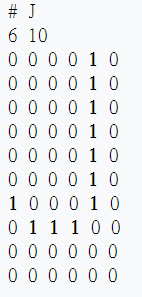
文字 -> 數字
a
0
b
1
c
2
.
.
.
z
25
a p p l e
0 15 15 11 4
那 !@#$ 這些?
ASCII Code
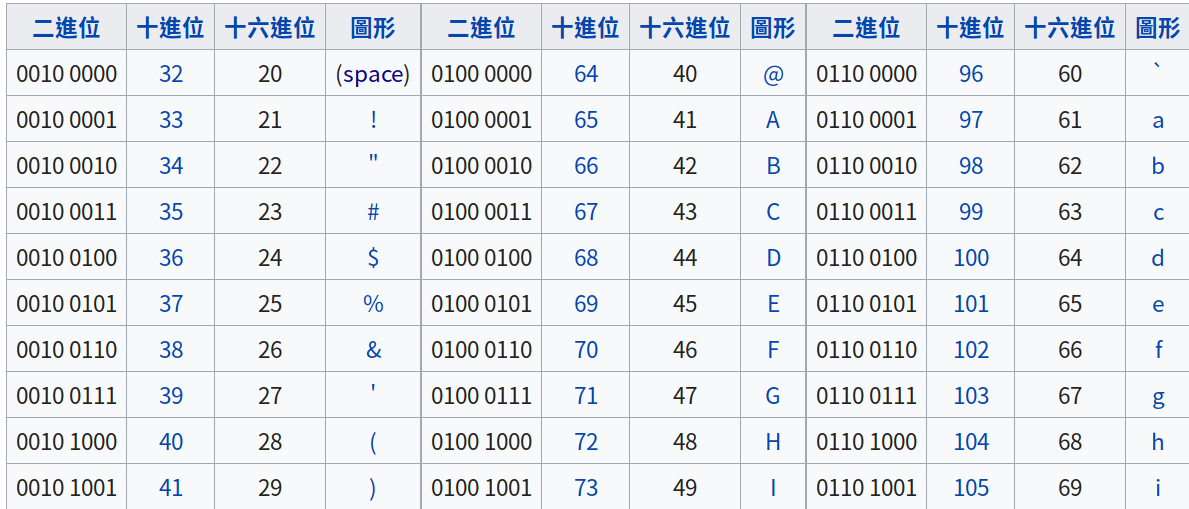
zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASCII
ASCII Code
a
97
b
98
c
99
.
.
.
z
122
A
65
B
66
C
67
.
.
.
Z
90
ASCII Code - Special Char
換行符號(\n)
10
水平定位符號(Tab)(\t)
9
怎麼用cout輸出字元?
告訴cout型態就好!
char c1 = 97;
std::cout << c1 << std::endl;a你真的記得起ASCII?
int c1 = 'a';
std::cout << c1 << std::endl;
97char c1 = 'a';
std::cout << c1 << std::endl;
跳脫字元
char c1 = '
';
std::cout << c1 << std::endl;
怎麼輸出換行?
No no no
char c1 = 10;
std::cout << c1 << std::endl;
跳脫字元
因為有些字真的很難表示,
所以我們用一些特殊的符號來表示。
C/C++/Py... lang 是以 \ 開頭。
(escape character)
跳脫字元
很難表示的字有很多嘛?
' 怎麼打?
(escape character)
'''*會被當字元
'a'跳脫字元
| 常見特殊字元 | 表示方法 |
|---|---|
| 換行 | '\n' |
| 水平定位 | '\t' |
| 字串結尾 | '\0' |
| ' | '\'' |
| \ | '\\' |
| " | '\"' |
| 回車 |
'\r' |
| 倒退 | '\b' |
喵!

char vs int
char 本身就是個數字。
- +-*/%^ 等常用數字運算符號都可以。
- 範圍是 -128 ~ 127 (因為char是1個byte or 8個bit)
char 本身就是個數字。
- 'b' == 'a' + 1
- 'A' == 'a' ^ ' '
- 'a' == 'A' ^ ' '
- 3 == 'd' - 'a'
- 'a' == ('z'-'a' + 'b'-'a') % 26 + 'a'
char 的小提醒
- 範圍很小,不要用來紀錄一些數值的東西。
- 只能是一個字。
- 那要輸出一串字呢?
Practice!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char c;
while( cin >> c ){
// 做你的事情
}
}
char 的 cin
Problem Description
a
d
b
e
c
f
x
a
y
b
z
c
Solution
a
100
b
101
97
98
d
e
c
102
99
f
x
123
y
124
120
121
97
98
z
125
122
99
a
b
c
w
25
119
z
Solution - A
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char c;
while( cin >> c ){
char v = c + 3;
if ( v > 'z' )
v -= 26;
cout << v;
}
cout << '\n';
}
Solution - B
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char c;
while( cin >> c ){
char v = ((c - 'a') + 3) % 26 + 'a';
cout << v;
}
cout << '\n';
}
文字 -> 數字 (ASCII)
a
97
b
98
c
99
.
.
.
z
97+25
a p p l e
97 112 112 108 101
字串是一種數列。
--> 陣列 !
When char meets array...
char S[] = {'a','p','p','l','e','\0'};
std::cout << S << std::endl;
apple陣列是不是很強啊?
陣列是不是很強啊?
如果是字元陣列,
cout都會一次輸出,
直到遇到0 (or '\0') 為止。
字元陣列的表示方法 - ""
char S[] = {'a','p','p','l','e',0};
std::cout << S << std::endl;
char S[] = "apple";
std::cout << S << std::endl;
==
字元陣列的表示方法
char S[] = {'a','\n','p','\t','e',0};
std::cout << S << std::endl;
char S[] = "a\np\te";
std::cout << S << std::endl;
==
字元陣列的Input
char S[100];
std::cin >> S;跟cin>>數字一樣,
只會吃到空白字元為止。
空白字元三巨頭 : ' ', '\t', '\n'
Example
char S[100];
while(cin >> S)
cout << "I get: " << S << endl;
Input:
abc def
ghiOutput:
I get: abc
I get: def
I get: ghi
str func
要#include <cstring>喔!
strlen(char S[])
回傳這個字串的長度。
Example
char S[100];
cin >> S;
cout << strlen(S);Input:
abcdefOutput:
6strcmp(char A[],char B[])
回傳 0 表示AB一樣。
Example
char S[100];
cin >> S;
cout << (strcmp(S,"QAQ") == 0);Input:
abcdef
-------
QAQOutput:
1
----
0strcpy(char A[],char B[])
把B複製到A。
Example
char A[100], B[100];
cin >> B;
strcpy(A, B);
cout << A;Input:
abcdefOutput:
abcdefchar array tips
(Optional)
char A[8] = {'a','b'};
A = {'c' , 'd'};[] Assignment problem
char B[8] = "ab";
B = "cd"; if(A == B){}你不會寫下面這樣:
所以你也不該寫下面這樣:
char A[8]="12345678";
char B[8]="Peipei";
std::cout << A << std::endl;
Length + 1 problem
猜猜看結果是什麼?
(A) 12345678
(B) 12345678Peipei
我也不知道。
如果你們用這份code,
需要-fpermissive才可以通過編譯。
B的理由?
char A[8]="12345678";char B[8]="Peipei";| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | '\0' |
|---|
A
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|
A
B
| P | e | i | P | e | i | '\0' |
|---|
Review
<cstring>
- strlen(S) : 回傳S的長度。(由第一個\0來決定長度)。
- strcmp(A,B) : 回傳0表示A和B一樣。
- strcpy(A, B) : 把B字串複製到A身上。
char
- 所有字都是數字,印出數字或文字差別在於int還是char。
- 跳脫符號 -> 一有打不出來的字,可以查跳脫符號表。
string (char array)
- 宣告: 用char陣列。可以用"..."代替{'.', '.', '.'}。
- 除了宣告以外,不能直接用a = "..." 或 a == b等等。
- 結尾是用 '\0' 來表示的,所以空間會比字串多一個字。
> 宣告要多一點空間。
Practice!
會移動的字串 - Marquee (Optional)
怎麼做跑馬燈呢?
ㄚ不是輸出就不能改了?
| 常見特殊字元 | 表示方法 |
|---|---|
| 換行 | '\n' |
| 水平定位 | '\t' |
| 字串結尾 | '\0' |
| ' | '\'' |
| \ | '\\' |
| " | '\"' |
| 回車 |
'\r' |
| 倒退 | '\b' |
跳脫字元
回車?倒退?
char S[] = "appleeee\rbanana";
std::cout << S << std::endl;
// bananaeechar S[] = "0123\baaaa";
std::cout << S << std::endl;
// 012aaaaHow 2 Sleep?
#include <windows.h>
int main(){
Sleep(3000);
// 睡3000ms。
}windows
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
usleep(3000);
// 睡3000ms。
}非windows
How 2 Animate?
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char A[] = "ABCD ";
char B[] = " ABCD ";
cout << A ;
Sleep(3000);
cout << '\r';
cout << B ;
}Solution
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char S[] = "OAO - QAQ ";
int slen = strlen(S), starting = 0;
while(true){
cout << '\r';
for(int i=starting, j=0 ; j<slen ; i++,j++ ){
cout << S[(i)%slen];
}
starting ++;
Sleep(100);
}
}字元 & 字串
By Arvin Liu
字元 & 字串
Teaching slide - char & char array
- 2,317



