Deep Learning the Bayesian way :
Moving Towards safer AI


ayush0016

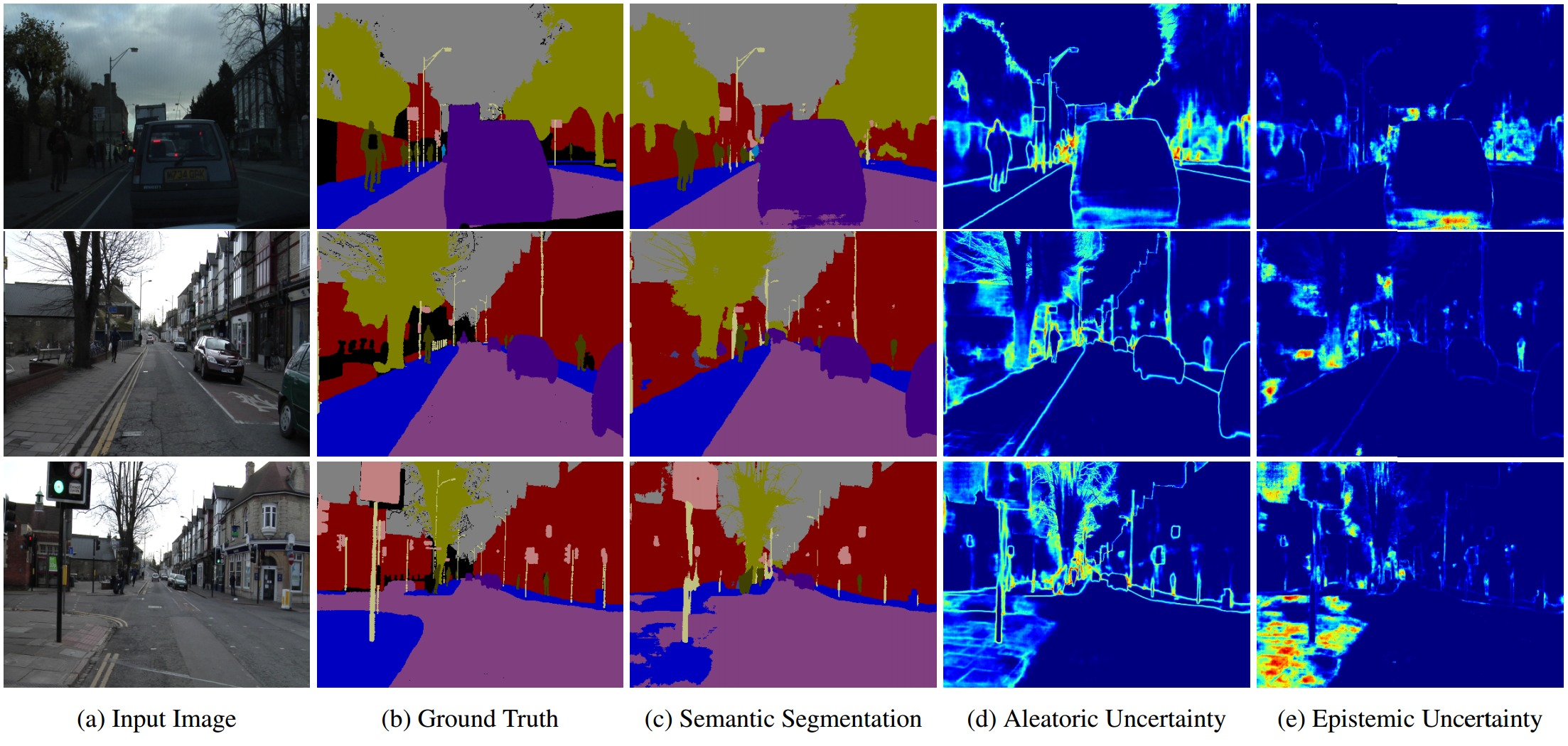
Uncertainty
What and

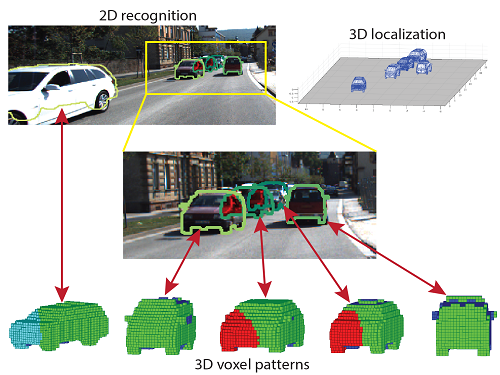
Aleatoric Uncertainty
A measure of what can not be understood from data.
Occlusions, lack of visual features, over/under exposed areas (glare & shading).

what and why ?
Epistemic Uncertainty
Measure of what model doesn’t know due to lack of training data.
what and
Bayesian Deep Learning
A field at the intersection between Deep learning and Bayesian probability theory
Deep Neural Networks
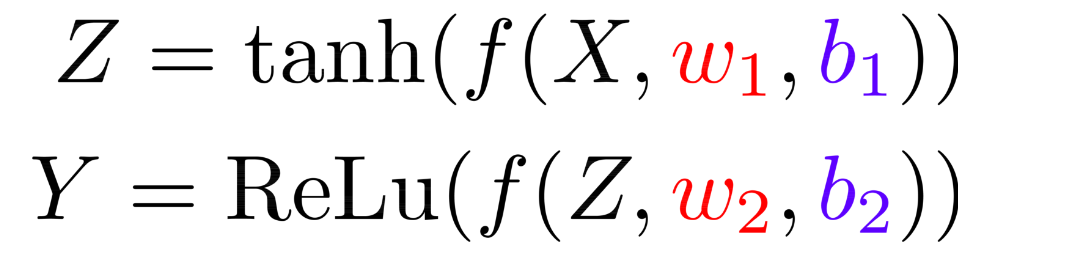
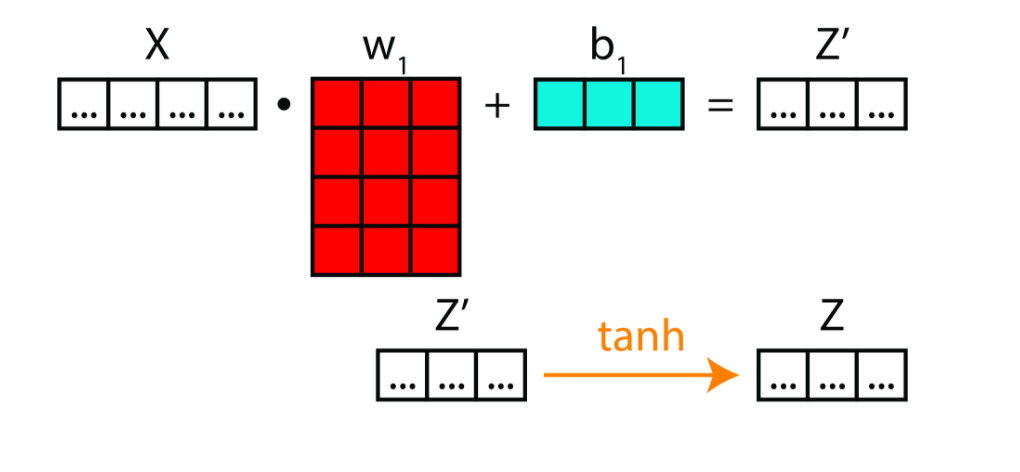
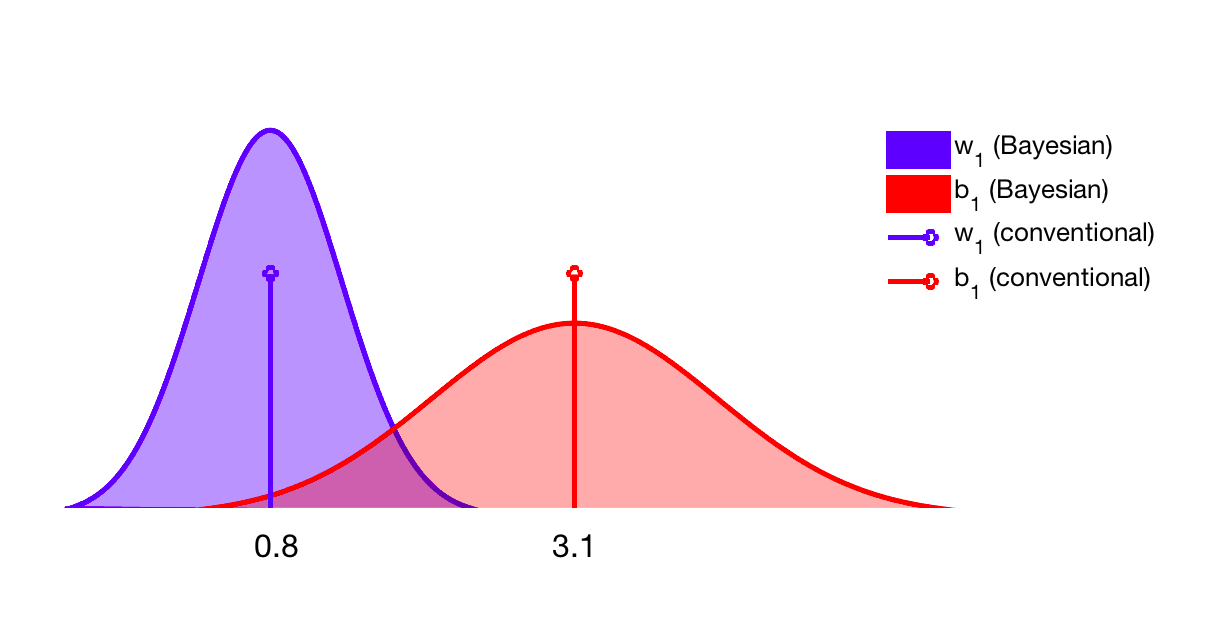
Bayesian Neural Network
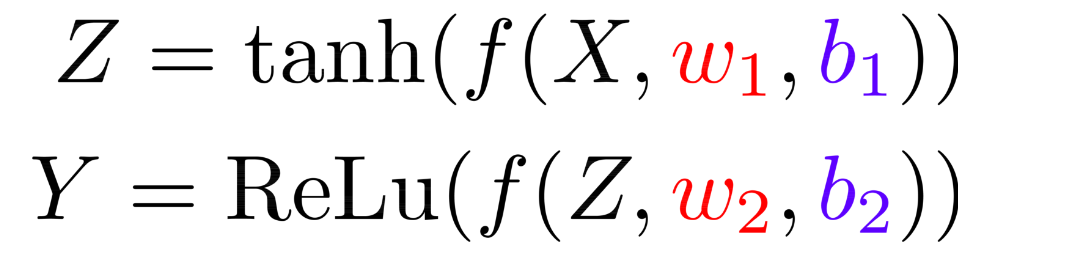
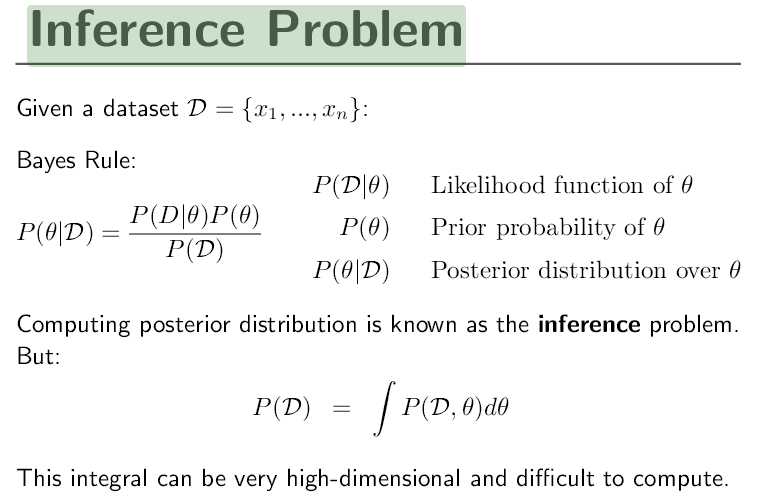
Bayes Theorem

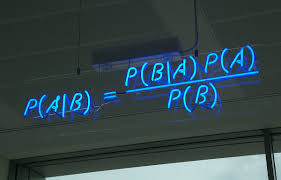
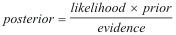
Approximation Techniques
- Variational Inference
- MC Dropout
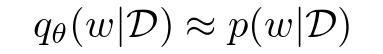
Variational Inference
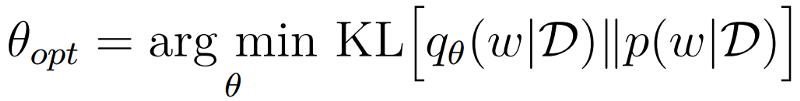
Variational inference is a Bayesian approach to estimate posteriors using an arbitrary distribution

Monte Carlo Dropout
Bayesian interpretation of the regularization technique known as “dropout”
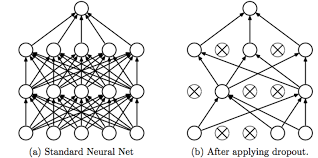
Dropout
What and
Regularization technique to prevent "overfitting"
Training
Testing Phase : Use all activations, but reduce them by a factor p (to account for the missing activations during training).
MC Dropout Key Idea
Dropout could be used to perform variational inference where the variational distribution is from a Bernoulli distribution (where the states are “on” and “off”).
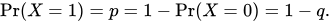
Bernoulli distribution
class LeNet_dropout(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet_dropout, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(F.dropout(self.conv1(x), training=True), 2))
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(F.dropout(self.conv2(x), training=True), 2))
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, training=True)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
def train(model, opt, epoch):
model.train()
lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 10))
opt.param_groups[0]['lr'] = lr
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
if args.cuda:
data, target = data.cuda(), target.cuda()
data, target = Variable(data), Variable(target)
opt.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(F.log_softmax(output), target)
loss.backward()
opt.step()
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)] lr: {}\tLoss: {:.6f}'
.format(epoch, batch_idx * len(data),
len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader),
lr, loss.data[0]))
def mcdropout_test(model):
model.train()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
T = 100
for data, target in test_loader:
if args.cuda:
data, target = data.cuda(), target.cuda()
data, target = Variable(data, volatile=True), Variable(target)
output_list = []
for i in xrange(T):
output_list.append(torch.unsqueeze(model(data), 0))
output_mean = torch.cat(output_list, 0).mean(0)
test_loss += F.nll_loss(F.log_softmax(output_mean), target, size_average=False).data[0] # sum up batch loss
pred = output_mean.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1] # get the index of the max log-probability
correct += pred.eq(target.data.view_as(pred)).cpu().sum()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nMC Dropout Test set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.2f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))

Thank You !
Questions ?
https://github.com/ayush1997/bdl
https://slides.com/ayush1997/ml-3/




ayush0016
ayushsingh97
ayush1997
ayush1997
ayushkumar97
Bayesian Deep Learning
By Ayush Singh
Bayesian Deep Learning
- 745



