Tell Firebase
to Go Fly A Kite:
Leveraging FaunaDB + Serverless Functions to add persistence to your React app on Netlify & Vercel.
Brett Haymaker, UI Engineer, Consultant & Instructor
I am not an expert in serverless architectures
🙅♂️
The point/question:
How can I very quickly add persistence services to my front end application?
firebase
vs
faunaDB
😒
The honeypot
🍯
Career value of faunaDB:
-
first-class GraphQL support
-
Netlify/Vercel integration
-
POE for Serverless functions
First Steps:
-
Sign up for Netlify Account
- authorize GitHub integration
-
Sign up / register FaunaDB account
- Can use Netlify OAuth
Within our React App, we need to install the following:
-
faunadb (dependency)
-
netlify-cli (dev-dependency)
npx netlify init
netlify.toml
[build]
functions = "functions"
# This will be run within Netlify to build the application
command = "npm run build"
# This is the directory that is published to netlify's CDN
publish = "build"
[dev]
# Local dev command. A.k.a npm start
# used by netlify-dev
command = "react-scripts start"
Text
Text
"start": "netlify dev"
A number of ways to create a FaunaDB instance exist:
- FaunaDB console (online dashboard)
- fauna-shell cli
- using the netlify fauna addon integration (we are going to opt to use this path)
npx netlify addons:create fauna npx netlify addons:auth fauna
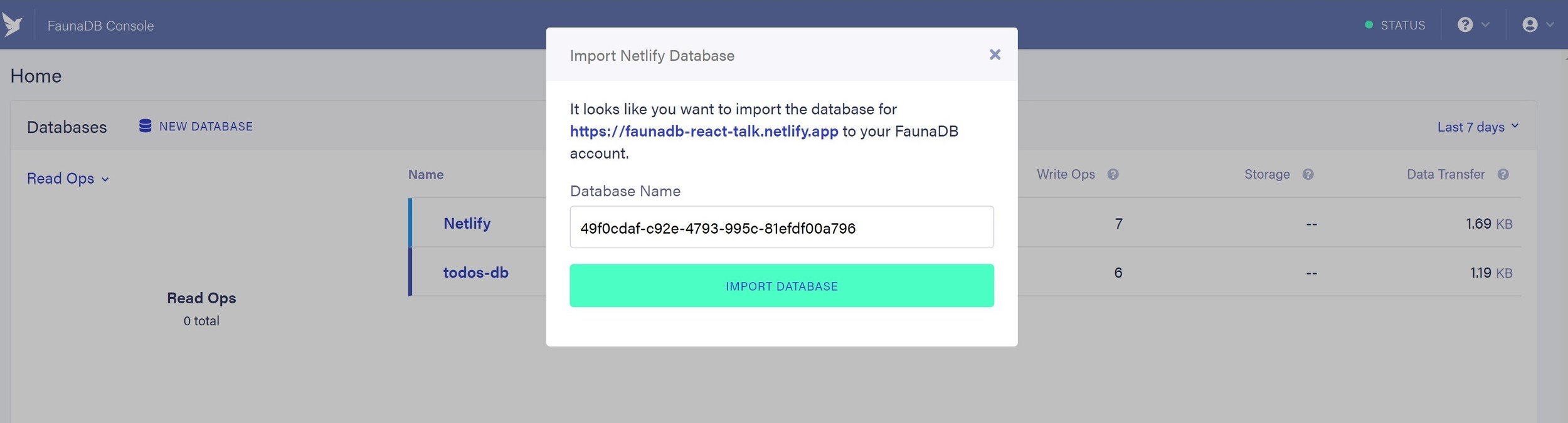
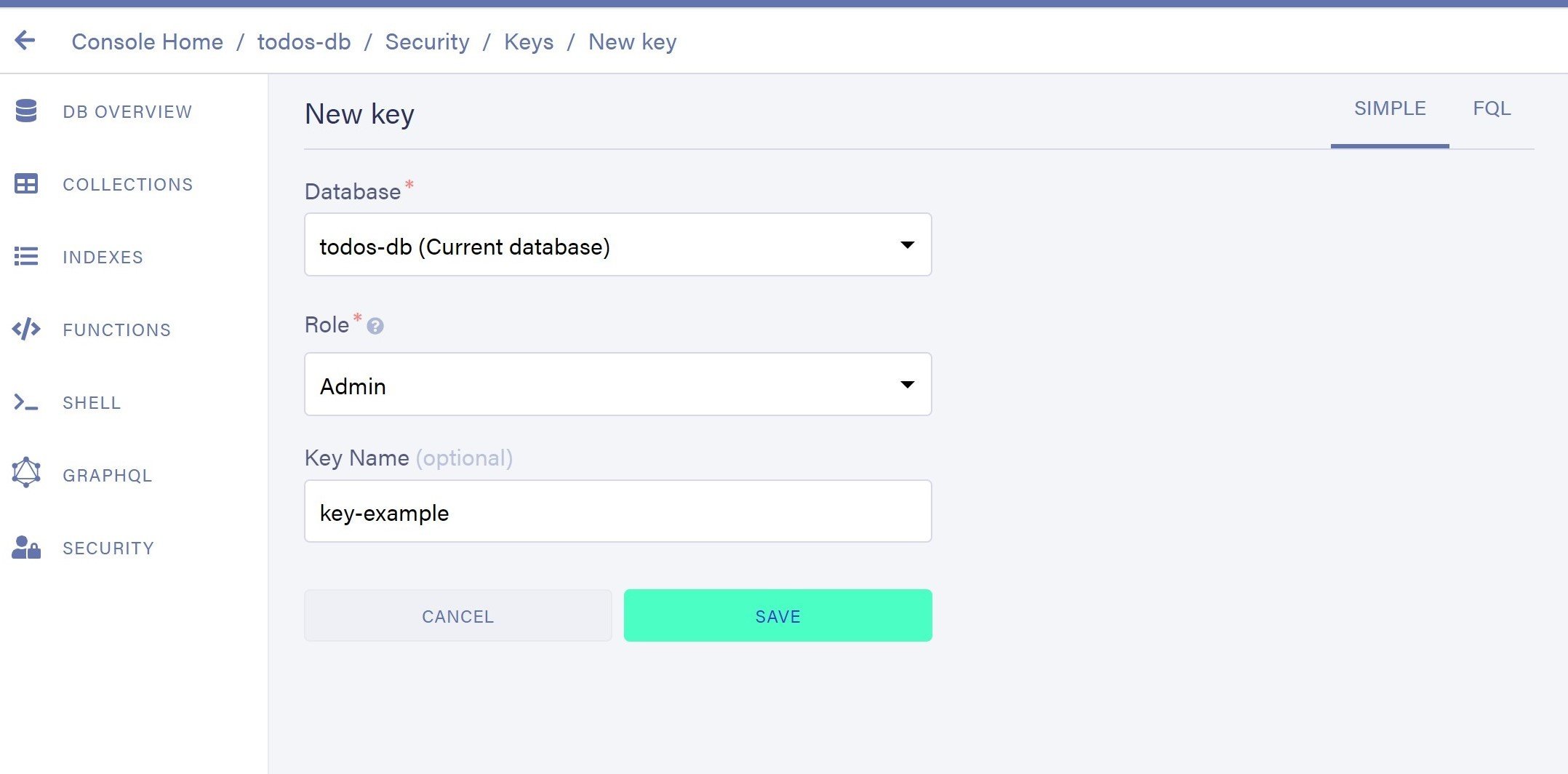
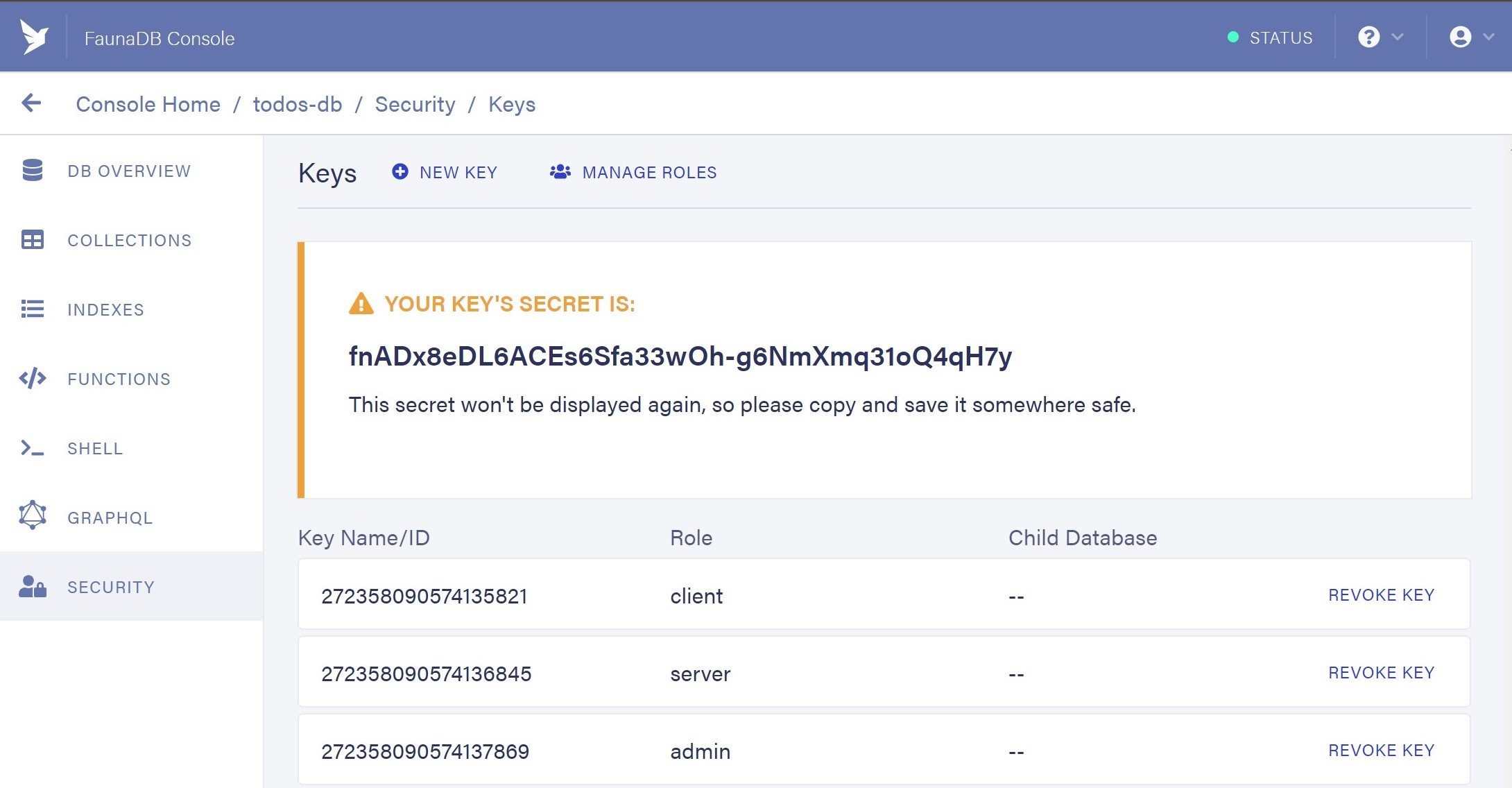
/* bootstrap database in your FaunaDB account */
const faunadb = require('faunadb');
const chalk = require('chalk');
const insideNetlify = insideNetlifyBuildContext();
const q = faunadb.query;
console.log(chalk.cyan('Creating your FaunaDB Database...\n'));
// 1. Check for required enviroment variables
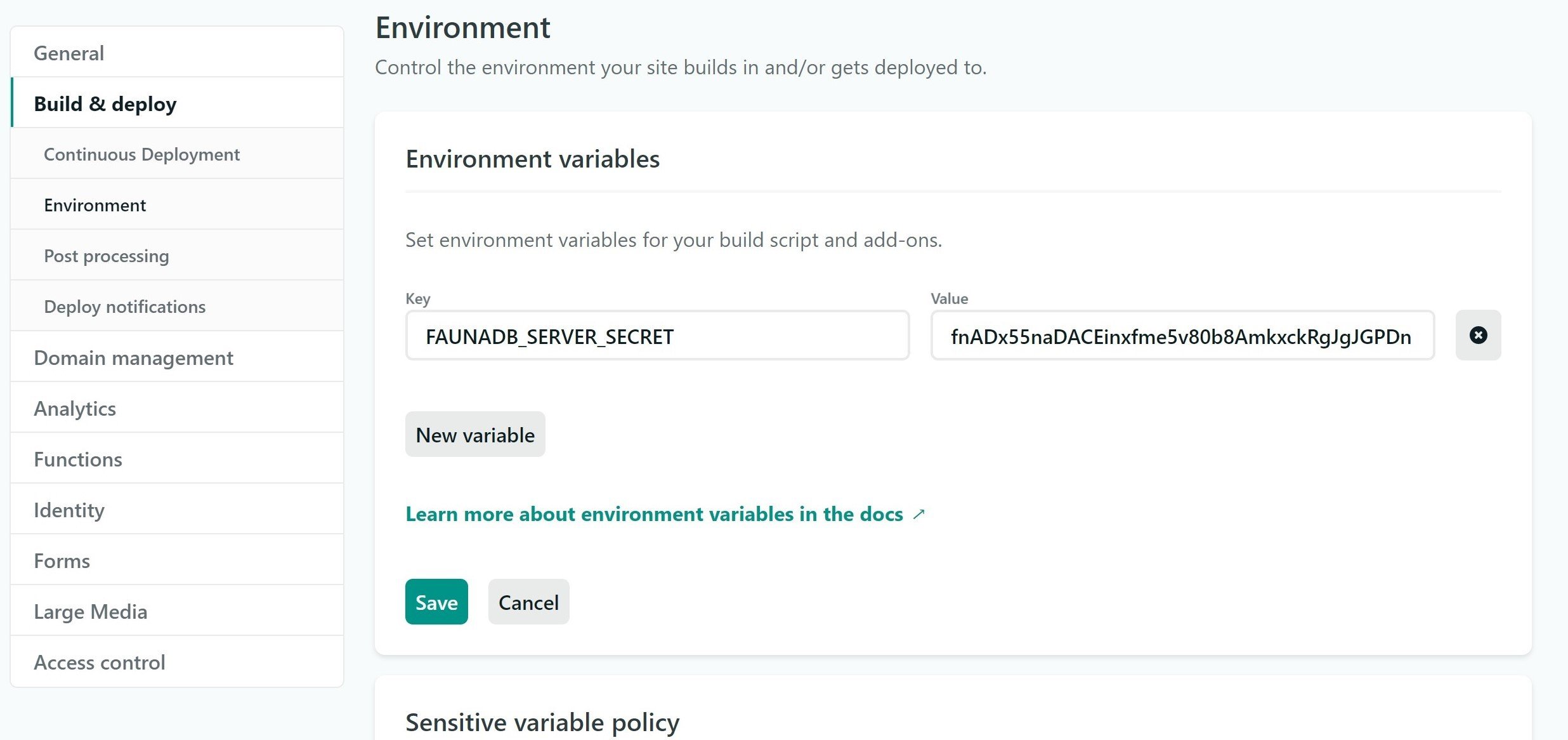
if (!process.env.FAUNADB_SERVER_SECRET) {
console.log(chalk.yellow('Required FAUNADB_SERVER_SECRET enviroment variable not found.'));
console.log(`Make sure you have created your Fauna databse with "netlify addons:create fauna"`);
console.log(`Then run "npm run bootstrap" to setup your database schema`);
if (insideNetlify) {
process.exit(1);
}
}
// Has var. Do the thing
if (process.env.FAUNADB_SERVER_SECRET) {
createFaunaDB(process.env.FAUNADB_SERVER_SECRET).then(() => {
console.log('Fauna Database schema has been created');
console.log('Claim your fauna database with "netlify addons:auth fauna"');
});
}
/* idempotent operation */
function createFaunaDB(key) {
console.log('Create the fauna database schema!');
const client = new faunadb.Client({
secret: key,
});
/* Based on your requirements, change the schema here */
return client
.query(q.Create(q.Ref('classes'), { name: 'todos' }))
.then(() => {
return client.query(
q.Create(q.Ref('indexes'), {
name: 'all_todos',
source: q.Ref('classes/todos'),
})
);
})
.catch((e) => {
// Database already exists
if (e.requestResult.statusCode === 400 && e.message === 'instance not unique') {
console.log('Fauna already setup! Good to go');
console.log('Claim your fauna database with "netlify addons:auth fauna"');
throw e;
}
});
}
/* util methods */
// Test if inside netlify build context
function insideNetlifyBuildContext() {
if (process.env.DEPLOY_PRIME_URL) {
return true;
}
return false;
}"bootstrap": "netlify dev:exec node ./scripts/bootstrap-fauna-database.js"
npm run bootstrap
Create / apply schema:
Creating serverless functions
exports.handler = function(event, context, callback) {
// your server-side functionality
}
// the handler receives an event object with details about the request itself like headers
// The context parameter includes information about the context in which the serverless function was called, like certain Identity user information, for example.
// The callback works much like the same parameter in an AWS Lambda function. Your handler should use the callback to return either an error (as the first parameter) or a response object, such as:Example todos-create.js
/* Import faunaDB sdk */
const faunadb = require('faunadb');
const q = faunadb.query;
/* export our lambda function as named "handler" export */
exports.handler = async (event, context) => {
/* configure faunaDB Client with our secret */
const client = new faunadb.Client({
secret: process.env.FAUNADB_SERVER_SECRET,
});
/* parse the string body into a useable JS object */
const data = JSON.parse(event.body);
console.log('Function `todo-create` invoked', data);
const todoItem = {
data: data,
};
/* construct the fauna query */
return client
.query(q.Create(q.Ref('classes/todos'), todoItem))
.then((response) => {
console.log('success', response);
/* Success! return the response with statusCode 200 */
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify(response),
};
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log('error', error);
/* Error! return the error with statusCode 400 */
return {
statusCode: 400,
body: JSON.stringify(error),
};
});
};Testing our functions locally:
npx netlify functions:invoke todos-create --port 62631 --payload "{\"text\": \"react talk\", \"complete\": false}"
npm run start
Using our functions in our app:
// util api methods
const create = (data) => {
return fetch('/.netlify/functions/todos-create', {
body: JSON.stringify(data),
method: 'POST',
}).then((response) => {
return response.json();
});
};
Thank you.
🙏
@brettHaymaker
Serverless functions + Netlify
By Brett Haymaker
Serverless functions + Netlify
- 194



