International Relations of the Middle East
In The News
Erdogan given increased powers after the coup attempt
Early February 2017, Turkey purge 330 academics. 7,316 academics have lost their Jobs since the Turkish coup attempt.
1500 deans of universities-fired.
3000 judges suspended
120 journalist jailed
150 news stations closed
October 2016, 70000 people had been arrested

Authoritarianism
The control of government and political society by an individual or cadre of individuals. The press, open and fair elections, demonstrations severely curtailed.
In the Middle East Authoritarian regimes utilize the law as a method of suspending legal rights
Emergency Law
Before the Arab spring Emergency laws were continuously active for Egypt and Syria
The suspension of civil rights, justification for judicial proceedings that do not follow constitution protocol, censorship of the press and cultural output. Usually enacted due to a perceived 'threat'
The impact of Authoritarian regimes on international relations
- Authoritarian rulers are primary decision makers but...
- Authoritarian rulers must also walk a fine line in pursuing their policy objectives
- popular sentiments
- personal desires
- transnational ties
- Authoritarian rulers must also walk a fine line in pursuing their policy objectives
- Rulers are also influenced by the factors of state formation
- what ideology was used in the founding of the state?

What do we get with authoritarianism?
A council for young women without women

Housing that does not address housing needs

Saad Ibrahim
sentenced to 7 years in prison

Hamza Ali Khateeb killed by Syrian Security forces

grew up poor in the Alawite (Shi'a)
Member of the Ba'ath party
Joins the military as a method toward social advancement.
1963 engages in coup plot with other military officers, establishes a Ba'ath government
Gains full power over the country in 1970
Hafez al- Assad (1930-2000)
- However, Alawites dispportionately in control over government
- Government utilizes law and institutions to centralize political power.
- Sectarianism a threat to Assad's power
- government produced a new constitution opening up the presidency to any sect.
- Assad gets a Shi'a cleric to confirm that Alewites are Muslims.
- From 1963-2011 Syria under Emergency Law
Life under Al Assad

Ba'ath Party
The Military
Alawite Community
Internal Security Forces
Friends and Family
Rural support
-
cracked down on Islamic opposition movements
- Eid al-Adha massacre
- 1980, Tadmoor Prison massacre
- 1982, Hama massacre
Routine torture continued under Bashar al-Assad.
Under Al-Assad
- Thriving secret police force engages in repression of political opponents.
Authoritarianism in the Middle East
- there is no innate incompatibility between Arab countries and democracy.
- There is a history of popular demonstration against leaders seen as neglectful.
- There is also history of 'silent' change.
-
The Arab world has also had persistent authoritarian regimes due to the sustained support of outside powers.
- a preference for stability
- concern for Israel
- geopolitical and economic interest
- Rentier states don't necessarily need approval of state action from citizens
Democracy
Some beliefs...
1. Real democracy looks the same everywhere.
2. Democracy is the solution of repression and human rights abuses.
3. Democracies are found where elections are present

Democracy promotion in the region
- Early 1990s was to supposed to witness a democratic wave
- End of the Cold War
- a partial turn toward neoliberal economic principles
- Neoliberalism: An Economic and Political world view
- democracy and free trade will lead to a reduction in conflict
- Emphasis on interdependence
Rulers have used the language and practices of Modernity to combat democratic reforms
Authoritarian Regimes demonstrate remarkable adaptability
Example:
Shah Reza Pahlavi promoting equal rights for women as well as education reform even has he actively repressed all forms of dissent through imprisonment and torture.
Sisi on Democracy
Authoritarian Regimes compliant with neoliberal economic demands...most of the time
Washington Consensus
a list of reforms that have been heavily exported to countries requesting economic loans from global monetary institutions
1. Property Rights
2. Deregulation
3. Tax Reform
4. Competitive exchange rate
5. privatization
6. Liberalization of interest rates
7. fiscal discipline
8. Liberalization of foreign direct Investment
9. trade liberalization
10. Reordering public expenditures
Funding for Authoritarian rulers detaches them from responding to indigenous democratic movements
6.5 Billion in military assistance from U.S. to Egypt between 2011 and 2015 (al-Monitor)
Foreign Economic Aid to the Middle East from the U.S. during 2014: 5.9 bill. (CNN)

Bahrain 2012

The Islands of Sanafir and Tiran, given to Saudi Arabia .
Saudi Arabia has given Sisi 4 billion in aid in 2015.
Iraq, Kuwait, Qatar, Libya, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iran are the largest oil producers within the region.
Rents: Income accrued from the payment for resources that allow governments to pay the cost of state
1. With Rents, states less prone to worry about productivity and efficiency
2. Large rents, make it easier for gov't leaders to ignore calls for more open government
Funding and Oil
On 20 March 2017, a barrel of oil cost $48.22 ( a barrel is 42 gallons)
Factors behind cost:
- Currently, the world market is flooded by oil.
- An increase in U.S. production
- Today, the United States has more recoverable oil than Saudi Arabia
- more pumping in Iraq
- An increase in U.S. production
- more energy efficient vehicles
Historic trends in the price of oil
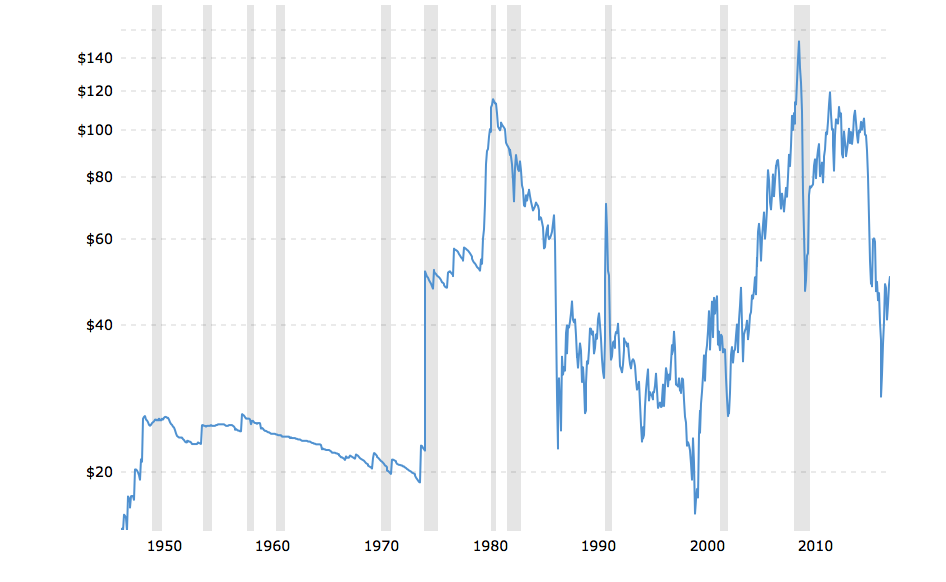
July 2008, the price of oil was $147.27
1. Informality
Because government is unsure of its population--where they live, where they work--they are unable to effectively control or tax them
2. Limited Resources
Oil is not an unlimited resource.
3. Persistent economic discontent
The gap between the rich and the poor is growing wider in the region. Along with the diminishment of the middle class, government elites have turned to promoting modern and costly societal transformation that actively excludes middle and working class.
Enduring threats to Authoritarian states
Copy of International Relations of the Middle East
By cesmit5
Copy of International Relations of the Middle East
- 829



