Homebrewing
"Life begins at 1.060"
History

Ancient History of Brewing
- Human directed fermentation dates to 7000 BC in China
- Developed independently anywhere cereal crops were domesticated
- The oldest surviving recipe is 3900 years old, part of a Sumerian poem honoring Ninkasi, the goddess of beer
- Prior to the industrial revolution, women dominated brewing in almost every culture
- Ancient Egyptian laborers were paid in beer
- Beers were thick, low in ABV, and served as a preserved, transportable liquid meal
Egyptian Brewery
A funerary model of a brewery and bakery from Thebes.
The model is from the 11th dynasty, roughly 2009-1998 BCE.

The Code of Hammurabi
Dating to the 1790s BCE, the code contains numerous laws regarding the purity and sale of beer.

Late Pre-Industrial Brewing
- By the early Tang Dynasty, barley based beers had been replaced by rice based brewed beverages
- By the late Medieval period, brewing in Europe was moving to Pubs and monasteries.
- Between 1350 and 1450 Hops replace other herbs as the primary preservative in European beers
- In 1516 the Reinheitsgebot is passed
- In 1620, the Pilgrims having run out of beer decide to land at Plymouth

The Industrial Revolution and Beyond
- 1750-1800 The thermometer and hydrometer are invented, steam power is introduced to English breweries
- In the early 1840s hoppy beers meant for export become popular, the IPA is born
- In 1875 Louis Pasteur explained the role of yeast in beer fermentation
- The golden age of American brewing sees a peak of 4,131 breweries in the 1870s
- In the 1890s refrigeration allows the shipping of beer by rail
Hydrometers
A tool to measure the specific gravity of a liquid, or the ratio of the density of the liquid to the density of water. This is used in beer making to determine the quantity of fermentable sugars present during the process. A post boil, pre-fermentation IPA will have a gravity measurement between 1.060 and 1.075.


Recent History
- 1915-1917 WWI rations cut the strength of beer, and the decline of small American breweries begins
- Prohibition closes breweries from 1919-1933
- In 1934 the beer can is invented
- Homebrewing remained illegal until 1978 when Jimmy Carter signed H.R. 1337 into law as part of a push for federal deregulation
- Within months the Brewers Association and Homebrewers Association are founded
H.R. 1337

Some Terms
- ABV - Alcohol % by volume
- Wort - pre-fermentation beer
- OG (Original Gravity) - Specific gravity
- SRM - spectrophotometric measurement of the color of wort
- IBU - International Bittering Units, ppm of iso-alpha acid present in finished beer (properly spectrophotometrically determined)
- HBU - Homebrew version of IBU (Alpha Acid % of Hops * oz)/gallons
Some Aroma Terms
- Diacetyl - chemicals responsible for buttery aroma in some pilsners
- Esters - fruity notes
- Organic Acids - sour/vinegar aromas found in sour beers
- Pyrazines - malty, bready aromas characteristic of most beers
- Terpenoids - wide range of hoppy aeromatics
Hops

Hops!
- Hops are the flowers of the Hops (Humulus lupulus) plant.
- They are native to the Hallertau region of Bavaria in Germany
- Germany, the US, and Ethopia dominate global production
- Alpha acids are the primary bittering compound relevant to brewing
- Essential oils provide hop flavor and aroma in brewing
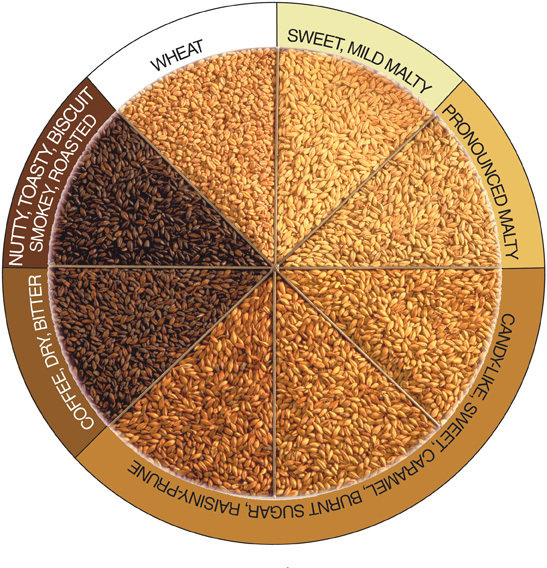
Malt
- Barley(or other grain) that has been sprouted and dried
- During sprouting enzymes attack the sacks holding starch and convert it into fermentable sugars
- Kilning, or drying, imparts color and suspends the enzymatic process
Yeast
- Fungus of the genus Saccharomyces
- Top fermenting yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae produce ales
- Bottom fermenting yeasts like Saccharomyces pastorianus lagers
- Produce alcohol by anaerobic(low oxygen) fermentation
- Yeast is also responsible for a number of flavors and aromas in beer
Commercially Available Yeast

BJCP Styles
- The Beer Judge Certification Program, est 1985, certified beer judges and codifies styles
- Styles are defined by color, bitterness, abv, OG, etc
- Styles are fairly broad an fuzzy at the edges
Styles
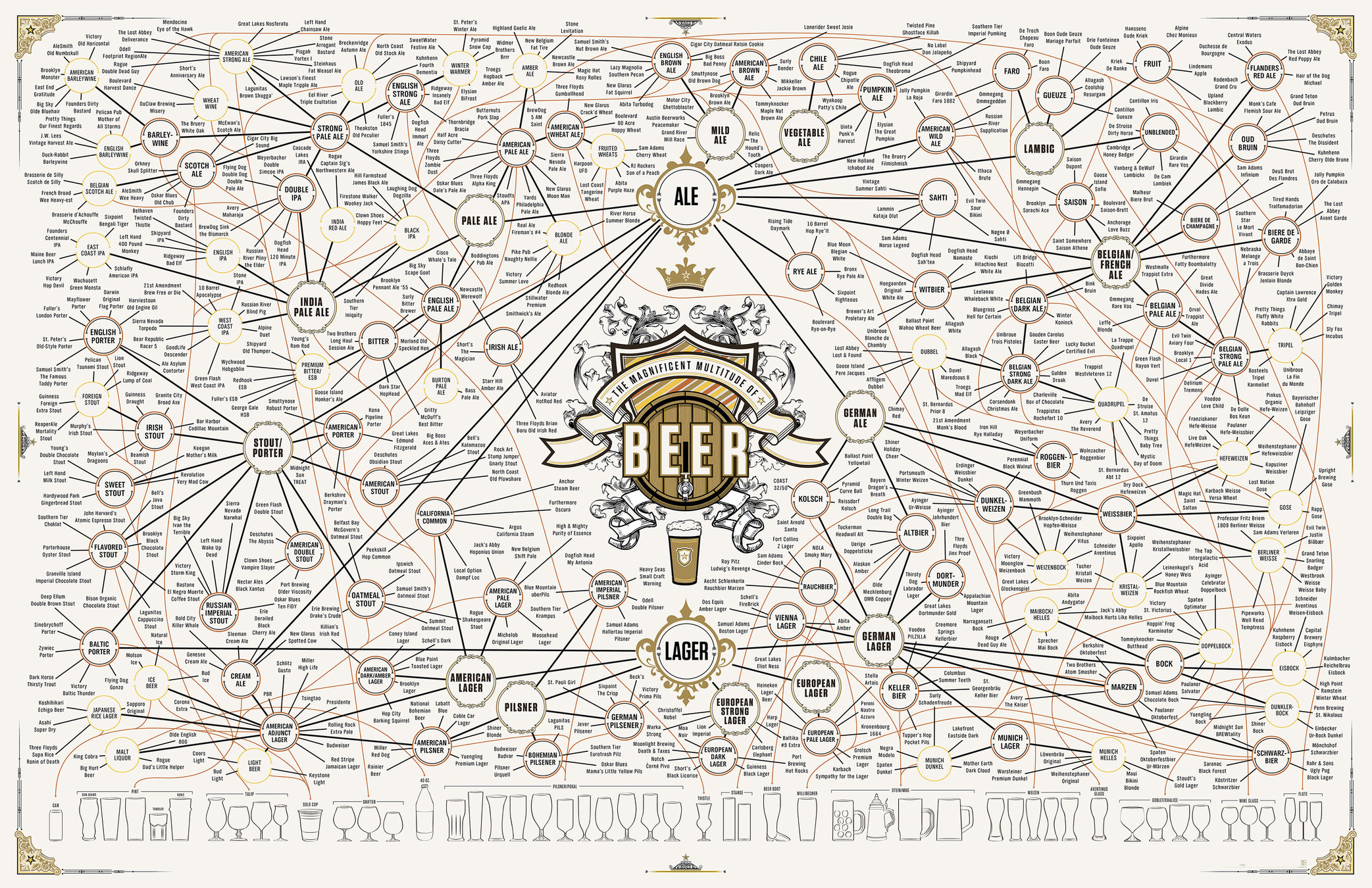
Styles!

Styles
The Process
- Recipe/Planning
- Mashing
- Sparging
- Boiling
- Hopping
- Sanitation
- Chilling
- Pitching
- Fermenting
- Sanitation
- Bottling/Kegging
- Enjoying
Planning
Planning a recipe can start with a beer you like, a BJCP style, a book, or just some inspiration. Software like BeerSmith is often used to manage recipes and the end to end process.

Mashing
This is the process of steeping the grains and extracting fermentable sugars and other organic compounds. The hot water reactivates the enzymes that are halted by the malting process, and these enzymes turn starches into sugars.


Sparging
- Part of the mashing process
- Second and third rinses of the mash extract extra sugars
- improves brew efficiency
Boiling
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Morbi nec metus justo. Aliquam erat volutpat.

Hoping
- Can be done pre-boil, during, or after the boil
- Timing determines the extraction of alpha acids
- Multiple types may be used in one beer
Pitching Yeast
Once the wort is cooled to roughly room temperature of the preferred pitch temperature of the yeast strain, yeast will be added. Different strains thrive at different temperatures. Brewers will often activate yeast by warming it to temperature and feeding it in the hours or day prior to pitching.

Fermenting
Temperature control and time are critical to yeast activity. Keeping the yeast at the right temperature prevents stress, which produces off flavors. Fermentation takes 1 to 2 weeks, and may involve multiple stages.
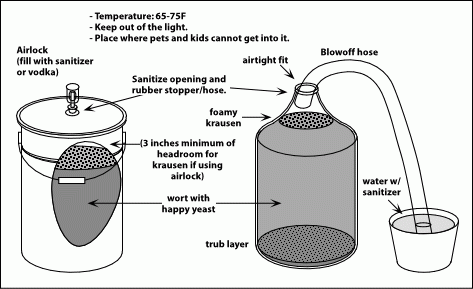
Fermentation Buckets

Bottling or Kegging
After fermentation, beer is drinkable, but isn't carbonated, and isn't easy to transport. If the yeast isn't filtered out it will continue to work and the beer will condition/age over time. Priming sugar is used in bottling when homebrewing to give the yeast extra sugar to produce CO2.

Thanks
and enjoy
Supplies from a recent brew

A belgian strong dark cherry beer I made. 18months old

A cat in my supply box

Old brew setup

One time we brewed like 100 gallons

When things go a little wrong

Home Brewing
By Chase Gilliam
Home Brewing
- 296



